每日一贴,今天的内容关键字为链表节点
1 数组合并排序
1.1 合并两个已排序好的数组
需要额定的存储空间用来存储合并结果
//merge two array which are already sorted
public static int[] merge(int[] a,int[] b){
/*
* array out of bound
*
* normal input:a!==null && b!==null
* special input:
* 1)a==null && b==null
* 2)a==null && b!=null or a!=null && b==null
*
* 0) base case:one of array is empty
* 1)how to remember where the array go:
* need aIndex,bIndex,resultIndex point to a,b,result
* 2)steps
* step1: compare(condition:neither array is empty)
* step2: copy the rest:
* if one of array is empty, copy the other to the reuslt
*/
//control input
if(a==null && b==null)
return null;
if(a==null && b!=null)
return b;
if(a!=null && b==null)
return a;
//result array
int aLength=a.length;
int bLength=b.length;
int resultLength=aLength+bLength;
int[] result=new int[resultLength];
//index pint to array
int aIndex=0, bIndex=0,resultIndex=0;
//step1
//base case:one of array is empty
while(aIndex < aLength && bIndex < bLength){
//first compare once
if(a[aIndex] 1.2 合并排序
package zyang.recursion;
import zyang.designPattern.adaper.A;
/**
* @author yangzhong E-mail: [email protected]
* @version 1.0
* @date 2012-11-12 上午9:13:17
* @fuction mergeSort
*/
public class MergeSort
{
private long[] workspace; //用于中间过程当中存储合并结果
//主程序
public long[] mergSort(long[] array)
{
workspace=new long[array.length];
recMergeSort(array, 0, array.length-1);
return array;
}
//分治法思绪 Divide-and -Conquer Algorithms
private void recMergeSort(long[] arr,int first,int end)
{
//递归结束条件:数组中只有一个元素时
//base case:if range is 1, no use sorting
if(first==end)
return;
else
{
//find midpoint
int mid=(first+end)/2;
//1sort left half
recMergeSort(arr, first, mid);
//2sort right half
recMergeSort(arr, mid+1, end);
//3merge them
merge(arr,first,mid,end);
}
}//end recMergeSort()
//合并已排好序的2个数组(2个数组是指一个数据从中间分开后的2个数组)
private void merge(long[] arr,int first1,int mid,int end2)
{
int resultIndex=0; //合并结果数组的指针
int start=first1; //存储数据合并起始位置
int end1=mid; // 第一个已排序好的数组范围为[first1,end1],first1用于指向该数组的指针
int first2=mid+1; // 第二个已排序好的数组范围为[first2,end2],first2用于指向该数组的指针
while(first1<=end1 && first2<=end2)
{
if(arr[first1]< arr[first2])
workspace[resultIndex++]=arr[first1++];
else
workspace[resultIndex++]=arr[first2++];
}
//如果一个数组已经没有数字可以比较,将其中一个剩余的数字全体copy到结果数组中
while(first1<=end1)
workspace[resultIndex++]=arr[first1++];
while(first2<=end2)
workspace[resultIndex++]=arr[end2++];
for(int i=0;i<=end2-start;i++){
// System.out.println(workspace[i]);
arr[start+i]=workspace[i];
}//end for
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
long[] test={67,28,30,21};
long[] result=new MergeSort().mergSort(test);
System.out.println("length:"+result.length);
for(int i=0;i注意在合并算法merge中需要将中间合并结果存入原始数组中,arr为最后合并排序后的数组,workspace用于存储中间合并的临时结果。
for(int i=0;i<=end2-start;i++){
arr[start+i]=workspace[i];
}//end for
2 单链表合并排序
2.1 有序单链表
有序单链表主要是增加新节点时,需要插入的节点位置是有序的
// -------------------------------------------------------------
class Link
{
public long dData; // data item
public Link next; // next link in list
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public Link(long dd) // constructor
{ dData = dd; }
// -------------------------------------------------------------
} // end class Link
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class SortedList
{
private Link first; // ref to first item on list
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public SortedList() // constructor (no args)
{ first = null; } // initialize list
// -------------------------------------------------------------
public void insert(Link k) // insert (in order)
{
//输入控制
if(k==null)
return ;
Link previous = null; // start at first
Link current = first;
// until end of list,
while (current != null && k.dData > current.dData) { // or key > current,
previous = current;
current = current.next; // go to next item
}
if (previous == null) // at beginning of list
first = k; // first --> k
else
// not at beginning
previous.next = k; // old prev --> k
k.next = current; // k --> old currnt
} // end insert()
每日一道理
古人云:“海纳百川,有容乃大。”人世间,不可能没有矛盾和争吵,我们要以磊落的胸怀和宽容的微笑去面对它 。哈伯德也曾说过:“宽恕和受宽恕的难以言喻的快乐,是连神明都会为之羡慕的极大乐事。”让我们从宽容中享受快乐,从谅解中体会幸福吧!
古人云:“海纳百川,有容乃大。”人世间,不可能没有矛盾和争吵,我们要以磊落的胸怀和宽容的微笑去面对它 。哈伯德也曾说过:“宽恕和受宽恕的难以言喻的快乐,是连神明都会为之羡慕的极大乐事。”让我们从宽容中享受快乐,从谅解中体会幸福吧!
2.1 合并两个已排序好的单链表
由于数组可以根据下标获得全部数组的值,而单链表只能根据第一个链表的节点循环获得所有节点的信息,所以在单链表合并的时候需要保存合并后的第一链表的节点地址。
总结:与数组合并排序多了一步,即肯定合并背面节点地址。
《剑指offer》上的面试题17:合并两个排序的链表,其递归算法有以下3个问题:
1、返回的不是合并后链表头节点地址
因为没有保存合并后链表头节点的地址,其pMergedHead其实是以后合并后的节点地址,而合并后的链表需要返回合并后链表头节点地址,您代码中返回的是pMergedHead是不对的。
2、没有考虑当一个链表已合并完,剩余一个链表还有节点的情况
3、递归算法结束的条件不对
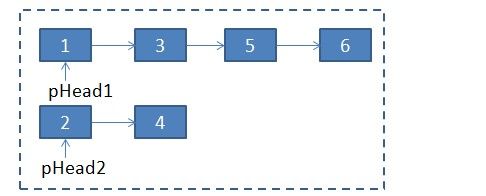
代码中只是对输入参数停止了控制,并没有递归结束的条件 我对该算法停止了改正(用java写了递归算法和非递归算法),例如合并下图中的2个已排好序的单链表
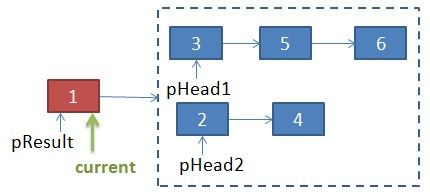
首先,肯定合并后链表的头节点
pResult用于保存合并后链表头节点地址,current指向以后合并后的节点
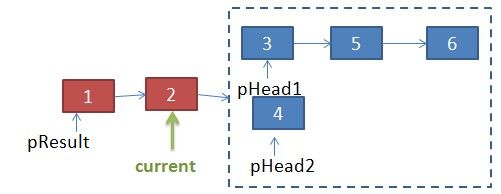
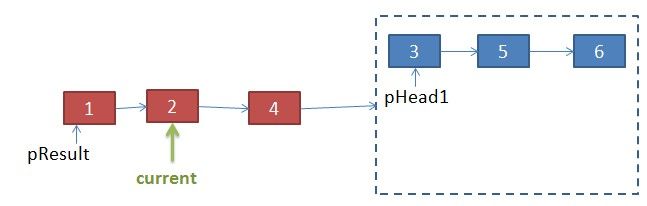
当合并完其中一个链表时(图中pHead2==null),只要要把剩余一个链表的节点连接到current的下个节点接口(即current.next=pHead1)
递归算法如下
class List{ //定义链表节点的数据结构
int value;
List next;
}
public List merge(List pHead1,List pHead2){
//输入控制
if(pHead1==null)
return pHead2;
if(pHead2==null)
return pHead1;
List pResult=null; //合并后链表的头指针
//肯定头节点
if(pHead1.value < pHead2.value){
pResult=pHead1;
pHead1=pHead1.next;
}//end if
else{
pResult=pHead2;
pHead2=pHead2.next;
}//end else
//比较后续节点
List current=pResult; //pResult用于保存链表头节点信息,current 用于保存以后合并后的节点
recMerge(pHead1,pHead2,current);
return pResult;
}//end merge
//合并排序好的2个链表(递归)
private void recMerge(List pHead1,List pHead2,List current){
//base case:当有一个链表已全体参加合并后的链表中时,递归结束,并将其中有剩于节点的那个链表连接到current前面
if(pHead1==null || pHead2==null){
//2个链表剩余节点直接连接到pResult中
if(pHead1!=null)
current.next=pHead1;
if(pHead2!=null)
current.next=pHead2;
return;
}//end if
if(pHead1.value//合并排序好的2个链表(非递归)
public List merge2(List pHead1,List pHead2){
//输入控制
if(pHead1==null)
return pHead2;
if(pHead2==null)
return pHead1;
List pResult=null; //合并后链表的头指针
//肯定头节点
if(pHead1.value < pHead2.value){
pResult=pHead1;
pHead1=pHead1.next;
}//end if
else{
pResult=pHead2;
pHead2=pHead2.next;
}//end else
//比较
List current=pResult; //pResult用于保存链表头节点信息,current 用于保存以后合并后的节点
while(pHead1!=null && pHead2!=null){
if(pHead1.value < pHead2.value){
current.next=pHead1;
pHead1=pHead1.next;
}//end if
else{
current.next=pHead2;
pHead2=pHead2.next;
}//end else
current=current.next; //current 用于保存以后合并后的节点
}//end while
//2个链表剩余节点直接连接到pResult中
if(pHead1!=null)
current.next=pHead1;
if(pHead2!=null)
current.next=pHead2;
return pResult;
}//merge()2.2 单链表合并排序
这里是先将链表转换为数组,然后对数组停止合并排序,然后对排序后的数组重新构建链表:
1)获得链表节点数组,,时间复杂度O(n),
2)对链表节点数组停止合并排序,时间复杂度O(nlogn)
3)对合并排序好的链表数组构建链表,时间复杂度O(n)
public class MergeLinkList {
class List{ //定义链表节点的数据结构
int value;
List next;
}
//链表递归排序,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
public Link merge(Link first){
//输入控制
if(first==null)
return first;
//获得链表节点数组,,时间复杂度O(n)
ArrayList al=new ArrayList();
while(first!=null){
al.add(first);
first=first.next;
}//end while
//对链表节点数组停止合并排序,时间复杂度O(nlogn)
Link[] arr=(Link[]) al.toArray();
// mergeSort(arr); //数组合并排序与下面一样,此处省略
//对合并排序好的链表数组构建链表,时间复杂度O(n)
return constructLinkList(arr);
}//end merge()
private Link constructLinkList(Link[] linkArray){
Link first=linkArray[0]; //头节点
Link current=first; //以后节点
for(int i=1;i
文章结束给大家分享下程序员的一些笑话语录: 程序员的愿望
有一天一个程序员见到了上帝.上帝: 小伙子,我可以满足你一个愿望.程序员: 我希望中国国家队能再次打进世界杯.
上帝: 这个啊!这个不好办啊,你还说下一个吧!
程序员: 那好!我的下一个愿望是每天都能休息6个小时以上.
上帝: 还是让中国国家打进世界杯.