Leetcode分类刷算法之二叉树专题
Leetcode二叉树问题
二叉树的遍历
1.二叉树的前序遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
非递归版本
public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)return res;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
root = stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
if (root.right != null) {
stack.push(root.right);
}
if (root.left != null) {
stack.push(root.left);
}
}
return res;
}
2. 二叉树的中序遍历
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();;
TreeNode cur = root;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) {
while (cur != null) {
### stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
res.add(node.val);
cur = node.right;
}
return res;
}
3. 二叉树的后序遍历
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
和前序遍历的代码几乎一样,不过这次先压入的是左节点,最后在reverse才是后续遍历
public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
root = stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
if (root.left != null) {
stack.push(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
stack.push(root.right);
}
}
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
4. 二叉树的层次遍历
102. 二叉树的层次遍历
public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
int count = queue.size();
while (count-- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
list.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
res.add(list);
}
return res;
}
5. 二叉树的层次遍历 II
5. 二叉树的层次遍历 II
在每层遍历完之后添加结果时,调用LinkedList的addFirst方法。
public List> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList> res = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int count = queue.size();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
while (count -- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
list.add(cur.val);
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
res.addFirst(list);
}
return res;
}
6. 二叉树的右视图
199. 二叉树的右视图
1.层序遍历:每次向结果集中添加每层最右边的元素
public List rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int count = queue.size();
while (count-- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (count == 0) {
res.add(cur.val);
}
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
return res;
}
7. 翻转二叉树
226. 翻转二叉树
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return null;
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left); //先得到左子树
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right); //先得到右子树
root.left = right; //交换
root.right = left;
return root;
}
层次遍历每次交换左右子树
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
if (root != null) queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
TreeNode temp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = temp;
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
return root;
}
8. 二叉搜索树迭代器
173. 二叉搜索树迭代器
考察非递归版本的中序遍历,这道题本质上是写一个二叉树的中序遍历的迭代器。内部设置一个栈,初始化的时候,存储从根节点到最左叶子节点的路径,在遍历的过程中,每次从栈中弹出一个元素,作为当前返回的结果,同时探测一下当前首节点时候存在右孩子,如果有的话,则仅需右孩子,并把从该右孩子到最左叶子节点的所有节点入栈。
class BSTIterator {
private Stack stack;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
stack = new Stack<>();
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
public int next() {
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if (cur.right != null) {
TreeNode node = cur.right;
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
}
return cur.val;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
public boolean hasNext() {
return !stack.isEmpty();
}
}
9. 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
Node 还是按照层次遍历从左到右遍历,只不过生成答案的时候如果是奇数层,则生成一个反向的LIST,调用其add(0,item)的方法。
public List> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)return res;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int count = queue.size();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
while (count -- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
if (depth % 2 == 0) {
list.add(cur.val);
}else {
list.add(0,cur.val);
}
}
res.add(list);
depth++;
}
return res;
}
10. 相同的树
100. 相同的树
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null)return true;
if (p == null || q == null)return false;
return p.val == q.val && isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
10. 对称二叉树
101. 对称二叉树
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return isSymmetric(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
if (left == null && right == null) return true;
if (left == null || right == null) return false;
return left.val == right.val && isSymmetric(left.left,right.right) && isSymmetric(left.right, right.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root.left);
stack.push(root.right);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode left = stack.pop();
TreeNode right = stack.pop();
if (left == null && right == null) continue;
if (left == null || right == null) return false;
if (left.val != right.val)return false;
stack.push(left.left);
stack.push(right.right);
stack.push(left.right);
stack.push(right.left);
}
return true;
}
11. 平衡二叉树
110. 平衡二叉树
树形dp
private static class ReturnData{
boolean isBalanced;
int height;
public ReturnData(boolean isBalanced, int height) {
this.isBalanced = isBalanced;
this.height = height;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return process(root).isBalanced;
}
public ReturnData process(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return new ReturnData(true, 0);
}
ReturnData left = process(root.left);
if(!left.isBalanced){
return new ReturnData(false,0);
}
ReturnData right = process(root.right);
if(!right.isBalanced){
return new ReturnData(false,0);
}
return Math.abs(left.height - right.height) > 1?
new ReturnData(false,0):
new ReturnData(true,Math.max(left.height,right.height)+1);
}
简洁版
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root) != -1;
}
private int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return 0;
int left = getHeight(root.left);
int right = getHeight(root.right);
if (left < 0 || right < 0 || Math.abs(left - right) > 1) return -1;
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
12. 二叉树展开为链表
114. 二叉树展开为链表
将左子树插到原来右子树的地方
将原来的右子树插到左子树的最右边的节点上。
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(root.right);
TreeNode temp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = null;
while (root.right != null) root = root.right;
root.right = temp;
}
13. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
要处理一个节点,可能需要最右边边的兄弟节点,首先想到广搜,但是广搜不是常数空间的。
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null)return root;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int count = queue.size();
Node pre = null;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
//从第二个节点开始,将前一个节点的pre指向当前节点
if (i > 0) {
pre.next = cur;
}
pre = cur;
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
解法二、迭代版
题目要求了空间复杂度,考虑不用队列应该怎么处理。需要解决三个问题。
- 每一层怎么遍历?
之前使用队列将下一层的节点保存了起来
这里的话,其实只需要提前把一个层的next构造完成,到了下一层的时候就可以遍历了 - 什么时候进入下一层?
之前是得到当前队列的元素的个数,然后遍历了那么多次?这里的话,主要到最右边的节点的next为null,所以可以办单当前遍历的节点是不是null - 怎么得到每层开头的节点?
之前队列把当前层的所有节点保存了起来,得到开头节点当然很容易
这里的话,我们需要额外的一个变量把它保存起来
三个问题都解决了,就可以写代码了。利用三个指针,start指向每一层的开始的节点,cur指向当前遍历的节点,pre指向当前遍历节点的前一个节点。
需要把pre的做孩子的next指向右孩子,pre右孩子的next指向cur的左孩子。
当cur变为null之后,只需要把pre的左孩子的next指向右孩子。
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null)return root;
Node pre = root;
Node cur = null;
Node start = pre;
while (pre.left != null) {
//遍历到了最右边的节点,要将pre和cur更新到下一层,并且用start记录
if (cur == null) {
pre.left.next = pre.right;
pre = start.left;
cur = start.right;
start = pre;
}else {//将下一层的next连接起来,同时pre、next后移
pre.left.next = pre.right;
pre.right.next = cur.left;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return root;
}
14. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
BFS的代码直接从上面的代码复制过来就上,一个都不用改
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null)return root;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node pre = null;
int count = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
if (i > 0) {
pre.next = cur;
}
pre = cur;
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return root;
}
当前节点为null就不处理就可以了。
怎么得到每次的开头的几点呢?用一个dummy指针,当连接第一个节点的时候,用dummy指针指向他,此外,之前用pre指针,把它当成tail指针可能会更好的理解。
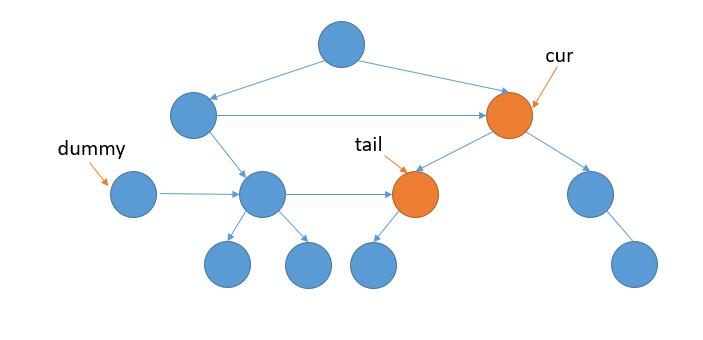
public Node connect(Node root) {
Node cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
Node dummy = new Node();
Node tail = dummy;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.left != null) {
tail.next = cur.left;
tail = tail.next;
}
if (cur.right != null) {
tail.next = cur.right;
tail = tail.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = dummy.next;
}
return root;
}
15. 恢复二叉搜索树
99. 恢复二叉搜索树
位置交换的所有可能:
- 根节点和左子树的某个数字交换:由于根节点大于左子树的所有数,所以交换后我们只要找到左子树的最大的节点即可。
- 根节点和右子树的某个数字交换: 由于根节点小于右子树中的所有数,所以交换的时候我们只要找到右子树的最小的节点即可。
- 左子树和右子树中的两个数字交换:找到最总数中最大的数,右子树中最小的数,及对应两个交换的数。
- 左子树中的两个数字交换
- 右子树中两个数字交换
public void recoverTree2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//寻找左子树中最大的节点
TreeNode maxLeft = getMaxOfBST(root.left);
//寻找右子树中最小的节点
TreeNode minRight = getMinOfBST(root.right);
if (minRight != null && maxLeft != null) {
//左边的大于根节点,右边的小于根节点,对应情况 3,左右子树中的两个数字交换
if ( maxLeft.val > root.val && minRight.val < root.val) {
int temp = minRight.val;
minRight.val = maxLeft.val;
maxLeft.val = temp;
}
}
if (maxLeft != null) {
//左边最大的大于根节点,对应情况 1,根节点和左子树的某个数做了交换
if (maxLeft.val > root.val) {
int temp = maxLeft.val;
maxLeft.val = root.val;
root.val = temp;
}
}
if (minRight != null) {
//右边最小的小于根节点,对应情况 2,根节点和右子树的某个数做了交换
if (minRight.val < root.val) {
int temp = minRight.val;
minRight.val = root.val;
root.val = temp;
}
}
//对应情况 4,左子树中的两个数进行了交换
recoverTree(root.left);
//对应情况 5,右子树中的两个数进行了交换
recoverTree(root.right);
}
//寻找树中最小的节点
private TreeNode getMinOfBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode minLeft = getMinOfBST(root.left);
TreeNode minRight = getMinOfBST(root.right);
TreeNode min = root;
if (minLeft != null && min.val > minLeft.val) {
min = minLeft;
}
if (minRight != null && min.val > minRight.val) {
min = minRight;
}
return min;
}
//寻找树中最大的节点
private TreeNode getMaxOfBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode maxLeft = getMaxOfBST(root.left);
TreeNode maxRight = getMaxOfBST(root.right);
TreeNode max = root;
if (maxLeft != null && max.val < maxLeft.val) {
max = maxLeft;
}
if (maxRight != null && max.val < maxRight.val) {
max = maxRight;
}
return max;
}
解法2中序遍历
交换的位置的话就是两种情况。
相邻的两个数字交换
[ 1 2 3 4 5 ] 中 2 和 3 进行交换,[ 1 3 2 4 5 ],这样的话只产生一组逆序的数字(正常情况是从小到大排序,交换后产生了从大到小),3 2。
我们只需要遍历数组,找到后,把这一组的两个数字进行交换即可。
不相邻的两个数字交换
[ 1 2 3 4 5 ] 中 2 和 5 进行交换,[ 1 5 3 4 2 ],这样的话其实就是产生了两组逆序的数字对。5 3 和 4 2。
所以我们只需要遍历数组,然后找到这两组逆序对,然后把第一组前一个数字和第二组后一个数字进行交换即完成了还原。
所以在中序遍历中,只需要利用一个 pre 节点和当前节点比较,如果 pre 节点的值大于当前节点的值,那么就是我们要找的逆序的数字。分别用两个指针 first 和 second 保存即可。如果找到第二组逆序的数字,我们就把 second 更新为当前节点。最后把 first 和 second 两个的数字交换即可。
TreeNode first = null;
TreeNode second = null;
TreeNode pre = null;
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
int temp = first.val;
first.val = second.val;
second.val = temp;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return;
inOrder(root.left);
if (pre != null && pre.val > root.val) {
if (first == null) { //第一次遇到逆序对
first = pre;
second = root;
}else { //第二次遇到逆序对
second = root;
}
}
pre = root;
inOrder(root.right);
}
二叉树的构建
16. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTree(preorder,0 ,preorder.length -1, inorder, 0, inorder.length -1) ;
}
private TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder,int preLeft, int preRight, int[] inorder, int inLeft, int inRight) {
if (preLeft > preRight || inLeft > inRight) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preLeft]);
for (int i = 0; i <= inRight; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == root.val) {
root.left = buildTree(preorder,preLeft + 1, preLeft + i - inLeft, inorder, inLeft, i - 1);
root.right = buildTree(preorder,preLeft + i - inLeft + 1,preRight, inorder, i + 1, inRight);
}
}
return root;
}
17. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return buildTree(inorder, 0 , inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0 , postorder.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int inLeft, int inRight, int[] postorder,int postLeft, int postRight) {
if (inLeft > inRight || postLeft > postRight) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postRight]);
for (int i = 0; i <= inRight; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == root.val) {
root.left = buildTree(inorder,inLeft, i - 1, postorder, postLeft,postLeft + i - inLeft - 1);
root.right = buildTree(inorder, i + 1, inRight, postorder, postLeft + i - inLeft, postRight - 1);
}
}
return root;
}
BST问题
18.验证二叉搜索树
98. 验证二叉搜索树
中序遍历记录前一个节点的值
Double pre = - Double.MAX_VALUE;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return true;
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
if (left) {
if (pre < root.val) {
pre = (double)root.val;
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
return false;
}
19.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
二分法 递归。
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null) return null;
return constructBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode constructBST(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right)return null;
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = constructBST(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = constructBST(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
20.有序链表转换二叉搜索树
109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
快慢指针找到链表的中间节点的前一个节点,mid作为root节点。
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode midPre = getMidPre(head);
ListNode mid = midPre.next;
midPre.next = null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(mid.val);
root.left = sortedListToBST(head);
root.right = sortedListToBST(mid.next);
return root;
}
private ListNode getMidPre(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return pre;
}
21.二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
中序遍历就可得到递增的序列,从而可以找到第k大的元素,时间复杂度是O
(k)。
private int count = 0;
private int res;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root,k);
return res;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) return;
inOrder(root.left, k);
count++;
if (count == k) {
res = root.val;
return;
}
inOrder(root.right, k);
}
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
int count = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
count++;
if (count == k)return node.val;
cur = node.right;
}
return -1;
}
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
int leftCount = count(root.left);
if (leftCount == k - 1)return root.val;
if (leftCount > k - 1) return kthSmallest(root.left, k);
return kthSmallest(root.right,k - leftCount - 1);
}
private int count(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
return 1 + count(node.left) + count(node.right);
}
22.不同的二叉搜索树
96. 不同的二叉搜索树
解法1递归 :
public int numTrees(int n) {
if (n == 0)return 0;
return numTrees(1 , n);
}
private int numTrees(int start, int end) {
int res = 0;
if (start >= end) {
return 1;
}
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
int leftTrees = numTrees(start, i - 1);
int rightTrees = numTrees(i + 1, end);
res += leftTrees * rightTrees;
}
return res;
}
public int numTrees(int n) {
if (n == 0)return 0;
return getTrees(n);
}
private int getTrees(int n) {
int res = 0;
if (n == 0 || n == 1){
return 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int leftTrees = getTrees(i - 1);//i - 1代表左子树节点的数量
int rightTrees = getTrees(n - i); //n - i代表右子树节点的数量
res += leftTrees * rightTrees;
}
return res;
}
记忆化搜索:
由于递归的分叉 会导致很多重复的计算,使用记忆化的技术,把递归过程中的解缓存起来,第二次需要的时候直接取出来。
public int numTrees(int n) {
if (n == 0)return 0;
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
return getTrees(n, map);
}
private int getTrees(int n, HashMap map) {
if (map.containsKey(n)) {
return map.get(n);
}
int res = 0;
if (n == 0 || n == 1) {
return 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int leftTree = getTrees(i - 1, map);
int rightTree = getTrees(n - i, map);
res += leftTree * rightTree;
}
map.put(n, res);
return res;
}
解法2 公式法 :
比如,以1为根的树的个数,等于左子树的个数乘以右子树的个数,左子树是0个元素的树,右子树是两个元素的数。以2为根的数的个数,等于左子树的个数乘上右子树的个数,左子树是1个元素的数,右子树也是1个元素的数,
当数组为1,2,3,…,n的时候,基于以下原则的构建的BST具有唯一性:
以i为根节点的树,其左孩子由[1,i - 1]构成,右孩子由[i + 1, n]构成
定义f(i)为以[1,i]能产生UniqueBinaryTree的数目,则如果数组为空,毫无疑问,只能有1中BST f(0) = 1;
如果数组仅有一个元素「1」只有一种BST f[1] = 1;
如果数组有两个元素那么有如下两种可能
f[2] = f[0] * f[1] (1 as root)
- f[1] * f[0] ( 2 as root)
f[3] = f[2] * f[0] + f[1] * f[1] + f[0] * f[2]
f[i] = f[k - 1] * f[i - k] (k 从1 到 i)
public int numTrees(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <=n; i++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= i; k++) {
dp[i] += dp[k - 1] * dp[i - k];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
假设n个节点存在BST的个数是G(n),f[i]表示已i为根的BST的个数
则:G(n)=f(1)+f(2)+f(3)+f(4)+…+f(n)
当i为根节点时,其左子树节点个数为i-1个,右子树节点为n-i,则
f(i)=G(i−1)∗G(n−i)
综合两个公式可以得到 卡特兰数 公式
G(n)=G(0)∗G(n−1)+G(1)∗(n−2)+…+G(n−1)∗G(0)
23. 不同的二叉搜索树 II
95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II
解法1:递归
求1 … n的所有可能
只需要把1作为根节点,[]空作为左子树,[2 …n]的所有可能作为右子树
2作为根节点,[1]作为左子树,[3 …n]的所有可能作为右子树
3作为根节点,[ 1 2]的所有可能作为左子树,[4 n]的所有可能作为右子树,然后左右子树和右子树两两组合
4作为根节点,[ 1 2 3]的所有可能作为左子树,[5 n ]的所有可能作为右子树,然后左右子树和右子树两两组合
…
n作为根节点,[1…n -1]的所有可能作为左子树,[]作为右子树
至于,[2 …n]的所有可能,以及[4 n]以及其他情况,可以利用上边的方法,把每个数字作为根节点,然后把所有可能的左子树和右子树组合起来即可。
public List generateTrees(int n) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (n == 0)return res;
return generateTrees(1, n);
}
private List generateTrees(int start, int end) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
if (start > end) { //此时没有数字,将null加入结果中
res.add(null);
return res;
}
if (start == end) { //只有一个数字,当前数字作为一棵树假如结果中
TreeNode tree = new TreeNode(start);
res.add(tree);
return res;
}
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { //尝试将每个数字作为根节点
List leftTrees = generateTrees(start, i - 1); //得到所有可能的左子树
List rightTrees = generateTrees(i + 1, end); //得到所有可能的右子树
//左右子树两两组合
for (TreeNode left : leftTrees) {
for (TreeNode right : rightTrees) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(i);
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
res.add(root);
}
}
}
return res;
}
解法2:动态规划
解法四 动态规划 2
仔细分析,可以发现一个规律,首先我们每次增加的数字大于之前的所有的数字,所以新增加的数字出现的位置只可能是根节点或者是根节点的右孩子,右孩子的右孩子,总之一定是右边,其次,新数字所在位置原来的子树,改为当前插入数字的做孩子即可,因为插入输入数字是最大的
24. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p , q);
}
if (p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p , q);
}
return root;
}
25. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
注意p,q必然存在树内, 且所有节点的值唯一!!!
递归思想, 对以root为根的(子)树进行查找p和q, 如果root == null || p || q 直接返回root
表示对于当前树的查找已经完毕, 否则对左右子树进行查找, 根据左右子树的返回值判断:
1. 左右子树的返回值都不为null, 由于值唯一左右子树的返回值就是p和q, 此时root为LCA
2. 如果左右子树返回值只有一个不为null, 说明只有p和q存在与左或右子树中, 最先找到的那个节点为LCA
3. 左右子树返回值均为null, p和q均不在树中, 返回null
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || p == root || q == root)return root; //3,5 3,1
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left != null && right != null)return root; //5,1
else if (left != null && right ==null)return left; //5,2 都在左子树的情况
else if (left == null && right != null)return right;//1,0 都在右子树的情况
return null;
}
26. 修剪二叉搜索树
669. 修剪二叉搜索树
当 node.val > R,那么修剪后的二叉树必定出现在节点的左边。
类似地,当node.val < L,那么修剪后的二叉树出现在节点的右边。
否则,我们将会修剪树的两边。
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int L, int R) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (R < root.val) return trimBST(root.left, L ,R);
if (L > root.val) return trimBST(root.right, L ,R);
root.left = trimBST(root.left, L ,R);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, L ,R);
return root;
}
27. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root ==null)return null;
int sum = 0;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.right;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
sum += node.val;
node.val = sum;
cur = node.left;
}
return root;
}
递归版
private int sum = 0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
return root;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return;
inOrder(root.right);
sum += root.val;
root.val = sum;
inOrder(root.left);
}
28. 两数之和 IV - 输入 BST
653. 两数之和 IV - 输入 BST
使用中序遍历得到数组之后,再利用双指针对数组进行查找。
应该注意到,这题不能分别用左右子树两部分来处理这种思想,因为两个带球的节点可能分别在左右子树中。
private ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root);
int left = 0, right = list.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = list.get(left) + list.get(right);
if (sum < k)left++;
else if (sum == k)return true;
else if (sum > k) right--;
}
return false;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return;
inOrder(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
29. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
int minGap = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private TreeNode preNode = null;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
return minGap;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return ;
inOrder(root.left);
if (preNode != null) {
minGap = Math.min(minGap, root.val - preNode.val);
}
preNode = root;
inOrder(root.right);
}
30. 二叉搜索树中的众数
501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
中序遍历preNode 记录前一个节点。
每次比较preNode 和当前遍历到的root是否相等,相等更新curCount, 如果curCount > maxCount则需要清空结果集。
TreeNode preNode = null;
int curCount = 1;
int maxCount = 1;
private ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
int[] res = new int[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
res[i] = list.get(i);
}
return res;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
inOrder(root.left);
if (preNode != null) {
if (preNode.val == root.val)curCount++;
else curCount = 1;
}
if (curCount > maxCount) {
maxCount = curCount;
list.clear();
list.add(root.val);
}else if (curCount == maxCount) {
list.add(root.val);
}
preNode = root;
inOrder(root.right);
}
二叉树的递归
二叉树是一个递归的数据结构,因此是一个用来考察递归思维能力的绝佳的数据结构,递归一定是深度优先搜索,由于在二叉树上,递归的味道更佳浓烈一些。二叉树的先序、中序、后序,遍历都可以看做是DFS,此外还有其他顺序的深度优先遍历。
31. 二叉树的最小深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root ==null)return 0;
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
if (left == 0 || right == 0)return left + right + 1;
return Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
32. 二叉树的最大深度
104. 二叉树的最大深度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
33. 路径总和
112. 路径总和
走到叶子节点才能判断
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)return false;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == sum)return true;
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
34. 路径总和 II
113. 路径总和 II
private List> res;
public List> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res;
pathSum(root,sum,new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
private void pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum , ArrayList temp) {
if (root == null)return;
temp.add(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == sum) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
pathSum(root.left, sum - root.val, temp);
pathSum(root.right, sum - root.val, temp);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
35. 路径总和 III
437. 路径总和 III
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)return 0;
return getCount(root, sum) + pathSum(root.left, sum) + pathSum(root.right, sum);
}
private int getCount(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null)return 0;
int count = 0;
if (root.val == sum) count++;
count += getCount(root.left, sum - root.val);
count += getCount(root.right, sum - root.val);
return count;
}
36. 二叉树中的最大路径和
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
可以利用最大连续子序和问题的思路,如果数组只有一个方向的话,那么BinaryTree其实只是左右两个方向而已。我们需要比较两个方向上的hi。
不过数组可以从到位遍历,二叉树怎么办呢?使用dfs,先算出左右子树的结果L 和R,如果L大于0,那么对后续的结果是有利的,我们加上L,如果R 大于0,那么对后续的结果也是有利的,继续加上R。
最后在return的时候,只返回一个方向上的值,为什么?这是因为在递归中,只能向父节点返回,不可能存在L -> root > R的路径,只可能是L -> root 或者 R -> root.
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return maxSum;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = dfs(root.left);
int right = dfs(root.right);
int sum = root.val;
if (left > 0) sum += left;
if (right > 0) sum += right;
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum , sum);
return Math.max(left, right) > 0 ? Math.max(left, right) + root.val : root.val;
}
37. 求根到叶子节点数字之和
129. 求根到叶子节点数字之和
计算从根到叶子节点生成的所有数字之和。
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return sum * 10 + root.val;
return dfs(root.left, sum * 10 + root.val) + dfs(root.right, sum * 10 + root.val);
}
38. 另一个树的子树
572. 另一个树的子树
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (s == null)return false;
return isEqual(s,t) || isSubtree(s.left, t) || isSubtree(s.right, t);
}
private boolean isEqual(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (t == null && s == null)return true;
if (t == null || s == null) return false;
if (s.val != t.val) return false;
return isEqual(s.left,t.left) && isEqual(s.right, t.right);
}
39. 左叶子之和
404. 左叶子之和
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return 0;
if (isLeaf(root.left))return root.left.val + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
}
private boolean isLeaf(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null)return false;
return node.left == null && node.right == null;
}
40. 最长同值路径
687. 最长同值路径
最长的路径可能有三种情况
- 在左子树的内部
- 在右子树的内部
- 在穿过左子树,根节点,右子树的一条路径中
设计一个递归函数,返回以该节点为根节点,向下走的最长同值路径。
以某个节点为根节点的最长同值路径就是,
如果该节点的值等于其左子树的值,则最长同值路径要加上左子树的最长同值路径,如果不等,左子树的路径为0
如果该节点的值等于其右子树的值,则最长同值路径要加上右子树的最长同值路径,如果不等,右子树的路径为0
private int res = 0;
public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return 0;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = dfs(root.left);
int right = dfs(root.right);
int leftPath = root.left != null && root.left.val == root.val ? left + 1 : 0;
int rightPath = root.right != null && root.right.val == root.val ? right + 1: 0;
res = Math.max(res, leftPath + rightPath);
return Math.max(leftPath, rightPath);
}
41. 打家劫舍 III
337. 打家劫舍 III
分为抢劫根节点和不抢劫根节点的两种情况,取二者的最大值
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)return 0;
int robRoot = root.val;
if (root.left != null ) {
robRoot += rob(root.left.left) + rob(root.left.right);
}
if (root.right != null) {
robRoot += rob(root.right.left) + rob(root.right.right);
}
int robChild = rob(root.left) + rob(root.right);
return Math.max(robChild, robRoot);
}
42. 二叉树中第二小的节点
671. 二叉树中第二小的节点
特殊的二叉树,每个节点的子节点数量只能为2或者0,如果一个节点有两个子节点的话,那么这个节点的值不大于它的子节点的值。
- 第二小的数字,定义两个变量存放第一小和第二小的数字
- 其中特别注意的是count计数器,如果二叉树只有一个数字的话,意味着second没有被赋值,那么count = 0,结果是 -1,如果count > 0,就输出second
int firstMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int secondMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int count = 0;
public int findSecondMinimumValue(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return count == 0 ? -1 : secondMin;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
if (root.val < firstMin) {
secondMin = firstMin;
firstMin = root.val;
}else if (root.val > firstMin && root.val <= secondMin) {
secondMin = root.val;
count++;
}
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
这题可以转换为求左右子节点中的最小值。
public int findSecondMinimumValue(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root,root.val);
}
//求左右子节点中的最小值。
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int value) {
if (root == null)return -1;
if (root.val > value) {
return root.val;
}
int left = dfs(root.left, value);
int right = dfs(root.right, value);
if (left >= 0 && right >= 0) { // [左5, 根3, 右7]
return Math.min(left , right);
}
return Math.max(left, right);// [左2, 根2, 右5]
}
Trie
43. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
private class Node {
boolean isWord;
Node[] next = new Node[26];
}
private Node root = new Node();
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
Node p = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if (p.next[c - 'a'] == null) {
p.next[c - 'a'] = new Node();
}
p = p.next[c - 'a'];
}
p.isWord = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
Node p = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
if (p.next[c - 'a'] == null) {
return false;
}
p = p.next[c - 'a'];
}
return p.isWord;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Node p = root;
for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) {
if (p.next[c - 'a'] == null) {
return false;
}
p = p.next[c - 'a'];
}
return true;
}