Android之ActivityManagerService启动详解
ActivityManagerService,简称AMS,具有管理Activity行为、控制activity的生命周期、派发消息事件、内存管理等功能,AMS的另外两个重要概念是两大核心功能是WindowManagerService.java和View.java。
分析ActivityManagerService的流程之前需要先下载Android的系统源码,相关下载可以参照下面的文章:中国大陆如何下载 Android 源码
用户从Launcher程序点击应用图标可启动应用的入口Activity,Activity启动时需要多个进程之间的交互,如下图所示。
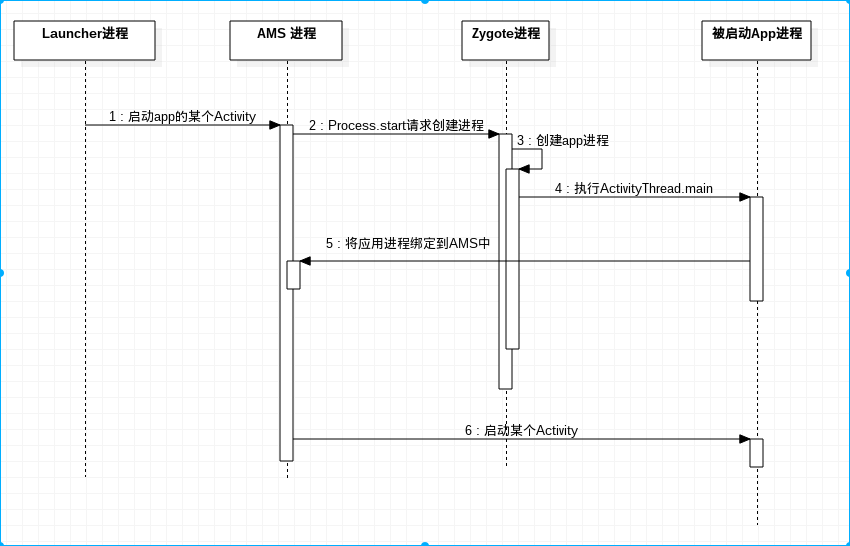
其中,AMS进程实际上是SystemServer进程,因为AMS只是SystemServer启动的一个服务而已,运行在SystemServer的某个线程中。
具体的,用户在Launcher程序里点击应用图标时,会通知ActivityManagerService启动应用的主Activity,ActivityManagerService发现这个应用还未启动,则会通知Zygote进程执行ActivityThread的main方法。应用进程接下来通知ActivityManagerService应用进程已启动,ActivityManagerService保存应用进程的一个代理对象,这样ActivityManagerService可以通过这个代理对象控制应用进程,然后ActivityManagerService通知应用进程创建主Activity的实例,并执行它的生命周期方法,也就是诸如OnCreadte()等方法。
Launcher启动
当点击应用程序图标后,Launcher 使用一个带有 Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK flag 的 Intent,调用 startActivity 方法来启动App。相关源码如下:
public static Intent makeLaunchIntent(Context context, LauncherActivityInfoCompat info,
UserHandleCompat user) {
long serialNumber = UserManagerCompat.getInstance(context).getSerialNumberForUser(user);
return new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN)
.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_LAUNCHER)
.setComponent(info.getComponentName())
.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED)
.putExtra(EXTRA_PROFILE, serialNumber);
}当点击app的图标时会执行如下的代码调用流程。
public void onClick(View v) {
...
Object tag = v.getTag();
if (tag instanceof ShortcutInfo) {
onClickAppShortcut(v);
}
...
}
protected void onClickAppShortcut(final View v) {
...
// Start activities
startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(v);
...
}
void startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(View v) {
...
// 得到launcher提供的启动这个app主activity的intent
intent = shortcut.intent;
...
boolean success = startActivitySafely(v, intent, tag);
...
}
boolean startActivitySafely(View v, Intent intent, Object tag) {
...
success = startActivity(v, intent, tag);
...
}
private boolean startActivity(View v, Intent intent, Object tag) {
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
...
startActivity(intent, optsBundle);
...
}从以上代码流程可知当Launcher启动一个app时,会在自己的startActivity()方法中为Intent中添加一个FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK flag,然后调用继承自Activity的startActivity()方法来进一步启动app。
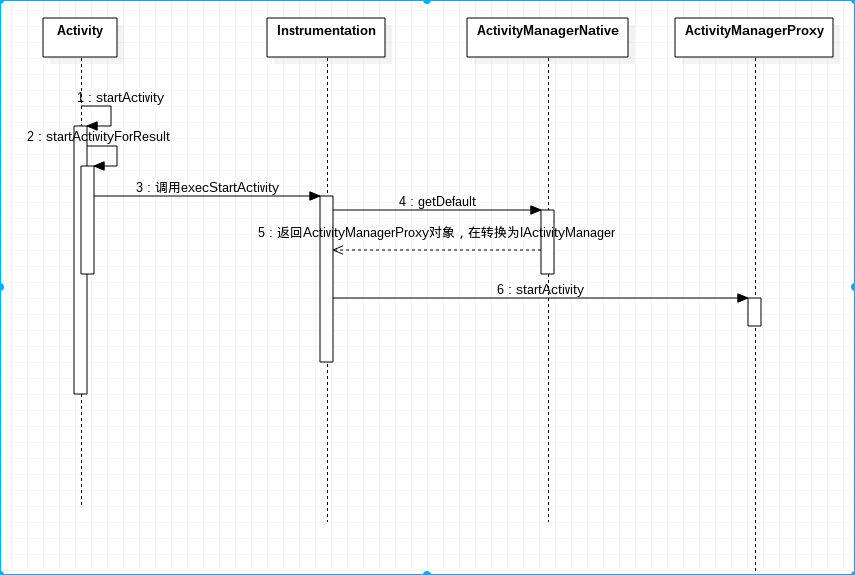
Activity向AMS发起请求启动App
Activity启动Activity的流程如下,具体可以查看相关的源码,需要注意的是Android 6.0的实现和8.0版本实现有略微的区别。
下面我们看一下ActivityThread类,ActivityThread类是Android应用进程的核心类,这个类包含了应用框架中其他重要的类。其源码如下:
public final class ActivityThread {
........
private ContextImpl mSystemContext;
static IPackageManager sPackageManager;
// 保存该app中所有的Activity
final ArrayMap mActivities = new ArrayMap<>();
// 保存该app中所有的service
final ArrayMap mServices = new ArrayMap<>();
// 保存该app中所有的provider
final ArrayMap mProviderMap
= new ArrayMap();
//管理应用的资源
private final ResourcesManager mResourcesManager;
// 存储包含代码,即dex文件的apk文件保存在该变量中
final ArrayMap> mPackages
= new ArrayMap>();
// 不包含代码,紧紧包含资源的apk放在该变量中
final ArrayMap> mResourcePackages
// 如果app中自己实现了Application的子类,并在清单文件中声明了,那么该变量就指向自己实现的那个子类对象
Application mInitialApplication;
AppBindData mBoundApplication;
// 用于binder通信,AMS通过它来调用应用的接口
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
// 主线程中的Handler
static Handler sMainThreadHandler; // set once in main()
final Looper mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
// H继承自Handler,mH用来发送和处理ApplicationThread通过binder接受的AMS请求
final H mH = new H();
.........
} ActivityThread类中没有定义数据结构来存储BroadcastReceiver对象,因为BroadcastReceiver对象生命周期很短暂,属于调用一次运行一次的类型,因此不需要保存其对象。AppBindData类为ActivityThread的内部类,定义如下,记录了与之绑定的app的相关数据。
static final class AppBindData {
LoadedApk info;
String processName;
ApplicationInfo appInfo;
List providers;
ComponentName instrumentationName;
Bundle instrumentationArgs;
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher;
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiAutomationConnection;
int debugMode;
boolean enableOpenGlTrace;
boolean restrictedBackupMode;
boolean persistent;
Configuration config;
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo;
/** Initial values for {@link Profiler}. */
ProfilerInfo initProfilerInfo;
public String toString() {
return "AppBindData{appInfo=" + appInfo + "}";
}
}
其中 ApplicationThread类型的变量mAppThread用于AMS所在app的接口,应用进程需要调用AMS提供的功能,而AMS也需要主动调用应用进程以控制应用进程并完成指定操作。ApplicationThread的运作流程如下图:
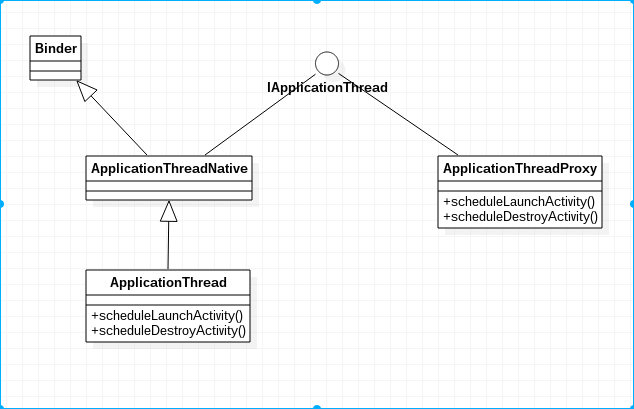
如上图可知,AMS通过IApplicationThread接口管理应用进程,ApplicationThread类实现了IApplicationThread接口,实现了管理应用的操作,ApplicationThread对象运行在应用进程里。ApplicationThreadProxy对象是ApplicationThread对象在AMS线程 (AMS线程运行在system_server进程)内的代理对象,AMS通过ApplicationThreadProxy对象调用ApplicationThread提供的功能,比如让应用进程启动某个Activity。ApplicationThread中的scheduleDestroyActivity的源码如下:
public final void scheduleDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finishing,
int configChanges) {
sendMessage(H.DESTROY_ACTIVITY, token, finishing ? 1 : 0,
configChanges);
}而Binder服务端的最终调用的是ActivityThread的sendMessage函数。
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2) {
sendMessage(what, obj, arg1, arg2, false);
}
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(
TAG, "SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what)
+ ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = obj;
msg.arg1 = arg1;
msg.arg2 = arg2;
if (async) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}而ActivityThread类中内部类H(继承自Handler,mH就是H的对象)中则定义了处理消息的方法,该函数用来处理接收到的数据。
AMS启动Activity
前面讲到AMS使用startActivity启动APP,为了加深印象在来看一下startActivity函数(需要注意的是,6.0和8.0的代码有细微的区别)。
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, options,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options, int userId) {
// 如果是隔离的应用的话,不允许其打开其他app的activity
// appid是99000-99999之间的属于隔离app
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId,
false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, options, false, userId, null, null);
}判断发起者是否是隔离的app,不允许隔离的app调用其他app。然后调用ActivityStackSupervisor类中的startActivityMayWait方法。
final int startActivityMayWait(
IApplicationThread caller,//AMS通过这个参数可以和发起者进行交互
int callingUid,//发起者uid
String callingPackage,//发起者包名
Intent intent, // 启动activity的intent
String resolvedType, // intent的类型,也就是MIME type
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession,
IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo,//用于接收startActivityForResult的结果,launcher启动app这种情景下没有用,为null
String resultWho,
int requestCode,//这个是调用者来定义其意义,若值大于等于0,则AMS内部保存该值并通过onActivityResult返回调用者,这里为-1
int startFlags,// 传入的为0
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo,
WaitResult outResult,
Configuration config,
Bundle options,
boolean ignoreTargetSecurity,
int userId,
IActivityContainer iContainer, // 传入的为null
TaskRecord inTask)/ // 传入为null
{
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
// 当启动一个app时 ,launcher会构造一个intent,前面已经介绍了,是一个显示的intent
// 所以这里为true,
boolean componentSpecified = intent.getComponent() != null;
// Don't modify the client's object!
// 创建一个新的intent,方便改动
intent = new Intent(intent);
// 收集 要启动的app的主activity的信息
ActivityInfo aInfo =
resolveActivity(intent, resolvedType, startFlags, profilerInfo, userId);
// 传入的该参数为null
ActivityContainer container = (ActivityContainer)iContainer;
synchronized (mService) {
if (container != null && container.mParentActivity != null &&
container.mParentActivity.state != RESUMED) {
// Cannot start a child activity if the parent is not resumed.
return ActivityManager.START_CANCELED;
}
....................................
final ActivityStack stack;
if (container == null || container.mStack.isOnHomeDisplay()) {
stack = mFocusedStack;
} else {
stack = container.mStack;
}
// 传入的config为null
stack.mConfigWillChange = config != null && mService.mConfiguration.diff(config) != 0;
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG_CONFIGURATION,
"Starting activity when config will change = " + stack.mConfigWillChange);
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (aInfo != null &&
(aInfo.applicationInfo.privateFlags
&ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_CANT_SAVE_STATE) != 0) {
.......................
}
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, resolvedType, aInfo,
voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho,
requestCode, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage,
realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags, options, ignoreTargetSecurity,
componentSpecified, null, container, inTask);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
if (stack.mConfigWillChange) {
.............
}
// 传入的为null
if (outResult != null) {
.......................
mService.wait(); //等待应用进程的activity启动完成
...........
}
.............
}
return res;
}
}
startActivityAsUser()方法最主要的目地是进行权限检查,检查发起者是否被隔离,是的话,是不允许调用别的app的activity的。startActivityMayWait()方法主要是利用传入的intent去向PMS搜集要启动的APP的信息,储存到aInfo中.。名字中有wait字眼,预示着该方法可能导致线程等待,不过在我们这个场景中不会出现这种情况,因为wait出现在对结果的处理中,我们这个场景中是不需要处理结果的。
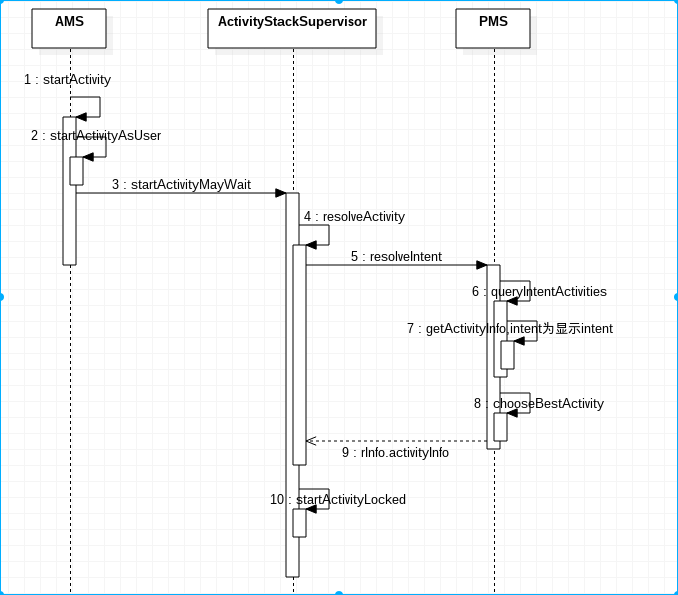
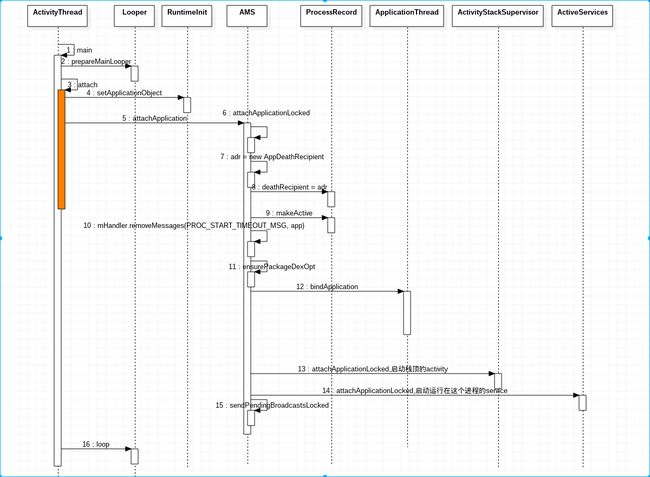
ActivityThread.main
Android APP的入口类在ActivityThread中,有一个Main函数,该函数的源码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
// 环境初始化,主要是app运行过程中需要使用到的系统路径
// 比如外部存储路径等等
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Set the reporter for event logging in libcore
EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());
//增加一个保存key的provider
AndroidKeyStoreProvider.install();
// 为应用社会当前用户的CA证书保存的位置
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
// 设置app进程的名字
// 通过前面的分析可知,前面的过程中已经设置过名字了,这里又改为了“pre-initialized”,不知道为啥,
// 因为后面还要在调用该方法,重新设置进程名字为app 包名或者app指定的名字。
Process.setArgV0("" );
// 创建主线程looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// 创建ActivityThread对象。
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
// 将创建的ActivityThread附加到AMS中,这样
// AMS就可以控制这个app中组件的生命周期了
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
//App主线程开始执行消息处理循环
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
}当ActivityThread对象创建之后,就开始调用其attach()方法,这是一个很重要的方法,参数为false表明是普通app进程。
private void attach(boolean system)
{
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
// app进程传入fasle
if (!system) {
ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ensureJitEnabled();
}
});
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("" ,
UserHandle.myUserId());
// mAppThread是ApplicationThread对象;
// 下面这个方法会把mAppThread放到RuntimeInit类中的静态变量mApplicationObject中
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
// 执行AMS的attachApplication方法
// 将mAppThread传入AMS,这样AMS就可以通过它来控制app了
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
// Watch for getting close to heap limit.
BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(new Runnable() {
............
});
} else {
..............
}
// add dropbox logging to libcore
DropBox.setReporter(new DropBoxReporter());
ViewRootImpl.addConfigCallback(new ComponentCallbacks2() {
.......
});
}其中,RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject方法源码如下:
public static final void setApplicationObject(IBinder app) {
mApplicationObject = app;
}AMS的attachApplication方法
attachApplication方法主要负责APP与AMS的绑定操作,该方法的源码如下:
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}该方法最终调用了attachApplicationLocked()方法。
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
ProcessRecord app;
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
// 在创建startProcessLocked()方法中调用Process.start()方法创建进程后
// 会以接收传递过来的进程号为索引,将ProcessRecord加入到AMS的mPidsSelfLocked中
// 这里可以以进程号从mPidsSelfLocked中拿到ProcessRecord
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
if (app == null) {
........
return false;
}
if (app.thread != null) {
handleAppDiedLocked(app, true, true);
}
// 注册app进程死亡通知处理机制,也就是创建监听app死亡的对象
// App进程死亡后,会调用AppDeathRecipient.binderDied()方法
final String processName = app.processName;
try {
AppDeathRecipient adr = new AppDeathRecipient(
app, pid, thread);
thread.asBinder().linkToDeath(adr, 0);
app.deathRecipient = adr;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
app.resetPackageList(mProcessStats);
startProcessLocked(app, "link fail", processName);
return false;
}
//调用ProcessStatsService开始记录process的状态
//该方法中将thread赋值给app.thread
app.makeActive(thread, mProcessStats);
// 初始化App进程优先级等信息
app.curAdj = app.setAdj = -100;
app.curSchedGroup = app.setSchedGroup = Process.THREAD_GROUP_DEFAULT;
app.forcingToForeground = null;
updateProcessForegroundLocked(app, false, false);
app.hasShownUi = false;
app.debugging = false;
app.cached = false;
app.killedByAm = false;
// 移除PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG消息
// 前面在AMS.startProcessLocked方法中会在调用Process.start()方法之后,将这个消息放入消息队列中
// 如果没有在规定的时间内将该消息移除消息队列,那么会导致进程启动超时
mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);
// mProcessesReady为true
boolean normalMode = mProcessesReady || isAllowedWhileBooting(app.info);
// 拿到App的provider
List<ProviderInfo> providers = normalMode ? generateApplicationProvidersLocked(app) : null;
........
// If the app is being launched for restore or full backup, set it up specially
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode = false;
if (mBackupTarget != null && mBackupAppName.equals(processName)) {
isRestrictedBackupMode = (mBackupTarget.backupMode == BackupRecord.RESTORE)
|| (mBackupTarget.backupMode == BackupRecord.RESTORE_FULL)
|| (mBackupTarget.backupMode == BackupRecord.BACKUP_FULL);
}
// 判断是否需要执行dex2oat命令
// 在app安装的时候,会执行一次dex2oat
// 当生成的oat文件被破外或者删除的时候,需要重新执行dex2oat
ensurePackageDexOpt(app.instrumentationInfo != null
? app.instrumentationInfo.packageName
: app.info.packageName);
// instrument app 技术先关
// 比如Android studio 开发时,修改某些代码时,没必要重新安装apk,即可查看之后的结果
// 后续单独在分析instrument技术
if (app.instrumentationClass != null) {
ensurePackageDexOpt(app.instrumentationClass.getPackageName());
}
....
// 调用ApplicationThread的bindApplication接口
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, app.instrumentationClass,
profilerInfo, app.instrumentationArguments, app.instrumentationWatcher,
app.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection, testMode, enableOpenGlTrace,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked());
updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
app.lastRequestedGc = app.lastLowMemory = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
............
return false;
}
....
boolean badApp = false;
boolean didSomething = false;
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
// 为true
if (normalMode) {
try {
// 执行ActivityStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
// Find any services that should be running in this process...
if (!badApp) {
try {
// 处理要运行这个进程中的service
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown starting services in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
// Check if a next-broadcast receiver is in this process...
if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) {
try {
// 处理广播
didSomething |= sendPendingBroadcastsLocked(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
// If the app died trying to launch the receiver we declare it 'bad'
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown dispatching broadcasts in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
........
if (!didSomething) {
updateOomAdjLocked();
}
return true;
}attachApplicationLocked函数比较长,首先以传入的app进程号为索引从AMS的mPidsSelfLocked中取出app进程的ProcessRecord对象。然后调用ProcessRecord对象的makeActive方法调用ProcessStatsService开始记录process的状态,接着将PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG消息,从消息循环中移除,检查是否重新执行dex2oat生成app的oat文件。
该方法主要做了一下四件事情:
- 调用ActivityThread的bindApplication方法去启动Application;
- 是调用ActivityStackSupervisor的attachApplicationLocked()方法去启动ActivityStack栈顶的Activity;
- 是ActiveServices调用的attachApplicationLocked()方法启动在当前App进程中的service;
- 是检查是否有广播broadcast到这个application,如果有则广播。
ApplicationThread.bindApplication方法
接下来重点分析下bindApplication()方法,这个方法最终效果是调用了App的Application对象的onCreate方法。其源码如下:
public final void bindApplication(
String processName, //ProcessRecord中记录的进程名字
ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List<ProviderInfo> providers, // app中的providers
ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo,
Bundle instrumentationArgs, //测试相关
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableOpenGlTrace, boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent,
Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map<String, IBinder> services,
Bundle coreSettings) {
if (services != null) {
// Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}
// 发送SET_CORE_SETTINGS消息
// 获取系统的设定并设置到ActivityThread中
setCoreSettings(coreSettings);
// 拿到PMS
IPackageManager pm = getPackageManager();
android.content.pm.PackageInfo pi = null;
try {
// 以包名从PMS中获得PackageInfo
pi = pm.getPackageInfo(appInfo.packageName, 0, UserHandle.myUserId());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
if (pi != null) {
// 该app是否设置了共享uid
boolean sharedUserIdSet = (pi.sharedUserId != null);
// app进程名字是否被设定为与包名不一致
// 默认情况下,app进程名字就是其包名
// 当显示设置process name 的时候可以执行进程的名字
boolean processNameNotDefault =
(pi.applicationInfo != null &&
!appInfo.packageName.equals(pi.applicationInfo.processName));
// 如果设置了共享uid或者进程名字设置为了其他名字,
// 这就导致该app可能运行在一个已经运行的进程中
boolean sharable = (sharedUserIdSet || processNameNotDefault);
// 如果app是单独的进程,那么要想VM注册相关信息
// 是就上就在/data/dalvik-cache/profiles/创建一个以包名为名字的空文件,另外两个参数没用到
if (!sharable) {
VMRuntime.registerAppInfo(appInfo.packageName, appInfo.dataDir,
appInfo.processName);
}
}
// 创建兵初始化AppBindData对象
// 在这里设置了进程名字,app的provider,ApplicationInfo
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providers;
// 测试相关
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableOpenGlTrace = enableOpenGlTrace;
// 是否允许adb backup
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
// 进程是否常驻内存,杀掉后,会被重启
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
// 发送BIND_APPLICATION消息
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);
}bindApplication()方法要通过PMS检查启动的app是否设置了共享uid,以及检查当前app进程的名字是否设定的与包名不一致,符合两者中的任一种情况下,则说明该app进程可能运行在另一个已经存在的进程中。
bindApplication()方法主要是创建和初始化了AppBindData对象,并发送两个消息:一个是SET_CORE_SETTINGS;另一个是BIND_APPLICATION。SET_CORE_SETTINGS主要是获取系统的设定并设置到ActivityThread中。BIND_APPLICATION用于启动App并安装所有的provider,并回调App的oncreate方法BIND_APPLICATION消息。
ActivityThread中处理BIND_APPLICATION消息的方法是handleBindApplication(),其源码如下:
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
mBoundApplication = data;
.......
// 设置进程的名字,因为前面ActivityThread.main将其设置为了""
Process.setArgV0(data.processName);
// 设置app在ddms中显示的进程名字
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName(data.processName,
UserHandle.myUserId());
// 普通app进程,一般情况下为false
// 除非xml设置persistent为true
// 带有persistent标记的进程在低内存设备中部支持使用硬件加速
if (data.persistent) {
if (!ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx()) {
HardwareRenderer.disable(false);
}
}
if (mProfiler.profileFd != null) {
mProfiler.startProfiling();
}
// 根据app编译时指定的sdk版本与当前系统sdk版本设置AsyncTask
if (data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion <= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB_MR1) {
AsyncTask.setDefaultExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR);
}
Message.updateCheckRecycle(data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion);
// 恢复时区和位置信息
TimeZone.setDefault(null);
Locale.setDefault(data.config.locale);
// 资源管理初始化设置
mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(data.config, data.compatInfo);
mCurDefaultDisplayDpi = data.config.densityDpi;
applyCompatConfiguration(mCurDefaultDisplayDpi);
// 设置AppBindData中LoadedApk info属性字段
// 这里会根据传入app的ActivityInfo和CompatibilityInfo创建一个LoadedApk对象
data.info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.appInfo, data.compatInfo);
// 如果应用没有指定使用设备的density,那么默认使用mdpi
if ((data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_SCREEN_DENSITIES)
== 0) {
mDensityCompatMode = true;
Bitmap.setDefaultDensity(DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT);
}
updateDefaultDensity();
// 创建ContextImpl上下文,里面也设计到了资源管理相关的内容 ,如从LoadedApk中提取资源
// 后续还需对其进行初始化
final ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, data.info);
// 普通app启动时,isIsolated为false
if (!Process.isIsolated()) {
//在沙箱目录中创建cache文件夹
final File cacheDir = appContext.getCacheDir();
if (cacheDir != null) {
//将创建的cache文件夹与属性"java.io.tmpdir"关联
System.setProperty("java.io.tmpdir", cacheDir.getAbsolutePath());
} else {
Log.v(TAG, "Unable to initialize \"java.io.tmpdir\" property due to missing cache directory");
}
// Use codeCacheDir to store generated/compiled graphics code
// 在沙箱目录创建code-cache文件夹
final File codeCacheDir = appContext.getCodeCacheDir();
if (codeCacheDir != null) {
setupGraphicsSupport(data.info, codeCacheDir);
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to setupGraphicsSupport due to missing code-cache directory");
}
}
// 设置时间格式
final boolean is24Hr = "24".equals(mCoreSettings.getString(Settings.System.TIME_12_24));
DateFormat.set24HourTimePref(is24Hr);
View.mDebugViewAttributes =
mCoreSettings.getInt(Settings.Global.DEBUG_VIEW_ATTRIBUTES, 0) != 0;
// 调试相关
if ((data.appInfo.flags &
(ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM |
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_UPDATED_SYSTEM_APP)) != 0) {
StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging();
}
if (data.appInfo.targetSdkVersion > 9) {
StrictMode.enableDeathOnNetwork();
}
NetworkSecurityPolicy.getInstance().setCleartextTrafficPermitted(
(data.appInfo.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_USES_CLEARTEXT_TRAFFIC) != 0);
if (data.debugMode != IApplicationThread.DEBUG_OFF) {
............
}
// Enable OpenGL tracing if required
if (data.enableOpenGlTrace) {
GLUtils.setTracingLevel(1);
}
// Allow application-generated systrace messages if we're debuggable.
boolean appTracingAllowed = (data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_DEBUGGABLE) != 0;
Trace.setAppTracingAllowed(appTracingAllowed);
/**
* Initialize the default http proxy in this process for the reasons we set the time zone.
*/
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
if (b != null) {
IConnectivityManager service = IConnectivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
try {
// 设置网络代理
final ProxyInfo proxyInfo = service.getProxyForNetwork(null);
Proxy.setHttpProxySystemProperty(proxyInfo);
} catch (RemoteException e) {}
}
// 为null
if (data.instrumentationName != null) {
..........
} else {
// 创建Instrumentation对象
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
}
if ((data.appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_LARGE_HEAP) != 0) {
dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
} else {
dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clampGrowthLimit();
}
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy savedPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWrites();
try {
// 创建app的Application对象
Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
mInitialApplication = app;
// don't bring up providers in restricted mode; they may depend on the
// app's custom Application class
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
List<ProviderInfo> providers = data.providers;
if (providers != null) {
installContentProviders(app, providers);
// For process that contains content providers, we want to
// ensure that the JIT is enabled "at some point".
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT, 10*1000);
}
}
// Do this after providers, since instrumentation tests generally start their
// test thread at this point, and we don't want that racing.
try {
// 执行instrumentation的onCreate()方法
mInstrumentation.onCreate(data.instrumentationArgs);
}
catch (Exception e) {
................
}
// 执行Application的onCreate生命周期方法
try {
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
...............
}
} finally {
StrictMode.setThreadPolicy(savedPolicy);
}
}handleBindApplication函数主要完成了如下的一些操作:
- 确定了进程的最终名字,以及其在ddms中显示的进程名字;
- 恢复进程的时区和位置信息;
- 调用getPackageInfoNoCheck()创建LoadApk对象;
- 创建ContextImpl对象,是AppContext;
- 设置网络代理;
- 创建Instrumentation对象。
LoadedApk
LoadedApk类用来记录描述一个被加载运行的APK,的代码、资源等信息。
public final class LoadedApk {
private static final String TAG = "LoadedApk";
private final ActivityThread mActivityThread; // App的ActivityThread对象
private ApplicationInfo mApplicationInfo; // 描述App信息的ApplicationInfo,如果App中重载了Application类,那么其类名会被记录在ApplicationInfo中
final String mPackageName;// app的包名
private final String mAppDir;// app在/data/app/<包名>路径
private final String mResDir;// 资源路径
private final String[] mSplitAppDirs;
private final String[] mSplitResDirs;
private final String[] mOverlayDirs;
private final String[] mSharedLibraries;// 共享java库
private final String mDataDir;//数据沙箱目录
private final String mLibDir;// native so库位置
private final File mDataDirFile;
private final ClassLoader mBaseClassLoader;//getPackageInfoNoCheck()创建的LoadedApk对象中该字段初始化为null
private final boolean mSecurityViolation;
private final boolean mIncludeCode;// 这个apk是否包含dex
private final boolean mRegisterPackage;
private final DisplayAdjustments mDisplayAdjustments = new DisplayAdjustments();
Resources mResources;
private ClassLoader mClassLoader;//
private Application mApplication;// 这个app的Application对象,如果App继承了Application,那么为其子类对象
private final ArrayMap> mReceivers
= new ArrayMap>();
private final ArrayMap> mUnregisteredReceivers
= new ArrayMap>();
private final ArrayMap> mServices
= new ArrayMap>();
private final ArrayMap> mUnboundServices
= new ArrayMap>();
int mClientCount = 0;
Application getApplication() {
return mApplication;
} 通过分析可知,在handleBindApplication()方法中通过调用getPackageInfoNoCheck()方法创建LoadedApk对象。getPackageInfoNoCheck()的源码如下:
public final LoadedApk getPackageInfoNoCheck(ApplicationInfo ai,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo) {
return getPackageInfo(ai, compatInfo, null, false, true, false);
}getPackageInfoNoCheck()又调用了getPackageInfo()。
private LoadedApk getPackageInfo(
ApplicationInfo aInfo, // app的Application信息
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, // 兼容性
ClassLoader baseLoader,// 传入null
boolean securityViolation,// 传入false
boolean includeCode,// 传入true
boolean registerPackage // 传入false
) {
// 要启动app的拥有者与当前系统用户不一致
final boolean differentUser = (UserHandle.myUserId() != UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.uid));
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
WeakReference ref;
if (differentUser) {
ref = null;
} else if (includeCode) {
// 如果包含了dex,那么从ActivityThread.mPackages中先查找是否已经有了apk对应的LoadedApk
ref = mPackages.get(aInfo.packageName);
} else {
// 如果没有包含了dex,那么从ActivityThread.mResourcePackages中先查找是否已经有了apk对应的LoadedApk
ref = mResourcePackages.get(aInfo.packageName);
}
// 如果前面已经从mPackages或者mResourcePackages中找到了apk对应的LoadedApk,那么就可以直接返回了
// 没有找到的话,就要创建LoadedApk对象了
if (packageInfo == null || (packageInfo.mResources != null
&& !packageInfo.mResources.getAssets().isUpToDate())) {
// 创建LoadedApk对象
packageInfo =
new LoadedApk(this, aInfo, compatInfo, baseLoader,
securityViolation, includeCode &&
(aInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HAS_CODE) != 0, registerPackage);
if (mSystemThread && "android".equals(aInfo.packageName)) {
packageInfo.installSystemApplicationInfo(aInfo,
getSystemContext().mPackageInfo.getClassLoader());
}
// 创建LoadedApk对象之后,将其加入对应的缓存列表中
if (differentUser) {
// Caching not supported across users
} else if (includeCode) {
mPackages.put(aInfo.packageName,
new WeakReference(packageInfo));
} else {
mResourcePackages.put(aInfo.packageName,
new WeakReference(packageInfo));
}
}
return packageInfo;
}
} 由以上代码可知,当要获取一个LoadedApk对象时,先从ActivityThread的两个缓存列表:mPackages和mResourcePackages中寻找,没找到的话才会新建LoadedApk对象,然后将其加入对应的缓存列表中。当找到apk对应的LoadedApk对象后,以此为参数创建Application的Context对象。
final ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, data.info);
static ContextImpl createAppContext(ActivityThread mainThread, LoadedApk packageInfo) {
if (packageInfo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("packageInfo");
return new ContextImpl(null, mainThread,
packageInfo, null, null, false, null, null, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY);
}
private ContextImpl(
ContextImpl container, // 传入null
ActivityThread mainThread,// app的ActivityThread对象
LoadedApk packageInfo, // apk对应的LoadedApk对象
IBinder activityToken, // 传入为null
UserHandle user, boolean restricted,
Display display, Configuration overrideConfiguration, int createDisplayWithId) {
mOuterContext = this;
mMainThread = mainThread;
mActivityToken = activityToken;
mRestricted = restricted;
if (user == null) {
user = Process.myUserHandle();
}
mUser = user;
// context中会记录apk对应的LoadedApk对象
mPackageInfo = packageInfo;
// 资源管理相关,后续单独开篇介绍
mResourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance();
..............
Resources resources = packageInfo.getResources(mainThread);
if (resources != null) {
if (displayId != Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY
|| overrideConfiguration != null
|| (compatInfo != null && compatInfo.applicationScale
!= resources.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale)) {
resources = mResourcesManager.getTopLevelResources(packageInfo.getResDir(),
packageInfo.getSplitResDirs(), packageInfo.getOverlayDirs(),
packageInfo.getApplicationInfo().sharedLibraryFiles, displayId,
overrideConfiguration, compatInfo);
}
}
mResources = resources;
if (container != null) {
mBasePackageName = container.mBasePackageName;
mOpPackageName = container.mOpPackageName;
} else {
// 记录app包名
mBasePackageName = packageInfo.mPackageName;
ApplicationInfo ainfo = packageInfo.getApplicationInfo();
if (ainfo.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID && ainfo.uid != Process.myUid()) {
mOpPackageName = ActivityThread.currentPackageName();
} else {
mOpPackageName = mBasePackageName;
}
}
// 内容提供者相关
mContentResolver = new ApplicationContentResolver(this, mainThread, user);
}在这个方法中创建了Classloader,以及Application对象。然后执行Application对象的attach方法,这个方法中又会调用attachBaseContext()方法。也就是说Application对象首先被执行的方法不是onCreate()方法,而是attach()方法。
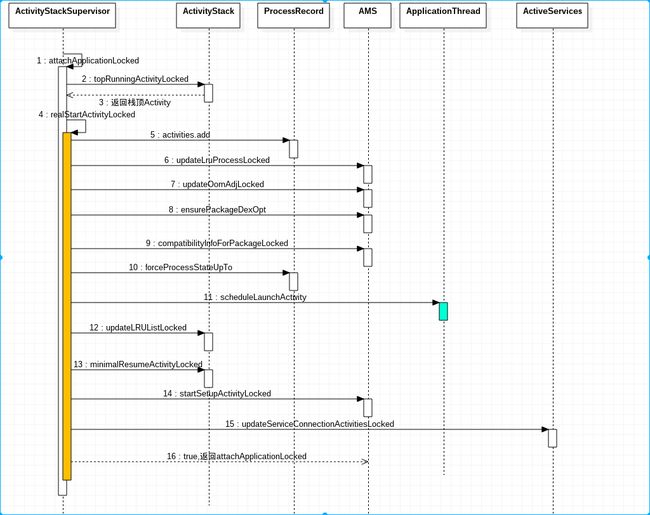
attachApplicationLocked
由ActivityThread.main的整体执行时序图中可知,启动activity的最终是attachApplicationLocked()方法。
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException {
final String processName = app.processName;
boolean didSomething = false;
for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
ArrayList stacks = mActivityDisplays.valueAt(displayNdx).mStacks;
for (int stackNdx = stacks.size() - 1; stackNdx >= 0; --stackNdx) {
final ActivityStack stack = stacks.get(stackNdx);
// 从 如何启动app中篇之Task的管理 可知,此时mFocusedStack指向即将要运行的activity所在的ActivityStack
// 下面这个方法就是为了从众多ActivityStack找到这个ActivityStack
if (!isFrontStack(stack)) {
continue;
}
// 找到了所需的ActivityStack
// 然后找到其栈顶的Activity,实际就是mTaskHistory数组末端的Task的顶端Activity
ActivityRecord hr = stack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
if (hr != null) {
if (hr.app == null && app.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uid
&& processName.equals(hr.processName)) {
try {
if (realStartActivityLocked(hr, app, true, true)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity "
+ hr.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
throw e;
}
}
}
}
}
if (!didSomething) {
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0);
}
return didSomething;
} ActivityStackSupervisor的流程调用关系可以用下面的流程图表示。