数据结构与算法(栈和队列)
首语
- 历经一个月的时间,自己终于搭建完成了个人网站,还在持续优化中,网站采用halo博客系统,功能非常强大!欢迎大家来我的网站逛逛。有什么建议可以留言!
网站地址:http://www.yanghujun.com
- 接下来我们开始第二节的数据结构学习,栈和队列。
栈
栈的顺序存储结构
栈的链式存储结构
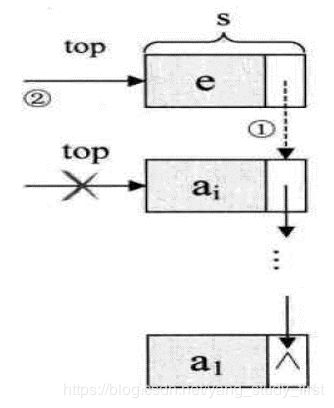
链栈的出入栈操作
s->data=e;
s->next=stack->top;
stack->top=s;
stack->count++;
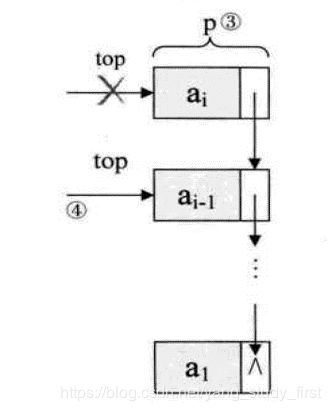
- 链栈的出栈操作
p=stack->top
stack->top=p->next;
free(p)
stack->count--;
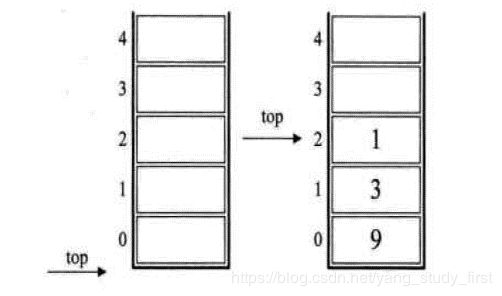
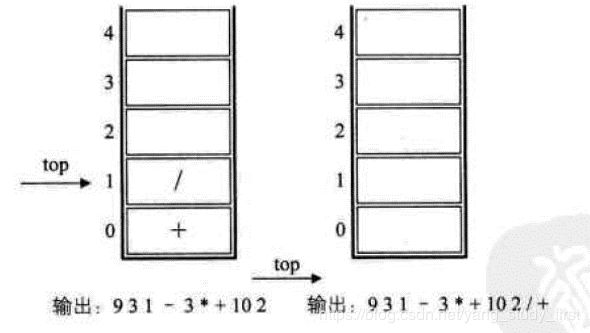
栈的经典实用(逆波兰表达式法)
中缀表达式转后缀表达式
数字输出,运算符进栈,括号匹配出栈,栈顶优先级低出栈。
代码实现
- 中缀表达式->后缀表达式
/**
* @param expression 逆波兰表达式
* 数字输出,运算符进栈,括号匹配出栈,栈顶优先级低出栈
* @return 后缀式链表
*/
public static LinkedList<String> parse(String expression) {
// 结果输出栈
LinkedList<String> output = new LinkedList<>();
// 运算符栈
Stack<Character> operators = new Stack<>();
// 字符串截取起始位置
int startPos = 0;
// 字符串截取末尾位置
int endPos = 0;
// 正序遍历表达式中的每一个字符c
for (char c : expression.toCharArray()) {
// 字符串截取的结束位置+1
++endPos;
// 判断字符c是否为运算符。
if (isOperator(c)) {
// 若运算符c之前有可保存的信息则将其作为一个整体保存至output链表。
if (startPos < endPos - 1)
output.add(expression.substring(startPos, endPos - 1));
// 更新字符串截取的起始位置
startPos = endPos;
// 若运算符c为左括号"(",则直接存入运算符栈。
if (c == '(') {
operators.push(c);
// 若运算符c为右括号")",则依次从运算符栈中弹出运算符并保存至output链表,直到遇到左括号为止。
} else if (c == ')') {
char op;
while (!operators.isEmpty() && (op = operators.pop()) != '(') {
output.add(String.valueOf(op));
}
// 若运算符c为非括号运算符(即:四则运算符号)
} else {
// 若运算符栈为空则直接将c压栈至运算符栈。
if (operators.isEmpty()) {
operators.push(c);
// 若运算符栈栈顶的运算符为左括号,则将c直接压栈至运算符栈。
} else if (operators.peek() == '(') {
operators.push(c);
// 若运算符c的优先级高于运算符栈栈顶的运算符优先级,则将c压栈至运算符栈。
} else if (getOperatorPriorityValue(c) > getOperatorPriorityValue(operators.peek())) {
operators.push(c);
// 若运算符c的优先级小于或等于运算符栈栈顶的运算符优先级,则依次从运算符栈中弹出运算符并保存至output链表,直到遇到左括号或c的优先级高于栈顶运算符优先级的为止。再将c压栈至运算符栈。
} else {
while (!operators.isEmpty() && getOperatorPriorityValue(c) <= getOperatorPriorityValue(operators.peek()) && operators.peek() != '(') {
output.add(String.valueOf(operators.pop()));
}
operators.push(c);
}
}
}
}
// 当表达式遍历完成后,将尚未保存的非运算符信息作为整体保存至output链表。若运算符栈中尚有运算符时,则依序弹出运算符到output链表。
if (startPos < expression.length()) output.add(expression.substring(startPos));
while (!operators.isEmpty()) {
output.add(String.valueOf(operators.pop()));
}
return output;
}
// 运算符
private final static char[] OP = new char[]{'+', '-', '*', '/', '(', ')'};
/**
* 判断字符是否是运算符
* @param op 运算符
* @return 是运算符返回true,不是则返回false
*/
public static boolean isOperator(char op) {
for (int i = 0; i < OP.length; ++i) {
if (op == OP[i])
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 获取运算符优先等级
* @param op 运算符
* @return 根据OP数组中运算符的顺序计算出运算符的优先等级:+ -是0级,* /是1级,( )是2级
*/
public static int getOperatorPriorityValue(char op) {
return (String.copyValueOf(OP).indexOf(op)) / 2;
}
- 后缀表达式计算
/**
* 表达式计算
* 先将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,再计算表达式的结果
* @param expression 表达式
* @return 运算结果
*/
public static double operation(String expression) {
// 使用逆波兰算法处理
LinkedList<String> rpnList = RPN.parse(expression);
// 保存每一步运算结果的操作数栈
Stack<Double> operands = new Stack<>();
// 若表达式第一位为运算符,则表达式无效
// 遍历逆波兰表达式中每一项元素
for (String elem : rpnList) {
// 若是运算符
if (RPN.isOperator(elem.charAt(0))) {
// 从操作数栈取出栈顶的两个操作数
double value2 = operands.pop();
double value1 = operands.pop();
// 获得运算结果
double result = binaryOperation(elem.charAt(0), value1, value2);
// 将计算结果压栈
operands.push(result);
// 如果是数值
} else {
operands.push(Double.parseDouble(elem));
}
}
// 返回操作数栈中唯一的元素
return operands.pop();
}
/**
* 二元运算
* @param operator 运算符
* @param value1 值1
* @param value2 值2
* @return 运算结果
*/
private static double binaryOperation(char operator, double value1, double value2) {
switch (operator) {
case '+':
return value1 + value2;
case '-':
return value1 - value2;
case '*':
return value1 * value2;
case '/':
if (value2 == 0) throw new ArithmeticException("/ by zero.");
return value1 / value2;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("");
}
}
栈(Stack)源码
/**
* Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly
* the same effect as:
*
* addElement(item)
* @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack.
* @return the item argument.
* @see java.util.Vector#addElement
*/
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
/**
* Adds the specified component to the end of this vector,
* increasing its size by one. The capacity of this vector is
* increased if its size becomes greater than its capacity.
* This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #add(Object) add(E)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
* @param obj the component to be added
*/
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
/**
* This implements the unsynchronized semantics of ensureCapacity.
* Synchronized methods in this class can internally call this
* method for ensuring capacity without incurring the cost of an
* extra synchronization.
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
/**
* Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that
* object as the value of this function.
* @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the Vector object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
/**
* Deletes the component at the specified index. Each component in
* this vector with an index greater or equal to the specified
* {@code index} is shifted downward to have an index one
* smaller than the value it had previously. The size of this vector
* is decreased by {@code 1}.
* The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than the current size of the vector.
*
This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #remove(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code remove} method returns the old value that was stored at the
* specified position.
* @param index the index of the object to remove
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
/**
* Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it
* from the stack.
*
* @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the Vector object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
/**
* Returns the component at the specified index.
* This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #get(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
* @param index an index into this vector
* @return the component at the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
队列
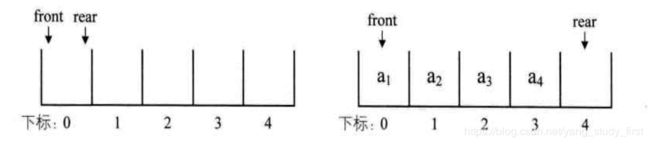
队列的顺序存储
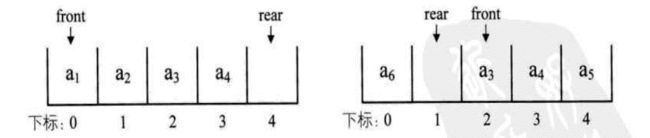
循环队列
队列的连式存储及结构模式
队列(Queue)源码
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector.
* @param e element to be appended to this Vector
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* This implements the unsynchronized semantics of ensureCapacity.
* Synchronized methods in this class can internally call this
* method for ensuring capacity without incurring the cost of an
* extra synchronization.
*
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}