Java BIO API及代码测试
文章目录
- 0.网络编程
- 1.JAVA最初的网络应用(BIO)
- 1.1服务端代码编写
- 1.2客户端代码编写
- 1.3升级版服务端代码(支持同时处理多连接)
- 1.4再次升级服务端代码(支持浏览器请求)
- 2.拓展学习:ServerSocket 类 及API 介绍
- 2.1 ServerSocket 类描述
- 2.2 ServerSocket (int) 构造方法
- 2.3 ServerSocket 中 setImpl()
- 2.4 ScoketImplFactroy 工厂接口 定义于 java.net 包下 面 SocketImplFactory
- 2.5 ServerSocket 类 中 的 accept()
- 3.总结
0.网络编程
网络编程指的是借助底层操作系统提供的API,进行网络应用程序的开发,不同语言,具有不同的实现,今天主要介绍,Java的最初BIO的实现。
1.JAVA最初的网络应用(BIO)
java最初提供的网络编程,位于 rt.jar 下面的 java.net 包 和 java.io 包 下,两者结合使用,实现了网络应用处理。
1.1服务端代码编写
public class BIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
java.net.ServerSocket serverSocket = new java.net.ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("服务器启动成功");
while (!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
java.net.Socket request = serverSocket.accept();// 阻塞
System.out.println("收到新连接 : " + request.toString());
try {
// 接收数据、打印
java.io.InputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream(); // net + i/o
java.io.BufferedReader reader = new java.io.BufferedReader(new java.io.InputStreamReader(inputStream, "utf-8"));
String msg;
while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null) { // 没有数据,阻塞
if (msg.length() == 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(msg);
}
System.out.println("收到数据,来自:"+ request.toString());
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
request.close();
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
serverSocket.close();
}
}
上面代码使用的是jdk自带的包,主要使用的是 java.net 包 和 java.io 包里面的内容。所以,可以不在集成工具中使用上述代码进行测试。(前提是需要配置Java的相关运行环境)
测试流程如下:
- 在本地创建 BIOServer.java 文件,并将上述代码复制粘贴至 新创建的 文件中 ,并保存。
- (WIN10举例)在CMD控制台中,使用 javac BIOServer.java 进行编译
- (WIN10举例)在CMD控制台中,使用 java BIOServer 即可运行上述代码
- 如果出现 找不到主类 ,这种情况的异常,请检查系统环境变量中是否置了CLASSPATH 环境变量。
- 可以直接删除 CLASSPATH 环境变量。
- 可以将javac编译出来的.class文件,拷贝至 CLASSPATH 环境变量对应的路径里面去。
- 上述两种解决方案都可以解决找不到主类的问题,但是确是不兼容的解决方案,二选一
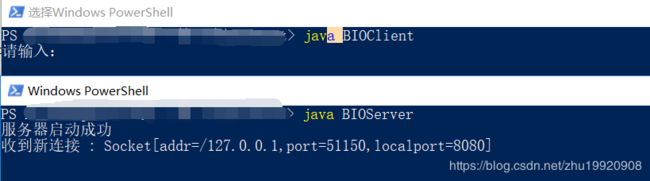
正常服务端启动效果图如下:
1.2客户端代码编写
public class BIOClient {
private static java.nio.charset.Charset charset = java.nio.charset.Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
java.net.Socket s = new java.net.Socket("localhost", 8080);
java.io.OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
java.util.Scanner scanner = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
out.write(msg.getBytes(charset)); // 阻塞,写完成
scanner.close();
s.close();
}
}
客户端的测试代码的使用,与服务端代码的方法相同
启动效果如下:
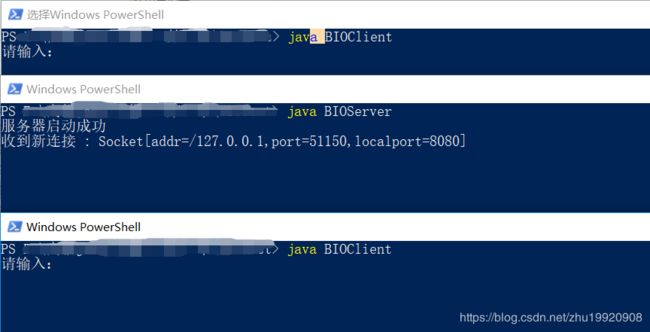
这里发现我们启动一个客户端的时候,会发现,可以连接到服务器,但是现实生活中的网络请求,需要处理大量的连接,因此这时候我们,需要模拟一个测试环境 —> 并发请求 测试,这里通过开启多个客户端,来模拟并发请求。
当我们开启新的客户端的时候,虽然启动成功,但是并没有像,第一次启动那样在服务打印出相应的请求,这是由什么原因造成的呢?
这里要回溯到BIOServer 中来查看代码的写法
while (!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
java.net.Socket request = serverSocket.accept();// 阻塞
...
}
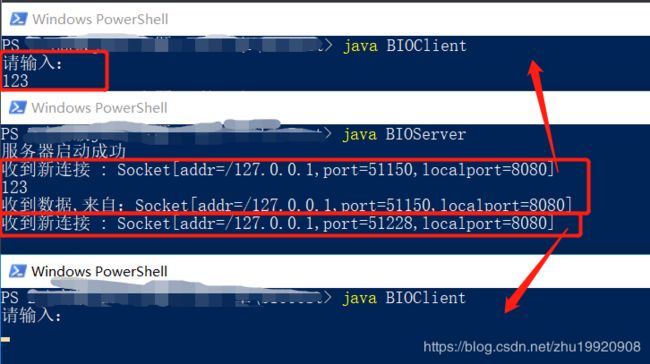
原因就是由于accept() 是一个阻塞方法,后面会详细介绍 ServerSocket 中的 accept() 。我们启动两个客户端的时候实际上是 两个请求,一个请求通过asscept() 获取到了资源,另一个请求在执行accept() 的时候,就处于阻塞状态了。所以 当第一个 请求没有释放资源的时候,第二个请求是不能继续执行相应的代码的。当第一台 客户端 的请求完成的时候,服务端又可以继续处理下一个请求了。效果如下:
上图表现出,当第一个客户端 完成 相应的 操作, 服务端读取到相应的数据的时候,阻塞方法解除,第二个客户端进来的时候服务端又因为如下代码,读取数据的时候被阻塞的状态
while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null) { // 没有数据,阻塞
if (msg.length() == 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(msg);
}
很明显,jdk最初的时候,不太适合网络编程,那有没有什么改进的方法呢? 这里可以借助多线程的方式,实现一台服务器并发处理多请求的需求。 服务端升级代码如下
1.3升级版服务端代码(支持同时处理多连接)
public class BIOServer1 {
private static java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService threadPool = java.util.concurrent.Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
java.net.ServerSocket serverSocket = new java.net.ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("多线程服务器启动成功");
while (!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
java.net.Socket request = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("收到新连接 : " + request.toString());
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
// 接收数据、打印
java.io.InputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
java.io.BufferedReader reader = new java.io.BufferedReader(new java.io.InputStreamReader(inputStream, "utf-8"));
String msg;
while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null) { // 阻塞
if (msg.length() == 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(msg);
}
System.out.println("收到数据,来自:"+ request.toString());
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
request.close();
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
serverSocket.close();
}
}
代码升级过程中,需要注意的是,线程池的定义,一定是作为成员变量,因为我们使用线程池的目的就是,控制线程数量,如果在请求中,去开启线程池,那么每个请求都会开启多个线程池,那这样,线程池就失去了应有的作用。这是写代码的时候需要care 的点!!!注意 线程池的使用,注意 线程池的使用,注意 线程池的使用 !!! 重要的事情说三遍。
将代码升级后,分别 启动服务端代码 和 客户端代码, 这里客户端代码没有改变,直接启动即可。
这里需要分析一波,我们写的服务端真的可以应对海量的请求吗?
这里还是需要从服务端的代码入手来分析一波,我们在获取到套接字后,将套接字放入线程池中去管理,而线程池又是有固定大小的,超出线程池的部分会进入等待队列,因此得出结论,上述代码,能支持多少并发请求,取决于线程池的核心线程数量。跟现在使用的 tomcat 等主流服务器还是有写出入,但这是单前技术条件下能实现的最佳效果,要不然也不会出现Java 的 nio 编程。
这里还需要思考一个问题, 现阶段我们的服务器架构,大多是B/S 架构,我们写的服务端代码,能相应浏览器的请求吗?
测试效果如下:
从浏览器的访问结果来看,这里是访问失败的,但是服务端却又打印出了相应的连接信息,这就奇怪了,这是由什么原因找错的呢? 其实这里,是Http 协议 造成的。详情,可以看博主的另一篇博客
https://blog.csdn.net/zhu19920908/article/details/90761840 (Http协议详解)
通过Http协议响应数据包,可以获知只要服务器返回对应的结果即可
1.4再次升级服务端代码(支持浏览器请求)
public class BIOServer2 {
private static java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService threadPool = java.util.concurrent.Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
java.net.ServerSocket serverSocket = new java.net.ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("服务器启动成功");
while (!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
java.net.Socket request = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("收到新连接 : " + request.toString());
threadPool.execute(() -> {
try {
// 接收数据、打印
java.io.InputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
java.io.BufferedReader reader = new java.io.BufferedReader(new java.io.InputStreamReader(inputStream, "utf-8"));
String msg;
while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null) {
if (msg.length() == 0) {
break;
}
System.out.println(msg);
}
System.out.println("收到数据,来自:"+ request.toString());
// 响应结果 200
java.io.OutputStream outputStream = request.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n".getBytes());
outputStream.write("Content-Length: 11\r\n\r\n".getBytes());
outputStream.write("Hello World".getBytes());
outputStream.flush();
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
request.close();
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
serverSocket.close();
}
}
这次升级,是对Http 协议的支持,也就是通过 Outputstream 对 http协议的请求进行一次响应。让服务器可以支持浏览器的访问。
测试效果如下:
服务端的显示情况:
通过上述方式,即实现了对Http协议的支持。
2.拓展学习:ServerSocket 类 及API 介绍
2.1 ServerSocket 类描述
/**
* This class implements server sockets. A server socket waits for
* requests to come in over the network. It performs some operation
* based on that request, and then possibly returns a result to the requester.
*
* 该类实现了 服务端套接字。 一个服务端套接字等待来自网络的请求到来。
* 它将在该请求之上进行一些工作,然后 可能 返回一个结果给请求者
*
* The actual work of the server socket is performed by an instance
* of the {@code SocketImpl} class. An application can
* change the socket factory that creates the socket
* implementation to configure itself to create sockets
* appropriate to the local firewall.
* 词汇: actual 真实的;实际的;
* appropriate to 将分配给…;
* 服务套接字真实的工作 是 由 SocketImpl 这个类的实例 执行的。
* 一个应用能够改变套接字 可以 更改创建套接字的 套接字工厂 来 配置自己以创建套接字的实现
* 用于适配本地防火墙
*
* @author unascribed
* @see java.net.SocketImpl
* @see java.net.ServerSocket#setSocketFactory(java.net.SocketImplFactory)
* @see java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel
* @since JDK1.0
*/
上面部分是 ServerSocket 的类描述,从该描述中,可以得知 ServerSocket 类 从 jdk 1.0 时代就已经存在了,并且处理网络请求的实例 是 由 SocketImpl()实现的,而且 这里面还有一个 工厂模式的 设计模式在里面,主要是使用 工厂模式来适配本地防火墙(如 Linux ,Windows , Linux 等系统的防火墙)
2.2 ServerSocket (int) 构造方法
/**
* Creates a server socket, bound to the specified port. A port number
* of {@code 0} means that the port number is automatically
* allocated, typically from an ephemeral port range. This port
* number can then be retrieved by calling {@link #getLocalPort getLocalPort}.
*
* 词汇: typically 典型地;通常;一般
* ephemeral 短暂的;
* retrieved 恢复;
* 创建一个服务套接字,绑定到特定的端口。如果端口号 是0 意味着 端口号 是自动获取的,通常来自短暂的端口范围。
* 这个端口 在调用后 getLocalPort() 被恢复。
*
* The maximum queue length for incoming connection indications (a
* request to connect) is set to {@code 50}. If a connection
* indication arrives when the queue is full, the connection is refused.
* 词汇: incoming 进来的
* indication 表明;标示;显示;象征
* 进入链接指示的 最大限度队列长度 (链接请求) 被设置成 50。
* 如果当队列满的时候连接指示到达,连接将被拒绝。
*
*
* If the application has specified a server socket factory, that
* factory's {@code createSocketImpl} method is called to create
* the actual socket implementation. Otherwise a "plain" socket is created.
*
* 如果应用 有指定的 服务套接字 工厂, 那么 工厂的 createSocketImpl() 会被调用 来创建
* 真实的 套接字 实现,否则 一个 “计划” 套接字会被创建
*
* If there is a security manager,
* its {@code checkListen} method is called
* with the {@code port} argument
* as its argument to ensure the operation is allowed.
* This could result in a SecurityException.
* 如果这里有一个安全管理器, 安全管理器的 checkListen()会 以 端口号 作为参数 被调用
* 作为 checkListen()方法的参数 要确保操作被 允许。 这可能会 有SecurityException
* 这样的异常。
*
* @param port the port number, or {@code 0} to use a port
* number that is automatically allocated.
*
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs when opening the socket.
* 如果在 打开 套接字 的时候 发生 i/o 错误 会抛出 IOException
* @exception SecurityException
* if a security manager exists and its {@code checkListen}
* method doesn't allow the operation.
* 如果是 安全管理器 退出 或是 checkListen() 不被 允许操作,出现 SecurityException异常
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the port parameter is outside
* the specified range of valid port values, which is between
* 0 and 65535, inclusive.
* 词汇 inclusive 包含
* 如果端口参数超出指定 可用的 值的范围,即 0 - 65535 ,包含(指闭区间)则出现IllegalArgumentException
*
* @see java.net.SocketImpl
* @see java.net.SocketImplFactory#createSocketImpl()
* @see java.net.ServerSocket#setSocketFactory(java.net.SocketImplFactory)
* @see SecurityManager#checkListen
*/
public ServerSocket(int port) throws IOException {
this(port, 50, null);
}
这里可以看出,套接字的构造方法调用的 是 ServerSocket(int, int ,InternetAddress) 的构造方法,ServerSocket(int,int,InternetAddress) 代码,及注释 如下:
/**
* Create a server with the specified port, listen backlog, and
* local IP address to bind to. The bindAddr argument
* can be used on a multi-homed host for a ServerSocket that
* will only accept connect requests to one of its addresses.
* If bindAddr is null, it will default accepting
* connections on any/all local addresses.
* The port must be between 0 and 65535, inclusive.
* A port number of {@code 0} means that the port number is
* automatically allocated, typically from an ephemeral port range.
* This port number can then be retrieved by calling
* {@link #getLocalPort getLocalPort}.
* 在指定的端口创建一个服务,监听 积压, 并且本地 IP 地址 去绑定。
* 绑定地址参数 可以被用来 多源 持有 一个 服务套接字 他将接受 该地址的链接请求。
* 如果 bindAddr 是空的话,他将默认 接收 任何本地 地址 的链接。
* 这个端口必须 在 0 到 65535 之间, 包含(指闭区间)。
* 端口号 是0 意味着 自动 分配,通常 是 一个 短暂 的端口 范围。
* 这个端口号 再被调用之后回收 {@link #getLocalPort getLocalPort} --> 可以看看该方法的实现。
*
* If there is a security manager, this method
* calls its {@code checkListen} method
* with the {@code port} argument
* as its argument to ensure the operation is allowed.
* This could result in a SecurityException.
* 如果这里有一个安全管理器,该构造方法 会 以 端口号 作为参数调用 checkListen() 来确认 操作是否被允许。
* 结果可能是得到一个安全异常。
*
* The {@code backlog} argument is the requested maximum number of
* pending connections on the socket. Its exact semantics are implementation
* specific. In particular, an implementation may impose a maximum length
* or may choose to ignore the parameter altogther. The value provided
* should be greater than {@code 0}. If it is less than or equal to
* {@code 0}, then an implementation specific default will be used.
*
* 词汇 exact 确切的
* semantics 语义
* impose 征收
* 代码中的 backlog 参数 是指 请求 连接 上 挂起连接的 最大限度 数量。
* backlog 这个参数的 确切语义 是 根据 特定的实现 而言的。
* 特定的情况下, 一个实现 可能 是 一个 征收的最大限度 或者 是选择 忽略的 参数 altogther。
* @param port the port number, or {@code 0} to use a port
* number that is automatically allocated.
* @param backlog requested maximum length of the queue of incoming
* connections.
* @param bindAddr the local InetAddress the server will bind to
* port 端口号,或者是 0 用来 自动分配
* backlog 到来连接 队列的 最大请求限度 长度
* bindAddr 服务器将要 绑定的 本地网络地址
* @throws SecurityException if a security manager exists and
* its {@code checkListen} method doesn't allow the operation.
* 安全异常 如果 一个 安全管理存在 并且 他的 checkListen() 不被允许操作。
*
* @throws IOException if an I/O error occurs when opening the socket.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if the port parameter is outside
* the specified range of valid port values, which is between
* 0 and 65535, inclusive.
* 如果 在打开 一些 套接字 的时候 发生 I/O 错误 ,则 抛出 IOException
* 如果端口参数 超过 指定 有效 端口号的 指定范围 ,指的是 0 - 65535,包含(闭区间)
*
* @see SocketOptions
* @see SocketImpl
* @see SecurityManager#checkListen
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public ServerSocket(int port, int backlog, InetAddress bindAddr) throws IOException {
setImpl();
if (port < 0 || port > 0xFFFF)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Port value out of range: " + port);
if (backlog < 1)
backlog = 50;
try {
bind(new InetSocketAddress(bindAddr, port), backlog);
} catch(SecurityException e) {
close();
throw e;
} catch(IOException e) {
close();
throw e;
}
}
2.3 ServerSocket 中 setImpl()
private void setImpl() {
if (factory != null) {
impl = factory.createSocketImpl();
checkOldImpl();
} else {
// No need to do a checkOldImpl() here, we know it's an up to date
// SocketImpl!
impl = new SocksSocketImpl();
}
if (impl != null)
impl.setServerSocket(this);
}
这个类中用到了 工厂设计模式,
ServerSocket 用 面向对象思维,来解读可以将它理解成一个人,一个专职负责与 底层操作系统 打交道 并且负责管理套接字的人,这里对于初始化套接字而言,
setImpl() 方法,就是这个人的职责体现之一,从上述代码中,我们获知到,这个方法中,利用工厂模式来 操作 套接字的,如果 工厂 没有被初始化,则 创建 一个套接字的实现,如果已经初始化了,就 通过 工厂创建一个套接字的实现,之后把当前对象传入套接字中。
2.4 ScoketImplFactroy 工厂接口 定义于 java.net 包下 面 SocketImplFactory
package java.net;
/**
* This interface defines a factory for socket implementations. It
* is used by the classes {@code Socket} and
* {@code ServerSocket} to create actual socket
* implementations.
* 该接口定义了 套接字 实现的 工厂。他将被 使用Socket 字节码 和ServerSocket 来创建真实的套接字实现
*
* @author Arthur van Hoff
* @see java.net.Socket
* @see java.net.ServerSocket
* @since JDK1.0
*/
public
interface SocketImplFactory {
/**
* Creates a new {@code SocketImpl} instance.
* 创建一个新的套接字实现
*
* @return a new instance of {@code SocketImpl}.
* @see java.net.SocketImpl
*/
SocketImpl createSocketImpl();
}
2.5 ServerSocket 类 中 的 accept()
/**
* Listens for a connection to be made to this socket and accepts
* it. The method blocks until a connection is made.
* 监听一个连接用来 创建这些套接字 和 接收 它。
* 这个方法处于阻塞 直到 一个连接 被创建。
*
* A new Socket {@code s} is created and, if there
* is a security manager,
* the security manager's {@code checkAccept} method is called
* with {@code s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()} and
* {@code s.getPort()}
* as its arguments to ensure the operation is allowed.
* This could result in a SecurityException.
* 一个新的 套接字 s 被创建,如果这里有 一个安全管理器, 安全管理器 会以
* s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress() 和 s.getPort() 的返回值 作为参数
* 调用 checkAccept() 来确定操作是否
* 被允许。 这可能会造成 SecurityException 的结果
*
* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs when waiting for a
* connection.
* 如果处于连接 等待 状态 由于 I/O 错误造成 则抛出 IOException。
* @exception SecurityException if a security manager exists and its
* {@code checkAccept} method doesn't allow the operation.
* 如果安全管理器存在并且 checkAccept() 不被 允许操作,则抛出SecurityException()。
* @exception SocketTimeoutException if a timeout was previously set with setSoTimeout and
* the timeout has been reached.
* 如果 以前 使用 setSoTimeout 设置了 超时时间,并且已经 达到超时时间 出现 SocketTimeoutException()
* @exception java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException
* if this socket has an associated channel, the channel is in
* non-blocking mode, and there is no connection ready to be
* accepted
* 词汇 associated 相关的
* 如果套接字 有 相关的 通道, 该通道 处于 非阻塞 状态,这里 没有 连接 准备好 去接收 则出现
* java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException 异常
*
* @return the new Socket
* @see SecurityManager#checkAccept
* @revised 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
public Socket accept() throws IOException {
if (isClosed())
throw new SocketException("Socket is closed");
if (!isBound())
throw new SocketException("Socket is not bound yet");
Socket s = new Socket((SocketImpl) null);
implAccept(s);
return s;
}
accept() 中 调用了 Socket(SocketImpl) 构造方法,创建了一个新的 Socket,这里需要跳转到Socket类查看其相关内容。
Socket 类描述如下
/**
* This class implements client sockets (also called just
* "sockets"). A socket is an endpoint for communication
* between two machines.
*
* 该类 实现了 客户端 套接字(也 仅仅 被称作 “套接字”)。套接字是两台机器之间通信的端点。
*
* The actual work of the socket is performed by an instance of the
* {@code SocketImpl} class. An application, by changing
* the socket factory that creates the socket implementation,
* can configure itself to create sockets appropriate to the local
* firewall.
* 词汇: actual 真实的,实际的,真正的
* 套接字的实际工作 由 SocketImpl 类的一个实例执行的。
* 一个应用,通过改变套接字工厂 来 创建 套接字 实现, 会配置自身 来创建 套接字 适应 本地防火墙。
*
* @author unascribed
* @see java.net.Socket#setSocketImplFactory(java.net.SocketImplFactory)
* @see java.net.SocketImpl
* @see java.nio.channels.SocketChannel
* @since JDK1.0
*/
通过Socket套接字 的类描述, 我们知道, 套接字是两台物理机器之间通信的端点(而且可以自动适配不同系统的防火墙)。
在accept()中 , 调用了 Socket (SocketImpl) 的实现
/**
* Creates an unconnected Socket with a user-specified
* SocketImpl.
* 创建一个 没有连接 的 套接字 通过 一个 用户-指定的 SocketImpl。
*
* @param impl an instance of a SocketImpl
* the subclass wishes to use on the Socket.
* 实现一个 SocketImpl 的实例,子类希望 在 套接字 上使用。
*
* @exception SocketException if there is an error in the underlying protocol,
* such as a TCP error.
* 词汇 underlying 根本的; 潜在的; 隐含的; 表面下的; 下层的; 构成…的基础; 作为…的原因;
* protocol 礼仪; 外交礼节; 条约草案; 议定书; 附件; 协议,规程,规约
* 如果 基础 协议 中存在问题,例如TCP 协议。
* @since JDK1.1
*/
protected Socket(SocketImpl impl) throws SocketException {
this.impl = impl;
if (impl != null) {
checkOldImpl();
this.impl.setSocket(this);
}
}
accept() 中 调用 Socket() 构造方法的时候,传递的就是 null,所以这里的操作只是将 Socket 实例中的 impl 属性置空。
/**
* Subclasses of ServerSocket use this method to override accept()
* to return their own subclass of socket. So a FooServerSocket
* will typically hand this method an empty FooSocket. On
* return from implAccept the FooSocket will be connected to a client.
* ServerSocket 的子类 使用 该方法 来重写 accept() 返回 他们自己套接字 的子类。
* 因此 fooserversocket通常会将此方法传递给一个 空的 FooSocket。
* 用来 返回 来自于 implAccept 的 FooSocket 将被链接到 一个客户端。
* @param s the Socket
* @throws java.nio.channels.IllegalBlockingModeException
* if this socket has an associated channel,
* and the channel is in non-blocking mode
* @throws IOException if an I/O error occurs when waiting
* for a connection.
* @since JDK1.1
* @revised 1.4
* @spec JSR-51
*/
protected final void implAccept(Socket s) throws IOException {
SocketImpl si = null;
try {
if (s.impl == null)
s.setImpl();
else {
s.impl.reset();
}
si = s.impl;
s.impl = null;
si.address = new InetAddress();
si.fd = new FileDescriptor();
getImpl().accept(si);
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkAccept(si.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(),
si.getPort());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (si != null)
si.reset();
s.impl = si;
throw e;
} catch (SecurityException e) {
if (si != null)
si.reset();
s.impl = si;
throw e;
}
s.impl = si;
s.postAccept();
}
3.总结
BIO(阻塞编程) 存在着天生的缺陷,因此才会出现NIO
大致可以总结成如下几点内容:
- BIO 的阻塞 注定他的命运不能处理大量的 连接请求。
- BIO 虽然有着天生的缺陷,但是是从jdk1.0时代就已经存在的元老级成员,因此需要了解一下。
- 关于 阻塞/非阻塞 的理解 :阻塞/非阻塞 是对 获取资源时操作的 描述 (比如获取 底层操作系统的端口号等,这些都属于资源)