本文是作者原创,版权归作者所有.若要转载,请注明出处.
本文RabbitMQ版本为rabbitmq-server-3.7.17,erlang为erlang-22.0.7.请各位去官网查看版本匹配和下载,也可以留言,我发安装包
首先我们看一下官网的图
上篇文章中我们介绍了第一个简单模式,本文我们来介绍其他2-5的模式,开始吧
Work queues工作队列模式
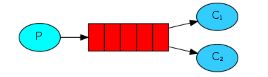
Work Queues与入门程序的简单模式相比,多了一个或一些消费端,多个消费端共同消费同一个队列中的消息。
应用场景:对于 任务过重或任务较多情况使用工作队列可以提高任务处理的速度。
Work Queues与入门程序的简单模式的代码是几乎一样的;可以完全复制,并复制多一个消费者进行多个消费者同时消费消息的测试。
1.消息生产者
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection; public class Producer { static final String QUEUE_NAME = "work_queue"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //创建连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); //创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明(创建)队列 /* 参数一:队列名称 参数二:是否定义持久化队列 参数三:是否独占本次连接 参数四:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 参数五:队列其他参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME,true,false,false,null); //要发送的消息 for(int i=1;i<=30;i++){ String message = "work_queue------->"+i; channel.basicPublish("",QUEUE_NAME,null,message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:"+message); } //释放资源 channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
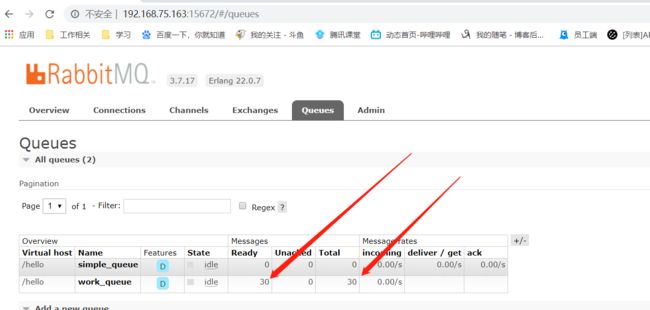
执行看结果
2.消息消费者(多个,这里演示两个)
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import java.io.IOException; public class Consumer1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //获取连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); //创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //创建队列:并设置消息处理 channel.queueDeclare(Producer.QUEUE_NAME,true,false,false,null); //监听消息 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override /* consumerTag :消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 envelope: 消息包内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重转标记(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) properties: 消息属性 body: 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println(""); System.out.println("=======================消费者1开始========================================="); System.out.println(""); //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("接收到的消息:" + new String(body, "UTF-8")); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("======================消费者1结束=========================================="); System.out.println(""); try { Thread.sleep(1000);//休眠一秒钟 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; /* 监听消息 参数一:队列名称 参数二:是否自动确认,设置为true表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复后会删除消息;设置为false则需要手动确认 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer); } }
第二个
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import java.io.IOException; public class Consumer2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //获取连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); //创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //创建队列:并设置消息处理 channel.queueDeclare(Producer.QUEUE_NAME,true,false,false,null); //监听消息 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) { @Override /* consumerTag :消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 envelope: 消息包内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重转标记(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) properties: 消息属性 body: 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println(""); System.out.println("=====================消费者2开始==========================================="); System.out.println(""); //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("接收到的消息:" + new String(body, "UTF-8")); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("======================消费者2结束=========================================="); System.out.println(""); try { Thread.sleep(1000);//休眠一秒钟 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; /* 监听消息 参数一:队列名称 参数二:是否自动确认,设置为true表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复后会删除消息;设置为false则需要手动确认 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer); } }
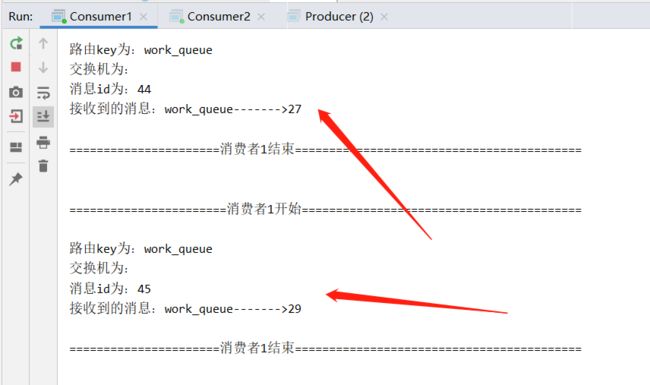
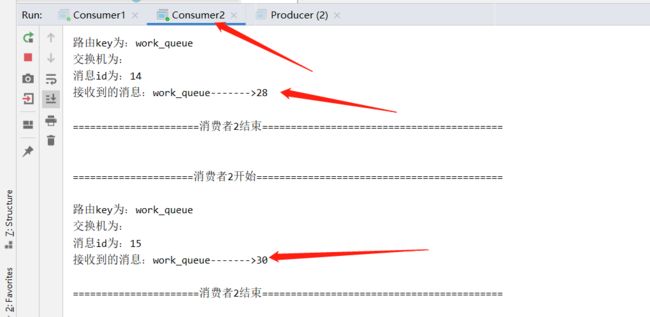
启动两个消费者,然后再启动生产者发送消息;到IDEA的两个消费者对应的控制台查看是否竞争性的接收到消息.查看结果
结论:在一个队列中如果有多个消费者,那么消费者之间对于同一个消息的关系是竞争的关系。
发布/订阅模式Publish/Subscribe
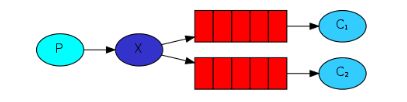
前面2个案例中,只有3个角色:
- P:生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序
- C:消费者:消息的接受者,会一直等待消息到来。
- queue:消息队列,图中红色部分
而在发布/订阅模型中,多了一个exchange角色,而且过程略有变化:
-
P:生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序,但是不再发送到队列中,而是发给X(交换机)
-
C:消费者,消息的接受者,会一直等待消息到来。
-
Queue:消息队列,接收消息、缓存消息。
-
Exchange:交换机,图中的X。一方面,接收生产者发送的消息。另一方面,知道如何处理消息,例如递交给某个特别队列、递交给所有队列、或是将消息丢弃。到底如何操作,取决于Exchange的类型。Exchange有常见以下4种类型:
- Fanout:广播,直接将消息路由到所有绑定的队列中,无须对消息的routingkey进行匹配操作。
- Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key 的队列.交换机在和queue进行binding时会设置routingkey,将消息发送到交换机时会设置对应的routingkey,只有这两个routingkey完全相同,交换机才会选择对应的binging进行消息路由。
- Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式) 的队列.
此类型和direct类型差不多,但direct类型要求routingkey完全相等,这里的routingkey可以有通配符:'*','#'。
其中'*'表示匹配一个单词, '#'则表示匹配没有或者多个单词
- header:其路由的规则是根据header来判断,其中的header就是binding时的arguments参数:header类型用的比较少
Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因此如果没有任何队列与Exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息会丢失!
总结:一般direct和topic用来具体的路由消息,如果要用广播的消息一般用fanout。header类型用的比较少
1.消息生产者
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil; import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection; /** * 发布与订阅使用的交换机类型为:fanout */ public class Producer { //交换机名称 static final String FANOUT_EXCHAGE = "fanout_exchange"; //队列名称 static final String FANOUT_QUEUE_1 = "fanout_queue_1"; //队列名称 static final String FANOUT_QUEUE_2 = "fanout_queue_2"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); /** * 声明交换机 * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:交换机类型,fanout、topic、direct、headers */ channel.exchangeDeclare(FANOUT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(FANOUT_QUEUE_1, true, false, false, null); channel.queueDeclare(FANOUT_QUEUE_2, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(FANOUT_QUEUE_1, FANOUT_EXCHAGE, ""); channel.queueBind(FANOUT_QUEUE_2, FANOUT_EXCHAGE, ""); for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { // 发送信息 String message = "你好;rabbitmq !发布订阅模式--" + i; /** * 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容 */ channel.basicPublish(FANOUT_EXCHAGE, "", null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message); } // 关闭资源 channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
执行,看结果
2.消息消费者(两个,分别在两个队列)
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import java.io.IOException; public class Consumer1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_1, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_1, Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, ""); //创建消费者;并设置消息处理 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override /** * consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf-8")); } }; //监听消息 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_1, true, consumer); } }
第二个
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import java.io.IOException; public class Consumer2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_2, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_2, Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, ""); //创建消费者;并设置消息处理 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override /** * consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("消费者2-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf-8")); } }; //监听消息 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_2, true, consumer); } }
3.测试
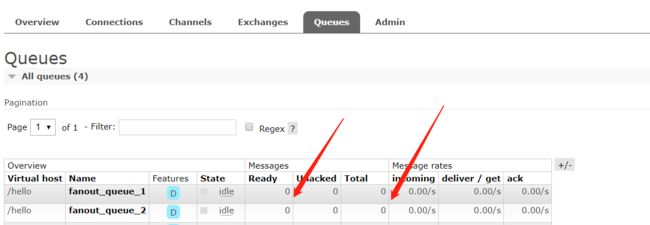
启动所有消费者,然后使用生产者发送消息;在每个消费者对应的控制台可以查看到生产者发送的所有消息;到达广播的效果。
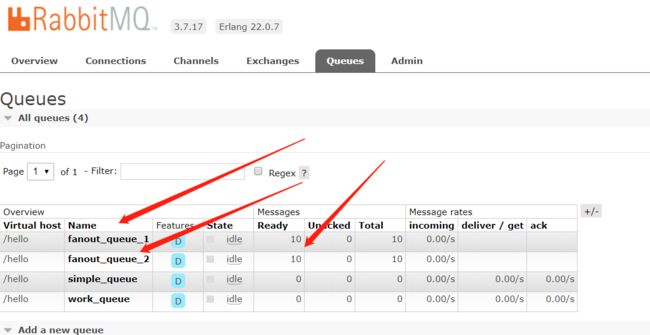
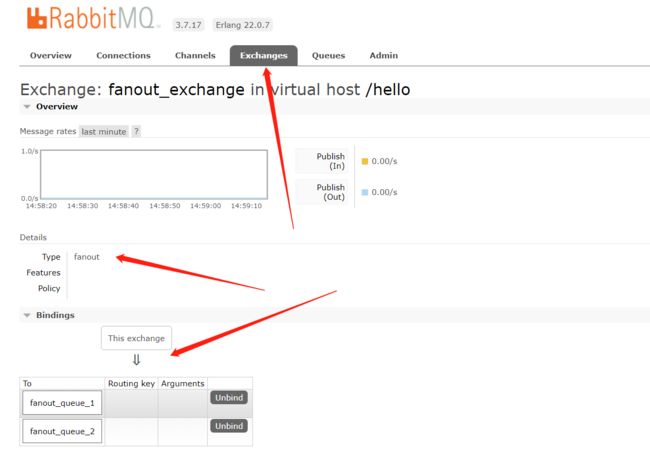
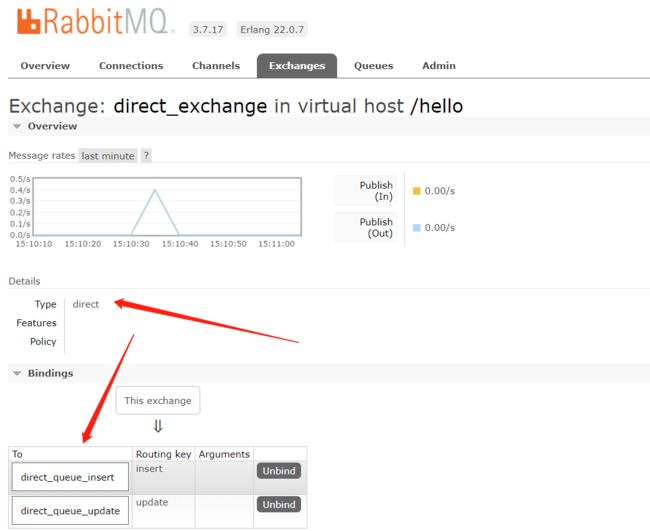
在执行完测试代码后,其实到RabbitMQ的管理后台找到Exchanges选项卡,点击 fanout_exchange 的交换机,可以查看到如下的绑定
小结:交换机需要与队列进行绑定,绑定之后;一个消息可以被多个消费者都收到。
发布订阅模式与工作队列模式的区别
1、工作队列模式不用定义交换机,而发布/订阅模式需要定义交换机。
2、发布/订阅模式的生产方是面向交换机发送消息,工作队列模式的生产方是面向队列发送消息(底层使用默认交换机)。
3、发布/订阅模式需要设置队列和交换机的绑定,工作队列模式不需要设置,实际上工作队列模式会将队列绑定到默认的交换机 。
Routing路由模式
图解:
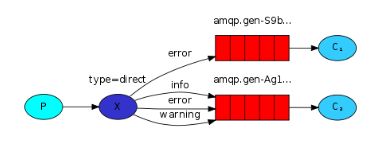
- P:生产者,向Exchange发送消息,发送消息时,会指定一个routing key。
- X:Exchange(交换机),接收生产者的消息,然后把消息递交给 与routing key完全匹配的队列
- C1:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 error 的消息
- C2:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 info、error、warning 的消息
路由模式特点:
- 队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个
RoutingKey(路由key) - 消息的发送方在 向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的
RoutingKey。 - Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的
Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey与消息的Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息
在编码上与 Publish/Subscribe发布与订阅模式 的区别是交换机的类型为:Direct,还有队列绑定交换机的时候需要指定routing key
1)生产者
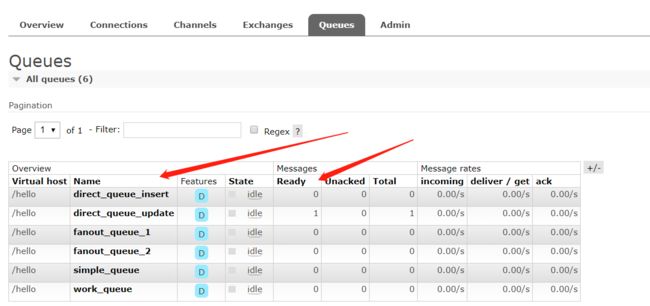
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil; import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection; /** * 路由模式的交换机类型为:direct */ public class Producer { //交换机名称 static final String DIRECT_EXCHAGE = "direct_exchange"; //队列名称 static final String DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT = "direct_queue_insert"; //队列名称 static final String DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE = "direct_queue_update"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); /** * 声明交换机 * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:交换机类型,fanout、topic、direct、headers */ channel.exchangeDeclare(DIRECT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, true, false, false, null); channel.queueDeclare(DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "insert"); channel.queueBind(DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "update"); // 发送信息 String message = "新增了商品。路由模式;routing key 为 insert " ; /** * 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容 */ channel.basicPublish(DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "insert", null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message); // 发送信息 message = "修改了商品。路由模式;routing key 为 update" ; /** * 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容 */ channel.basicPublish(DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "update", null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message); // 关闭资源 channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
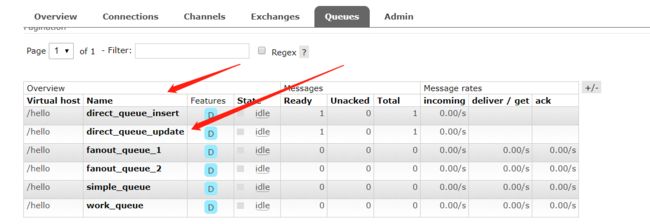
执行看结果
2)消费者1
public class Consumer1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //获取连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "insert"); //创建消费者;并设置消息处理 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override /** * consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf-8")); } }; //监听消息 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, true, consumer); } }
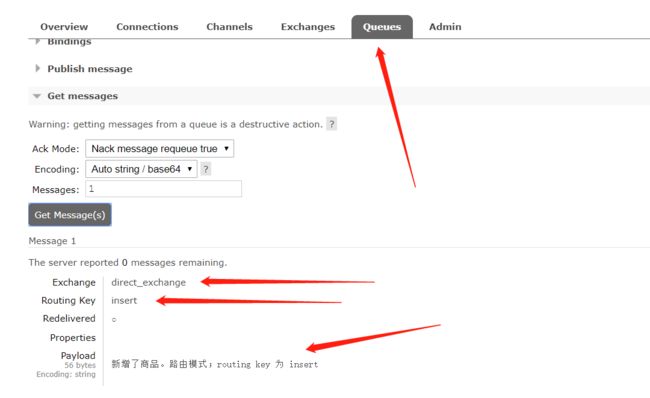
执行,看结果
可以看到insert的那条消息被消费了
3)消费者2
public class Consumer2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "update"); //创建消费者;并设置消息处理 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override /** * consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("消费者2-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf-8")); } }; //监听消息 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, true, consumer); } }
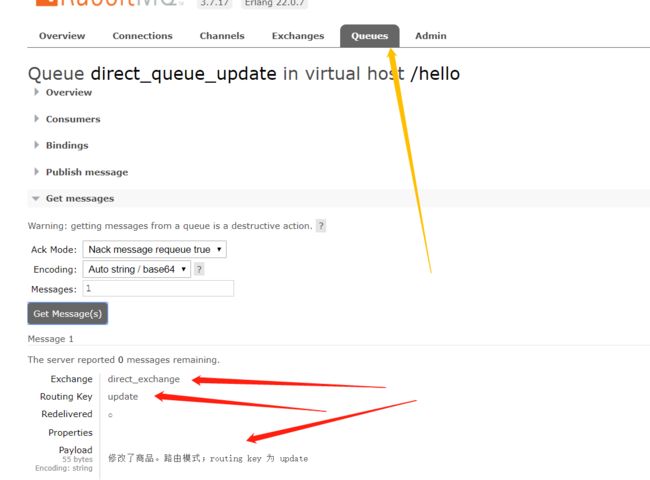
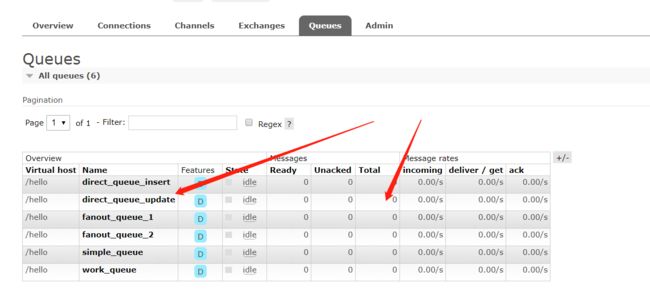
看结果
在消费者对应的控制台可以查看到生产者发送对应routing key对应队列的消息;到达按照需要接收的效果。
Routing模式要求队列在绑定交换机时要指定routing key,消息会转发到符合routing key的队列。
Topics通配符模式
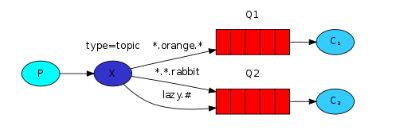
模式说明
Topic类型与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定Routing key 的时候使用通配符!
Routingkey 一般都是有一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以”.”分割,例如: item.insert
通配符规则:
#:匹配一个或多个词
*:匹配不多不少恰好1个词
举例:
item.#:能够匹配item.insert.abc 或者 item.insert
item.*:只能匹配item.insert
1)生产者
public class Producer { //交换机名称 static final String TOPIC_EXCHAGE = "topic_exchange"; //队列名称 static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_1 = "topic_queue_1"; //队列名称 static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_2 = "topic_queue_2"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); /** * 声明交换机 * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:交换机类型,fanout、topic、topic、headers */ channel.exchangeDeclare(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC); // 发送信息 String message = "新增了商品。Topic模式;routing key 为 item.insert " ; channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.insert", null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message); // 发送信息 message = "修改了商品。Topic模式;routing key 为 item.update" ; channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.update", null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message); // 发送信息 message = "删除了商品。Topic模式;routing key 为 product.delete" ; channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "product.delete", null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message); // 发送信息 message = "其他的信息发送过来了。。。。" ; channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.delete.abc", null, message.getBytes()); System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message); // 关闭资源 channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
执行,看结果
2)消费者1
public class Consumer1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.#"); //channel.queueBind(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.delete"); //创建消费者;并设置消息处理 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override /** * consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf-8")); } }; //监听消息 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, true, consumer); } }
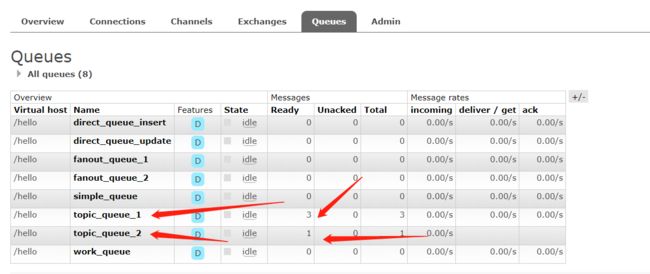
执行,看结果
可以看到,队列topic_queue_1里的消息都被消费了
3)消费者2
public class Consumer2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //获取连接 Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 创建频道 Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //声明交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC); // 声明(创建)队列 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */ channel.queueDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_2, true, false, false, null); //队列绑定交换机 channel.queueBind(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_2, Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "*.delete"); //创建消费者;并设置消息处理 DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override /** * consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志(收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */ public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { //路由key System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey()); //交换机 System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange()); //消息id System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag()); //收到的消息 System.out.println("消费者2-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf-8")); } }; //监听消息 /** * 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */ channel.basicConsume(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_2, true, consumer); } }
执行,看结果
可以看到,队列topic_queue_2里的消息也被消费了
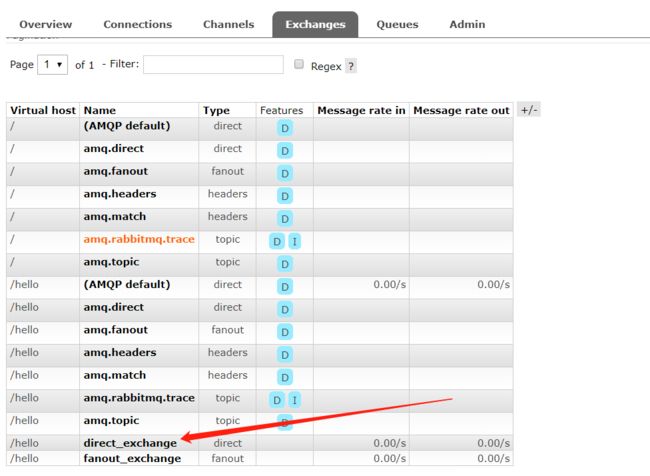
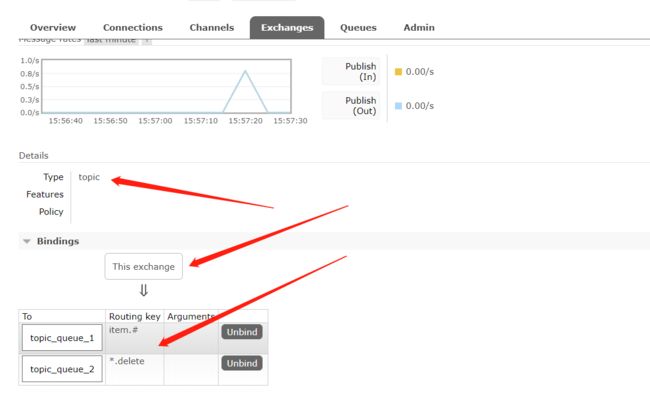
在执行完测试代码后,其实到RabbitMQ的管理后台找到Exchanges选项卡,点击 topic_exchange 的交换机,可以查看到如下的绑定:
Topic主题模式可以实现 Publish/Subscribe发布与订阅模式 和 Routing路由模式 的功能;只是Topic在配置routing key 的时候可以使用通配符,显得更加灵活。
模式总结
RabbitMQ工作模式:
1、简单模式 HelloWorld 一个生产者、一个消费者,不需要设置交换机(使用默认的交换机)
2、工作队列模式 Work Queue 一个生产者、多个消费者(竞争关系),不需要设置交换机(使用默认的交换机)
3、发布订阅模式 Publish/subscribe 需要设置类型为fanout的交换机,并且交换机和队列进行绑定,当发送消息到交换机后,交换机会将消息发送到绑定的队列
4、路由模式 Routing 需要设置类型为direct的交换机,交换机和队列进行绑定,并且指定routing key,当发送消息到交换机后,交换机会根据routing key将消息发送到对应的队列
5、通配符模式 Topic 需要设置类型为topic的交换机,交换机和队列进行绑定,并且指定通配符方式的routing key,当发送消息到交换机后,交换机会根据routing key将消息发送到对应的队列