mget批量查询
- 批量查询的好处
就是一条一条的查询,比如说要查询100条数据,那么就要发送100次网络请求,这个开销还是很大的
如果进行批量查询的话,查询100条数据,就只要发送1次网络请求,网络请求的性能开销缩减100倍 - mget批量查询的语法
GET _mget { "docs":[ { "_index":"test_index", "_type":"test_type", "_id":1 }, { "_index":"test_index", "_type":"test_type", "_id":2 } ] }
 View Code
View Code{ "took": 2, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 9, "max_score": 1, "hits": [ { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "AWypxxLYFCl_S-ox4wvd", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_content": "my test" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "8", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_field": "test client 2" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "10", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_field1": "test1", "test_field2": "updated test2" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "2", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_content": "my test" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "4", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_field": "test test" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "6", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_field": "test test" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "1", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_field1": "test field1", "test_field2": "test field2" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "7", "_score": 1, "_source": { "test_field": "test client 1" } }, { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "11", "_score": 1, "_source": { "num": 0, "tags": [] } } ] } }
-
如果查询的document是一个index下的不同type的话
GET /test_index/_mget { "docs" : [ { "_type" : "test_type", "_id" : 1 }, { "_type" : "test_type", "_id" : 2 } ] }
- 如果查询的数据都在同一个index下的同一个type下,最简单了
GET /test_index/test_type/_mget { "ids": [1, 2] }
可以说mget是很重要的,一般来说,在进行查询的时候,如果一次性要查询多条数据的话,那么一定要用batch批量操作的api
尽可能减少网络开销次数,可能可以将性能提升数倍,甚至数十倍,非常非常之重要
bulk批量增删改
bulk语法
POST /_bulk { "delete": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "3" }} { "create": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "12" }} { "test_field": "test12" } { "index": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "2" }} { "test_field": "replaced test2" } { "update": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "1", "_retry_on_conflict" : 3} } { "doc" : {"test_field2" : "bulk test1"} }
有哪些类型的操作可以执行呢?
- delete:删除一个文档,只要1个json串就可以了
- create:PUT /index/type/id/_create,强制创建
- index:普通的put操作,可以是创建文档,也可以是全量替换文档
- update:执行的partial update操作
bulk api对json的语法,有严格的要求,每个json串不能换行,只能放一行,同时一个json串和一个json串之间,必须有一个换行
示例:
POST _bulk {"delete":{"_index":"test_index","_type":"test_type","_id":10}} {"create":{"_index":"test_index","_type":"test_type","_id":3}} {"test_field":"test3"} {"create":{"_index":"test_index","_type":"test_type","_id":2}} {"test_field":"test2"} {"index":{"_index":"test_index","_type":"test_type","_id":4}} {"test_field":"test4"} {"index":{"_index":"test_index","_type":"test_type","_id":2}} {"test_field":"replaces test2"} {"update":{"_index":"test_index","_type":"test_type","_id":1}} {"doc":{"test_field2":"partial updated test1"}}
{ "took": 17, "errors": true, "items": [ { "delete": { "found": true, "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "10", "_version": 3, "result": "deleted", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "status": 200 } }, { "create": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "3", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "created": true, "status": 201 } }, { "create": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "2", "status": 409, "error": { "type": "version_conflict_engine_exception", "reason": "[test_type][2]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [17])", "index_uuid": "d7GOSxVnTNKYuI8x7cZfkA", "shard": "2", "index": "test_index" } } }, { "index": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "4", "_version": 2, "result": "updated", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "created": false, "status": 200 } }, { "index": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "2", "_version": 18, "result": "updated", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "created": false, "status": 200 } }, { "update": { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "1", "_version": 3, "result": "updated", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "status": 200 } } ] }
bulk操作中,任意一个操作失败,是不会影响其他的操作的,但是在返回结果里,会告诉你异常日志
BulkIndex语法:(指定Index)
POST /test_index/_bulk { "delete": { "_type": "test_type", "_id": "3" }} { "create": { "_type": "test_type", "_id": "12" }} { "test_field": "test12" } { "index": { "_type": "test_type" }} { "test_field": "auto-generate id test" } { "index": { "_type": "test_type", "_id": "2" }} { "test_field": "replaced test2" } { "update": { "_type": "test_type", "_id": "1", "_retry_on_conflict" : 3} } { "doc" : {"test_field2" : "bulk test1"} }
BulkIndex语法:(指定Index、type)
POST /test_index/test_type/_bulk { "delete": { "_id": "3" }} { "create": { "_id": "12" }} { "test_field": "test12" } { "index": { }} { "test_field": "auto-generate id test" } { "index": { "_id": "2" }} { "test_field": "replaced test2" } { "update": { "_id": "1", "_retry_on_conflict" : 3} } { "doc" : {"test_field2" : "bulk test1"} }
bulk size最佳大小:bulk request会加载到内存里,如果太大的话,性能反而会下降,因此需要反复尝试一个最佳的bulk size。一般从1000~5000条数据开始,尝试逐渐增加。另外,如果看大小的话,最好是在5~15MB之间。
Elasticsearch document数据路由原理
我们知道,一个index的数据会被分成多个分片shard,所以说一个document只能存在与一个shard中。
当客户端创建document的时候,elasticsearch此时就需要决定这个document是放在这个index的哪个分片shard中,这个过程就称之为document routing,即数据路由。
document数据路由算法
算法;shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shards
举个例子,假设一个index有5个primary shard(p0,p1,p2,p3,p4)。每次对index的一个document进行增删改查的时候,都会带过来一个routing number,默认就是这个documentd的_id(可能是手动指定,也可以是自动生成),routing=_id。
假设_id=1,那么就会将routing=1这个routing值传入一个hash函数中,产生一个routing值的hash值,假设hash(routing)=21,然后将hash函数产生的值对这个index的primary shard的数量求余数,21 % 5 = 1
也就决定了这个document就放在p1上。
注意:此这个计算过程就可以看出,决定一个document在哪个shard上,最重要的值就是routing值,默认是_id,也可以手动指定,相同的routing值,每次过来,从hash函数中生成的hash值一定是相同的。无论最后计算的hash值是多少,对number_of_primary_shards求余数,结果一定在0~number_of_primary_shards之间。
决定一个document在哪个shard上,最重要的一个值就是routing值,默认是_id,也可以手动指定,相同的routing值,每次过来,从hash函数中,产出的hash值一定是相同的
_id or custom routing value
默认的routing就是_id
也可以在发送请求的时候,手动指定一个routing value,比如说put /index/type/id?routing=user_id
手动指定routing value是很有用的,可以保证说,某一类document一定被路由到一个shard上去,那么在后续进行应用级别的负载均衡,以及提升批量读取的性能的时候,是很有帮助的
routing实战
- 测试一下默认的routing
//先插入数据 PUT /test_index/test_doc/10 { "test_field": "test10 routing _id" } //获取数据不带routing参数 GET /test_index/test_doc/10 { "_index" : "test_index", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "10", "_version" : 1, "_seq_no" : 0, "_primary_term" : 1, "found" : true, "_source" : { "test_field" : "test10 routing _id" } } //获取数据带routing参数 参数值为_id GET /test_index/test_doc/10?routing=10 { "_index" : "test_index", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "10", "_version" : 1, "_seq_no" : 0, "_primary_term" : 1, "found" : true, "_source" : { "test_field" : "test10 routing _id" } }
- 测试带上routing值
//先插入数据 PUT /test_index/test_doc/11?routing=12 { "test_field": "test routing not _id" } //获取数据不带routing参数 GET /test_index/test_doc/11 { "_index" : "test_index", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "11", "found" : false } //获取数据带routing参数 参数值为自定义的值 GET /test_index/test_doc/11?routing=12 { "_index" : "test_index", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "11", "_version" : 1, "_seq_no" : 9, "_primary_term" : 1, "_routing" : "12", "found" : true, "_source" : { "test_field" : "test routing not _id" } }
主分片数量不可变
通过上面的分析,特别是路由算法,我们不难知道,在我们最开始创建索引的时候,确定了primary shard的数量,之后根据路由算法,每个document就被路由到了指定的shard上面,之后的各种操作路由规则都是一样的。试想一下,如果我们改变了primary shard的数量,那么路由算法取余的时候值可能就跟之前的不一样了,就会被路由到其它的shard上面去,就会导致数据混乱,本该已经存在的document,可能通过查询根本查不到,某种程度上说这也会造成数据的丢失。
document增删改内部原理,写一致性机制
document增删改内部原理
- 对于客户端首先会选择一个节点node发送请求过去,这个节点node就是协调节点coordinating node
- 协调节点coordinating node会对docuemnt数据进行路由,将请求转发给对应的node(含有primary shard)
- 实际上node的primary shard会处理请求,然后将数据同步到对应的含有replica shard的node
- 协调节点coordinating node如果发现含有primary shard的node和所有的含有replica shard的node都搞定之后,就会返回响应结果给客户端
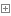
下面手工画图展示一下上面的过程:
假设我们有2个节点,5个primary shard replica=1
- 客户端发送增删改请求给协调节点node2
- 协调节点node2将请求路由到含有primary shard的node1
- node1处理请求,并同步数据到对应的含有replica shard的node2
- 协调节点node2如果发现含有primary shard的node1以及所有含有replica shard的node2都搞定了,就会返回响应结果给客户端
写一致性机制(已经被移除,替换为wait_for_active_shards)
consistency
默认情况下,主分片需要法定数量或大部分的分片副本(其中分片副本可以是主分片或副本分片)在尝试写入操作之前可用。这是为了防止将数据写入网络分区的 “wrong side”。法定人数定义如下:
int((primary + number_of_replicas)/ 2)+ 1
允许的值consistency是one(仅主要分片),all (主要和所有副本),或默认quorum或大多数分片副本。
请注意,它number_of_replicas是索引设置中指定的副本数,而不是当前活动的副本数。如果您已指定索引应具有三个副本,则仲裁将如下所示:
int( (primary + 3 replicas) / 2 ) + 1 = 4
但是,如果仅启动两个节点,则将没有足够的活动分片副本来满足仲裁,并且您将无法索引或删除任何文档。
timeout
如果可用的分片副本不足,会发生什么?Elasticsearch等待,希望会出现更多的分片。默认情况下,它将等待最多1分钟。如果需要,可以使用timeout参数让它更快地中止:100是100毫秒,30s是30秒。
注意
默认情况下,新索引具有一个副本,这意味着应该需要两个活动分片副本以满足需要的quorum。但是,这些默认设置会阻止我们对单节点群集执行任何有用的操作。为避免此问题,仅当number_of_replicas大于1时才强制要求仲裁。
移除consistency这个参数之后,用wait_for_active_shards这个参数替代了。
原因就是,consistency检查是在Put之前做的。然而,虽然检查的时候,shard满足quorum,但是真正从primary shard写到replica之前,仍会出现shard挂掉,但Update Api会返回succeed。因此,这个检查并不能保证replica成功写入,甚至这个primary shard是否能成功写入也未必能保证。
为了提高对系统写入的弹性,使用wait_for_active_shards,可以将索引操作配置为在继续操作之前等待一定数量的活动分片副本。如果必需数量的活动分片副本不可用,则写入操作必须等待并重试,直到必需的分片副本已启动或发生超时。默认情况下,写入操作仅等待主分片在继续(即wait_for_active_shards=1)之前处于活动状态。
注意,此设置大大降低了写入操作不写入所需数量的分片副本的可能性,但它并未完全消除这种可能性,因为此检查在写入操作开始之前发生。一旦写入操作正在进行,复制在任何数量的分片副本上仍然可能失败,但仍然可以在主分片上成功。在_shards写操作的响应部分揭示了其复制成功/失败碎片的份数。
Elasticsearch document查询内部原理
查询请求打过来Elasticsearch内部做了什么?
- 客户端发送请求到任意一个node,这个node就成为了协调节点coordinating node
- 协调节点coordinating node会对document进行路由,将请求转发到包含该document的对应的node上面去,此时会使用round-robin随机轮询算法,在primary shard以及所有的replica shard中随机选择一个,让打过来的读请求实现负载均衡
- 接收请求的node会返回document给协调节点coordinating node
- 协调节点将document数据返回给客户端
对于读取请求,协调节点将在每个请求上选择不同的分片副本以平衡负载; 它循环遍历所有碎片副本。
在索引文档时,文档可能已经存在于主分片上但尚未复制到副本分片。在这种情况下,副本可能会报告文档不存在,而主副本可能会成功返回文档。索引请求将成功返回给用户后,该文档将在主分片和所有副本分片上可用。
最后简单描述一下随机轮询算法:
举个例子,比如一个协调节点coordinating接受到一个document的4次请求,就会使用随机轮询算法,循环遍历所有shard,将4次请求均匀的打在所有shard上面,比如有4个shard,就会每个shard各一个请求。
bulk api的奇特json格式与底层性能优化关系
为什么bulk要采用这种奇特的json格式?
由于bulk中的每个操作都可能要转发到不同的node的shard去执行,假设我们不用这种奇特的json格式,采用比较良好的json数组格式,允许任意的换行,整个可读性非常棒,读起来很爽。但是ES拿到这种标准格式的json串之后,要按照下述流程去进行执行处理。
格式如下:
[{ "action": { }, "data": { } }]
- 将json数组解析为JSONArray对象,这个时候,整个数据,就会在内存中出现一份一摸一样的拷贝,一份数据是json文本,一份数据是JSONArray对象
- 解析json数组里面的每个json,对每个请求中的document进行路由
- 为路由到同一个shard上的多个请求,创建一个请求数组
- 将这个请求数组序列化
- 将序列化后的请求数组发送到对应的节点上去
不难看出这样就会耗费更多的内存,更多的jvm gc开销。
假设一个场景,对于bulk size的大小一般建议在几千条,大小在10MB左右,所以说,可怕的事情来了。假设说现在100个bulk请求发送到了一个节点上去,然后每个请求是10MB,100个请求就是1000MB=1G,然后每个请求的json都copy一份JSONArray对象,此时内存中的占用就会翻倍,就会占用2GB的内存,甚至还不止,因为弄成JSONArray对象之后,还可能会多弄一些其它的数据结构,2GB+的内存占用。
占用更多的内存可能就会积压其它请求的内存使用量,比如说最重要的搜索请求,分析请求等等。此时就可能会导致其它请求的性能急速下降,另外的话,占用内存更多,就会导致java虚拟机的垃圾回收次数更多,更加频繁,每次要回收的垃圾对象更多,耗费的时间更多,导致ES的java虚拟机停止工作线程的时间更多。
而使用这个奇特格式的json
{"action": {"meta"}}\n
{"data"}\n
{"action": {"meta"}}\n
{"data"}\n
- 不用将其转换为json对象,不会出现内存中的相同数据的拷贝,直接按照换行符切割json
- 对每两个一组的json,读取meta,进行document路由
- 直接将对应的json发送到node上去
和标准格式的json相比,最大的优势在于不需要将json数组解析为一个JSONArray对象,形成一份大数据的拷贝,浪费内存空间,尽可能的保证性能。
示例:
PUT _bulk {"index": {"_index": "test","_type":"test_doc", "_id": "1"}} {"field1": "value1", "field2": "value2"} {"index": {"_index": "test","_type":"test_doc", "_id": "2"}} {"field1": "value1 id2", "field2": "value2 id2"} {"delete": {"_index": "test","_type":"test_doc", "_id": "2"}} {"create": {"_index": "test","_type":"test_doc", "_id": "3"}} {"field1": "value3"} {"update": {"_index": "test", "_type":"test_doc","_id": "1"}} {"doc": {"field2": "value2"}}
{ "took": 136, "errors": false, "items": [ { "index": { "_index": "test", "_type": "test_doc", "_id": "1", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "created": true, "status": 201 } }, { "index": { "_index": "test", "_type": "test_doc", "_id": "2", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "created": true, "status": 201 } }, { "delete": { "found": true, "_index": "test", "_type": "test_doc", "_id": "2", "_version": 2, "result": "deleted", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "status": 200 } }, { "create": { "_index": "test", "_type": "test_doc", "_id": "3", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "created": true, "status": 201 } }, { "update": { "_index": "test", "_type": "test_doc", "_id": "1", "_version": 1, "result": "noop", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "status": 200 } } ] }