- java1.8是现在用的最多的版本,HashMap是现在用的最多的map,HashMap的源码可以说是面试必备技能,今天我们试图分析一下源码。
- 之前我们分析java1.7的hashMap说它有一个问题,链表过长,java8引入了红黑树解决
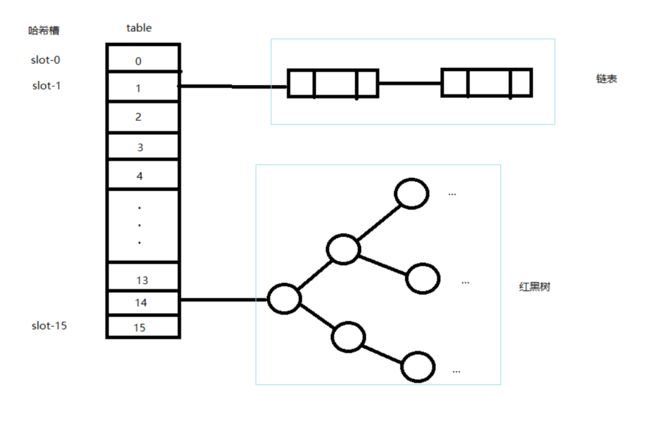
- 结构:数组加链表,链表过长时裂变为红黑树
一、先看整体的数据结构
首先我们注意到数据是存放在一个Node数组里面
transient Node[] table;
接着我们看一下Node
static class Node implements Map.Entry {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
我们注意到这是一个单链表,next指向下一个节点。
二、我们先看简单的get方法
接着我们看一下get(Object key)方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
实际调用的getNode方法
final Node getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
我们来一步步分析,首先定位到数据在数组的下标: (n - 1) & hash
找到数组的第一个node:first
first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]
如果first为null直接返回
如果first的key和get里面的key相等,则返回first的value
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
如果first的key和get里面的key不相等,判断first是不是TreeNode,如果不是,则一直找链表的next,直到key和所传的key相等
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
如果first的key和get里面的key不相等,判断first是不是TreeNode,如果是,则调用getTreeNode方法查找
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
我们看一下TreeNode的数据结构
static final class TreeNode extends LinkedHashMap.Entry {
TreeNode parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
......
......
}
再看下LinkedHashMap.Entry
static class Entry extends HashMap.Node {
Entry before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
我们注意到LinkedHashMap.Entry把单链表扩展成了双向链表
TreeNode把双向链表扩张成了红黑树
我们在来看一下getTreeNode方法
final TreeNode getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {
return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null);
}
root()是查询根节点,接着看一下find方法
final TreeNode find(int h, Object k, Class kc) {
TreeNode p = this;
do {
int ph, dir; K pk;
TreeNode pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
p = pl;
else if (ph < h)
p = pr;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if (pl == null)
p = pr;
else if (pr == null)
p = pl;
else if ((kc != null ||
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;
else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)
return q;
else
p = pl;
} while (p != null);
return null;
}
- 如上,要查询的key的hash为h,依次遍历节点,如果节点的hash>h,则把节点的左节点赋值给节点,如果节点的hash
- 链表的查询效率是n,它的效率是log2(n)
三、put方法
接着我们看一下put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
实际调用putVal
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
我们一行行分析
先是拿到数组的长度:
n = (tab = resize()).length;
取到数据在数组的下标:i = (n - 1) & hash
取到下标i对应的节点p = tab[i]
p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]
如果p为null,则新建一个node:
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
如果p不为null,判断p的key和传的key是否相等,相等则返回p
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
如果p不为null,判断p的key和传的key是否相等,不相等,如果是TreeNode,则放入红黑树里面
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
如果p不为null,判断p的key和传的key是否相等,不相等,如果不是TreeNode,则一直遍历next节点,直到节点的key和传的key相等
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
... ...
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
如果一直遍历到最后也没找到,则新建一个节点,并把它放在链表的末尾
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
最后新建节点的时候有一个树化 的判断
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
TREEIFY_THRESHOLD的值为8,超过8个则由链表转换成红黑树
我们来看一个这个方法
final void treeifyBin(Node[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
取到链表的首节点:e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]
replacementTreeNode方法实际是new一个TreeNode
TreeNode replacementTreeNode(Node p, Node next) {
return new TreeNode<>(p.hash, p.key, p.value, next);
}
do while操作是做了一个转换,单链表转换成双向链表
TreeNode hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
最后一句hd.treeify(tab);是调用树化的方法,我们看一下这个方法
final void treeify(Node[] tab) {
TreeNode root = null;
for (TreeNode x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
else {
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class kc = null;
for (TreeNode p = root;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
TreeNode xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}
注意这个方法的this是下标为i的数组的首节点
如果root为空,初始化root,根节点是黑色
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
- 外面的for循环,遍历next节点,把所有的节点插入进树里面
- 里面的For循环,通过hash对比判断左节点还是右节点,从根节点找左右节点,并把左右节点当成根节点往下找,直到左节点或者右节点为空,把它安装在这里
我们先看一下红黑树的特性,在看下面的balanceInsertion(root, x)方法
红黑树的特性:
- (1)每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色。
- (2)根节点是黑色。
- (3)每个叶子节点(NIL)是黑色。 [注意:这里叶子节点,是指为空(NIL或NULL)的叶子节点!]
- (4)如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
- (5)从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
static TreeNode balanceInsertion(TreeNode root,
TreeNode x) {
x.red = true;
for (TreeNode xp, xpp, xppl, xppr;;) {
if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {
x.red = false;
return x;
}
else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null)
return root;
if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) {
if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) {
xppr.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
else { !!
if (x == xp.right) {
root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateRight(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
else {
if (xppl != null && xppl.red) {
xppl.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
else {
if (x == xp.left) {
root = rotateRight(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateLeft(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
}
}
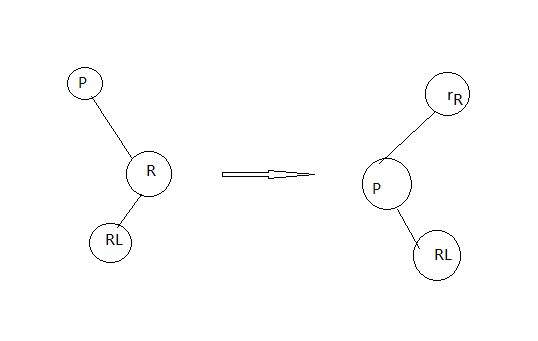
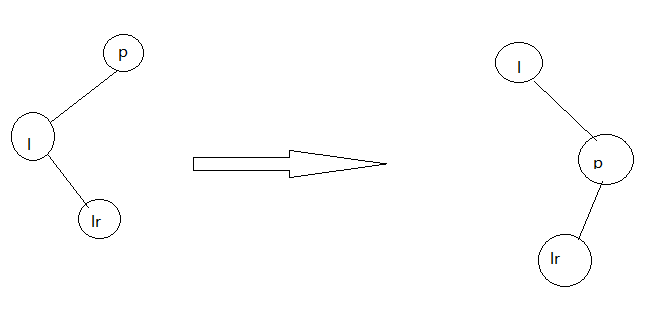
通过判断决定是左旋转还是右旋转,如上标两个感叹号的地方,是右节点没有,树不平衡了,此时x等于xp.right,这时候就左旋,否则就右旋
左旋转
static TreeNode rotateLeft(TreeNode root,
TreeNode p) {
TreeNode r, pp, rl;
if (p != null && (r = p.right) != null) {
if ((rl = p.right = r.left) != null)
rl.parent = p;
if ((pp = r.parent = p.parent) == null)
(root = r).red = false;
else if (pp.left == p)
pp.left = r;
else
pp.right = r;
r.left = p;
p.parent = r;
}
return root;
}
右旋转
static TreeNode rotateRight(TreeNode root,
TreeNode p) {
TreeNode l, pp, lr;
if (p != null && (l = p.left) != null) {
if ((lr = p.left = l.right) != null)
lr.parent = p;
if ((pp = l.parent = p.parent) == null)
(root = l).red = false;
else if (pp.right == p)
pp.right = l;
else
pp.left = l;
l.right = p;
p.parent = l;
}
return root;
}
最后,把根节点设置在第一位
/**
* Ensures that the given root is the first node of its bin.
*/
static void moveRootToFront(Node[] tab, TreeNode root) {
int n;
if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) {
int index = (n - 1) & root.hash;
TreeNode first = (TreeNode)tab[index];
if (root != first) {
Node rn;
tab[index] = root;
TreeNode rp = root.prev;
if ((rn = root.next) != null)
((TreeNode)rn).prev = rp;
if (rp != null)
rp.next = rn;
if (first != null)
first.prev = root;
root.next = first;
root.prev = null;
}
assert checkInvariants(root);
}
}
如果已经是红黑树了,插入进节点的方法
/**
* Tree version of putVal.
*/
final TreeNode putTreeVal(HashMap map, Node[] tab,
int h, K k, V v) {
Class kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
TreeNode root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;
for (TreeNode p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
if (!searched) {
TreeNode q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))
return q;
}
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
}
TreeNode xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
Node xpn = xp.next;
TreeNode x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode)xpn).prev = x;
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));
return null;
}
}
}
和上面基本差不多,也是平衡,旋转,把root置为first。
四、总结
- java7的结构是数组加链表,java8增加了红黑树,效率提升
- java7新增的数据是插入在链表的头部,java8是尾部