C# ModBus Tcp读写数据 与服务器进行通讯
前言
本文将使用一个NuGet公开的组件技术来实现一个ModBus TCP的客户端,方便的对Modbus tcp的服务器进行读写,这个服务器可以是电脑端C#设计的,也可以是PLC实现的,也可以是其他任何支持这个通信协议的服务器。
在Visual Studio 中的NuGet管理器中可以下载安装,也可以直接在NuGet控制台输入下面的指令安装:
|
1
|
Install-Package HslCommunication
|
NuGet安装教程 http://www.cnblogs.com/dathlin/p/7705014.html
技术支持QQ群:592132877 (组件的版本更新细节也将第一时间在群里发布)组件API地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dathlin/p/7703805.html
关于两种模式
在PLC端,包括三菱和西门子篇二以及Modbus Tcp客户端的访问器上,都支持两种模式,短连接模式和长连接模式,现在就来解释下什么原理。
短连接:每次读写都是一个单独的请求,请求完毕也就关闭了,如果服务器的端口仅仅支持单连接,那么关闭后这个端口可以被其他连接复用,但是在频繁的网络请求下,容易发生异常,会有其他的请求不成功,尤其是多线程的情况下。
长连接:创建一个公用的连接通道,所有的读写请求都利用这个通道来完成,这样的话,读写性能更快速,即时多线程调用也不会影响,内部有同步机制。如果服务器的端口仅仅支持单连接,那么这个端口就被占用了,比如三菱的端口机制,西门子的Modbus tcp端口机制也是这样的。以下代码默认使用短连接,方便测试。
在短连接的模式下,每次请求都是单独的访问,所以没有重连的困扰,在长连接的模式下,如果本次请求失败了,在下次请求的时候,会自动重新连接服务器,直到请求成功为止。另外,尽量所有的读写都对结果的成功进行判断。
特别感谢
- 网友:陈恩富 对float,int数据的读取测试,才修复了权重位颠倒的BUG。
- 网友:U4幸福的蜗牛 发现了博客上错误的一个方法名称,已于2018年1月8日13:34:39更新。并反馈了一些特殊设备(modbus tcp服务器)的读取数据的BUG。已修复。
随便聊聊
只要是网络访问,就会存在主从的区别,此处的设计模式是客户端主动请求服务器数据,然后接收服务器的反馈数据,支持原生的指令收发,支持其他一些方便的API收发。特殊功能码需要使用原生收发的API,本组件支持如下的功能操作:
- 0x01 读取线圈的操作,
- 0x02 读取离散的操作,
- 0x03 读取寄存器的值,
- 0x05 写一个线圈操作,
- 0x06 写一个寄存器值,
- 0x0F 批量写线圈操作,
- 0x10 批量写寄存器值,
如果你的设备需要这些功能之外的数据,可以使用原生API方法,但是这个方法的前提就是你对MODBUS TCP协议非常清晰才可以,如果你不了解这个协议,可以参照下面的博客说明:
http://blog.csdn.net/thebestleo/article/details/52269999
如果你需要搭建自己的ModBus服务器,可以参照这边文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/dathlin/p/7782315.html
在你开发自己的客户端程序之前,可以先用MODBUS测试工具进行测试,以下地址的一个开源项目就是基于这个组件开发的Modbus tcp测试工具,可直接用于读写测试。
https://github.com/dathlin/ModBusTcpTools
访问测试项目
下面的一个项目是这个组件的访问测试项目,您可以进行初步的访问的测试,免去了您写测试程序的麻烦,这个项目是和三菱,西门子PLC的访问写在一起的。可以同时参考。
https://github.com/dathlin/HslCommunicationDemo
Reference
ModBus组件所有的功能类都在 HslCommunication.ModBus命名空间,所以再使用之前先添加
|
1
2
|
using
HslCommunication.ModBus;
using
HslCommunication;
|
How to Use
实例化:
在使用读写功能之前必须先进行实例化:
|
1
|
private
ModBusTcpClient busTcpClient =
new
ModBusTcpClient(
"192.168.1.195"
, 502, 0xFF);
// 站号255
|
上面的实例化指定了服务器的IP地址,端口号(一般都是502),以及自己的站号,允许设置为0-255,后面的两个参数有默认值,在实例化的时候可以省略。
|
1
|
private
ModBusTcpClient busTcpClient =
new
ModBusTcpClient(
"192.168.1.195"
);
// 端口号502,站号0
|
上面两个声明选择其中一个就行了。然后实例化之后(也可以放在窗体的Load方法中)就可以调用下面的方法切换为长连接了,
|
1
|
modBusTcpClient.ConnectServer();
|
以下代码演示常用的读写操作,为了方便起见,不再对IsSuccess判断,一般都是成功的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
private
void
userButton30_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 读取操作
bool
coil100 = busTcpClient.ReadBoolCoil(100).Content;
// 读取线圈100的通断
short
short100 = busTcpClient.ReadShortRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100的short值
ushort
ushort100 = busTcpClient.ReadUShortRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100的ushort值
int
int100 = busTcpClient.ReadIntRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100-101的int值
uint
uint100 = busTcpClient.ReadUIntRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100-101的uint值
float
float100 = busTcpClient.ReadFloatRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100-101的float值
long
long100 = busTcpClient.ReadLongRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100-103的long值
ulong
ulong100 = busTcpClient.ReadULongRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100-103的ulong值
double
double100 = busTcpClient.ReadDoubleRegister(100).Content;
// 读取寄存器100-103的double值
string
str100 = busTcpClient.ReadStringRegister(100, 5).Content;
// 读取100到104共10个字符的字符串
// 写入操作
busTcpClient.WriteOneCoil(100,
true
);
// 写入线圈100为通
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, (
short
)12345);
// 写入寄存器100为12345
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, (
ushort
)45678);
// 写入寄存器100为45678
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, 123456789);
// 写入寄存器100-101为123456789
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, (
uint
)123456778);
// 写入寄存器100-101为123456778
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, 123.456);
// 写入寄存器100-101为123.456
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, 12312312312414L);
//写入寄存器100-103为一个大数据
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, 12634534534543656UL);
// 写入寄存器100-103为一个大数据
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100, 123.456d);
// 写入寄存器100-103为一个双精度的数据
busTcpClient.WriteRegister(100,
"K123456789"
);
}
|
下面再分别讲解严格的操作,以及批量化的复杂的读写操作,假设你要读取1000个M,循环读取1千次可能要3秒钟,如果用了下面的批量化读取,只需要50ms,但是需要你对字节的原理比较熟悉才能得心应手的处理
读取线圈API:
在此处举例读取地址为0,长度为10的线圈数量,但是需要注意的是,读取出来的数据是byte[]类型的,还需要处理一下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
private
void
userButton8_Click(
object
sender,EventArgs e)
{
HslCommunication.OperateResult<
byte
[]> read = busTcpClient.ReadCoil(0, 10);
if
(read.IsSuccess)
{
// 共返回2个字节,以下展示手动处理位,分别获取10和线圈的通断情况
bool
coil_0 = (read.Content[0] & 0x01) == 0x01;
bool
coil_1 = (read.Content[0] & 0x02) == 0x02;
bool
coil_2 = (read.Content[0] & 0x04) == 0x04;
bool
coil_3 = (read.Content[0] & 0x08) == 0x08;
bool
coil_4 = (read.Content[0] & 0x10) == 0x10;
bool
coil_5 = (read.Content[0] & 0x20) == 0x20;
bool
coil_6 = (read.Content[0] & 0x40) == 0x40;
bool
coil_7 = (read.Content[0] & 0x80) == 0x80;
bool
coil_8 = (read.Content[1] & 0x01) == 0x01;
bool
coil_9 = (read.Content[1] & 0x02) == 0x02;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(read.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
当然也可以用组件提供的数据转换API实现数据提取:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
private
void
userButton9_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
HslCommunication.OperateResult<
byte
[]> read = busTcpClient.ReadCoil(0, 10);
if
(read.IsSuccess)
{
// 共返回2个字节,一次性获取所有节点的通断
bool
[] result = HslCommunication.BasicFramework.SoftBasic.ByteToBoolArray(read.Content, 10);
bool
coil_0 = result[0];
bool
coil_1 = result[1];
bool
coil_2 = result[2];
bool
coil_3 = result[3];
bool
coil_4 = result[4];
bool
coil_5 = result[5];
bool
coil_6 = result[6];
bool
coil_7 = result[7];
bool
coil_8 = result[8];
bool
coil_9 = result[9];
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(read.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
读取离散数据:
读取离散数据和读取线圈的代码几乎是一致的,处理方式也是一致的,只是方法名称改成了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
private
void
userButton8_Click(
object
sender,EventArgs e)
{
HslCommunication.OperateResult<
byte
[]> read = busTcpClient.ReadDiscrete(0, 10);
if
(read.IsSuccess)
{
// 共返回2个字节,以下展示手动处理位,分别获取10和线圈的通断情况
bool
coil_0 = (read.Content[0] & 0x01) == 0x01;
bool
coil_1 = (read.Content[0] & 0x02) == 0x02;
bool
coil_2 = (read.Content[0] & 0x04) == 0x04;
bool
coil_3 = (read.Content[0] & 0x08) == 0x08;
bool
coil_4 = (read.Content[0] & 0x10) == 0x10;
bool
coil_5 = (read.Content[0] & 0x20) == 0x20;
bool
coil_6 = (read.Content[0] & 0x40) == 0x40;
bool
coil_7 = (read.Content[0] & 0x80) == 0x80;
bool
coil_8 = (read.Content[1] & 0x01) == 0x01;
bool
coil_9 = (read.Content[1] & 0x02) == 0x02;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(read.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
private
void
userButton9_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
HslCommunication.OperateResult<
byte
[]> read = busTcpClient.ReadDiscrete(0, 10);
if
(read.IsSuccess)
{
// 共返回2个字节,一次性获取所有节点的通断
bool
[] result = HslCommunication.BasicFramework.SoftBasic.ByteToBoolArray(read.Content, 10);
bool
coil_0 = result[0];
bool
coil_1 = result[1];
bool
coil_2 = result[2];
bool
coil_3 = result[3];
bool
coil_4 = result[4];
bool
coil_5 = result[5];
bool
coil_6 = result[6];
bool
coil_7 = result[7];
bool
coil_8 = result[8];
bool
coil_9 = result[9];
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(read.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
读取寄存器数据:
假设我们需要读取地址为0,长度为10的数据,也即是10个数据,每个数据2个字节,总计20个字节的数据。下面解析数据前,先进行了假设,你在解析自己的数据前可以参照下面的解析
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
private
void
userButton10_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
HslCommunication.OperateResult<
byte
[]> read = busTcpClient.ReadRegister(0, 10);
if
(read.IsSuccess)
{
// 共返回20个字节,每个数据2个字节,高位在前,低位在后
// 在数据解析前需要知道里面到底存了什么类型的数据,所以需要进行一些假设:
// 前两个字节是short数据类型
byte
[] buffer =
new
byte
[2];
buffer[0] = read.Content[1];
buffer[1] = read.Content[0];
short
value1 = BitConverter.ToInt16(buffer, 0);
// 接下来的2个字节是ushort类型
buffer =
new
byte
[2];
buffer[0] = read.Content[3];
buffer[1] = read.Content[2];
ushort
value2 = BitConverter.ToUInt16(buffer, 0);
// 接下来的4个字节是int类型
buffer =
new
byte
[4];
buffer[0] = read.Content[7];
buffer[1] = read.Content[6];
buffer[2] = read.Content[5];
buffer[3] = read.Content[4];
int
value3 = BitConverter.ToInt32(buffer, 0);
// 接下来的4个字节是float类型
buffer =
new
byte
[4];
buffer[0] = read.Content[11];
buffer[1] = read.Content[10];
buffer[2] = read.Content[9];
buffer[3] = read.Content[8];
float
value4 = BitConverter.ToSingle(buffer, 0);
// 接下来的全部字节,共8个字节是规格信息
string
speci = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(read.Content, 12, 8);
// 已经提取完所有的数据
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(read.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
写一个线圈:
写一个线圈,这个相对比较简单,假设我们需要写入线圈0,为通
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
private
void
userButton11_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteOneCoil(0,
true
);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
写一个寄存器:
写一个寄存器的操作也是非常的方便,在这里提供了三个重载的方法,允许使用三种方式写入:分别写入,short,ushort,byte三种:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private
void
userButton12_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
short
value = -1234;
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteOneRegister(0, value);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private
void
userButton12_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
ushort
value = 56713;
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteOneRegister(0, value);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private
void
userButton12_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 0x00为高位,0x10为低位
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteOneRegister(0, 0x00, 0x10);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
批量写入线圈:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
private
void
userButton13_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 线圈0为True,线圈1为false,线圈2为true.....等等,以此类推,数组长度多少,就写入多少线圈
bool
[] value =
new
bool
[] {
true
,
false
,
true
,
true
,
false
,
false
};
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteCoil(0, value);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
批量写入寄存器:
第一种情况写入一串short数组,这种情况比较简单:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private
void
userButton14_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
short
[] value =
new
short
[] { -1234, 467, 12345 };
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteRegister(0, value);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
第二情况写入一串ushort数组,也是比较简单:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
private
void
userButton14_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
ushort
[] value =
new
ushort
[] { 46789, 467, 12345 };
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteRegister(0, value);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
比较复杂的是写入自定义的数据,按照上述读取寄存器,解析的方式反着来就可以实现了,比如我需要写入寄存器0,寄存器1共同组成的一个int数据,那么我们这么写:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
private
void
userButton15_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
int
value = 12345678;
// 等待写入的一个数据
byte
[] buffer = BitConverter.GetBytes(value);
Array.Reverse(buffer);
// 这个是必须的
HslCommunication.OperateResult write = busTcpClient.WriteRegister(0, buffer);
if
(write.IsSuccess)
{
// 写入成功
textBox1.Text =
"写入成功"
;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(write.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
其他数据参考这个就行,如果有不明白的,可以联系上面的QQ群。
模式切换(支持热切换,想什么时候切换都可以):
上面默认都是使用短连接的机制,如果需要使用长连接的话,这种通讯模式更加稳定。多线程已经同步。
|
1
2
3
4
|
private
void
userButton11_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
modBusTcpClient.ConnectServer();
}
|
执行完这一行代码后,一般在实例化后面就可以切换长连接了,会返回一个OperateResult对象,连接成功IsSuccess为True,后面所有的读写操作都调用同一个通信通道。如果想要切换回短连接。
|
1
|
modBusTcpClient.ConnectClose();
|
究极数据操作,使用原生的报文来操作数据:
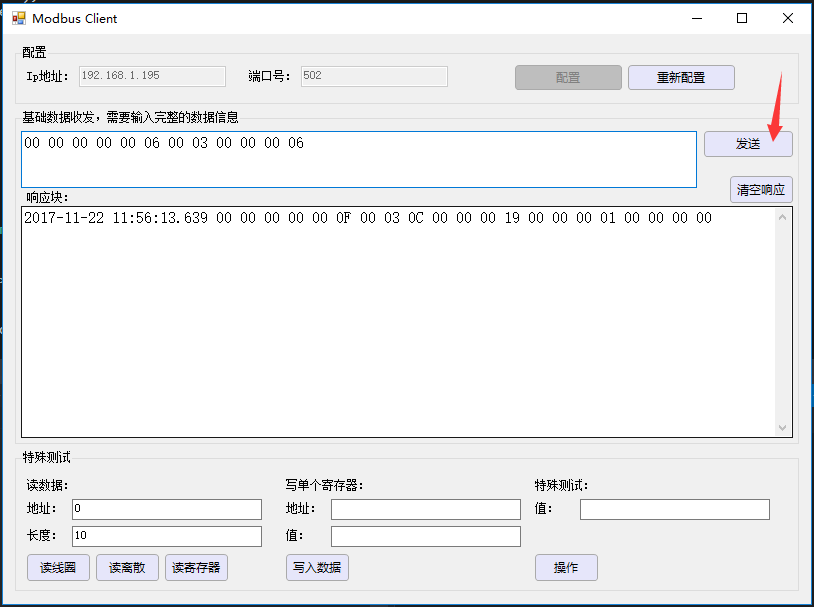
传入一个字节数组,数据内容和原生的数据一致,比如我要通过原生API读取寄存器地址为0,长度为3的数据,那么字节的HEX标识形式为 00 00 00 00 00 06 00 03 00 00 00 03
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
private
void
userButton2_Click(
object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
byte
[] data = HslCommunication.BasicFramework.SoftBasic.HexStringToBytes(
"00 00 00 00 00 06 00 03 00 00 00 03"
);
HslCommunication.OperateResult<
byte
[]> read = busTcpClient.ReadFromServerCore(data);
if
(read.IsSuccess)
{
// 获取结果,并转化为Hex字符串,方便显示
string
result = HslCommunication.BasicFramework.SoftBasic.ByteToHexString(read.Content,
' '
);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show(read.ToMessageShowString());
}
}
|
上述代码在操作时用了一个转化机制,输入为十六进制的文本,转化为byte[]数据,中间的分割符可以为空格,可以为'-',也可以为',','_'等等等等,调用了组件基础的数据转化功能。