图像理解(Image Captioning)(1)CNN部分
Image Captioning
- 一、 应用领域
- 二、 原理
- 三、使用的环境与数据集
- 3.1. **环境**
- 3.2. **数据集**
- 四、网络模型
- 4.1 理想⽹络模型
- 4.1.1 CNN网络模型
- 五、实现步骤
- 总体步骤:
- 5.1 使⽤keras创建VGG16定义的CNN⽹络结构
- 5.2 提取图像特征
一、 应用领域
二、 原理
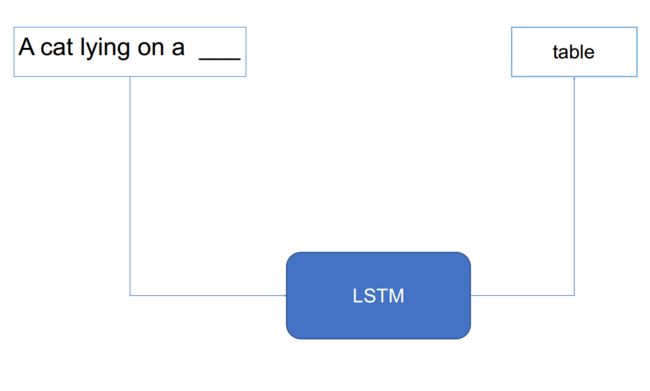
- CNN(卷积神经⽹络)
- LSTM(递归神经⽹络)
- DNN(深度神经⽹络)
- 从图像特征和⽂字串(sequence)
的特征预测下⼀个单词
通过链接这两个网络,使用CNN提取图像特征,再使用LSTM提取文本特征,再通过多层的DNN网络即可实现将文本特征与图像特征的链接实现图像理解
三、使用的环境与数据集
3.1. 环境
3.2. 数据集
(Framing Image Description as a Ranking Task: Data, Models and Evaluation Metrics, 2013.)
• Flickr8K
• 8000 图像, 每幅图5个标题, 描述图像⾥⾯的事物和事件
• 不包含著名⼈物和地点
• 分为3个集合: 6000个训练图像, 1000个开发图像, 1000个测试图像
终极⽬标: ⾃动⽣成图像英⽂标题, 与⼈类⽣成的标题们越相似越好
四、网络模型
4.1 理想⽹络模型
4.1.1 CNN网络模型
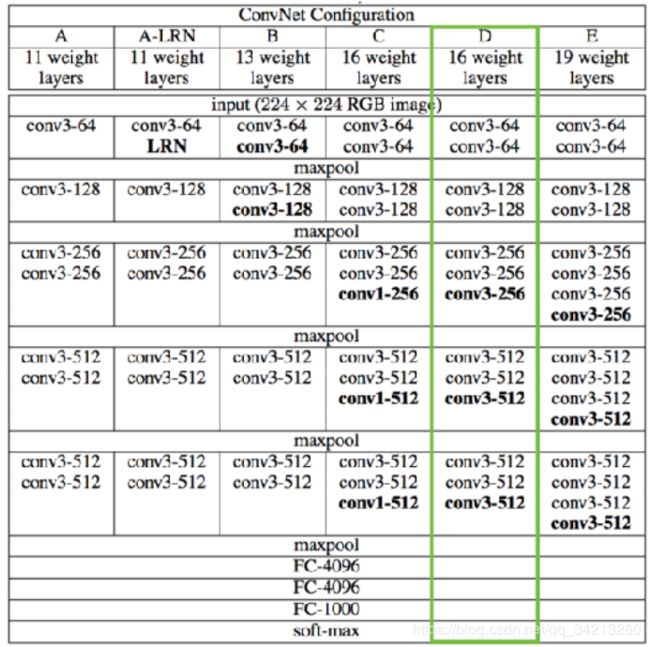
CNN模型我们以VGG16为例(也可以选择其他模型均可)
GG16 (Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Visual Recognition)
Tips:
因为VGG16 CNN 原本的⽬标是分类, 基于ImageNet数据集进⾏训练,训练所需的时间⽐较⼤,需要4个GPU训练3个星期左右。因此我们使用迁移学习(transfer learning),基本保留网络原有的结构和权重,只略微调整VGG16的⽹络输出结构为图像标题⽣成服务:
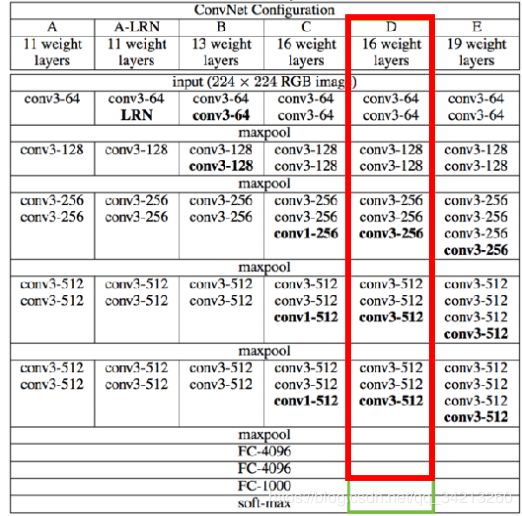
• VGG16 的最后⼀层是将倒数第⼆层4096维的输出转为1000维的输出作为1000类别的分类概率
• 我们可以去除最后⼀层,将倒数第⼆层的4096维的输出作为图像标题⽣成模型的图像特征,如下图红色框中所示。
五、实现步骤
总体步骤:
- 提取图像的特征(利⽤VGG16的修改模型)
- 初始化图像标题为”startseq”
- 循环如下步骤:
- 将图像标题转换为整数数组,每⼀个标题的单词对应于唯⼀⼀个整数
- 将图像特征和当前的图像标题作为输⼊, 预测标题的下⼀个单词, 假设单词为word1
- 将word1添加到当前标题的结尾
- 如果word1的值为”endseq”, 或者当前标题的⻓度达到了标题最⼤⻓度, 退出循环
- 此刻的图像标题就是预测的值
5.1 使⽤keras创建VGG16定义的CNN⽹络结构
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Flatten
from keras.layers import Conv2D
from keras.layers import MaxPooling2D
def generate_vgg16():
"""
搭建VGG16网络结构
:return: VGG16网络
"""
input_shape = (224, 224, 3)
model = Sequential([
Conv2D(64, (3, 3), input_shape=input_shape, padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)),
Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(128, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)),
Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)),
Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)),
Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(512, (3, 3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)),
Flatten(),
Dense(4096, activation='relu'),
Dense(4096, activation='relu'),
Dense(1000, activation='softmax')
])
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = generate_vgg16()
model.summary()
5.2 提取图像特征
`目标:将flicker8k的图像⽂件转为图像特征, 保存为字典pickle⽂件`
- 从给定的VGG16⽹络结构⽂件和⽹络权值⽂件, 创建VGG16⽹络
def load_vgg16_model():
"""从当前目录下面的 vgg16_exported.json 和 vgg16_exported.h5 两个文件中导入 VGG16 网络并返回创建的网络模型
# Returns
创建的网络模型 model
"""
json_file = open("vgg16_exported.json", "r")
loaded_model_json = json_file.read()
json_file.close()
model=model_from_json(loaded_model_json)
model.load_weights("vgg16_exported.h5")
return model
- 修改⽹络结构(去除最后⼀层)
model=load_vgg16_model()
# pop the last layer
model.layers.pop()
model = Model(inputs=model.inputs, outputs=model.layers[-1].output)
- 利⽤修改的⽹络结构,提取flicker8k数据集中所有图像的特征,使⽤字典存储, key为⽂件名, value为⼀个⽹络的输出。
def extract_features(directory):
features = dict()
for fn in listdir(directory):
fn=directory+'/'+fn
arr=load_img_as_np_array(fn, target_size=(224, 224))
# 改变数组的形态,增加一个维度(批处理输入的维度)
arr=arr.reshape((1,arr.shape[0],arr.shape[1],arr.shape[2]))
# 预处理图像作为VGG模型的输入
arr = preprocess_input(arr)
# 计算特征
feature =model.predict(arr, verbose=0)
# 分离文件名和路径以及分离文件名和后缀
(filepath, tempfilename) = os.path.split(fn)
(filename, extension) = os.path.splitext(tempfilename)
id=tempfilename
print(id)
features[id]=feature
return features
- 将字典保存为features.pkl⽂件(使⽤pickle库)
features = extract_features(directory)
print('提取特征的文件个数:%d' % len(features))
print(keras.backend.image_data_format())
#保存特征到文件
dump(features, open('features.pkl', 'wb'))