机器学习学习笔记 Logistic回归的实现
Logistic Regression
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import os
pdData = pd.read_csv("C:/Users/TianYi ZHENG/Desktop/LogiReg_data2.txt",header = None,names=["Exam1","Exam2","Admitted"])
pdData.head()
| Exam1 | Exam2 | Admitted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 34.623660 | 78.024693 | 0 |
| 1 | 30.286711 | 43.894998 | 0 |
| 2 | 35.847409 | 72.902198 | 0 |
| 3 | 60.182599 | 86.308552 | 1 |
| 4 | 79.032736 | 75.344376 | 1 |
pdData.shape
(100, 3)
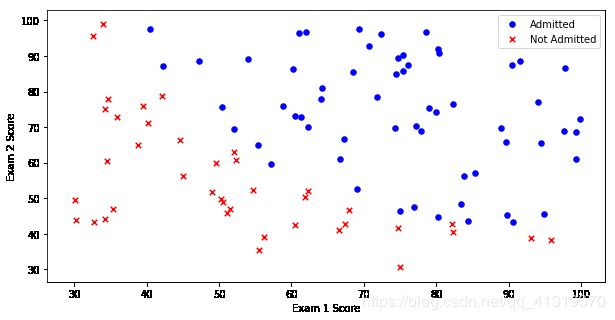
positive = pdDate[pdDate['Admitted']==1] #指定正例
negative = pdDate[pdDate['Admitted']==0] #指定负例
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,5))
ax.scatter(positive['Exam1'],positive['Exam2'], s = 30, c ='b',marker='o',label = 'Admitted' ) #散点图 蓝色 o
ax.scatter(negative['Exam1'],negative['Exam2'], s = 30, c ='r',marker='x',label = 'Not Admitted' )
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel("Exam 1 Score")
ax.set_ylabel("Exam 2 Score")
Text(0,0.5,'Exam 2 Score')
The logistic regression
目标:建立分类器(求解出三个参数 $\theta_0 \theta_1 \theta_2 $)
设定阈值,根据阈值判断录取结果
要完成的模块
-
sigmoid: 映射到概率的函数 -
model: 返回预测结果值 -
cost: 根据参数计算损失 -
gradient: 计算每个参数的梯度方向 -
descent: 进行参数更新 -
accuracy: 计算精度
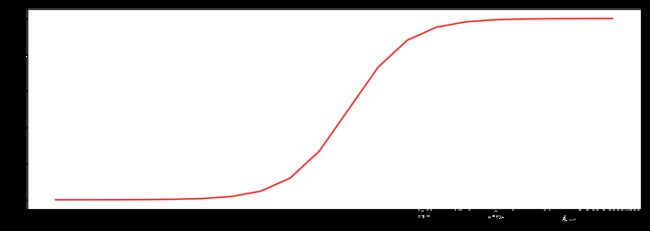
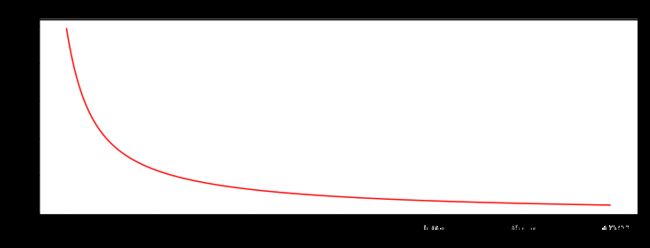
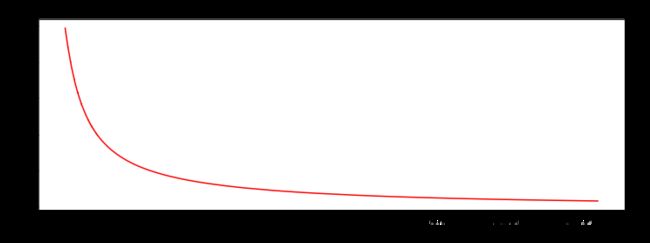
sigmoid 函数
g ( z ) = 1 1 + e − z g(z) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-z}} g(z)=1+e−z1
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
nums = np.arange(-10, 10, step=1) #creates a vector containing 20 equally spaced values from -10 to 10
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,4))
ax.plot(nums, sigmoid(nums), 'r')
[]
Sigmoid
- g : R → [ 0 , 1 ] g:\mathbb{R} \to [0,1] g:R→[0,1]
- g ( 0 ) = 0.5 g(0)=0.5 g(0)=0.5
- g ( − ∞ ) = 0 g(- \infty)=0 g(−∞)=0
- g ( + ∞ ) = 1 g(+ \infty)=1 g(+∞)=1
def model(X, theta):
return sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T))
( θ 0 θ 1 θ 2 ) × ( 1 x 1 x 2 ) = θ 0 + θ 1 x 1 + θ 2 x 2 \begin{array}{ccc} \begin{pmatrix}\theta_{0} & \theta_{1} & \theta_{2}\end{pmatrix} & \times & \begin{pmatrix}1\\ x_{1}\\ x_{2} \end{pmatrix}\end{array}=\theta_{0}+\theta_{1}x_{1}+\theta_{2}x_{2} (θ0θ1θ2)×⎝⎛1x1x2⎠⎞=θ0+θ1x1+θ2x2
pdData.insert(0, 'Ones', 1) # in a try / except structure so as not to return an error if the block si executed several times
# set X (training data) and y (target variable)
orig_data = pdData.as_matrix() # convert the Pandas representation of the data to an array useful for further computations
cols = orig_data.shape[1]
X = orig_data[:,0:cols-1]
y = orig_data[:,cols-1:cols]
# convert to numpy arrays and initalize the parameter array theta
#X = np.matrix(X.values)
#y = np.matrix(data.iloc[:,3:4].values) #np.array(y.values)
theta = np.zeros([1, 3])
X[:5]
array([[ 1. , 34.62365962, 78.02469282],
[ 1. , 30.28671077, 43.89499752],
[ 1. , 35.84740877, 72.90219803],
[ 1. , 60.18259939, 86.3085521 ],
[ 1. , 79.03273605, 75.34437644]])
y[:5]
array([[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 1.],
[ 1.]])
theta
array([[ 0., 0., 0.]])
X.shape, y.shape, theta.shape
((100, 3), (100, 1), (1, 3))
损失函数
将对数似然函数去负号
D ( h θ ( x ) , y ) = − y log ( h θ ( x ) ) − ( 1 − y ) log ( 1 − h θ ( x ) ) D(h_\theta(x), y) = -y\log(h_\theta(x)) - (1-y)\log(1-h_\theta(x)) D(hθ(x),y)=−ylog(hθ(x))−(1−y)log(1−hθ(x))
求平均损失
J ( θ ) = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n D ( h θ ( x i ) , y i ) J(\theta)=\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^{n} D(h_\theta(x_i), y_i) J(θ)=n1i=1∑nD(hθ(xi),yi)
def cost(X, y, theta):
left = np.multiply(-y, np.log(model(X, theta)))
right = np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - model(X, theta)))
return np.sum(left - right) / (len(X))
cost(X, y, theta)
0.6931471805599453
计算梯度
∂ J ∂ θ j = − 1 m ∑ i = 1 n ( y i − h θ ( x i ) ) x i j \frac{\partial J}{\partial \theta_j}=-\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^n (y_i - h_\theta (x_i))x_{ij} ∂θj∂J=−m1i=1∑n(yi−hθ(xi))xij
def gradient(X, y, theta):
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)
error = (model(X, theta)- y).ravel()
for j in range(len(theta.ravel())): #for each parmeter
term = np.multiply(error, X[:,j])
grad[0, j] = np.sum(term) / len(X)
return grad
Gradient descent
比较3中不同梯度下降方法
STOP_ITER = 0
STOP_COST = 1
STOP_GRAD = 2
def stopCriterion(type, value, threshold):
#设定三种不同的停止策略
if type == STOP_ITER: return value > threshold
elif type == STOP_COST: return abs(value[-1]-value[-2]) < threshold
elif type == STOP_GRAD: return np.linalg.norm(value) < threshold
import numpy.random
#洗牌
def shuffleData(data):
np.random.shuffle(data)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data[:, 0:cols-1]
y = data[:, cols-1:]
return X, y
import time
def descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
#梯度下降求解
init_time = time.time()
i = 0 # 迭代次数
k = 0 # batch
X, y = shuffleData(data)
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape) # 计算的梯度
costs = [cost(X, y, theta)] # 损失值
while True:
grad = gradient(X[k:k+batchSize], y[k:k+batchSize], theta)
k += batchSize #取batch数量个数据
if k >= n:
k = 0
X, y = shuffleData(data) #重新洗牌
theta = theta - alpha*grad # 参数更新
costs.append(cost(X, y, theta)) # 计算新的损失
i += 1
if stopType == STOP_ITER: value = i
elif stopType == STOP_COST: value = costs
elif stopType == STOP_GRAD: value = grad
if stopCriterion(stopType, value, thresh): break
return theta, i-1, costs, grad, time.time() - init_time
def runExpe(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
#import pdb; pdb.set_trace();
theta, iter, costs, grad, dur = descent(data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha)
name = "Original" if (data[:,1]>2).sum() > 1 else "Scaled"
name += " data - learning rate: {} - ".format(alpha)
if batchSize==n: strDescType = "Gradient"
elif batchSize==1: strDescType = "Stochastic"
else: strDescType = "Mini-batch ({})".format(batchSize)
name += strDescType + " descent - Stop: "
if stopType == STOP_ITER: strStop = "{} iterations".format(thresh)
elif stopType == STOP_COST: strStop = "costs change < {}".format(thresh)
else: strStop = "gradient norm < {}".format(thresh)
name += strStop
print ("***{}\nTheta: {} - Iter: {} - Last cost: {:03.2f} - Duration: {:03.2f}s".format(
name, theta, iter, costs[-1], dur))
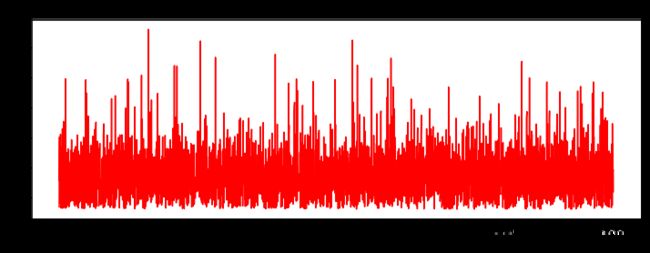
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12,4))
ax.plot(np.arange(len(costs)), costs, 'r')
ax.set_xlabel('Iterations')
ax.set_ylabel('Cost')
ax.set_title(name.upper() + ' - Error vs. Iteration')
return theta
#选择的梯度下降方法是基于所有样本的
n=100
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.000001)
***Original data - learning rate: 1e-06 - Gradient descent - Stop: 5000 iterations
Theta: [[-0.00027127 0.00705232 0.00376711]] - Iter: 5000 - Last cost: 0.63 - Duration: 0.76s
array([[-0.00027127, 0.00705232, 0.00376711]])
设定阈值 1E-6, 差不多需要110 000次迭代
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_COST, thresh=0.000001, alpha=0.001)
***Original data - learning rate: 0.001 - Gradient descent - Stop: costs change < 1e-06
Theta: [[-5.13364014 0.04771429 0.04072397]] - Iter: 109901 - Last cost: 0.38 - Duration: 16.83s
array([[-5.13364014, 0.04771429, 0.04072397]])
根据梯度变化停止
设定阈值 0.05,差不多需要40 000次迭代
runExpe(orig_data, theta, n, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.05, alpha=0.001)
***Original data - learning rate: 0.001 - Gradient descent - Stop: gradient norm < 0.05
Theta: [[-2.37033409 0.02721692 0.01899456]] - Iter: 40045 - Last cost: 0.49 - Duration: 6.43s
array([[-2.37033409, 0.02721692, 0.01899456]])
对比不同的梯度下降方法
Stochastic descent
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 1, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.001)
***Original data - learning rate: 0.001 - Stochastic descent - Stop: 5000 iterations
Theta: [[-0.37896481 0.03153973 -0.04710148]] - Iter: 5000 - Last cost: 1.21 - Duration: 0.24s
array([[-0.37896481, 0.03153973, -0.04710148]])
把学习率调小一些
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 1, STOP_ITER, thresh=15000, alpha=0.000002)
***Original data - learning rate: 2e-06 - Stochastic descent - Stop: 15000 iterations
Theta: [[-0.00202359 0.00985934 0.00081675]] - Iter: 15000 - Last cost: 0.63 - Duration: 0.70s
array([[-0.00202359, 0.00985934, 0.00081675]])
速度快,但稳定性差,需要很小的学习率
Mini-batch descent
runExpe(orig_data, theta, 16, STOP_ITER, thresh=15000, alpha=0.001)
***Original data - learning rate: 0.001 - Mini-batch (16) descent - Stop: 15000 iterations
Theta: [[-1.03349106 0.04033884 0.0204417 ]] - Iter: 15000 - Last cost: 0.94 - Duration: 0.95s
array([[-1.03349106, 0.04033884, 0.0204417 ]])
浮动仍然比较大,我们来尝试下对数据进行标准化
将数据按其属性(按列进行)减去其均值,然后除以其方差。最后得到的结果是,对每个属性/每列来说所有数据都聚集在0附近,方差值为1
from sklearn import preprocessing as pp
scaled_data = orig_data.copy()
scaled_data[:, 1:3] = pp.scale(orig_data[:, 1:3])
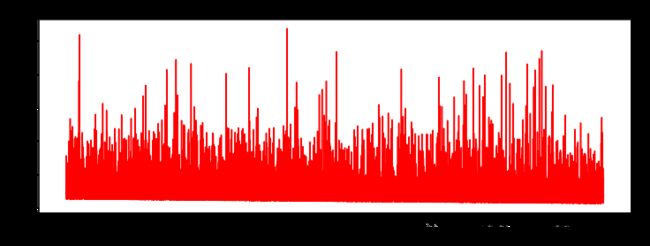
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, n, STOP_ITER, thresh=5000, alpha=0.001)
***Scaled data - learning rate: 0.001 - Gradient descent - Stop: 5000 iterations
Theta: [[0.3080807 0.86494967 0.77367651]] - Iter: 5000 - Last cost: 0.38 - Duration: 0.82s
array([[0.3080807 , 0.86494967, 0.77367651]])
原始数据,只能达到达到0.61,而我们得到了0.38个在这里!
所以对数据做预处理是非常重要的
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, n, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.02, alpha=0.001)
***Scaled data - learning rate: 0.001 - Gradient descent - Stop: gradient norm < 0.02
Theta: [[1.0707921 2.63030842 2.41079787]] - Iter: 59422 - Last cost: 0.22 - Duration: 9.90s
array([[1.0707921 , 2.63030842, 2.41079787]])
更多的迭代次数会使得损失下降的更多!
theta = runExpe(scaled_data, theta, 1, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.002/5, alpha=0.001)
***Scaled data - learning rate: 0.001 - Stochastic descent - Stop: gradient norm < 0.0004
Theta: [[1.14872847 2.79313214 2.56603965]] - Iter: 72609 - Last cost: 0.22 - Duration: 4.12s
随机梯度下降更快,但是我们需要迭代的次数也需要更多,所以还是用batch的比较合适!!!
runExpe(scaled_data, theta, 16, STOP_GRAD, thresh=0.002*2, alpha=0.001)
***Scaled data - learning rate: 0.001 - Mini-batch (16) descent - Stop: gradient norm < 0.004
Theta: [[1.15237244 2.80130244 2.57547463]] - Iter: 790 - Last cost: 0.22 - Duration: 0.07s
array([[1.15237244, 2.80130244, 2.57547463]])
精度
#设定阈值
def predict(X, theta):
return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in model(X, theta)]
scaled_X = scaled_data[:, :3]
y = scaled_data[:, 3]
predictions = predict(scaled_X, theta)
correct = [1 if ((a == 1 and b == 1) or (a == 0 and b == 0)) else 0 for (a, b) in zip(predictions, y)]
accuracy = (sum(map(int, correct)) % len(correct))
print ('accuracy = {0}%'.format(accuracy))
accuracy = 89%
备注:按照唐宇迪老师的课程实现的!