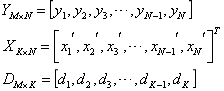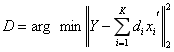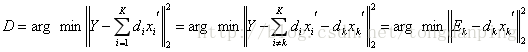稀疏表示(二)——KSVD算法详解(结合代码和算法思路)
鉴于很多人要代码,我放到网盘里吧:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1sVMl3s-c7U1aaI9jzr3DTw 提取码: 55wx
——————————————————————我是分割线————————————————————————————
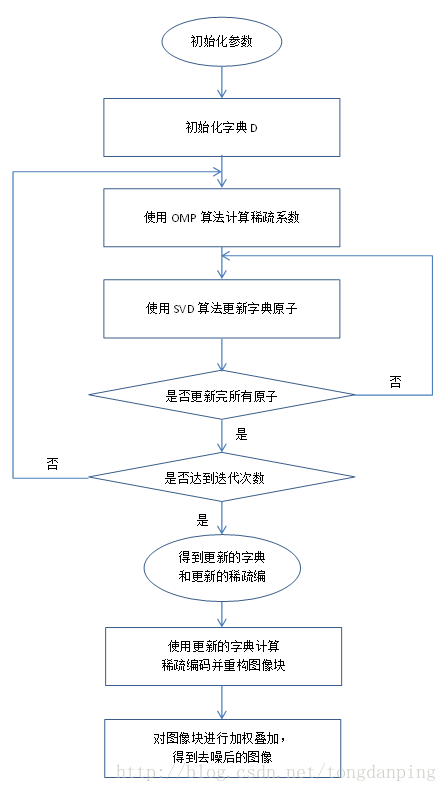
KSVD是一种稀疏表示中字典学习的算法,其名字的由来是该算法要经过K此迭代,且每一次迭代都要使用SVD分解。
在KSVD去噪算法中,稀疏编码可以使用OMP或者任意其它的稀疏编码算法,KSVD是用于字典更新的算法,KSVD在字典更新的过程中,每次只更新一个原子和对应的稀疏编码向量,在更新该原子时,其它原子是不变的,每次更新完字典的所有原子就同时更新了系数编码系数,这叫作一次迭代,在KSVD算法中,可以选择稀疏表示的第2种模型或者第3种模型见我的上一篇文章 ,在程序中可以通过参数 errorFlag来设置,如果errorFlag 为0,表示是用第2种模型,如果errorFlag 为1,表示是用第3种模型。在程序中的参数说明如下:
% errorFlag... if =0, a fix number of coefficients is
% used for representation of each signal. If so, param.L must be
% specified as the number of representing atom. if =1, arbitrary number
% of atoms represent each signal, until a specific representation error
% is reached. If so, param.errorGoal must be specified as the allowed
% error.在这里,我们使用第2种模式,也就是令errorFlag 为0。
整个KSVD的算法流程如下:
字典的初始化可以选取原始数据中的K个原子,或者使用一个固定的字典,比如DCT字典。
稀疏表示的两个主要阶段如下:
第一阶段:稀疏编码
对于模型:![]()
此时的字典是已知的,利用OMP算法,计算得到稀疏编码矩阵X,在得到X后,进入第二阶段。
第二阶段:字典学习
在第一阶段中已经计算好了X,因此模型可以简化为:![]()
在这里把矩阵用向量表示:
即把一个秩为K的矩阵分解为K个秩为1 的矩阵相加,现在假设我们要跟新第k列的原子,那么其他原子固定,即
这里看出,当更新第k个原子的时候,只考虑第k个原子和稀疏向量带来的表示误差,这里问题就转化为求解一个最接近![]() 的秩为1的矩阵,得到该矩阵以后,通过SVD分解,就可以得到更新后的
的秩为1的矩阵,得到该矩阵以后,通过SVD分解,就可以得到更新后的![]() 和
和![]() (这里请看文章末尾的TIP1对SVD分解的简单介绍)。但是这样更新以后的
(这里请看文章末尾的TIP1对SVD分解的简单介绍)。但是这样更新以后的![]() 非零的位置和更新前不再一样,甚至可能不再是稀疏的,这就违背了稀疏表示的初衷,因此在这里,应该做一点处理:
非零的位置和更新前不再一样,甚至可能不再是稀疏的,这就违背了稀疏表示的初衷,因此在这里,应该做一点处理:
在这里,我们只保留上一次迭代中使用到了第k个原子的![]() 计算
计算![]() 的最小误差来更新
的最小误差来更新![]() 和
和![]() 。
。
接下来,我们将结合KSVD去噪的程序来说明KSVD算法的流程。KSVD去噪算法可以在pudn上下载,去噪的程序denoiseImageKSVD.m 和 KSVD算法的程序 KSVD.m 都在文章末尾。接下来我们将把程序的每个部分提出来分析其功能。
KSVD的核心程序如下:
在程序中使用了I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries()函数来更新![]() 和
和![]() 。
。
rPerm = randperm(size(Dictionary,2));%size(Dictionary,2)=256 ,该函数产生1到256的随机的整数
for j = rPerm %j的值为从1到256的随机整数值(没有重复的)
[betterDictionaryElement,CoefMatrix,addedNewVector] = I_findBetterDictionaryElement(Data,...
[FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary],j+size(FixedDictionaryElement,2),...
CoefMatrix,param.L);
Dictionary(:,j) = betterDictionaryElement;
replacedVectorCounter = replacedVectorCounter+addedNewVector;
end这个函数是随机的更新字典中的每个向量,其中I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries()函数是这样的:
function [betterDictionaryElement,CoefMatrix,NewVectorAdded] = I_findBetterDictionaryElement(Data,Dictionary,j,CoefMatrix,numCoefUsed)
relevantDataIndices = find(CoefMatrix(j,:));
% 查找出系数矩阵中每一行中非0元素的序号,即使用了第j个原子的的序号
if (length(relevantDataIndices)<1) %(length(relevantDataIndices)==0) %如果系数矩阵为空,则进行如下的语句 。 如果relevantDataIndices为0,说明没有patch表达需要用到第j个原子,则执行以下语句,称为语句块1
ErrorMat = Data-Dictionary*CoefMatrix;
ErrorNormVec = sum(ErrorMat.^2);
[d,i] = max(ErrorNormVec);
betterDictionaryElement = Data(:,i);
betterDictionaryElement = betterDictionaryElement./sqrt(betterDictionaryElement'*betterDictionaryElement);%归一化
betterDictionaryElement = betterDictionaryElement.*sign(betterDictionaryElement(1));
CoefMatrix(j,:) = 0;
NewVectorAdded = 1%%%%%实验证明(针对w.jpg图像),值累加了一次
% liuzhe=1 没进行此句,说明稀疏矩阵的每一行都有非零的元素
return;
end
%如果length(relevantDataIndices)不为0,也就是说有patch的表达使用到了第j个原子,则执行以下语句,称为语句块2
NewVectorAdded = 0;
tmpCoefMatrix = CoefMatrix(:,relevantDataIndices); %将稀疏矩阵中使用了第j个原子的系数向量取出来,tmpCoefMatrix尺寸为:256*length(relevantDataIndices)
tmpCoefMatrix(j,:) = 0;% the coeffitients of the element we now improve are not relevant.
errors =(Data(:,relevantDataIndices) - Dictionary*tmpCoefMatrix); % vector of errors that we want to minimize with the new element D:64*256 tmpCoefMatrix尺寸为:256*length(relevantDataIndices) Data(:,relevantDataIndices):64*relevantDataIndices
%%在这里使用SVD就可以达到|| errors - beta*element ||_F^2误差最小的效果
[betterDictionaryElement,singularValue,betaVector] = svds(errors,1);%%%%%%%仅仅取出了第一主分量,betterDictionaryElement*singularValue*betaVector'近似的可以表示errors
CoefMatrix(j,relevantDataIndices) = singularValue*betaVector';%这里把SVD向量的左奇异矩阵的第一主向量作为更新的字典原子dk,把奇异值和右奇异向量的第一主向量的乘积作为更新的稀疏向量xk
对I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries()函数进行分析:
如果上一次迭代中没有任何图像块的系数表示使用过第j个原子,则if语句条件成立,那么利用上一次的稀疏矩阵计算![]() 并把误差最大的一项(第i项)提取出来,并把原始数据中的对应的Data(:,i)作为更新的原子,这样做的原因是把Data(:,i)作为更新的原子,这样就把最大误差消除为0.
并把误差最大的一项(第i项)提取出来,并把原始数据中的对应的Data(:,i)作为更新的原子,这样做的原因是把Data(:,i)作为更新的原子,这样就把最大误差消除为0.
如果上一次迭代中使用过第j个原子,也就是if条件不成立,那么就执行语句块2,在语句块2中,把上一次迭代中使用了第j个原子的xk提取出来,并且计算![]() ,利用SVD算法可以得到
,利用SVD算法可以得到![]() 的最小二乘解,并把SVD算法的左奇异矩阵的第一主向量作为更新的字典原子dk,把右奇异矩阵的第一主向量和最大的奇异值的乘积作为更新的稀疏向量xk。
的最小二乘解,并把SVD算法的左奇异矩阵的第一主向量作为更新的字典原子dk,把右奇异矩阵的第一主向量和最大的奇异值的乘积作为更新的稀疏向量xk。
以下是有详细注释的程序
denoiseImageKSVD.m
function [IOut,output] = denoiseImageKSVD(Image,sigma,K,varargin)
%==========================================================================
% P E R F O R M D E N O I S I N G U S I N G A D I C T I O N A R Y
% T R A I N E D O N N O I S Y I M A G E
%==========================================================================
% function IOut = denoiseImageKSVD(Image,sigma,K,varargin)
% denoise an image by sparsely representing each block with the
% already overcomplete trained Dictionary, and averaging the represented parts.
% Detailed description can be found in "Image Denoising Via Sparse and Redundant
% representations over Learned Dictionaries", (appeared in the
% IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, Vol. 15, no. 12, December 2006).
% This function may take some time to process. Possible factor that effect
% the processing time are:
% 1. number of KSVD iterations - the default number of iterations is 10.
% However, fewer iterations may, in most cases, result an acceleration in
% the process, without effecting the result too much. Therefore, when
% required, this parameter may be re-set.
% 2. maxBlocksToConsider - The maximal number of blocks to train on. If this
% number is larger the number of blocks in the image, random blocks
% from the image will be selected for training.
% ===================================================================
% INPUT ARGUMENTS : Image - the noisy image (gray-level scale)
% sigma - the s.d. of the noise (assume to be white Gaussian).
% K - the number of atoms in the trained dictionary.
% Optional arguments:
% 'blockSize' - the size of the blocks the algorithm
% works. All blocks are squares, therefore the given
% parameter should be one number (width or height).
% Default value: 8.
% 'errorFactor' - a factor that multiplies sigma in order
% to set the allowed representation error. In the
% experiments presented in the paper, it was set to 1.15
% (which is also the default value here).
% 'maxBlocksToConsider' - maximal number of blocks that
% can be processed. This number is dependent on the memory
% capabilities of the machine, and performances?
% considerations. If the number of available blocks in the
% image is larger than 'maxBlocksToConsider', the sliding
% distance between the blocks increases. The default value
% is: 250000.
% 'slidingFactor' - the sliding distance between processed
% blocks. Default value is 1. However, if the image is
% large, this number increases automatically (because of
% memory requirements). Larger values result faster
% performances (because of fewer processed blocks).
% 'numKSVDIters' - the number of KSVD iterations processed
% blocks from the noisy image. If the number of
% blocks in the image is larger than this number,
% random blocks from all available blocks will be
% selected. The default value for this parameter is:
% 10 if sigma > 5, and 5 otherwise.
% 'maxNumBlocksToTrainOn' - the maximal number of blocks
% to train on. The default value for this parameter is
% 65000. However, it might not be enough for very large
% images
% 'displayFlag' - if this flag is switched on,
% announcement after finishing each iteration will appear,
% as also a measure concerning the progress of the
% algorithm (the average number of required coefficients
% for representation). The default value is 1 (on).
% 'waitBarOn' - can be set to either 1 or 0. If
% waitBarOn==1 a waitbar, presenting the progress of the
% algorithm will be displayed.
% OUTPUT ARGUMENTS : Iout - a 2-dimensional array in the same size of the
% input image, that contains the cleaned image.
% output.D - the trained dictionary.
% =========================================================================
% first, train a dictionary on the noisy image
reduceDC = 1;
[NN1,NN2] = size(Image);
waitBarOn = 1;
if (sigma > 5)%%%sigma=50 numIterOfKsvd = 10;
numIterOfKsvd = 10;
else
numIterOfKsvd = 5;
end
C = 1.15;
maxBlocksToConsider = 260000;
slidingDis = 1;
bb = 8;
maxNumBlocksToTrainOn = 65000;
displayFlag = 1;
hh=length(varargin)%%%%%%%%%%%测试一下能不能进入下面的for循环中去。
% for argI = 1:2:length(varargin)
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'slidingFactor'))
% slidingDis = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'errorFactor'))
% C = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'maxBlocksToConsider'))
% maxBlocksToConsider = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'numKSVDIters'))
% numIterOfKsvd = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'blockSize'))
% bb = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'maxNumBlocksToTrainOn'))
% maxNumBlocksToTrainOn = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'displayFlag'))
% displayFlag = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% if (strcmp(varargin{argI}, 'waitBarOn'))
% waitBarOn = varargin{argI+1};
% end
% end
if (sigma <= 5)
numIterOfKsvd = 5;
end
%%
% first, train a dictionary on blocks from the noisy image
%把图像分块并向量化,如果分块数大于最大训练分块数,那么随机选择图像块组成blkMatrix
if(prod([NN1,NN2]-bb+1)> maxNumBlocksToTrainOn)
randPermutation = randperm(prod([NN1,NN2]-bb+1)); %1:prod([NN1,NN2]-bb+1) 随机排列
selectedBlocks = randPermutation(1:maxNumBlocksToTrainOn); %选择前maxNumBlocksToTrainOn个patch来进行字典训练
% P = randperm(N) returns a vector containing a random permutation of the
%integers 1:N. For example, randperm(6) might be [2 4 5 6 1 3].
blkMatrix = zeros(bb^2,maxNumBlocksToTrainOn); %字典大小确定 : bb^2 * maxNumBlocksToTrainOn
for i = 1:maxNumBlocksToTrainOn
[row,col] = ind2sub(size(Image)-bb+1,selectedBlocks(i));
%[row,col]=ind2sub(SIZ,IND)表示把IND的索引在SIZ的矩阵中用row和col的下标表示,row表示横坐标,col表示纵坐标
currBlock = Image(row:row+bb-1,col:col+bb-1);
blkMatrix(:,i) = currBlock(:);
end
else
blkMatrix = im2col(Image,[bb,bb],'sliding');%%%%%%%8*8=64 所以blkMatrix矩阵大小为:64*[(NN1-bb+1)*(NN2-bb+1)]
end
param.K = K;%%%K=256 4*8*8=256
param.numIteration = numIterOfKsvd ;%sigma=50 所以numIterOfKsvd = 10;
param.errorFlag = 1; % decompose signals until a certain error is reached. do not use fix number of coefficients.
param.errorGoal = sigma*C;
param.preserveDCAtom = 0;
%计算一个DCT字典作为初始化字典
Pn=ceil(sqrt(K));%%Pn=16
DCT=zeros(bb,Pn);%%bb=8
for k=0:1:Pn-1,
V=cos([0:1:bb-1]'*k*pi/Pn);
if k>0, V=V-mean(V); end;
DCT(:,k+1)=V/norm(V);
end;
DCT=kron(DCT,DCT);%%%%%跟DCT中的代码一样的 64*256的矩阵
param.initialDictionary = DCT(:,1:param.K );%%%% 取了256列。也就是全部都取了
param.InitializationMethod = 'GivenMatrix';
if (reduceDC)%%reduceDC=1
vecOfMeans = mean(blkMatrix);
blkMatrix = blkMatrix-ones(size(blkMatrix,1),1)*vecOfMeans;%%%减去平均数 blkMatrix矩阵大小为:64*[(NN1-bb+1)*(NN2-bb+1)]
end
if (waitBarOn)%waitBarOn=1
counterForWaitBar = param.numIteration+1;%param.numIteration = numIterOfKsvd ; =10
h = waitbar(0,'Denoising In Process ...');
param.waitBarHandle = h;
param.counterForWaitBar = counterForWaitBar;
end
param.displayProgress = displayFlag;%displayFlag = 1;
[Dictionary,output] = KSVD(blkMatrix,param);%%%%%%%最核心的函数%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
output.D = Dictionary;
%这里得到的Dictionary就是KSVD迭代更新好的最终的Dictionnary
if (displayFlag)%displayFlag = 1;
disp('finished Trainning dictionary');
end
% denoise the image using the resulted dictionary
errT = sigma*C;
IMout=zeros(NN1,NN2);
Weight=zeros(NN1,NN2);
%blocks = im2col(Image,[NN1,NN2],[bb,bb],'sliding');
while (prod(floor((size(Image)-bb)/slidingDis)+1)>maxBlocksToConsider)
slidingDis = slidingDis+1;
end
[blocks,idx] = my_im2col(Image,[bb,bb],slidingDis);
if (waitBarOn)
newCounterForWaitBar = (param.numIteration+1)*size(blocks,2);
end
%%
%用KSVD得到的字典计算稀疏系数
% go with jumps of 30000
for jj = 1:30000:size(blocks,2)
if (waitBarOn)
waitbar(((param.numIteration*size(blocks,2))+jj)/newCounterForWaitBar);
end
jumpSize = min(jj+30000-1,size(blocks,2));
if (reduceDC)
vecOfMeans = mean(blocks(:,jj:jumpSize));
blocks(:,jj:jumpSize) = blocks(:,jj:jumpSize) - repmat(vecOfMeans,size(blocks,1),1);
end
%Coefs = mexOMPerrIterative(blocks(:,jj:jumpSize),Dictionary,errT);
Coefs = OMPerr(Dictionary,blocks(:,jj:jumpSize),errT); %使用OMP计算稀疏系数
if (reduceDC)
blocks(:,jj:jumpSize)= Dictionary*Coefs + ones(size(blocks,1),1) * vecOfMeans;
else
blocks(:,jj:jumpSize)= Dictionary*Coefs ;
end
end
%%
%用计算得到的稀疏系数,来进行重构patch,然后按照权重进行叠加
count = 1;
Weight = zeros(NN1,NN2);
IMout = zeros(NN1,NN2);
[rows,cols] = ind2sub(size(Image)-bb+1,idx);
for i = 1:length(cols)
col = cols(i); row = rows(i);
block =reshape(blocks(:,count),[bb,bb]);
IMout(row:row+bb-1,col:col+bb-1)=IMout(row:row+bb-1,col:col+bb-1)+block;
Weight(row:row+bb-1,col:col+bb-1)=Weight(row:row+bb-1,col:col+bb-1)+ones(bb);
count = count+1;
end;
if (waitBarOn)
close(h);
end
IOut = (Image+0.034*sigma*IMout)./(1+0.034*sigma*Weight);
KSVD.m
function [Dictionary,output] = KSVD(...
Data,... % an nXN matrix that contins N signals (Y), each of dimension n.
param)
% =========================================================================
% K-SVD algorithm
% =========================================================================
% The K-SVD algorithm finds a dictionary for linear representation of
% signals. Given a set of signals, it searches for the best dictionary that
% can sparsely represent each signal. Detailed discussion on the algorithm
% and possible applications can be found in "The K-SVD: An Algorithm for
% Designing of Overcomplete Dictionaries for Sparse Representation", written
% by M. Aharon, M. Elad, and A.M. Bruckstein and appeared in the IEEE Trans.
% On Signal Processing, Vol. 54, no. 11, pp. 4311-4322, November 2006.
% =========================================================================
% INPUT ARGUMENTS:
% Data an nXN matrix that contins N signals (Y), each of dimension n.
% param structure that includes all required
% parameters for the K-SVD execution.
% Required fields are:
% K, ... the number of dictionary elements to train
% K 原子个数
% numIteration,... number of iterations to perform.
% numIteration 迭代次数
% errorFlag... if =0, a fix number of coefficients is
% used for representation of each signal. If so, param.L must be
% specified as the number of representing atom. if =1, arbitrary number
% of atoms represent each signal, until a specific representation error
% is reached. If so, param.errorGoal must be specified as the allowed
% error.
% preserveDCAtom... if =1 then the first atom in the dictionary
% is set to be constant, and does not ever change. This
% might be useful for working with natural
% images (in this case, only param.K-1
% atoms are trained).
% (optional, see errorFlag) L,... % maximum coefficients to use in OMP coefficient calculations.
% (optional, see errorFlag) errorGoal, ... % allowed representation error in representing each signal.
% InitializationMethod,... mehtod to initialize the dictionary, can
% be one of the following arguments:
% * 'DataElements' (initialization by the signals themselves), or:
% * 'GivenMatrix' (initialization by a given matrix param.initialDictionary).
% (optional, see InitializationMethod) initialDictionary,... % if the initialization method
% is 'GivenMatrix', this is the matrix that will be used.
% (optional) TrueDictionary, ... % if specified, in each
% iteration the difference between this dictionary and the trained one
% is measured and displayed.
% displayProgress, ... if =1 progress information is displyed. If param.errorFlag==0,
% the average repersentation error (RMSE) is displayed, while if
% param.errorFlag==1, the average number of required coefficients for
% representation of each signal is displayed.
% =========================================================================
% OUTPUT ARGUMENTS:
% Dictionary The extracted dictionary of size nX(param.K).
% output Struct that contains information about the current run. It may include the following fields:
% CoefMatrix The final coefficients matrix (it should hold that Data equals approximately Dictionary*output.CoefMatrix.
% ratio If the true dictionary was defined (in
% synthetic experiments), this parameter holds a vector of length
% param.numIteration that includes the detection ratios in each
% iteration).
% totalerr The total representation error after each
% iteration (defined only if
% param.displayProgress=1 and
% param.errorFlag = 0)
% numCoef A vector of length param.numIteration that
% include the average number of coefficients required for representation
% of each signal (in each iteration) (defined only if
% param.displayProgress=1 and
% param.errorFlag = 1)
% =========================================================================
%isfield(param,'displayProgress'):表示的是param中是否含有displayPrograess,如果含有则返回1,没有则返回0
if (~isfield(param,'displayProgress'))%%%原来的程序中含有param.displayProgress = displayFlag;%displayFlag = 1; 所以此句也不会执行
param.displayProgress = 0;
end
totalerr(1) = 99999;%代表的累积误差
if (isfield(param,'errorFlag')==0)%%%param.errorFlag = 1; 此句也不会执行
param.errorFlag = 0;
end
if (isfield(param,'TrueDictionary'))%%%param中没有TrueDictionary
displayErrorWithTrueDictionary = 1;
ErrorBetweenDictionaries = zeros(param.numIteration+1,1);
ratio = zeros(param.numIteration+1,1);
else
displayErrorWithTrueDictionary = 0;%%执行此句
ratio = 0;%看开头的说明
end
if (param.preserveDCAtom>0) %param.preserveDCAtom = 0; 表示是否保留第一个字典列向量
FixedDictionaryElement(1:size(Data,1),1) = 1/sqrt(size(Data,1));
else
FixedDictionaryElement = [];%执行此句
end
% coefficient calculation method is OMP with fixed number of coefficients
if (size(Data,2) < param.K)% 这句的意思是判断原始数据的patch向量化以后的列数是否小于字典的原子数。 K=256 size(Data)=249*249 此句不满足if条件
disp('Size of data is smaller than the dictionary size. Trivial solution...');
Dictionary = Data(:,1:size(Data,2)); %如果小于就把原始数据向量化以后的矩阵作为字典
return;
elseif (strcmp(param.InitializationMethod,'DataElements'))%%比较两个字符串是否相等 param.InitializationMethod = 'GivenMatrix';
Dictionary(:,1:param.K-param.preserveDCAtom) = Data(:,1:param.K-param.preserveDCAtom);
elseif (strcmp(param.InitializationMethod,'GivenMatrix'))%% param.InitializationMethod = 'GivenMatrix'; 执行此句
Dictionary(:,1:param.K-param.preserveDCAtom) = param.initialDictionary(:,1:param.K-param.preserveDCAtom);%param.initialDictionary = DCT(:,1:param.K );%%%% 取了256列。也就是全部都取了
%param.preserveDCAtom=0 param.K-param.preserveDCAtom=K=256 初始化字典就是DCT字典
end
% reduce the components in Dictionary that are spanned by the fixed
% elements
if (param.preserveDCAtom)% 这句是判断是否要保留字典的第一个原子不更新。 param.preserveDCAtom = 0; 此句不执行
tmpMat = FixedDictionaryElement \ Dictionary;
Dictionary = Dictionary - FixedDictionaryElement*tmpMat;
end
%%进入正题了!!!!!
%normalize the dictionary. 对字典进行归一化
Dictionary = Dictionary*diag(1./sqrt(sum(Dictionary.*Dictionary)));%64*256 *256*256(可以借助帮助文档):diag(1./sqrt(sum(Dictionary.*Dictionary))) 将sum(Dictionary.*Dictionary)作为对角线生成一个对角的矩阵
%上一句的作用:把Dictionary的每一列数据除以该列数据的平方和,从而进行归一化
Dictionary = Dictionary.*repmat(sign(Dictionary(1,:)),size(Dictionary,1),1); % multiply in the sign of the first element. 64*256 64*256
totalErr = zeros(1,param.numIteration);%param.numIteration = numIterOfKsvd=10 ; %sigma=50 所以numIterOfKsvd = 10;
%%
% the K-SVD algorithm starts here.
for iterNum = 1:param.numIteration %param.numIteration = numIterOfKsvd=10
% find the coefficients
if (param.errorFlag==0) %param.errorFlag = 1;
%CoefMatrix = mexOMPIterative2(Data, [FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary],param.L);
CoefMatrix = OMP([FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary],Data, param.L); %size(Data,2)=249*249
else
%CoefMatrix = mexOMPerrIterative(Data, [FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary],param.errorGoal);
CoefMatrix = OMPerr([FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary],Data, param.errorGoal);%%%%%%%%%%param.errorGoal = sigma*C; 稀疏矩阵
param.L = 1;
end
replacedVectorCounter = 0;
rPerm = randperm(size(Dictionary,2));%size(Dictionary,2)=256 测试一下就知道该函数的用法了(产生1到256的随机的整数,没有重合的整数)
for j = rPerm %j的值为从1到256的随机整数值(没有重复的)
[betterDictionaryElement,CoefMatrix,addedNewVector] = I_findBetterDictionaryElement(Data,...%%%%%%%%参考基于块结构化字典学习
[FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary],j+size(FixedDictionaryElement,2),...
CoefMatrix,param.L);
Dictionary(:,j) = betterDictionaryElement;%%%%%已看懂
if (param.preserveDCAtom)%param.preserveDCAtom = 0; 此句不执行
tmpCoef = FixedDictionaryElement\betterDictionaryElement;
Dictionary(:,j) = betterDictionaryElement - FixedDictionaryElement*tmpCoef;
Dictionary(:,j) = Dictionary(:,j)./sqrt(Dictionary(:,j)'*Dictionary(:,j));
end
replacedVectorCounter = replacedVectorCounter+addedNewVector;%%%%实验证明(针对w.jpg图像),值累加了一次
end
if (iterNum>1 & param.displayProgress)%param.displayProgress = 1
if (param.errorFlag==0)%param.errorFlag = 1;
output.totalerr(iterNum-1) = sqrt(sum(sum((Data-[FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary]*CoefMatrix).^2))/prod(size(Data)));
disp(['Iteration ',num2str(iterNum),' Total error is: ',num2str(output.totalerr(iterNum-1))]);
else %执行此句
output.numCoef(iterNum-1) = length(find(CoefMatrix))/size(Data,2);%%CoefMatrix中所有非0元素的长度/DATA的列数=平均每列非零系数的个数
disp(['Iteration ',num2str(iterNum),' Average number of coefficients: ',num2str(output.numCoef(iterNum-1))]);
end
end
if (displayErrorWithTrueDictionary ) %displayErrorWithTrueDictionary = 0;
[ratio(iterNum+1),ErrorBetweenDictionaries(iterNum+1)] = I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries(param.TrueDictionary,Dictionary);%%%%%%
disp(strcat(['Iteration ', num2str(iterNum),' ratio of restored elements: ',num2str(ratio(iterNum+1))]));
output.ratio = ratio;
end
Dictionary = I_clearDictionary(Dictionary,CoefMatrix(size(FixedDictionaryElement,2)+1:end,:),Data);%%%%%%%%%%size(FixedDictionaryElement,2)=0 CoefMatrix有256行
% h = waitbar(0,'Denoising In Process ...');
% param.waitBarHandle = h;
if (isfield(param,'waitBarHandle'))
waitbar(iterNum/param.counterForWaitBar);
end
end
output.CoefMatrix = CoefMatrix;
Dictionary = [FixedDictionaryElement,Dictionary];%% FixedDictionaryElement = [];%执行此句
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% findBetterDictionaryElement
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%将字典原子D的解定义为U中的第一列,将系数向量CoefMatrix的解定义为V的第一列与S(1,1)的乘积
function [betterDictionaryElement,CoefMatrix,NewVectorAdded] = I_findBetterDictionaryElement(Data,Dictionary,j,CoefMatrix,numCoefUsed)
if (length(who('numCoefUsed'))==0)
numCoefUsed = 1;
% liu=1%%%%没有进行此句,说明if条件不满足。
end
relevantDataIndices = find(CoefMatrix(j,:)); % the data indices that uses the j'th dictionary element. 查找出系数矩阵中每一行中非0元素的序号 参考DCT字典的程序:relevantDataIndices = find(Coefs(3,:));
if (length(relevantDataIndices)<1) %(length(relevantDataIndices)==0) 如果系数矩阵为空,则进行如下的语句 。 如果relevantDataIndices为0,说明没有patch表达粗腰用到第j个原子
ErrorMat = Data-Dictionary*CoefMatrix;
ErrorNormVec = sum(ErrorMat.^2);
[d,i] = max(ErrorNormVec);
betterDictionaryElement = Data(:,i);%ErrorMat(:,i); %
betterDictionaryElement = betterDictionaryElement./sqrt(betterDictionaryElement'*betterDictionaryElement);%归一化
betterDictionaryElement = betterDictionaryElement.*sign(betterDictionaryElement(1));
CoefMatrix(j,:) = 0;
NewVectorAdded = 1%%%%%实验证明(针对w.jpg图像),值累加了一次
% liuzhe=1 没进行此句,说明稀疏矩阵的每一行都有非零的元素
return;
end
NewVectorAdded = 0;
tmpCoefMatrix = CoefMatrix(:,relevantDataIndices); %将稀疏矩阵中非0 的取出来 tmpCoefMatrix尺寸为:256*length(relevantDataIndices)
tmpCoefMatrix(j,:) = 0;% the coeffitients of the element we now improve are not relevant.
errors =(Data(:,relevantDataIndices) - Dictionary*tmpCoefMatrix); % vector of errors that we want to minimize with the new element D:64*256 tmpCoefMatrix尺寸为:256*length(relevantDataIndices) Data(:,relevantDataIndices):64*relevantDataIndices
% % the better dictionary element and the values of beta are found using svd.
% % This is because we would like to minimize || errors - beta*element ||_F^2.
% % that is, to approximate the matrix 'errors' with a one-rank matrix. This
% % is done using the largest singular value.
%%在这里使用SVD就可以达到|| errors - beta*element ||_F^2误差最小的效果
[betterDictionaryElement,singularValue,betaVector] = svds(errors,1);%%%%%%%仅仅取出了第一主分量 errors的大小为;64*relevantDataIndices M=64 N=relevantDataIndices betterDictionaryElement*singularValue*betaVector'近似的可以表示errors
%a=[1 2 3 4;5 6 7 8;9 10 11 12;2 4 6 7.99999]; [u,s,v]=svds(a) u*s*v' [u,s,v]=svds(a,1):取出的第一主成分
%对于svds函数:a为M*N的矩阵,那么u:M*M S:M*N(简写成M*M) V=N*M V'=M*N
%对于svd函数:a为M*N的矩阵, 那么u:M*M S:M*N V=N*N V'=N*N
%将字典原子D的解定义为U中的第一列,将系数向量CoefMatrix的解定义为V的第一列与S(1,1)的乘积 这个是核心 核心 核心!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
CoefMatrix(j,relevantDataIndices) = singularValue*betaVector';% *signOfFirstElem s*v' [u,s,v]=svds(a,1):取出的第一主成分 ,所以此时s*v'矩阵大小为 1*N,即CoefMatrix(j,relevantDataIndices)也为:1*N betterDictionaryElement:M*1,即64*1的向量
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% findDistanseBetweenDictionaries
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function [ratio,totalDistances] = I_findDistanseBetweenDictionaries(original,new)
% first, all the column in oiginal starts with positive values.
catchCounter = 0;
totalDistances = 0;
for i = 1:size(new,2)
new(:,i) = sign(new(1,i))*new(:,i);
end
for i = 1:size(original,2)
d = sign(original(1,i))*original(:,i);
distances =sum ( (new-repmat(d,1,size(new,2))).^2);
[minValue,index] = min(distances);
errorOfElement = 1-abs(new(:,index)'*d);
totalDistances = totalDistances+errorOfElement;
catchCounter = catchCounter+(errorOfElement<0.01);
end
ratio = 100*catchCounter/size(original,2);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% I_clearDictionary
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function Dictionary = I_clearDictionary(Dictionary,CoefMatrix,Data)
T2 = 0.99;
T1 = 3;
K=size(Dictionary,2); %%K=256
Er=sum((Data-Dictionary*CoefMatrix).^2,1); % remove identical atoms(删除相同的原子) 列求和 CoefMatrix(j,relevantDataIndices)的大小为256*relevantDataIndices
G=Dictionary'*Dictionary; %256*256 G表示不同的原子求内积,可以认为是计算相似性 G 的大小是 K*K
G = G-diag(diag(G));%例如:G=magic(3) diag(diag(G)) 也就是将对角的元素赋值为0
for jj=1:1:K,
if max(G(jj,:))>T2 | length(find(abs(CoefMatrix(jj,:))>1e-7))<=T1 , %G(jj,:))>T2 表示两个原子间相似性很高,大于0.99
%length(find(abs(CoefMatrix(jj,:))>1e-7) 表示这使用到第jj个原子的patch少于3个
[val,pos]=max(Er);
clearDictionary=1%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%测试满足if条件的有多少次
Er(pos(1))=0;%将最大误差处的值赋值为0
Dictionary(:,jj)=Data(:,pos(1))/norm(Data(:,pos(1)));%%norm(Data(:,pos(1)):求向量的模 此整句相当于把误差最大的列归一化
G=Dictionary'*Dictionary;
G = G-diag(diag(G));
end;
end;