@(Linux network)
netfilter struct 整理
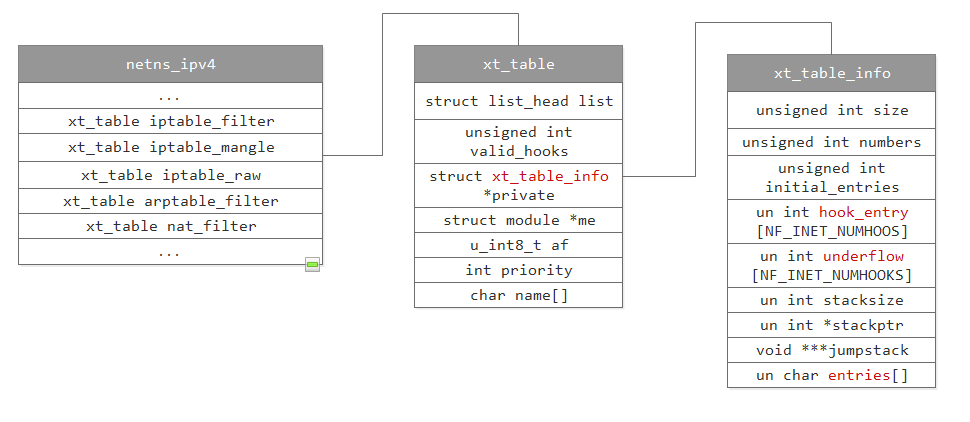
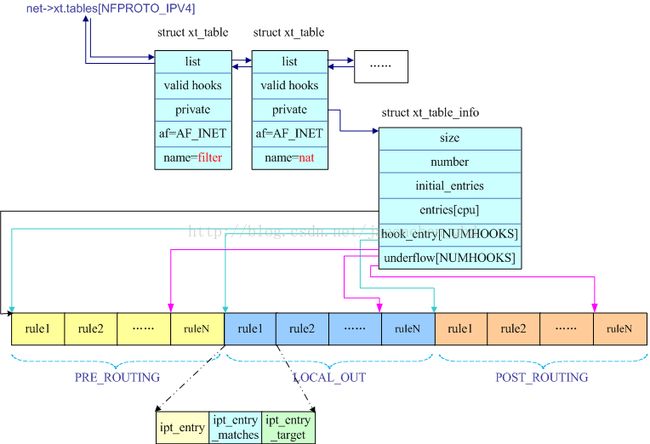
结构体关系图
阐述了结构体之间的关联
xt_table
在net->netns_ipv4结构体中,包含了如下几个xt_table
- iptable_filter
- iptable_mangle
- iptable_raw
- arptable_filter
- nat_filter
struct xt_table {
struct list_head list;//xt_table list
/* What hooks you will enter on */
// 此table中包含的chain,譬如nat table就不包含forward chain
// 在hook point,会去执行相应nf_hook[][] list上的hook_fn. 而不同的hook_fn会去查对应模块的table.
// 就是说, nat 注册的hook_fn 不会去在nat table中查找forward chain
unsigned int valid_hooks;
/* Man behind the curtain... */
// 具体存储table 内容
struct xt_table_info *private;
/* Set this to THIS_MODULE if you are a module, otherwise NULL */
struct module *me;
u_int8_t af; /* address/protocol family */
int priority; /* hook order */
/* A unique name... */
// 表名
const char name[XT_TABLE_MAXNAMELEN];
};下面来看private指针指向的结构体,这个结构体中具体存储了xt_entry结构体,每个xt_entry对应一条规则。
struct xt_table_info {
/* Size per table */
// table 的大小
unsigned int size;
/* Number of entries: FIXME. --RR */
// 包含的entry个数
unsigned int number;
/* Initial number of entries. Needed for module usage count */
// table的起始entry offset
unsigned int initial_entries;
/* Entry points and underflows */
// hook_entry[] 存储了每个chain 对应的起始entry offset
// underflow[] 存储了每个chain 最后一个entry的offset
unsigned int hook_entry[NF_INET_NUMHOOKS];
unsigned int underflow[NF_INET_NUMHOOKS];
/*
* Number of user chains. Since tables cannot have loops, at most
* @stacksize jumps (number of user chains) can possibly be made.
*/
// scott added:
// we can only jump form hook chains to user chains, PRE_ROUTING-> POST_ROUTING are not supported.
// so stacksize is the number of user chains and the max value of jump times.
// And also, jumpstack can only store child chain entry.
// 当chain之间发生jump的时候(A->B),只需要将A中当前的entry push进stack即可。所以jumpstack最大只需要存储user chains个数的entry.
// 如果B chain的某个entry target为XT_RETURN,则从stack中pop出A中的entry,并顺着A chain往下匹配.
unsigned int stacksize;
unsigned int __percpu *stackptr;
// 等同于 jumpstack[cpuid][entry*]
void ***jumpstack;
//保存的entries
unsigned char entries[0] __aligned(8);
};ipt_entry
ipt_entry具体的定义了每一条规则,例如
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -s 12.12.12.12 -ptcp --dport 808 -j DROP
/* This structure defines each of the firewall rules. Consists of 3 parts which are*/
// 1) general IP header stuff
// 2) match specific stuff
// 3) the target to perform if the rule matches
struct ipt_entry {
//存放了标准匹配
struct ipt_ip ip;
/* Mark with fields that we care about. */
unsigned int nfcache;
/* Size of ipt_entry + matches */
// 指定了target 元素的地址
// target_offset = elems + sizeof(xt_match) * numof(matchs)
__u16 target_offset;
/* Size of ipt_entry + matches + target */
// 下一个xt_entry的地址
__u16 next_offset;
/* Back pointer */
// 从哪个entry 过来的
unsigned int comefrom;
/* Packet and byte counters. */
// 计数 packet 和 byte?
struct xt_counters counters;
/* The matches (if any), then the target. */
// elems中保存了xt_match 和 xt_target.
// xt_match 和 xt_target 地址偏移在 target_offset指定
unsigned char elems[0];
};ipt_entry 看起来还是比较简单的,下面这张图解释的对ipt_entry比较清楚:
注意,ipt_ip结构中存放的是标准匹配,如 ip , netmask ,prototype,interface 等,扩展匹配等才存放在xt_match结构中。
/* Yes, Virginia, you have to zero the padding. */
struct ipt_ip {
/* Source and destination IP addr */
struct in_addr src, dst;
/* Mask for src and dest IP addr */
struct in_addr smsk, dmsk;
char iniface[IFNAMSIZ], outiface[IFNAMSIZ];
unsigned char iniface_mask[IFNAMSIZ], outiface_mask[IFNAMSIZ];
/* Protocol, 0 = ANY */
__u16 proto;
/* Flags word */
//SYN, ACK, FIN, RST ...
__u8 flags;
/* Inverse flags */
__u8 invflags;
};xt_entry_match
xt_entry_match 中主要保存了拓展match,在iptables中用-m 表示,在下例中,使用拓展socket match:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -m socket -j DIVERT
struct xt_entry_match {
union {
struct {
__u16 match_size;
/* Used by userspace */
char name[XT_EXTENSION_MAXNAMELEN];
__u8 revision;
} user;
struct {
__u16 match_size;
/* Used inside the kernel */
struct xt_match *match;
} kernel;
/* Total length */
__u16 match_size;
} u;
unsigned char data[0];
};注意: 在/usr/include /下的头文件,提供的都是用户态编写程序的接口。只有真正kernel src中提供的include文件,才是编写内核代码时需要引入的头文件。
例如 xt_entry_match,在/usr/include/linux/netfilter/x_tables.h中和内核代码 /usr/src/kernels/3.10.0-514.el7.x86_64/include/linux/netfilter/都有定义,但是只有内核代码文件中才包含xt_match结构的定义。用户文件中是没有次结构定义的。
union struct
这块是用户和内核共同操作的一块地址。当我们通过iptables添加规则的时候,用户态也会创建xt_entry_match结构,并将user.name设置为match名称,内核拿到此结构后,通过name的值,找到匹配的xt_match结构,并使kernel.match指向它。也就是说,name的值会被覆盖,但是没有关系,因为存储在table chain中的时候,xt_entry_match不需要name,只需要xt_match即可。
这里我们需要关注的xt_match结构体,其具体指向了一个匹配
xt_match
xt_match是内核的匹配模块,需要先注册,才能使用。
xt_register_match(&pktsize_match);
也就是说,xt_match结构体是公用的,当创建多个xt_entry_match的时候,其指向的都是match list中的该match, 但是xt_entry_match是不同的。
struct xt_match {
//extend match list?
struct list_head list;
//match name
const char name[XT_EXTENSION_MAXNAMELEN];
u_int8_t revision;
/* Return true or false: return FALSE and set *hotdrop = 1 to
force immediate packet drop. */
/* Arguments changed since 2.6.9, as this must now handle
non-linear skb, using skb_header_pointer and
skb_ip_make_writable. */
//match 函数,判断sk_buff是否满足该match,入参为sk_buff报文 以及
//xt_action_param 用来match和target的参数
bool (*match)(const struct sk_buff *skb,
struct xt_action_param *);
/* Called when user tries to insert an entry of this type. */
// 新建match entry的时候check
int (*checkentry)(const struct xt_mtchk_param *);
/* Called when entry of this type deleted. */
// 删除该类型match 的时候调用
void (*destroy)(const struct xt_mtdtor_param *);
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
/* Called when userspace align differs from kernel space one */
void (*compat_from_user)(void *dst, const void *src);
int (*compat_to_user)(void __user *dst, const void *src);
#endif
/* Set this to THIS_MODULE if you are a module, otherwise NULL */
struct module *me;
const char *table;
unsigned int matchsize;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
unsigned int compatsize;
#endif
unsigned int hooks;
unsigned short proto;
unsigned short family;
};注意: 这里重要的match指针函数,
bool (*match)(const struct sk_buff *skb, struct xt_action_param *);skb 为需要处理的报文,xt_action_param则指向了匹配规则,网口信息等。这个后面还需要看这个参数是怎么构建以及传入的。
xt_action_param
mtach或者target操作的时候,传入的参数。这个结构体是被xt_match和xt_target公用的,因此很多参数采用union
// struct xt_action_param - parameters for matches/targets
//
// @match: the match extension
// @target: the target extension
// @matchinfo: per-match data
// @targetinfo: per-target data
// @in: input netdevice
// @out: output netdevice
// @fragoff: packet is a fragment, this is the data offset
// @thoff: position of transport header relative to skb->data
// @hook: hook number given packet came from
// @family: Actual NFPROTO_* through which the function is invoked
// (helpful when match->family == NFPROTO_UNSPEC)
//
// Fields written to by extensions:
//
// @hotdrop: drop packet if we had inspection problems
// Network namespace obtainable using dev_net(in/out)
struct xt_action_param {
union {
const struct xt_match *match;
const struct xt_target *target;
};
union {
//配置的match 匹配参数
const void *matchinfo, *targinfo;
};
const struct net_device *in, *out;
//分片报文的偏移量
int fragoff;
unsigned int thoff;
//packet从哪个hook点过来的
unsigned int hooknum;
u_int8_t family;
//hotdrop = 1立刻丢掉此packet
bool hotdrop;
};xt_entry_target
创建iptable 规则时指定的动作,xt_entry_target依赖xt_target,extend target 需要register到xt_af[pf].target list.
xt_entry_target , xt_target 和 xt_entry_match,xt_match的结构类似。
struct xt_entry_target {
union {
struct {
__u16 target_size;
/* Used by userspace */
char name[XT_EXTENSION_MAXNAMELEN];
__u8 revision;
} user;
struct {
__u16 target_size;
/* Used inside the kernel */
struct xt_target *target;
} kernel;
/* Total length */
__u16 target_size;
} u;
unsigned char data[0];
};/* Registration hooks for targets. */
struct xt_target {
struct list_head list;
const char name[XT_EXTENSION_MAXNAMELEN];
u_int8_t revision;
/* Returns verdict. Argument order changed since 2.6.9, as this
must now handle non-linear skbs, using skb_copy_bits and
skb_ip_make_writable. */
unsigned int (*target)(struct sk_buff *skb,
const struct xt_action_param *);
/* Called when user tries to insert an entry of this type:
hook_mask is a bitmask of hooks from which it can be
called. */
/* Should return 0 on success or an error code otherwise (-Exxxx). */
int (*checkentry)(const struct xt_tgchk_param *);
/* Called when entry of this type deleted. */
void (*destroy)(const struct xt_tgdtor_param *);
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
/* Called when userspace align differs from kernel space one */
void (*compat_from_user)(void *dst, const void *src);
int (*compat_to_user)(void __user *dst, const void *src);
#endif
/* Set this to THIS_MODULE if you are a module, otherwise NULL */
struct module *me;
const char *table;
unsigned int targetsize;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
unsigned int compatsize;
#endif
unsigned int hooks;
unsigned short proto;
unsigned short family;
RH_KABI_RESERVE(1)
RH_KABI_RESERVE(2)
RH_KABI_RESERVE(3)
RH_KABI_RESERVE(4)
};