C语言数据结构之单链表
线性表的链式存储结构
单链表是一种链式存取的数据结构,用一组地址任意的存储单元存放线性表中的数据元素。链表中的数据是以结点来表示的,每个结点的构成:元素(数据元素的映象) + 指针(指示后继元素存储位置),元素就是存储数据的存储单元,指针就是连接每个结点的地址数据。
1、链接存储方法
链接方式存储的线性表简称为链表(Linked List)。
链表的具体存储表示为:
① 用一组任意的存储单元来存放线性表的结点(这组存储单元既可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的)
② 链表中结点的逻辑次序和物理次序不一定相同。为了能正确表示结点间的逻辑关系,在存储每个结点值的同时,还必须存储指示其后继结点的地址(或位置)信息(称为指针(pointer)或链(link))
链式存储是最常用的存储方式之一,它不仅可用来表示线性表,而且可用来表示各种非线性的数据结构。
2、结点结构
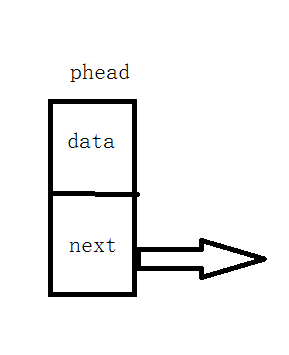
data域——存放结点值的数据域
next域——存放结点的直接后继的地址(位置)的指针域(链域)
带头结点的单链表:头结点的data不保存信息,next指针指向链表的第一个具有data域结点。
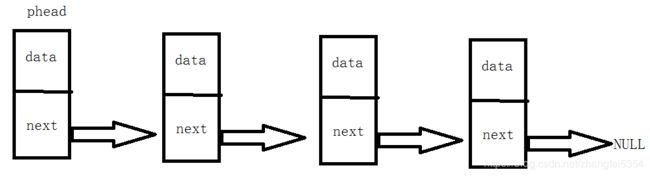
链表通过每个结点的链域将线性表的n个结点按其逻辑顺序链接在一起的,每个结点只有一个链域的链表称为单链表(Single Linked List)。单链表的最大特点是可以将物理地址上不连续的数据连接起来,通过指针来对物理地址进行操作,实现增删改查等功能。
线性表链式存储结构的建立
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
}Node,*List;
2、主要操作
void InitList(List plist);//初始化单链表
bool Insert_head(List plist,int val);//头插法
bool Insert_tail(List plist,int val);//尾插法
bool Insert_pos(List plist,int pos,int val);//pos 位置插入
Node *Search_pre(List plist,int key);//查找 key 的前驱
bool Delete(List plist,int key);//删除 key 这个结点
bool IsEmpty(List plist);//是否为空
void Destroy(List plist);//摧毁函数(如果有动态开辟内存)
int GetLength(List plist);//得到单链表的长度
void Show(List plist);//打印单链表
1、初始化单链表
void initList(List plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
plist->next = NULL;
}
2.得到一个节点
static Node *getNode(int val)
{
Node *pGet = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(pGet != NULL);
pGet->data = val;
pGet ->next = NULL;
return pGet;
}
3.头插法
要注意 与放入的数据顺序相反
bool Insert_head(List plist,int val)//头插法
{
Node *pGet = getNode(val);
pGet->next = plist->next;
plist ->next = pGet;
return true;
}
4.尾插法
操作注意 要用的一个pcur指针指向尾部
与放入的数据顺序相同
bool Insert_tail(List plist,int val)//尾插法
{
Node *pcur = plist;
while(pcur -> next!=NULL)
{
pcur = pcur->next;
}
Node *pGet = getNode(val);
pGet->next = pcur ->next;
return true;
}
5.pos 位置插入
bool Insert_pos(List plist,int pos,int val)//pos 位置插入
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if(pos<0||pos>GetLength(plist))
{
return false;
}
Node *pGet = getNode(val);
Node *pcur = plist->next;
for(int i =0;inext;
}
pGet->next = pcur->next;
pcur ->next = pGet;
return true;
}
6.查找 key 的前驱
Node *Search_pre(List plist,int key)//查找 key 的前驱
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
if(IsEmpty(plist))
{
return NULL;
}
Node *pcur = plist->next;
while(pcur!=NULL)
{
if(pcur->next->data==key)
{
return pcur;
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
7.删除 key 这个结点
注意 删除一个节点必须找到该节点的前驱,而不是找到该节点
bool Delete(List plist,int key)//删除 key 这个结点
{
Node *pcur = Search_pre(plist,key);
if(pcur==NULL)
{
return false;
}
Node *Del = pcur->next;
pcur->next = Del->next;
free(Del);
Del = NULL;
return true;
}
8.是否为空
bool IsEmpty(List plist)//是否为空
{
if(plist->next==NULL)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
9.摧毁函数
void Destroy(List plist)//摧毁函数(如果有动态开辟内存)
{
Node* pcur = NULL;
while(plist->next!=NULL)
{
pcur = plist->next;
free(pcur);
plist = plist->next;
}
pcur = NULL;
}
10.得到单链表的长度
int GetLength(List plist)//得到单链表的长度
{
int count = 0;
Node *pcur = plist->next;//指向第一个节点
while(pcur!= NULL)
{
pcur = pcur->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
11.打印
void Show(List plist)//打印单链表
{
Node *pcur = plist;
while(pcur->next != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",pcur->data);
pcur = pcur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
test.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include"LinkList.h"
int main()
{
Node head;
InitList(&head);
for(int i = 0; i < 10;i++)
{
Insert_tail(&head,i);
}
Insert_tail(&head,100);
Show(&head);
Insert_pos(&head,3,99);
Show(&head);
Delete(&head,5);
Show(&head);
int len = GetLength(&head);
printf("len == %d\n",len);
Destroy(&head);
return 0;
}