【算法总结】B+树的实现
【参考资料】
从B树、B+树、B*树谈到R 树
【B+树是什么】
b+树是b树的变种。b+树与b树最大的不同在于:b+树的关键字数量跟孩子节点数量一致,这与b树不一样。并且,b+树的叶子节点包含有所有关键字及其对应信息,非叶子节点只包含部分关键字(这部分关键字相当于边界索引),不含具体数据,下面这幅图就说明了问题:
![]()
===========抄录自july的博客===============
【备注】:根据我连日的查找资料及对比,我认为这幅图片没有出错,这幅图片很好地诠释了b+树。叶子节点的q是右边兄弟的指针,这个很方便扫库。
【b+树的操作】
【添加关键字】
请注意,因为b+树的叶子节点包含所有关键字及对应的数据,二非叶子节点包含了各个节点的边界,一旦边界值改变了,譬如在叶子节点“5,8,9”插入“4”,那么从根节点到叶子节点这条路径上的边界“5”必须全部改变成4。--还有一点,所有的插入操作先插入到叶子,然后根据性质判断是否边界值改变了,还是需要分裂---分裂必然导致父亲节点的边界值改变。
【删除关键字】
删除同理,必须留意边界值是否改变及是否需要借用关键字及是否需要合并节点。
【b+树操作演示】
说明:这棵b+树的阶为3,则最多三个关键字,最多三个子树,最少2个关键字,最少两个子树。
【插入操作演示】
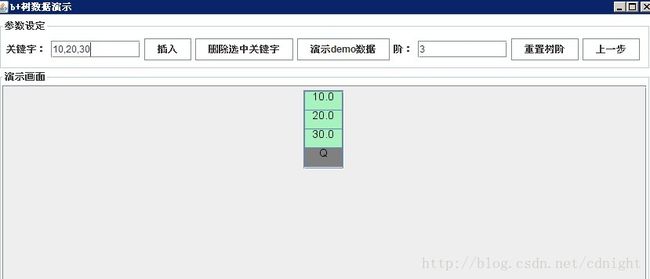
【分别插入关键字 10、20、30,此时根节点为叶节点,同时没有满足分裂条件,故放到同一个叶节点里面】
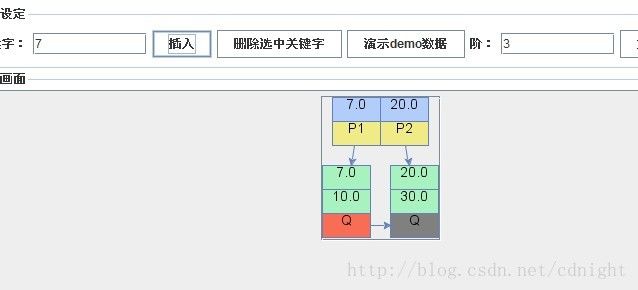
【插入关键字7,这时候根节点的关键字数量大于m(m=3),所以需要分裂成为两个子节点(叶节点)】
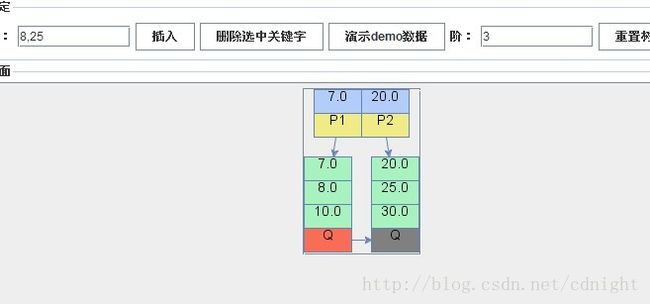
【分别插入关键字8、25,叶子节点被填满,没有符合分裂条件,不需要分裂。】
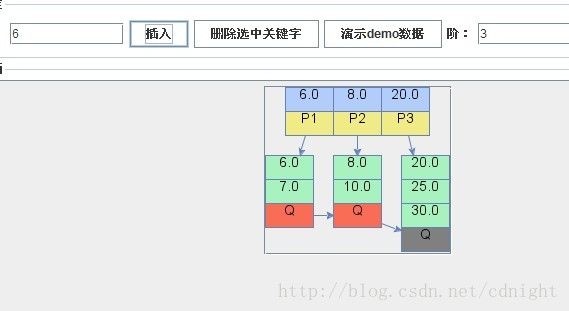
【插入关键字6,注意,6是少于所有关键字的,根据我的算法,6将放到最左边的叶子节点里面,并且递归设置每一个父亲的第一位数目(则该路径上第一个关键字都改6),同时,叶子节点关键字大于m(m=3),需要分裂,具体算法可以查看我的下一篇博文的具体代码,里面已经包含解释】
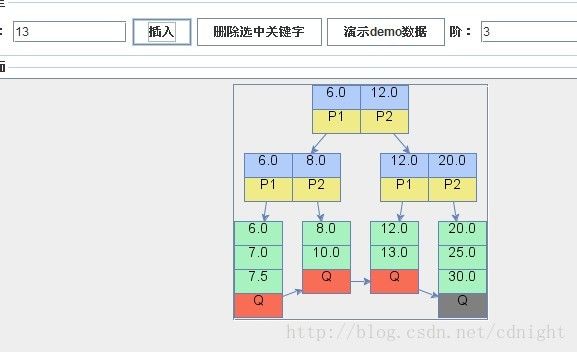
【分别插入关键字 7.5、12】
【插入关键字13,叶子节点满足分裂条件,分裂以后递归调整b+树的形状】
【插入关键字6.5,满足分裂条件,分裂之。】
【删除操作演示】
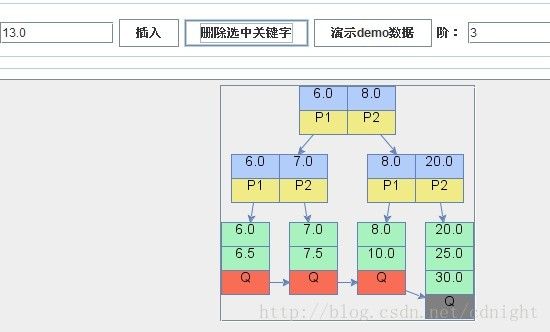
【删除关键字12.0,删除后叶子节点关键字数量少于min(min=2),通过检查可知,右侧兄弟有多余的关键字,从右侧兄弟那里借一个关键字,具体算法可以参看我下一篇博文的代码,里面有注释。】
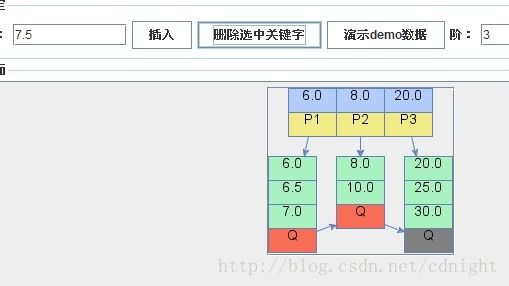
【删除关键字13.0,删除后关键字数量少于min,并且左右兄弟都没有多余的关键字,所以只能够合并叶子节点,合并后需要递归进行树形结构调整,具体算法参看下一篇博文。】
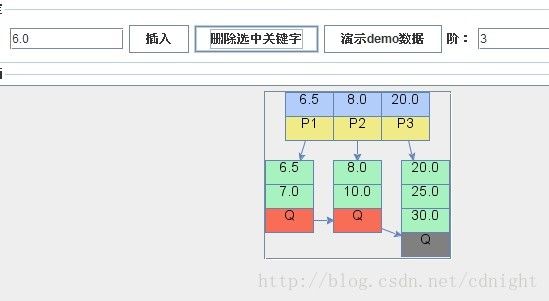
【删除关键字7.5,删除后满足合并条件,进行合并并递归调整树形。】
【删除关键字6.0,删除关键字6.0后,关键字数量==min,符合树形结构,但是父节点的关键字代表的是界限,就本算法而言,父亲节点的关键字要大于或等于它对应子节点或叶子节点的所有关键字,所以,这里必须进行父亲节点下界关键字的调整,必要时(当最左边叶子节点的第一个关键字改变了的情况下)甚至需要将同一路径的所有第一个关键字都改变,具体算法参看下一篇博文。】
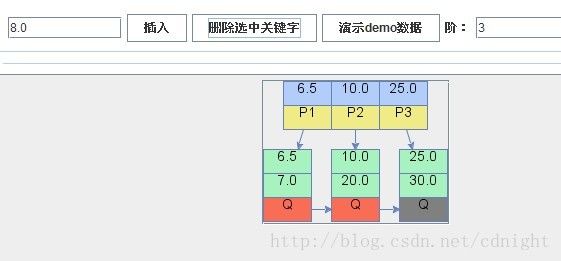
【删除关键字8.0,删除后需要向右边兄弟借一个关键字。】
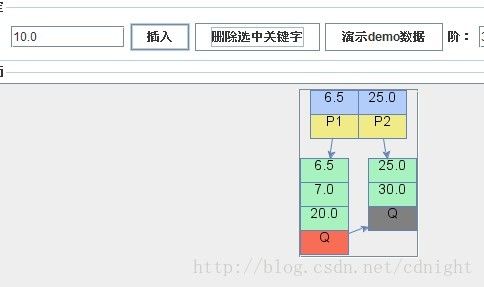
【删除关键字10.0,需要合并。】
【b+树java版实现的核心代码】
package BPlusTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class INode {
public boolean isLeaf=false;
public INode parent=null;
public ArrayList keys=new ArrayList();
public ArrayList childNodes=new ArrayList();
}
package BPlusTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TreeLeaf extends INode {
public ArrayListpackage BPlusTree;
public class TreeNode extends INode {
}
package BPlusTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TreeGen {
private int _m=4;//--最大子树数目
private int _min=2;//--最小关键字
public int getM(){
return _m;
}
public int getMin(){
return _min;
}
private INode _rootNode=new TreeLeaf();
public TreeGen(int m){
_m=m;
_min=(int)Math.ceil((double)((double)_m/(double)2));
}
/**
*
* 复制当前的数组,变成一个不同的值。
* 这个用来记录上一步骤的结果,免得到时候找不回以前的方法了。
*
* */
public static TreeGen getCopyGen(TreeGen gen ){
TreeGen _gen1=new TreeGen(gen.getM());
ArrayList arrList=gen.getAllKeyList();
for(float f1:arrList){
_gen1.insert(f1);
}
return _gen1;
}
public void setGen(int m,int min,INode inode){
_m=m;
_min=min;
_rootNode=inode;
}
public INode getRootNode(){
return _rootNode;
}
/**
* b+树的插入算法,这里解释一下流程:
* 1、当最初插入关键字的时候,即根节点就是叶子节点,那么直接插入,假如插入后根节点的关键字数量大于m,那么需要分裂;
* 2、寻找需要插入到的叶子节点,假如已经包含该关键字,报错,否则插入该关键字,查看关键字数量是否达到分裂条件,假如达到,则进行分裂操作。
* 必须注意的是,我这里的b+树对于大小的判断是:第一个子树的关键字必然大于或等于父亲的第一个关键字,小于父亲第二个关键字,如此类推,
* 网上的算法也有第一个子树的所有关键字都小于或等于父亲的第一个关键字这种。
* 我采用的算法意味着在处理(插入)一个小于所有关键字的关键字时候,需要寻找最左边的叶子节点,插入,然后修改该路径所有节点的第一个索引为该关键字,
* 同时需要进行正常的检查分裂操作
* */
public boolean insert(float indexNO){
//--假如是前几次插入,根节点为空或者下面都没有子树,那么就直接变成叶子节点。
if(_rootNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
if(_rootNode.isLeaf==false){
TreeLeaf myRoot=new TreeLeaf();
myRoot.isLeaf=true;
for(float keyNO:_rootNode.keys){
myRoot.keys.add(keyNO);
}
_rootNode=myRoot;
}
//--插入关键字。
int indexLOC=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:_rootNode.keys){
if(f1==indexNO){
return false;//包含该关键字,无法插入。
}
if(indexNO>f1){
indexLOC=cindex;
}
if(indexNOf1){
indexLOC=cindex;
}
if(indexNO0){
int indexLoc=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float key:currentNode.keys){
if(indexNO=key){
indexLoc=cindex;
}
cindex++;
}
/**
* 假如是-1,表示所有的数都比它大,表明b+树里面没有这个数,请回。
* */
if(indexLoc==-1){
return;
}
else{
recursion_to_serach(currentNode.childNodes.get(indexLoc), indexNO);
return;
}
}
else{
int indexLoc=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float key:currentNode.keys){
if((float)indexNO==(float)key){
indexLoc=cindex;
_research_result=currentNode;
break;
}
cindex++;
}
}
}
private void recursion_changeMinimun(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return;
}
if(currentNode.keys.get(0)!=indexNO){
currentNode.keys.remove(0);
currentNode.keys.add(0, indexNO);
}
recursion_changeMinimun(currentNode.parent, indexNO);
}
private boolean insertIndexNO(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return false;
}
int indexLOC=-1;
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:currentNode.keys){
if(f1==indexNO){
return false;
}
if(indexNO>f1){
indexLOC=cindex;
}
if(indexNOiNO){
indexLoc=cindex;
}
if(indexNO==iNO){
return null;//---节点里面包含该关键字,那么只能说,已经插入同样的关键字了,返回null
}
cindex++;
}
//--假如这个关键字是最少的,那么就直接找到最左边的叶子节点。
if(indexLoc==-1){
return recursion_getLeftLeaf(currentNode);
}
else{
return recursion_search_suitable_leaf(currentNode.childNodes.get(indexLoc), indexNO);
}
}
private TreeLeaf recursion_getLeftLeaf(INode currentNode){
if(currentNode==null){
return null;
}
if(currentNode.isLeaf==true){
return (TreeLeaf)currentNode;
}
if(currentNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
return null;
}
return recursion_getLeftLeaf(currentNode.childNodes.get(0));
}
/**
* 在插入关键字后,需要对当前节点及其父节点进行树形调整。
* */
private void recurse_division_after_insert(INode currentNode){
//--当前节点符合条件,那么不用分裂
if(currentNode.keys.size()<=_m){
return;
}
TreeLeaf currentLeaf=null;
TreeNode currentNode2=null;
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
if(currentNode.isLeaf==true){
currentLeaf=(TreeLeaf)currentNode;
TreeLeaf rightLeaf=new TreeLeaf();
rightLeaf.parent=currentLeaf.parent;
rightLeaf.isLeaf=true;
rightLeaf.rightBrother=currentLeaf.rightBrother;
currentLeaf.rightBrother=rightLeaf;
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:currentLeaf.keys){
if(cindex>=_min){
rightLeaf.keys.add(f1);
if(currentLeaf.values.size()>cindex){
rightLeaf.values.add(currentLeaf.values.get(cindex));
}
}
cindex++;
}
int theOriginTotal=currentLeaf.keys.size();
for(int i1=theOriginTotal-1;i1>=_min;i1--){
currentLeaf.keys.remove(i1);
if(currentLeaf.values.size()>i1){
currentLeaf.values.remove(i1);
}
}
//---假如父节点为空,那么直接开一个父节点。
if(currentLeaf.parent==null){
TreeNode theRoot=new TreeNode();
theRoot.keys.add( currentLeaf.keys.get(0));
theRoot.keys.add(rightLeaf.keys.get(0));
theRoot.childNodes.add(currentLeaf);
theRoot.childNodes.add(rightLeaf);
currentLeaf.parent=theRoot;
rightLeaf.parent=theRoot;
_rootNode=theRoot;
return;
}
else{
int cLindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
parentNode.keys.add(cLindex+1, rightLeaf.keys.get(0));
parentNode.childNodes.add(cLindex+1, rightLeaf);
recurse_division_after_insert(parentNode);
return;
}
}
else{
currentNode2=(TreeNode)currentNode;
TreeNode normalNode=currentNode2;
TreeNode rightBrother=new TreeNode();
rightBrother.parent=parentNode;
int originTotal=normalNode.keys.size();
for(int i1=_min;i1<=originTotal-1;i1++){
rightBrother.keys.add(normalNode.keys.get(i1));
normalNode.childNodes.get(i1).parent=rightBrother;
rightBrother.childNodes.add(normalNode.childNodes.get(i1));
}
for(int i1=originTotal-1;i1>=_min;i1--){
normalNode.childNodes.remove(i1);
normalNode.keys.remove(i1);
}
if(parentNode==null){
//--假如父节点为空,那么只能另起节点分裂了。
TreeNode theRoot=new TreeNode();
theRoot.keys.add(normalNode.keys.get(0));
theRoot.keys.add(rightBrother.keys.get(0));
theRoot.childNodes.add(normalNode);
theRoot.childNodes.add(rightBrother);
normalNode.parent=theRoot;
rightBrother.parent=theRoot;
_rootNode=theRoot;
return;
}
else{
int cLindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(normalNode);
parentNode.keys.add(cLindex+1, rightBrother.keys.get(0));
parentNode.childNodes.add(cLindex+1, rightBrother);
recurse_division_after_insert(parentNode);
return;
}
}
}
/**
* B+树的删除有几种情形(假如这是算法的话,这就是删除算法了)。
* 原则:
* 1、所有的删除操作都是在叶子节点进行的,每次删除都请先定位相关叶子节点;
* 2、必须保持b+树的原则,具体举例(以本文实现的B+树算法而言),除了根节点,所有节点的关键字数量必须大于或等于_min,
* 小于或等于_m,当小于_min的时候,可以这样处理:
* 2A、假如左右叶子节点有多余的关键字,可以向左右借;
* 2B、假如左右节点没有,那么只能合并节点,然后递归。(这种情况是进行递归的唯一情况)。
*
* 其实这些操作与B树的操作类似。
* */
public boolean delete(float indexNO){
INode currentNode=search(indexNO);
if(currentNode==null){
return false;
}
/**
*假如该节点是根节点,那么删了就删了,不用怕。
* */
if(currentNode.parent==null&¤tNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
int indexLoc=getIndexLocation(currentNode, indexNO);
if(indexLoc==-1){
return false;
}
else{
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 假如该节点是根节点,但是并非叶节点----不可能的情况,因为删除必须从叶节点开始!
* */
else if(currentNode.parent==null&¤tNode.childNodes.size()>0){
return false;
}
/**
* 假如该节点不是根节点,但是也并非叶节点----请明白删除必须从叶节点开始的含义!
* */
else if(currentNode.parent!=null&¤tNode.childNodes.size()>0){
return false;
}
/**
* 假如该节点是叶子节点。
*
* */
else if(currentNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
/**
* 假如叶子节点的关键字数量足够,那么直接删除。
* */
if(currentNode.keys.size()>_min){
int indexLoc=getIndexLocation(currentNode, indexNO);
/**
* 假如删除的是第一个关键字,请注意了,这种时候,它的上一级的第一位都必须更换成新的位置
* */
if(indexLoc==0){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
return true;
}
/**
* 否则,直接删除。
* */
else{
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 关键字数量不足,这时候:
* 1、看看左右节点有没有可以使用的,有的话,那么就借用并调整树形;
* 2、没有的话就删除,合并然后递归调整树形。
* */
else{
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
int indexLoc=getIndexLocation(currentNode, indexNO);
int cNodePindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
if(cNodePindex==-1){
return false;
}
INode leftBrother=null;
INode rightBrother=((TreeLeaf)currentNode).rightBrother;
if(cNodePindex>0){
leftBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(cNodePindex-1);
}
/**
* 有左侧节点并且左侧节点有足够的关键字,借用之。
* */
if(leftBrother!=null&&leftBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
currentNode.keys.add(0, leftBrother.keys.get(leftBrother.keys.size()-1));
leftBrother.keys.remove(leftBrother.keys.size()-1);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
return true;
}
/**
* 有右侧节点并且右侧节点有足够的关键字,借用之。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null&&rightBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
currentNode.keys.add(rightBrother.keys.get(0));
rightBrother.keys.remove(0);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, rightBrother, 0.0f);
if(indexLoc==0){
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
}
return true;
}
/**
* 最麻烦的情况也是需要递归的情况出现了,左右都没有足够的关键字,只能合并了,搞不好
* b+树会层层合并,高度最后减-1。
* */
else{
/**
* 跟左侧兄弟合并
* */
if(leftBrother!=null){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
if(indexLoc==0){
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
}
for(float f1:currentNode.keys){
leftBrother.keys.add(f1);
}
((TreeLeaf)leftBrother).rightBrother=((TreeLeaf)currentNode).rightBrother;
parentNode.keys.remove(cNodePindex);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(cNodePindex);
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return true;
}
/**
* 跟右侧兄弟合并。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null){
currentNode.keys.remove(indexLoc);
if(indexLoc==0){
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(null, currentNode, 0.0f);
}
for(float f1:rightBrother.keys){
currentNode.keys.add(f1);
}
((TreeLeaf)currentNode).rightBrother=((TreeLeaf)rightBrother).rightBrother;
parentNode.keys.remove(cNodePindex+1);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(cNodePindex+1);
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 其他情况不受理。
* */
else{
return false;
}
}
private void recursion_handler_after_deletion(INode curretNode){}
private void recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(INode childNode,INode currentNode,float firstIndexNO){
if(currentNode==null){
return;
}
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
/**
* 假如是叶节点,那么就从这里开始。
* */
if(currentNode.isLeaf==true){
if(parentNode!=null){
float myFirst=currentNode.keys.get(0);
int pIndex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(currentNode,parentNode, myFirst);
}
return;
}
else{
int childIndexLoc=currentNode.childNodes.indexOf(childNode);
if(childIndexLoc==-1){
return;
}
if((float)currentNode.keys.get(childIndexLoc)==firstIndexNO){}
else{
if(childIndexLoc>0){
currentNode.keys.remove(childIndexLoc);
currentNode.keys.add(childIndexLoc,firstIndexNO);
if(parentNode!=null){
float cIndexNO=currentNode.keys.get(0);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(currentNode,parentNode, cIndexNO);
}
return;
}
else if(childIndexLoc==0){
currentNode.keys.remove(0);
currentNode.keys.add(0,firstIndexNO);
float cIndexNO=currentNode.keys.get(0);
recursion_handler_firstOneDelete(currentNode, parentNode, cIndexNO);
return;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
}
private int getIndexLocation(INode currentNode,float indexNO){
int indexLoc=-1;
if(currentNode==null){
return indexLoc;
}
int cindex=0;
for(float f1:currentNode.keys){
if(f1==indexNO){
indexLoc=cindex;
break;
}
cindex++;
}
return cindex;
}
/**
* 当叶子节点需要合并,那么必须递归进行处理合并。
* */
private void recursion_combination(INode currentNode){
if(currentNode==null){
return;
}
INode parentNode=currentNode.parent;
if(currentNode.keys.size()>=_min){
return;
}
/**
* 假如这个节点只有1,这种情况只会发生在刚好分成两份的根节点被删除一个然后需要合并,叶子节点合并后的情况,那么
* 只能rootNode改变一下。
* */
if(currentNode.keys.size()==1&&parentNode==null){
_rootNode=currentNode.childNodes.get(0);
_rootNode.parent=null;
return;
}
/**
* 否则,这个是根节点,有两个关键字是可以的。
* */
if(parentNode==null&¤tNode.keys.size()>=2){
return;
}
INode leftBrother=null;
INode rightBrother=null;
int theCPindex=parentNode.childNodes.indexOf(currentNode);
if(theCPindex==-1){
return;
}
if(theCPindex==0){
rightBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(1);
}
else if(theCPindex==parentNode.childNodes.size()-1){
leftBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(theCPindex-1);
}
else{
leftBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(theCPindex-1);
rightBrother=parentNode.childNodes.get(theCPindex+1);
}
/**
* 假如左侧有空余的关键字,那么就借用。
* */
if(leftBrother!=null&&leftBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.add(0, leftBrother.keys.get(leftBrother.keys.size()-1));
currentNode.childNodes.add(0,leftBrother.childNodes.get(leftBrother.childNodes.size()-1));
currentNode.childNodes.get(0).parent=currentNode;
leftBrother.keys.remove(leftBrother.keys.size()-1);
leftBrother.childNodes.remove(leftBrother.childNodes.size()-1);
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex);
parentNode.keys.add(theCPindex,currentNode.keys.get(0));
return;
}
/**
* 假如右侧有空余关键字。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null&&rightBrother.keys.size()>_min){
currentNode.keys.add(rightBrother.keys.get(0));
currentNode.childNodes.add(rightBrother.childNodes.get(0));
currentNode.childNodes.get(currentNode.childNodes.size()-1).parent=currentNode;
rightBrother.keys.remove(0);
rightBrother.childNodes.remove(0);
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex+1);
parentNode.keys.add(theCPindex+1,rightBrother.keys.get(0));
return;
}
/**
* 都没有多余的话,只能合并了,需要递归检查。
* */
else{
/**
* 假如左侧兄弟有,那么与左边兄弟合并。
* */
if(leftBrother!=null){
for(Float key1:currentNode.keys){
leftBrother.keys.add(key1);
}
for(INode tmpNode:currentNode.childNodes){
tmpNode.parent=leftBrother;
leftBrother.childNodes.add(tmpNode);
}
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(theCPindex);
/**
* 合并完毕,递归到上一级再合并。
* */
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return;
}
/**
* 假如有右边兄弟,那么与右边合并。
* */
else if(rightBrother!=null){
for(Float key1:rightBrother.keys){
currentNode.keys.add(key1);
}
for(INode tmpNode:rightBrother.childNodes){
tmpNode.parent=currentNode;
currentNode.childNodes.add(tmpNode);
}
parentNode.keys.remove(theCPindex+1);
parentNode.childNodes.remove(theCPindex+1);
/**
* 合并完毕,递归。
* */
recursion_combination(parentNode);
return;
}
else{
return;
}
}
}
private TreeLeaf _leaf_tmp=null;
private void recursion_search_first_leaf(INode currNode){
if(currNode==null){
return;
}
if(currNode.isLeaf){
_leaf_tmp=(TreeLeaf)currNode;
return;
}
else{
if(currNode.childNodes.size()<=0){
return;
}
else{
recursion_search_first_leaf(currNode.childNodes.get(0));
return;
}
}
}
public TreeLeaf getFirstLeaf(){
_leaf_tmp=null;
recursion_search_first_leaf(_rootNode);
return _leaf_tmp;
}
public ArrayList getAllKeyList(){
ArrayList flist=new ArrayList();
TreeLeaf fLeaf=getFirstLeaf();
while(fLeaf!=null){
for(float f2:fLeaf.keys){
flist.add(f2);
}
fLeaf=fLeaf.rightBrother;
}
return flist;
}
}
【b+树demo及资源下载】
b+树演示工具