PCA人脸识别,附matlab代码和详细注释
选用ORL_92x112人脸数据集,共包含了40张人脸,每张人脸有10张不同姿态图像。代码中人脸矩阵中每一行对应一个人脸,每一列对应一个属性。完整的数据集和代码可以在这里下载:http://download.csdn.net/download/jzwong/10106036
代码
读入原始人脸数据集,默认选择每个类中的前5张图像做训练
% Revised by Jianzhu Wang email:jzwangATbjtuDOTeduDOTcn
function T = CreateTrainingSet(TrainingSetPath)
TrainFiles = dir(TrainingSetPath);
Train_Class_Number = 0;
for i = 1:size(TrainFiles,1)
if not(strcmp(TrainFiles(i).name,'.')|strcmp(TrainFiles(i).name,'..')|strcmp(TrainFiles(i).name,'Thumbs.db'))
Train_Class_Number = Train_Class_Number + 1; % Number of all images in the training database
end
end
%% Construction of 2D matrix from 1D image vectors
T = [];
Each_Class_Train_Num=5; % Choose top-5 faces in each class for training
for i = 1 : Train_Class_Number
str='';
str = strcat(TrainingSetPath,'\s',int2str(i),'\');
for j=1:Each_Class_Train_Num
tmpstr='';
tmpstr=strcat(str,int2str(j),'.bmp');
img=imread(tmpstr);
if length(size(img))>2
img=rgb2gray(img);
end
vecimg=double(reshape(img,1,size(img,1)*size(img,2)));
T=cat(1,T,vecimg);
end
end生成特征脸
function [MeanFace, MeanNormFaces, EigenFaces] = EigenfaceCore(T)
% Description: This function gets a 2D matrix, containing all training image vectors
% Input:T is a 2D matrix containing all 1D image vectors. Suppose we
% totally choose P training images with the same size of M*N. Each training
% image is then vectorized into a 'row' vector with length equals to M*N.
% That is , we finally get a P*MN 2D matrix.
% Output:
% MeanFace - (1*MN) mean vector of faces
% EigenFaces -
%- (M*Nx(P-1)) Eigen vectors of the covariance matrix of the training database
% MeanNormFaces - (M*NxP) Matrix of centered image vectors
%% Calculate meanface
MeanFace=mean(T,1);%(Default each row in T corresponds to a face)
TrainNumber=size(T,1); % We totally have Train_Number training images
%% Mean-normalize
MeanNormFaces=[];
for i=1:TrainNumber
MeanNormFaces(i,:)=double(T(i,:)-MeanFace);
end
%% Recall some linear algebra theory
% If a matrix with size M*N, then matrices AA' and A'*A have same non-zero
% eigenvales. And if x is an eigenvector of AA', then A'x is eigenvector of
% A'A. This can be easily proved. Note that if x is eigenvector of a
% matrix, then a*x (a is a constant) is also the eigenvector of the matrix.
% Thus, eigenvector result for A'A obtained from matlab may not be same as A'x.
% Use L to replace covariance matrix C=A'*A so as to decrease dimension
L=MeanNormFaces*MeanNormFaces';
[E, D] = eig(L);
%sort eigenvalues and corresponding eigenvectors
eigenValue=diag(wrev(diag(D)));
%accroding to the eigenvector relationship between AA' and A'A
EE=MeanNormFaces'*E;
eigenVector=fliplr(EE);
EigenFaces=[];
SumOfAllEigenValue=sum(eigenValue(:));
TmpSumOfEigenValue=0;
for i=1:size(eigenValue,1)
TmpSumOfEigenValue=TmpSumOfEigenValue+eigenValue(i,i);
ChooseEigenValueNum=i;
if(TmpSumOfEigenValue/SumOfAllEigenValue>0.85) %默认计贡献率达到85%以上即可
break;
end
end
for i=1:ChooseEigenValueNum
EigenFaces(i,:)=eigenVector(:,i)';
end
end将待分类人脸往特征脸上做变换,距离最小的类别标签作为当前人脸的类别
function OutputName = Recognition(TestImagePath, MeanFace, MeanNormFaces, EigenFaces)
% Description: This function compares two faces by projecting the images into facespace and
% measuring the Euclidean distance between them.
% Input: TestImagePath - Path of test face image
% MeanFace -(1*MN) mean vector, which is one
% of the output of 'EigenfaceCore.m'
%
% MeanNormFaces -(P*MN) matrix with each row
% represents a mean-normalized
% face, which is one of the output
% of 'EigenfaceCore.m'
% EigenFaces
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Projecting centered image vectors into facespace
% All centered images are projected into facespace by multiplying in
% Eigenface basis's. Projected vector of each face will be its corresponding
% feature vector.
ProjectedImages = [];
% I think here should be the number of centered training faces rather than
% number of eigenfaces
Train_Number = size(MeanNormFaces,1);
for i = 1 : Train_Number
temp = (EigenFaces*MeanNormFaces(i,:)')'; % Projection of centered images into facespace
ProjectedImages(i,:) =temp; % each row corresponds to a feature
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Extracting the PCA features from test image
InputImage = imread(TestImagePath);
VecInput=reshape(InputImage,1,size(InputImage,1)*size(InputImage,2));
MeanNormInput = double(VecInput)-MeanFace; % Centered test image
ProjectedTestImage = (EigenFaces*MeanNormInput')'; % Test image feature vector
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Calculating Euclidean distances
% Euclidean distances between the projected test image and the projection
% of all centered training images are calculated. Test image is
% supposed to have minimum distance with its corresponding image in the
% training database.
Euc_dist = [];
for i = 1 : Train_Number
temp = ( norm( ProjectedTestImage - ProjectedImages(i,:) ) )^2;
Euc_dist = [Euc_dist temp];
end
[Euc_dist_min , Recognized_index] = min(Euc_dist);
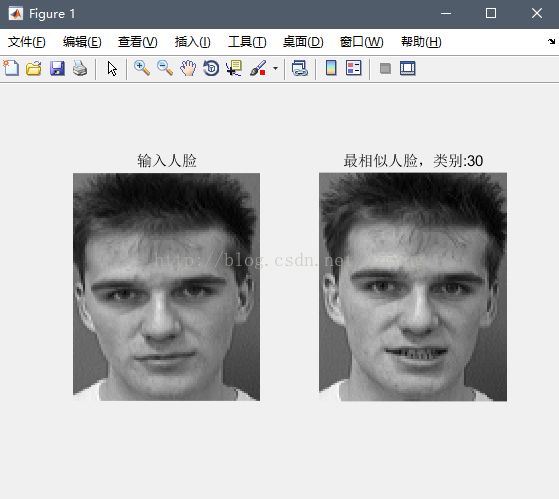
OutputName = strcat('s',int2str((Recognized_index-1)/5+1),'class');
figure,
subplot(121);
imshow(InputImage,[]);
title('输入人脸');
subplot(122);
imshow(reshape((MeanNormFaces(Recognized_index,:)+MeanFace),112,92),[]);
title(strcat('最相似人脸,类别:',int2str((Recognized_index-1)/5+1)));结果示意图
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/cvlabs/archive/2010/05/11/1733041.html