火焰图(FlameGraph)的使用
文章目录
- 1. Perf基础
- 1.1 Perf的安装
- 1.2 Perf的使用
- 2. 火焰图
- 2.1 生成火焰图
- 2.2 生成红蓝差分火焰图
- 2.3 oncpu/offcpu
- 参考文档:
1. Perf基础
1.1 Perf的安装
ubuntu 18.04:
sudo apt install linux-tools-common linux-tools-4.15.0-106-generic linux-cloud-tools-4.15.0-106-generic
1.2 Perf的使用
1、查看perf支持的监控event:
$ sudo perf list
List of pre-defined events (to be used in -e):
alignment-faults [Software event]
bpf-output [Software event]
context-switches OR cs [Software event]
cpu-clock [Software event]
cpu-migrations OR migrations [Software event]
dummy [Software event]
emulation-faults [Software event]
major-faults [Software event]
minor-faults [Software event]
page-faults OR faults [Software event]
task-clock [Software event]
L1-dcache-load-misses [Hardware cache event]
L1-dcache-loads [Hardware cache event]
L1-dcache-stores [Hardware cache event]
L1-icache-load-misses [Hardware cache event]
2、使用perf stat查看程序运行过程中各种event的统计:
$ sudo perf stat cp -r ~/test test.bak
Performance counter stats for 'cp -r /home/test test.bak':
268.941065 task-clock (msec) # 0.688 CPUs utilized
764 context-switches # 0.003 M/sec
0 cpu-migrations # 0.000 K/sec
158 page-faults # 0.587 K/sec
cycles
instructions
branches
branch-misses
0.390780362 seconds time elapsed
默认统计8种event在程序运行过程中的计数,如上所示。也可以使用-e选项来自定义使用的event。
3、使用perf record和perf report命令来进行更详细的分析:
perf stat命令只能记录event发生的次数,perf record在此基础之上可以记录event发生时详细的数据(比如IP、堆栈等等)。可以自定义需要记录的event,可以自定义记录数据的格式。
$ sudo perf record -g -F 99 cp -r ~/test test.bak
$ sudo perf report -g -i perf.data
Samples: 11 of event 'cpu-clock', Event count (approx.): 111111110
Children Self Command Shared Object Symbol
+ 100.00% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe
+ 100.00% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] do_syscall_64
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp libc-2.27.so [.] __GI___libc_write
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] sys_write
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] vfs_write
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] __vfs_write
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] new_sync_write
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] ext4_file_write_iter
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] __generic_file_write_iter
+ 54.55% 0.00% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] generic_perform_write
+ 45.45% 36.36% cp [kernel.kallsyms] [k] mpt_put_msg_frame
+ 45.45% 0.00% cp [unknown] [k] 0x2f6c77702f656d6f
+ 45.45% 0.00% cp [unknown] [k] 0x00007ffdde07f73f
+ 45.45% 0.00% cp cp [.] 0x0000000000004441
perf record默认只使用了1种event cpu-clock,cpu-clock使用的是高精度定时器来进行定时采样。
-F 99选项指定了采样频率99HZ。
-g选项指定了输出数据中包含调用堆栈。
perf record默认数据输出文件为perf.data。
2. 火焰图
火焰图是用图形化的方式来展现perf等工具采集的性能数据,对数据进行统计和分析,方便找出性能热点。
首先我们下载Brendan D. Gregg大神开发的火焰图工具:
git clone https://github.com/brendangregg/FlameGraph.git
在https://github.com/brendangregg/FlameGraph.git主页有生成火焰图的详细说明。
2.1 生成火焰图
下面是一个实际例子,我们首先用perf record抓取perf数据,再使用脚本生成火焰图:
$ sudo perf record -g -F 99 -- cp -r ~/aaa/ ./aaa.test
$ sudo perf script -i perf.data > out.perf
$ ../FlameGraph/stackcollapse-perf.pl out.perf > out.floded
$ ../FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl out.floded > cp.svg
$ ls
cp.svg aaa.test out.floded out.perf perf.data
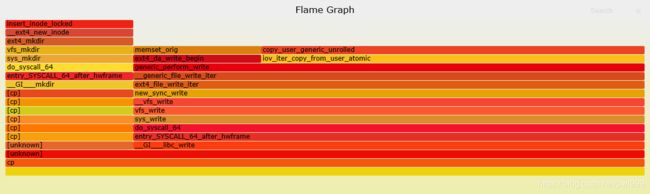
火焰图中的每一个方框是一个函数,方框的长度,代表了它的执行时间,所以越宽的函数,执行越久。火焰图的楼层每高一层,就是更深一级的函数被调用,最顶层的函数,是叶子函数。
火焰图的含义:
火焰图是基于 stack 信息生成的 SVG 图片, 用来展示 CPU 的调用栈。
y 轴表示调用栈, 每一层都是一个函数. 调用栈越深, 火焰就越高, 顶部就是正在执行的函数, 下方都是它的父函数.
x 轴表示抽样数, 如果一个函数在 x 轴占据的宽度越宽, 就表示它被抽到的次数多, 即执行的时间长. 注意, x 轴不代表时间, 而是所有的调用栈合并后, 按字母顺序排列的.
火焰图是 SVG 图片, 用浏览器打开可以与用户互动。
对于正在运行的程序 可以直接使用 pert stat -p pid 或者perf record -g -e cpu-clock -pid生成perf.data数据用于分析。
2.2 生成红蓝差分火焰图
在某些情况下我们关心的是加上某项功能后,性能的对比情况。这种情况下需要用到差分火焰图来进行分析:
首先我们使用perf record抓取一次新的数据:
$ sudo perf record -g -F 99 -- cp -r ~/bbb/ ./bbb.test
$ sudo perf script -i perf.data > out1.perf
$ ../FlameGraph/stackcollapse-perf.pl out1.perf > out1.floded
$ ../FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl out1.floded > cp1.svg
$ ../FlameGraph/difffolded.pl out.floded out1.floded > diff1.floded
$
$ ../FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl --negate diff1.floded > diff1.svg
在对比新旧数据,使用对比结果给cp.svg重新上色:
$ ../FlameGraph/difffolded.pl out.floded out1.floded > diff1.floded
$
$ ../FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl --negate diff1.floded > diff1.svg
而在红/蓝差分火焰图中, 使用不同的颜色来表示两个文件中的差异部分。红色表示增长, 蓝色表示衰减:
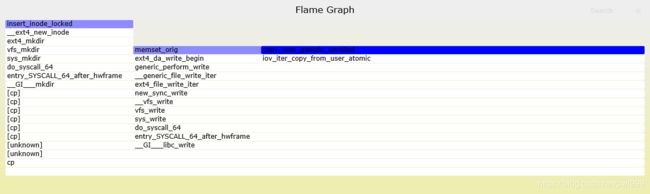
虽然红/蓝差分火焰图很有用, 但实际上还是有一个问题 : 如果一个代码执行路径完全消失了, 那么在火焰图中就找不到地方来标注蓝色. 你只能看到当前的 CPU 使用情况, 而不知道为什么会变成这样.一个办法是, 将对比顺序颠倒, 画一个相反的差分火焰图。
2.3 oncpu/offcpu
以上都是on-cpu火焰图,理解了系统的CPU的走向的分析。但是,很多时候,单纯地看on-cpu的情况(什么代码在耗费CPU),并不能解决性能问题,因为有时候性能差的原因瓶颈不一定在CPU上面,而是在off-cpu的时间,比如:
1、进程进入系统调用执行io动作,io动作的延迟
2、进程等待mutex锁的时间
3、内存被交换,swap的时间
4、内存不够的时候,执行直接内存回收的时间
5、进程被抢占调度走、或者时间片用完被调度走的时间(runqueue太大)
这一类数据使用bpfcc-tools来采样,具体使用可以参考:用off-cpu火焰图进行Linux性能分析。
参考文档:
1.www.brendangregg.com/
2.Linux perf
3.Linux下用火焰图进行性能分析