浅析蓝牙nrf51822程序框架
这篇先分析一下提供模板的框架部分程序。
这里以模板的代码(灯和按键)为例:
http://download.csdn.net/download/dfsae/9987318
1.主函数
NRF51822的框架还是采用事件驱动框架。先从主函数进行分析
int main(void)
{
// Initialize
leds_init(); //led初始化,硬件配置
timers_init();
gpiote_init(); //中断初始化
buttons_init();
ble_stack_init();
scheduler_init();
gap_params_init();
services_init();
advertising_init();
conn_params_init();
sec_params_init();
// Start execution
timers_start();
advertising_start();
// Enter main loop
for (;;)
{
app_sched_execute();
power_manage();
}
}
主函数里做一些初始化,再启动定时器和广播,在主循环里实现任务调度和电源管理power_manage();
1.1.定时器
NRF51822的定时器由队列进行多个定时器的管理。
1.1.1.数据结构
定时器主要放在timer_node_t结构体组成数组中进行集中管理,存储的方式具体看timers_init中的解析。
timer_node_t的结构如下:
typedef struct
{
timer_alloc_state_t state; /**< 定时器分配状态 */
app_timer_mode_t mode; /**< 定时器模式 */
uint32_t ticks_to_expire; /**< 上一次定时器中断到终止的ticks. */
uint32_t ticks_at_start; /**< 当前当定时器启动的RTC计数值. */
uint32_t ticks_first_interval; /**< 第一次定时器间隔的ticks */
uint32_t ticks_periodic_interval; /**< 时间周期 */
bool is_running; /**< True代表运行, False其他. */
app_timer_timeout_handler_t p_timeout_handler; /**< 指向当定时器倒是后调用的函数 */
void * p_context; /**<通用目标指针. 当定时器到时时,将进行超时处理。 */
app_timer_id_t next; /**<下一个运行定时器的id*/
} timer_node_t;
app_timer.c中为定时器队列提供了基础的添加移除操作。
1.1.2.初始化函数
主函数中调用timers_init实现定时器的初始化
static void timers_init(void)
{
// Initialize timer module, making it use the scheduler
APP_TIMER_INIT(APP_TIMER_PRESCALER, APP_TIMER_MAX_TIMERS, APP_TIMER_OP_QUEUE_SIZE, true);
}
#define APP_TIMER_INIT(PRESCALER, MAX_TIMERS, OP_QUEUES_SIZE, USE_SCHEDULER) \
do \
{ \
static uint32_t APP_TIMER_BUF[CEIL_DIV(APP_TIMER_BUF_SIZE((MAX_TIMERS), \
(OP_QUEUES_SIZE) + 1), \
sizeof(uint32_t))]; \
uint32_t ERR_CODE = app_timer_init((PRESCALER), \
(MAX_TIMERS), \
(OP_QUEUES_SIZE) + 1, \
APP_TIMER_BUF, \
(USE_SCHEDULER) ? app_timer_evt_schedule : NULL); \
APP_ERROR_CHECK(ERR_CODE); \
} while (0)
该初始化调用了app_timer.c中的app_timer_init,同时根据USE_SCHEDULER来设置回调函数app_timer_evt_schedule。
static __INLINE uint32_t app_timer_evt_schedule(app_timer_timeout_handler_t timeout_handler,
void * p_context)
{
app_timer_event_t timer_event;
timer_event.timeout_handler = timeout_handler;
timer_event.p_context = p_context;
return app_sched_event_put(&timer_event, sizeof(timer_event), app_timer_evt_get);
}
app_timer_evt_schedule中做了:
1>.生成一个事件。
2>.通过事件调度的API(app_sched_event_put)发送事件。
uint32_t app_timer_init(uint32_t prescaler,//预分频器
uint8_t max_timers,//最大时间
uint8_t op_queues_size,
void * p_buffer,
app_timer_evt_schedule_func_t evt_schedule_func)
{
int i;
// 检查缓冲区是否正确字对齐
if (!is_word_aligned(p_buffer))
{
return NRF_ERROR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
if (p_buffer == NULL)// 检查空缓冲区
{
return NRF_ERROR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
rtc1_stop(); // RTC停止防止定时器时间移除后重新初始化
m_evt_schedule_func = evt_schedule_func;//如果有调度则:app_timer_evt_schedule
// Initialize timer node array初始化定时器节点数组APP_TIMER_BUF
m_node_array_size = max_timers;
mp_nodes = p_buffer;
for (i = 0; i < max_timers; i++)
{
mp_nodes[i].state = STATE_FREE;
mp_nodes[i].is_running = false;
}
// Skip timer node array
p_buffer = &((uint8_t *)p_buffer)[max_timers * sizeof(timer_node_t)];
// Initialize users array
m_user_array_size = APP_TIMER_INT_LEVELS;
mp_users = p_buffer;
// Skip user array
p_buffer = &((uint8_t *)p_buffer)[APP_TIMER_INT_LEVELS * sizeof(timer_user_t)];
// 初始化 operation队列
for (i = 0; i < APP_TIMER_INT_LEVELS; i++)
{
timer_user_t * p_user = &mp_users[i];
p_user->first = 0;
p_user->last = 0;
p_user->user_op_queue_size = op_queues_size;
p_user->p_user_op_queue = p_buffer;
// Skip operation queue
p_buffer = &((uint8_t *)p_buffer)[op_queues_size * sizeof(timer_user_op_t)];
}
m_timer_id_head = TIMER_NULL;
m_ticks_elapsed_q_read_ind = 0;
m_ticks_elapsed_q_write_ind = 0;
NVIC_ClearPendingIRQ(SWI0_IRQn);
NVIC_SetPriority(SWI0_IRQn, SWI0_IRQ_PRI);
NVIC_EnableIRQ(SWI0_IRQn);
rtc1_init(prescaler);
m_ticks_latest = rtc1_counter_get();
return NRF_SUCCESS;
}
定时器初始化主要做了以下:
1>.设置事件回调函数(如果有),绑定的是app_timer_evt_schedule函数。
2>.初始化分配传进来数目的定时器,并分配好对应的空间
在app_timer.c中,定义了一些内部变量来管理整个定时器系统,一些参数放在传入的内存中保存。内存中的存放如下:
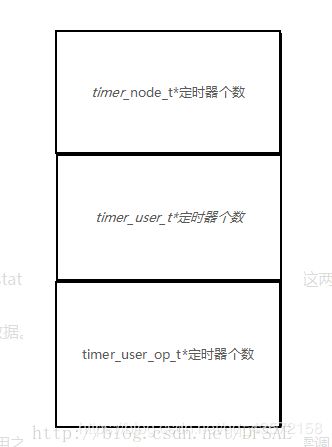
最开始的内存中保存每个定时器的分配状态(state)以及是否运行状态(is_running),这两个都是timer_node_t 结构体中的参数。
中间存放timer_user_t结构体的数据
最后一块存放对应的timer_user_op_t结构体数据。
3>.设置开启中断
1.1.2.创建定时器函数
在一开始分配完成定时器后,后续定时器在使用之前可以由用户自定义进行分配。分配只需调用app_timer_create函数即可。用户传入该定时器的工作模式和回调函数,正常情况下会找到空闲的定时器放在p_timer_id中返回,即用户得到当前分配的定时器id。过程中只修改了对应ID的mp_nodes的值。比如在该例程中初始化button的最后就分配了一个定时器。
uint32_t app_timer_create(app_timer_id_t * p_timer_id,
app_timer_mode_t mode,
app_timer_timeout_handler_t timeout_handler)
{
int i;
if (mp_nodes == NULL)
{
return NRF_ERROR_INVALID_STATE;
}
if (timeout_handler == NULL)
{
return NRF_ERROR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
if (p_timer_id == NULL)
{
return NRF_ERROR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
// 寻找看空闲的定时器
for (i = 0; i < m_node_array_size; i++)
{
if (mp_nodes[i].state == STATE_FREE)
{
mp_nodes[i].state = STATE_ALLOCATED;
mp_nodes[i].mode = mode;
mp_nodes[i].p_timeout_handler = timeout_handler;
*p_timer_id = i;
return NRF_SUCCESS;
}
}
return NRF_ERROR_NO_MEM;
}
1.1.3.定时器中断
app_timer.c中提供了一些对底层RTC进行操作的函数:
rtc1_init —— 初始化
rtc1_start —— 启动定时器
rtc1_stop —— 终止定时器
rtc1_counter_get —— 获得定时器的计数值
rtc1_compare0_set —— 设置过零比较器
RTC1_IRQHandler —— 定时器中断处理函数
从中断处理这里开始说起。
void RTC1_IRQHandler(void)
{
// 清除事件
NRF_RTC1->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] = 0;
NRF_RTC1->EVENTS_COMPARE[1] = 0;
NRF_RTC1->EVENTS_COMPARE[2] = 0;
NRF_RTC1->EVENTS_COMPARE[3] = 0;
NRF_RTC1->EVENTS_TICK = 0;
NRF_RTC1->EVENTS_OVRFLW = 0;
timer_timeouts_check();// 检测是否有到时间
}
timer_timeouts_check函数负责会设定的对应的应用是否到时间的定时器的检测。
static void timer_timeouts_check(void)
{
if (m_timer_id_head != TIMER_NULL) //处理到时间的定时器
{
app_timer_id_t timer_id;
uint32_t ticks_elapsed;
uint32_t ticks_expired;
// 初始化实际经过的ticks为0
ticks_expired = 0;
// ticks_elapsed(到期时间)在这里被得到, 现在的计数和上次计数的差值
ticks_elapsed = ticks_diff_get(rtc1_counter_get(), m_ticks_latest);
// Auto variable containing the head of timers expiring
timer_id = m_timer_id_head;
// 到时所有定时器 ticks_elapsed 并且获得ticks_expired (到期时间)
while (timer_id != TIMER_NULL)
{
timer_node_t * p_timer;
p_timer = &mp_nodes[timer_id]; //获得当前定时器节点
// 未超时则什么都不做
if (ticks_elapsed < p_timer->ticks_to_expire)
{
break;
}
// 递减ticks_elapsed(经过时间)值并获得expired ticks (到期时间)
ticks_elapsed -= p_timer->ticks_to_expire;
ticks_expired += p_timer->ticks_to_expire;
// 检测下一个定时器
timer_id = p_timer->next;
//回调
timeout_handler_exec(p_timer);
}
// 准备向m_ticks_elapsed队列中加ticks过期的队列
if (m_ticks_elapsed_q_read_ind == m_ticks_elapsed_q_write_ind)
{
// 读需要等于写序号。这意味着ticks_expired新值需要被存储在新的地址
// 在m_ticks_elapsed队列(作为双缓冲区实现的。)
// 检测是否有队列溢出
if (++m_ticks_elapsed_q_write_ind == CONTEXT_QUEUE_SIZE_MAX)
{
// 队列溢出. 因此,写索引指向队列的开始
m_ticks_elapsed_q_write_ind = 0;
}
}
// 队列的ticks到时.
m_ticks_elapsed[m_ticks_elapsed_q_write_ind] = ticks_expired;
timer_list_handler_sched();
}
}
static void timeout_handler_exec(timer_node_t * p_timer)
{
if (m_evt_schedule_func != NULL)
{
uint32_t err_code = m_evt_schedule_func(p_timer->p_timeout_handler,
p_timer->p_context);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
}
else
{
p_timer->p_timeout_handler(p_timer->p_context);
}
}
它这里的ticks_elapsed和ticks_expired我也被绕的晕乎乎的。但是抛开这个。这个函数的本意是对超时的定时器用他们一开始设置的回调函数的回调。下面的按键可以参考。调用的回调函数有两个m_evt_schedule_func 和 p_timer->p_timeout_handler。当有调度机制的时候调用前者,发送给调度内核,最后在主循环中来进行timer_create时绑定的回调函数调度。在这个例子中默认调用的都是app_timer_evt_schedule。如果没有调度机制则直接调用timer_create时绑定的回调函数。
还有一个SWI0中断,软件中断。
SWI0_IRQHandler ——SWI0中断,程序里很多地方会置位这个中断。比如前面提到的timer_timeouts_check。
SWI0中断中执行所有定时器更新
void SWI0_IRQHandler(void)
{
timer_list_handler();
}
static void timer_list_handler(void)
{
app_timer_id_t restart_list_head = TIMER_NULL;
uint32_t ticks_elapsed;
uint32_t ticks_previous;
bool ticks_have_elapsed;
bool compare_update;
app_timer_id_t timer_id_head_old;
// 备份上一次已知的tick和List头
ticks_previous = m_ticks_latest;
timer_id_head_old = m_timer_id_head;
// 获得过去的ticks数
ticks_have_elapsed = elapsed_ticks_acquire(&ticks_elapsed);
// 处理链表缺失
compare_update = list_deletions_handler();
//处理到时间的定时器
if (ticks_have_elapsed)
{
expired_timers_handler(ticks_elapsed, ticks_previous, &restart_list_head);
compare_update = true;
}
// 处理插入列表
if (list_insertions_handler(restart_list_head))
{
compare_update = true;
}
// 必要时更新比较寄存器
if (compare_update)
{
compare_reg_update(timer_id_head_old);
}
}
1.1.4.启动定时器
app_timer_start函数来启动某个定时器。这个函数里面有调用timer_start_op_schedule函数。这里分配函数为什么有个参数是mp_users
uint32_t app_timer_start(app_timer_id_t timer_id, uint32_t timeout_ticks, void * p_context)
{
uint32_t timeout_periodic;
// Schedule timer start operation
timeout_periodic = (mp_nodes[timer_id].mode == APP_TIMER_MODE_REPEATED) ? timeout_ticks : 0;
return timer_start_op_schedule(user_id_get(),
timer_id,
timeout_ticks,
timeout_periodic,
p_context);
}
static uint32_t timer_start_op_schedule(timer_user_id_t user_id,
app_timer_id_t timer_id,
uint32_t timeout_initial,
uint32_t timeout_periodic,
void * p_context)
{
app_timer_id_t last_index;
//分配一个操作队列
timer_user_op_t * p_user_op = user_op_alloc(&mp_users[user_id], &last_index);
if (p_user_op == NULL)
{
return NRF_ERROR_NO_MEM;
}
p_user_op->op_type = TIMER_USER_OP_TYPE_START;
p_user_op->timer_id = timer_id;
p_user_op->params.start.ticks_at_start = rtc1_counter_get();
p_user_op->params.start.ticks_first_interval = timeout_initial;
p_user_op->params.start.ticks_periodic_interval = timeout_periodic;
p_user_op->params.start.p_context = p_context;
user_op_enque(&mp_users[user_id], last_index);
timer_list_handler_sched();
return NRF_SUCCESS;
}
1.2.按键
按键初始化,在buttons数组中定义了所有的用到的按键及其配置。具体意思参考app_button_cfg_t 结构体。
按键这里变量:
m_detection_delay_timer_id定时器。这个定时器用来计算延时,它在初始化中被创建,并设置计时时间到后回调detection_delay_timeout_handler函数。
static void buttons_init(void)
{
// Note: Array must be static because a pointer to it will be saved in the Button handler
// module.
static app_button_cfg_t buttons[] =
{
{WAKEUP_BUTTON_PIN, false, BUTTON_PULL, NULL},
{LEDBUTTON_BUTTON_PIN_NO, false, BUTTON_PULL, button_event_handler}
};
APP_BUTTON_INIT(buttons, sizeof(buttons) / sizeof(buttons[0]), BUTTON_DETECTION_DELAY, true);
}
#define APP_BUTTON_INIT(BUTTONS, BUTTON_COUNT, DETECTION_DELAY, USE_SCHEDULER) \
do \
{ \
uint32_t ERR_CODE = app_button_init((BUTTONS), \
(BUTTON_COUNT), \
(DETECTION_DELAY), \
(USE_SCHEDULER) ? app_button_evt_schedule : NULL); \
APP_ERROR_CHECK(ERR_CODE); \
} while (0)
同样,初始化中设置事件回调函数(如果有),绑定的是app_button_evt_schedule函数。这个函数里面的操作和定时器里面的操作差不多。
uint32_t app_button_init(app_button_cfg_t * p_buttons,
uint8_t button_count,
uint32_t detection_delay,
app_button_evt_schedule_func_t evt_schedule_func)
{
uint32_t err_code;
if (detection_delay < APP_TIMER_MIN_TIMEOUT_TICKS)
{
return NRF_ERROR_INVALID_PARAM;
}
//保存配置.
mp_buttons = p_buttons;
m_button_count = button_count;
m_detection_delay = detection_delay;
m_evt_schedule_func = evt_schedule_func;
uint32_t pins_transition_mask = 0;
while (button_count--)
{
app_button_cfg_t * p_btn = &p_buttons[button_count];
nrf_gpio_cfg_input(p_btn->pin_no, p_btn->pull_cfg); //硬件配置
pins_transition_mask |= (1 << p_btn->pin_no); //创建用户中断注册屏蔽位
}
// Register button module as a GPIOTE user.
err_code = app_gpiote_user_register(&m_gpiote_user_id,
pins_transition_mask,
pins_transition_mask,
gpiote_event_handler);
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
return err_code;
}
// Create polling timer.
return app_timer_create(&m_detection_delay_timer_id,
APP_TIMER_MODE_SINGLE_SHOT,
detection_delay_timeout_handler);
}
按键初始化中的操作主要是对按键部分管理的变量做了个初始化,然后配置了硬件和中断部分,并且设置了中断回调函数gpiote_event_handler,标记了引脚电平状态。
当按键被按下后,系统首先会回调gpiote_event_handler函数。同时设置对应的延时参数后启动的定时器计时。
static void gpiote_event_handler(uint32_t event_pins_low_to_high, uint32_t event_pins_high_to_low)
{
uint32_t err_code;
// 开始检测计时器。如果定时器正在运行,检测周期重新开始
//注意: 使用app_timer_start()中的p_context参数来向定时器句柄传递引脚状态
STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(void *) == sizeof(uint32_t));
err_code = app_timer_stop(m_detection_delay_timer_id); //停止定时器
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
// The impact in app_button of the app_timer queue running full is losing a button press.
// The current implementation ensures that the system will continue working as normal.
return;
}
m_pin_transition.low_to_high = event_pins_low_to_high;
m_pin_transition.high_to_low = event_pins_high_to_low;
err_code = app_timer_start(m_detection_delay_timer_id,
m_detection_delay,
(void *)(event_pins_low_to_high | event_pins_high_to_low));
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
// The impact in app_button of the app_timer queue running full is losing a button press.
// The current implementation ensures that the system will continue working as normal.
}
}
当检测延时时间达到后调用detection_delay_timeout_handler回调函数,这个函数里面又会调用button_handler_execute按键按下的执行函数。在这个函数中会调用前面的回调函数app_button_evt_schedule发送事件给调度内核。当下次内核调度这个事件的时候,就会调度按键响应事件了,在这个例子中LEDBUTTON_BUTTON_PIN_NO按下调用button_event_handler,这个是修改服务中特性的值,这里先不讲。
static void detection_delay_timeout_handler(void * p_context)
{
uint32_t err_code;
uint32_t current_state_pins;
//获得当前引脚状态
err_code = app_gpiote_pins_state_get(m_gpiote_user_id, ¤t_state_pins);
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
return;
}
uint8_t i;
// 按下按键检测,执行按键句柄
for (i = 0; i < m_button_count; i++)
{
app_button_cfg_t * p_btn = &mp_buttons[i];
if (((m_pin_transition.high_to_low & (1 << p_btn->pin_no)) != 0)
&& (p_btn->button_handler != NULL))
{
//如果对应按键有效为高电平,然后从高到低跳变的释放过程
if(p_btn->active_state == APP_BUTTON_ACTIVE_HIGH)
{
button_handler_execute(p_btn, APP_BUTTON_RELEASE);
}
//如果对应按键有效为低电平,然后从高到低跳变的按下过程
else
{
button_handler_execute(p_btn, APP_BUTTON_PUSH);
}
}
else if (((m_pin_transition.low_to_high & (1 << p_btn->pin_no)) != 0)
&& (p_btn->button_handler != NULL))
{
//如果对应按键有效为高电平,然后从低到高跳变的按下过程
if(p_btn->active_state == APP_BUTTON_ACTIVE_HIGH)
{
button_handler_execute(p_btn,APP_BUTTON_PUSH);
}
//如果对应按键有效为低电平,然后从低到高跳变的释放过程
else
{
button_handler_execute(p_btn,APP_BUTTON_RELEASE);
}
}
}
}
static void button_handler_execute(app_button_cfg_t * p_btn, uint32_t transition)
{
if (m_evt_schedule_func != NULL)
{
uint32_t err_code = m_evt_schedule_func(p_btn->button_handler, p_btn->pin_no,transition);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
}
else
{
if(transition == APP_BUTTON_PUSH)
{
p_btn->button_handler(p_btn->pin_no, APP_BUTTON_PUSH);
}
else if(transition == APP_BUTTON_RELEASE)
{
p_btn->button_handler(p_btn->pin_no, APP_BUTTON_RELEASE);
}
}
}
有明白的可以加群:805601459(备注CSDN)进行交流。本文仅限于内部交流,禁止商用!