区块链框架 Tendermint 入门教程
Tendermint 是一个模块化的区块链应用框架, 能够实现拜占庭容错 (BFT), 它主要包括两部分:
Tendermint Core:
实现了 p2p 网络;在节点之间共享区块和交易;
实现了拜占庭容错的共识算法,确定了不更改改的交易顺序;
ABCI Interface,具体的逻辑处理层,可以基于不同的语言 (Golang, JS) 来实现;在这一层实现交易的验证处理以及查询等操作。
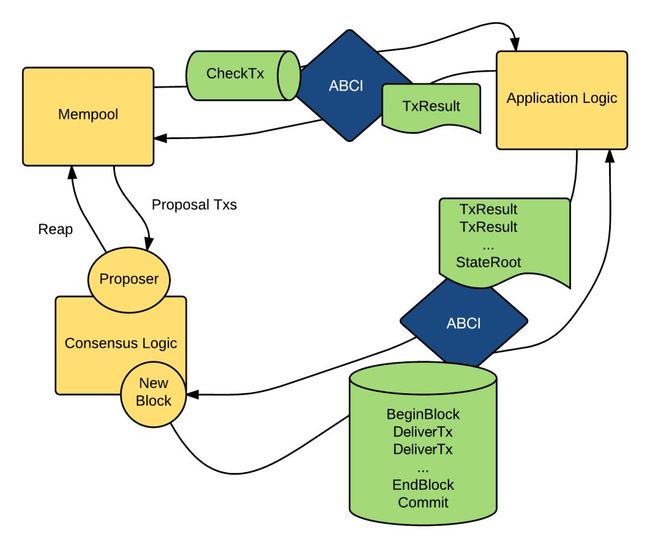
这两部分会分别对应两个不同的进程,Core 和 ABCI 建立了三个连接:
一个用于验证交易的连接,交易验证通过后会被广播到 mempoll 里;
一个用于区块的 proposal;
最后一个连接用于查询应用的状态;
下图是两者的 Workflow:
Core and ABCI communication
基于 Tendermint 的 Key-Value 存储示例
Tendermint 内置了一个 KV 存储的应用示例,我们可以跑下这个示例:
安装
需要先安装好 tendermint 和 abci-cli:
go get -u github.com/tendermint/tendermint/cmd/tendermint
go get -u github.com/tendermint/abci
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/tendermint/abci
make install
验证是否安装成功:
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ which tendermint
/Users/hbliu/go/bin/tendermint
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ which abci-cli
/Users/hbliu/go/bin/abci-cli
启动
初始化节点配置:
tendermint init
启动 KV 存储应用:
abci-cli kvstore
启动 Tendermint 节点:
tendermint node --consensus.create_empty_blocks=false
其中后面的参数是禁止 Tendermint 节点定期产生空的 block。
创建交易
在 Tendermint 中创建 key 为 name, value 为 hbliu 的存储:
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ curl -s 'localhost:46657/broadcast_tx_commit?tx="name=hbliu"'
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "",
"result": {
"check_tx": {
"fee": {}
},
"deliver_tx": {
"tags": [
{
"key": "YXBwLmNyZWF0b3I=",
"value": "amFl"
},
{
"key": "YXBwLmtleQ==",
"value": "bmFtZQ=="
}
],
"fee": {}
},
"hash": "BA0C60A3F391B35DEAE8A7E6E0491E9B2E0BA497",
"height": 2
}
}
返回的 Response 中的 key 和 value 使用了 base64 进行了编码, 我们可以通过命令 base64 对其进行解码:
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ echo "YXBwLmtleQ==" | base64 -D
app.key
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ echo "bmFtZQ==" | base64 -D
name
查询下我们之前的信息有没有成功写入:
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ curl -s 'localhost:46657/abci_query?data="name"'
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "",
"result": {
"response": {
"log": "exists",
"index": "-1",
"key": "bmFtZQ==",
"value": "aGJsaXU="
}
}
}
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ echo "bmFtZQ==" | base64 -D
name
➜ blog git:(hexo) ✗ echo "aGJsaXU=" | base64 -D
hbliu
在浏览器中打开 http://localhost:46657 可以显示当前所有支持的 API。
示例代码介绍
上述示例的代码存储在 Github(https://github.com/tendermint/abci/blob/master/example/kvstore/kvstore.go) 上。下面我们对这部分代码做一个简单的介绍。
在我们调用 broadcast_tx_commit 的时候,会先调用 CheckTx,验证通过后会把 TX 加入到 mempool 里。在 kvstore 示例中没有对 transaction 做检查,直接通过:
func (app *KVStoreApplication) CheckTx(tx []byte) types.ResponseCheckTx {
return types.ResponseCheckTx{Code: code.CodeTypeOK}
}
放到 mempool 里的 TX 会被定期广播到所有节点。当 Tendermint 选出了 Proposal 节点后,它便会从 mempool 里选出一系列的 TXs,将它们组成一个 Block,广播给所有的节点。节点在收到 Block 后,会对 Block 里的所有 TX 执行 DeliverTX 操作,同时对 Block 执行 Commit 操作。
我们调用 broadcast_tx_commit 返回的结果其实就是 DeliverTX 返回的结果:
func (app *KVStoreApplication) DeliverTx(tx []byte) types.ResponseDeliverTx {
var key, value []byte
parts := bytes.Split(tx, []byte("="))
if len(parts) == 2 {
key, value = parts[0], parts[1]
} else {
key, value = tx, tx
}
app.state.db.Set(prefixKey(key), value)
app.state.Size += 1
tags := []cmn.KVPair{
{[]byte("app.creator"), []byte("jae")},
{[]byte("app.key"), key},
}
return types.ResponseDeliverTx{Code: code.CodeTypeOK, Tags: tags}
}
可以看出它会从输入参数中解析出 key 和 value,最后保存在应用的 State 中。
当所有的 TX 被处理完之后需要调用 Commit 来更新整个区块的状态,包括高度加 1 等:
func (app *KVStoreApplication) Commit() types.ResponseCommit {
// Using a memdb - just return the big endian size of the db
appHash := make([]byte, 8)
binary.PutVarint(appHash, app.state.Size)
app.state.AppHash = appHash
app.state.Height += 1
saveState(app.state)
return types.ResponseCommit{Data: appHash}
}
References
Tendermint Introduction(http://tendermint.readthedocs.io/projects/tools/en/develop/introduction.html)
出处:https://hiberabyss.github.io/2018/04/02/tendermint-introduction-1/
版权申明:内容来源网络,版权归原创者所有。除非无法确认,我们都会标明作者及出处,如有侵权烦请告知,我们会立即删除并表示歉意。谢谢。
架构文摘
ID:ArchDigest
互联网应用架构丨架构技术丨大型网站丨大数据丨机器学习
![]()
更多精彩文章,请点击下方:阅读原文