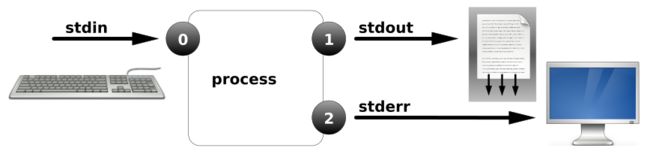
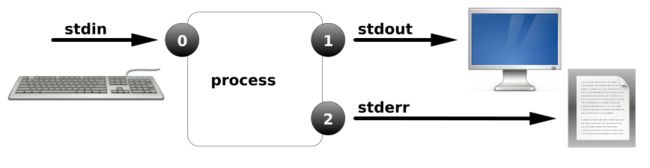
一、I/O重定向
标准输入,标准输出,标准错误
file descriptors (FD, 文件描述符或Process I/O channels);
进程使用文件描述符来管理打开的文件
[root@linux ~]# ls /proc/$$/fd
0 1 2 3 4
0, 1, and 2, known as standard input, standard output, and standard error
输出重定向(覆盖,追加)
正确输出:1> 1>> 等价于 > >>
错误输出:2> 2>>
案例1:输出重定向(覆盖)
[root@linux ~]# date 1> date.txt
案例2:输出重定向(追加)
[root@linux ~]# date >> date.txt
案例3:错误输出重定向
[root@linux ~]# ls /home/ /aaaaaaaaa >list.txt
ls: 无法访问/aaaaaaaaa: 没有那个文件或目录
[root@linux ~]# ls /home/ /aaaaaaaaa >list.txt 2>error.txt //重定向到不同的位置
案例4:正确和错误都输入到相同位置
[root@linux ~]# ls /home/ /aaaaaaaaa &>list.txt //混合输出
案例5:正确和错误都输入到相同位置
[root@linux ~]# ls /home/ /aaaaaaaaa >list.txt 2>&1 //重定向到相同的位置
案例6:重定向到空设备/dev/null
[root@linux ~]# ls /home/ /aaaaaaaaa >list.txt 2>/dev/null //空设备,即将产生的输出丢掉
[root@linux ~]# ls /home/ /aaaaaaaaa &>/dev/null //空设备,即将产生的输出丢掉
案例7:脚本中使用重定向
[root@linux ~]# vim ping1.sh
ping -c1 10.18.40.100
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "10.18.40.100 is up."
else
echo "10.18.40.100 is down!"
fi
[root@linux ~]# vim ping1.sh
[root@linux ~]# chmod +x ping1.sh
[root@linux ~]# ./ping1.sh
[root@linux ~]# vim ping1.sh
ping -c1 10.18.40.100 &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "10.18.40.100 is up."
else
echo "10.18.40.100 is down!"
fi
案例8:脚本中使用重定向
[root@linux ~]# vim ping2.sh
ping -c1 10.18.40.100 &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ];then
echo "10.18.40.100 is up." >>up.txt
else
echo "10.18.40.100 is down!" >>down.txt
fi
[root@linux ~]# vim ping2.sh
[root@linux ~]# chmod +x ping1.sh
[root@linux ~]# ./ping2.sh
二、输入重定向
标准输入:< 等价 0<
案例1:
[root@linux ~]# mail alice //没有改变输入的方向,默认键盘
Subject: hello
1111
2222
3333
.
EOT
[root@linux ~]# su - alice
[alice@alice ~]$ mail
Heirloom Mail version 12.5 7/5/10. Type ? for help.
"/var/spool/mail/alice": 1 message 1 new
>N 1 root Mon Jul 31 15:16 20/617 "hello"
[root@linux ~]# mail -s "test01" alice < /etc/hosts //输入重定向,来自于文件
案例2:
[root@linux ~]# grep 'root' //没有改变输入的方向,默认键盘,此时等待输入...
yang sss
sssrootssss..
sssrootssss..
[root@linux ~]# grep 'root' < /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
案例3:
[root@linux ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/file1.txt bs=1M count=2
[root@linux ~]# dd /file2.txt bs=1M count=20
案例4:mysql表结构导入
[root@linux ~]# mysql -uroot -p123 < bbs.sql
案例5:at
[root@linux ~]# at now +5 min
at> useradd yang99
at>
job 1 at Mon Jul 31 15:29:00 2017
[root@linux ~]# vim at.txt
sudo useradd yang100
sudo useradd yang102
[root@liwei ~]# at now +2 min <a.txt
job 2 at Mon Jul 31 15:27:00 2017
三、综合案例
案例1:利用重定向建立多行的文件(手动执行shell命令)
[root@linux ~]# echo "111" > file1.txt
[root@linux ~]# cat file1.txt
111
[root@linux ~]# cat >file2.txt
111
222
333
444
^D
[root@linux ~]# cat file2.txt
案例2:利用重定向建立多行的文件 脚本script创建多行文件
[root@linux ~]# vim create_file.sh
cat >file200.txt <<EOF
111
222
333
yyy
ccc
EOF
[root@linux ~]# bash create_file.sh
[root@linux ~]# cat file200.txt
111
222
333
yyy
ccc
案例3: 脚本中利用重定向打印消息
[root@linux ~]# cat create_file.sh
cat <<-EOF
111
222
333
yyy
ccc
EOF
[root@linux ~]# bash create_file.sh
111
222
333
yyy
ccc
[root@liwei ~]# vim yang.sh
cat <<-EOF
+------------------------------------------------+
| |
| ====================== |
| 虚拟机基本管理 v4.0 |
| by sky_king |
| ====================== |
| 1. 安装KVM |
| 2. 安装或重置CentOS-6.8 |
| 3. 安装或重置CentOS-7.3 |
| 4. 安装或重置RHEL-6.4 |
| 5. 安装或重置Windows-7 |
| 6. 删除所有虚拟机 |
| q. 退出管理程序 |
| |
+------------------------------------------------+
EOF
案例4
[root@linux ~]# ls; date &>/dev/null //希望两条命令输出都重定向 ??
[root@linux ~]# ls &>/dev/null; date &>/dev/null
[root@linux ~]# (ls; date) &>/dev/null
[root@linux ~]# (while :; do date; sleep 2; done) & //在后台运行,但输出依然在前台终端
[1] 6229
[root@linux ~]# 2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:12:42 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:12:44 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:12:46 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:12:48 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:12:50 CST
[root@linux ~]# (while :; do date; sleep 2; done) &>date.txt &
[root@linux ~]# tailf /date.txt
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:15:29 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:15:31 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:15:33 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:15:35 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:15:37 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:15:39 CST
2017年 08月 01日 星期二 10:15:41 CST