蚁群算法Python3可运行代码
原理就不再赘述了,直接上代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab
coordinates = np.array([[565.0, 575.0], [25.0, 185.0], [345.0, 750.0], [945.0, 685.0], [845.0, 655.0],
[880.0, 660.0], [25.0, 230.0], [525.0, 1000.0], [580.0, 1175.0], [650.0, 1130.0],
[1605.0, 620.0], [1220.0, 580.0], [1465.0, 200.0], [1530.0, 5.0], [845.0, 680.0],
[725.0, 370.0], [145.0, 665.0], [415.0, 635.0], [510.0, 875.0], [560.0, 365.0],
[300.0, 465.0], [520.0, 585.0], [480.0, 415.0], [835.0, 625.0], [975.0, 580.0],
[1215.0, 245.0], [1320.0, 315.0], [1250.0, 400.0], [660.0, 180.0], [410.0, 250.0],
[420.0, 555.0], [575.0, 665.0], [1150.0, 1160.0], [700.0, 580.0], [685.0, 595.0],
[685.0, 610.0], [770.0, 610.0], [795.0, 645.0], [720.0, 635.0], [760.0, 650.0],
[475.0, 960.0], [95.0, 260.0], [875.0, 920.0], [700.0, 500.0], [555.0, 815.0],
[830.0, 485.0], [1170.0, 65.0], [830.0, 610.0], [605.0, 625.0], [595.0, 360.0],
[1340.0, 725.0], [1740.0, 245.0]])
def getdistmat(coordinates):
num = coordinates.shape[0]
distmat = np.zeros((52, 52))
for i in range(num):
for j in range(i, num):
distmat[i][j] = distmat[j][i] = np.linalg.norm(coordinates[i] - coordinates[j])
return distmat
distmat = getdistmat(coordinates)
numant = 40 # 蚂蚁个数
numcity = coordinates.shape[0] # 城市个数
alpha = 1 # 信息素重要程度因子
beta = 5 # 启发函数重要程度因子
rho = 0.1 # 信息素的挥发速度
Q = 1
iter = 0
itermax = 250
etatable = 1.0 / (distmat + np.diag([1e10] * numcity)) # 启发函数矩阵,表示蚂蚁从城市i转移到矩阵j的期望程度
pheromonetable = np.ones((numcity, numcity)) # 信息素矩阵
pathtable = np.zeros((numant, numcity)).astype(int) # 路径记录表
distmat = getdistmat(coordinates) # 城市的距离矩阵
lengthaver = np.zeros(itermax) # 各代路径的平均长度
lengthbest = np.zeros(itermax) # 各代及其之前遇到的最佳路径长度
pathbest = np.zeros((itermax, numcity)) # 各代及其之前遇到的最佳路径长度
while iter < itermax:
# 随机产生各个蚂蚁的起点城市
if numant <= numcity: # 城市数比蚂蚁数多
pathtable[:, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(0, numcity))[:numant]
else: # 蚂蚁数比城市数多,需要补足
pathtable[:numcity, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(0, numcity))[:]
pathtable[numcity:, 0] = np.random.permutation(range(0, numcity))[:numant - numcity]
length = np.zeros(numant) # 计算各个蚂蚁的路径距离
for i in range(numant):
visiting = pathtable[i, 0] # 当前所在的城市
unvisited = set(range(numcity)) # 未访问的城市,以集合的形式存储{}
unvisited.remove(visiting) # 删除元素;利用集合的remove方法删除存储的数据内容
for j in range(1, numcity): # 循环numcity-1次,访问剩余的numcity-1个城市
# 每次用轮盘法选择下一个要访问的城市
listunvisited = list(unvisited)
probtrans = np.zeros(len(listunvisited))
for k in range(len(listunvisited)):
probtrans[k] = np.power(pheromonetable[visiting][listunvisited[k]], alpha) \
* np.power(etatable[visiting][listunvisited[k]], alpha)
cumsumprobtrans = (probtrans / sum(probtrans)).cumsum()
cumsumprobtrans -= np.random.rand()
k = listunvisited[(np.where(cumsumprobtrans > 0)[0])[0]] # python3中原代码运行bug,类型问题;鉴于此特找到其他方法
# 通过where()方法寻找矩阵大于0的元素的索引并返回ndarray类型,然后接着载使用[0]提取其中的元素,用作listunvisited列表中
# 元素的提取(也就是下一轮选的城市)
pathtable[i, j] = k # 添加到路径表中(也就是蚂蚁走过的路径)
unvisited.remove(k) # 然后在为访问城市set中remove()删除掉该城市
length[i] += distmat[visiting][k]
visiting = k
length[i] += distmat[visiting][pathtable[i, 0]] # 蚂蚁的路径距离包括最后一个城市和第一个城市的距离
# 包含所有蚂蚁的一个迭代结束后,统计本次迭代的若干统计参数
lengthaver[iter] = length.mean()
if iter == 0:
lengthbest[iter] = length.min()
pathbest[iter] = pathtable[length.argmin()].copy()
else:
if length.min() > lengthbest[iter - 1]:
lengthbest[iter] = lengthbest[iter - 1]
pathbest[iter] = pathbest[iter - 1].copy()
else:
lengthbest[iter] = length.min()
pathbest[iter] = pathtable[length.argmin()].copy()
# 更新信息素
changepheromonetable = np.zeros((numcity, numcity))
for i in range(numant):
for j in range(numcity - 1):
changepheromonetable[pathtable[i, j]][pathtable[i, j + 1]] += Q / distmat[pathtable[i, j]][
pathtable[i, j + 1]] # 计算信息素增量
changepheromonetable[pathtable[i, j + 1]][pathtable[i, 0]] += Q / distmat[pathtable[i, j + 1]][pathtable[i, 0]]
pheromonetable = (1 - rho) * pheromonetable + changepheromonetable # 计算信息素公式
iter += 1 # 迭代次数指示器+1
print("iter:", iter)
# 做出平均路径长度和最优路径长度
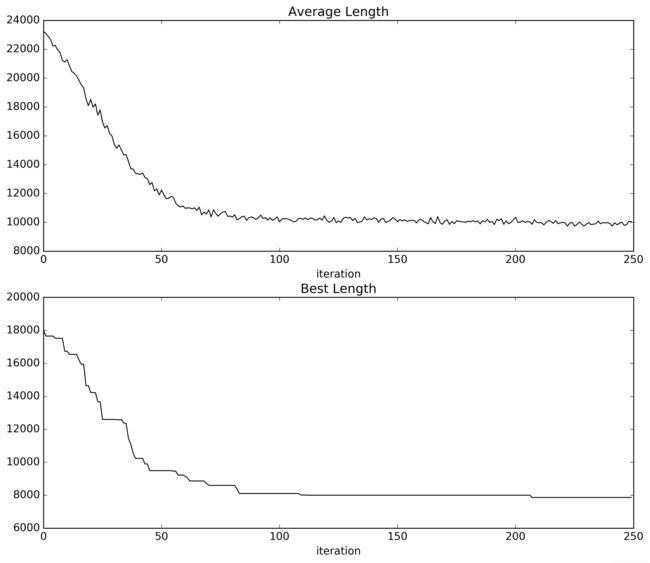
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=1, figsize=(12, 10))
axes[0].plot(lengthaver, 'k', marker=u'')
axes[0].set_title('Average Length')
axes[0].set_xlabel(u'iteration')
axes[1].plot(lengthbest, 'k', marker=u'')
axes[1].set_title('Best Length')
axes[1].set_xlabel(u'iteration')
fig.savefig('average_best.png', dpi=500, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
# 作出找到的最优路径图
bestpath = pathbest[-1]
plt.plot(coordinates[:, 0], coordinates[:, 1], 'r.', marker=u'$\cdot$')
plt.xlim([-100, 2000])
plt.ylim([-100, 1500])
for i in range(numcity - 1):
m = int(bestpath[i])
n = int(bestpath[i + 1])
plt.plot([coordinates[m][0], coordinates[n][0]], [coordinates[m][1], coordinates[n][1]], 'k')
plt.plot([coordinates[int(bestpath[0])][0],coordinates[int(n)][0]],[coordinates[int(bestpath[0])][1],coordinates[int(n)][1]],'b')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_title("Best Path")
ax.set_xlabel('X axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y_axis')
plt.savefig('best path.png', dpi=500, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
结果: