文章目录
- 1.基本概念及创建
- DataFrame的数据结构
- DataFrame的创建方法(5种)
- 2.索引
- 选择行
- 选择列
- df.loc用法
- df.iloc用法
- 布尔型索引
- 多重索引
- Pandas基本技巧
- 数据查看、转置
- 添加与修改
- 删除
- 对齐
- 排序:sort_values
- 排序:sort_index
- 课后作业
- 作业一:用四种不同的方法,创建以下Dataframe(保证columns和index一致,值不做要求)
- 作业二:如图创建Dataframe(4*4,值为0-100的随机数),通过索引得到以下值① 索引得到b,c列的所有值② 索引得到第三第四行的数据③ 按顺序索引得到two,one行的值④ 索引得到大于50的值
- 作业三:创建一个3*3,值在0-100区间随机值的Dataframe(如图),分别按照index和第二列值大小,降序排序
- 作业四:创建一个5*2,值在0-100区间随机值的Dataframe(如图)df1,通过修改得到df2
1.基本概念及创建
DataFrame的数据结构
'''
"二维数组"Dataframe:是一个表格型的数据结构,包含一组有序的列,其列的值类型可以是数值、字符串、布尔值等。
Dataframe中的数据以一个或多个二维块存放,不是列表、字典或一维数组结构。
'''
data = {'name':['Jack','Tom','Mary'],
'age':[18,19,20],
'gender':['m','m','w']}
frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(frame)
print(type(frame))
print(frame.index,'\n该数据类型为:',type(frame.index))
print(frame.columns,'\n该数据类型为:',type(frame.columns))
print(frame.values,'\n该数据类型为:',type(frame.values))
age gender name
0 18 m Jack
1 19 m Tom
2 20 w Mary
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex(start=0, stop=3, step=1)
该数据类型为: <class 'pandas.indexes.range.RangeIndex'>
Index(['age', 'gender', 'name'], dtype='object')
该数据类型为: <class 'pandas.indexes.base.Index'>
[[18 'm' 'Jack']
[19 'm' 'Tom']
[20 'w' 'Mary']]
该数据类型为: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
DataFrame的创建方法(5种)
data1 = {'a':[1,2,3],
'b':[3,4,5],
'c':[5,6,7]}
data2 = {'one':np.random.rand(3),
'two':np.random.rand(3)}
print(data1)
print(data2)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2)
print(df1)
print(df2)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1, columns = ['b','c','a','d'])
print(df1)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1, columns = ['b','c'])
print(df1)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2, index = ['f1','f2','f3'])
print(df2)
{'a': [1, 2, 3], 'c': [5, 6, 7], 'b': [3, 4, 5]}
{'one': array([ 0.00101091, 0.08807153, 0.58345056]), 'two': array([ 0.49774634, 0.16782565, 0.76443489])}
a b c
0 1 3 5
1 2 4 6
2 3 5 7
one two
0 0.001011 0.497746
1 0.088072 0.167826
2 0.583451 0.764435
b c a d
0 3 5 1 NaN
1 4 6 2 NaN
2 5 7 3 NaN
b c
0 3 5
1 4 6
2 5 7
one two
f1 0.001011 0.497746
f2 0.088072 0.167826
f3 0.583451 0.764435
data1 = {'one':pd.Series(np.random.rand(2)),
'two':pd.Series(np.random.rand(3))}
data2 = {'one':pd.Series(np.random.rand(2), index = ['a','b']),
'two':pd.Series(np.random.rand(3),index = ['a','b','c'])}
print(data1)
print(data2)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2)
print(df1)
print(df2)
{'one': 0 0.892580
1 0.834076
dtype: float64, 'two': 0 0.301309
1 0.977709
2 0.489000
dtype: float64}
{'one': a 0.470947
b 0.584577
dtype: float64, 'two': a 0.122659
b 0.136429
c 0.396825
dtype: float64}
one two
0 0.892580 0.301309
1 0.834076 0.977709
2 NaN 0.489000
one two
a 0.470947 0.122659
b 0.584577 0.136429
c NaN 0.396825
ar = np.random.rand(9).reshape(3,3)
print(ar)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(ar)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(ar, index = ['a', 'b', 'c'], columns = ['one','two','three'])
print(df1)
print(df2)
[[ 0.54492282 0.28956161 0.46592269]
[ 0.30480674 0.12917132 0.38757672]
[ 0.2518185 0.13544544 0.13930429]]
0 1 2
0 0.544923 0.289562 0.465923
1 0.304807 0.129171 0.387577
2 0.251819 0.135445 0.139304
one two three
a 0.544923 0.289562 0.465923
b 0.304807 0.129171 0.387577
c 0.251819 0.135445 0.139304
data = [{'one': 1, 'two': 2}, {'one': 5, 'two': 10, 'three': 20}]
print(data)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['a','b'])
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = ['one','two'])
print(df1)
print(df2)
print(df3)
[{'one': 1, 'two': 2}, {'one': 5, 'three': 20, 'two': 10}]
one three two
0 1 NaN 2
1 5 20.0 10
one three two
a 1 NaN 2
b 5 20.0 10
one two
0 1 2
1 5 10
data = {'Jack':{'math':90,'english':89,'art':78},
'Marry':{'math':82,'english':95,'art':92},
'Tom':{'math':78,'english':67}}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df1)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data, columns = ['Jack','Tom','Bob'])
df3 = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ['a','b','c'])
print(df2)
print(df3)
Jack Marry Tom
art 78 92 NaN
english 89 95 67.0
math 90 82 78.0
Jack Tom Bob
art 78 NaN NaN
english 89 67.0 NaN
math 90 78.0 NaN
Jack Marry Tom
a NaN NaN NaN
b NaN NaN NaN
c NaN NaN NaN
2.索引
选择行
'''
Dataframe既有行索引也有列索引,可以被看做由Series组成的字典(共用一个索引)
选择列 / 选择行 / 切片 / 布尔判断
'''
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(12).reshape(3,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
data1 = df['a']
data2 = df[['a','c']]
print(data1,type(data1))
print(data2,type(data2))
print('-----')
data3 = df.loc['one']
data4 = df.loc[['one','two']]
print(data2,type(data3))
print(data3,type(data4))
a b c d
one 72.615321 49.816987 57.485645 84.226944
two 46.295674 34.480439 92.267989 17.111412
three 14.699591 92.754997 39.683577 93.255880
one 72.615321
two 46.295674
three 14.699591
Name: a, dtype: float64 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a c
one 72.615321 57.485645
two 46.295674 92.267989
three 14.699591 39.683577 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
-----
a c
one 72.615321 57.485645
two 46.295674 92.267989
three 14.699591 39.683577 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a 72.615321
b 49.816987
c 57.485645
d 84.226944
Name: one, dtype: float64 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
选择列
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(12).reshape(3,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('-----')
data1 = df['a']
data2 = df[['b','c']]
print(data1)
print(data2)
data3 = df[:1]
print(data3,type(data3))
a b c d
one 88.490183 93.588825 1.605172 74.610087
two 45.905361 49.257001 87.852426 97.490521
three 95.801001 97.991028 74.451954 64.290587
-----
one 88.490183
two 45.905361
three 95.801001
Name: a, dtype: float64
b c
one 93.588825 1.605172
two 49.257001 87.852426
three 97.991028 74.451954
a b c d
one 88.490183 93.588825 1.605172 74.610087 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
df.loc用法
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df1)
print(df2)
print('-----')
data1 = df1.loc['one']
data2 = df2.loc[1]
print(data1)
print(data2)
print('单标签索引\n-----')
data3 = df1.loc[['two','three','five']]
data4 = df2.loc[[3,2,1]]
print(data3)
print(data4)
print('多标签索引\n-----')
data5 = df1.loc['one':'three']
data6 = df2.loc[1:3]
print(data5)
print(data6)
print('切片索引')
a b c d
one 73.070679 7.169884 80.820532 62.299367
two 34.025462 77.849955 96.160170 55.159017
three 27.897582 39.595687 69.280955 49.477429
four 76.723039 44.995970 22.408450 23.273089
a b c d
0 93.871055 28.031989 57.093181 34.695293
1 22.882809 47.499852 86.466393 86.140909
2 80.840336 98.120735 84.495414 8.413039
3 59.695834 1.478707 15.069485 48.775008
-----
a 73.070679
b 7.169884
c 80.820532
d 62.299367
Name: one, dtype: float64
a 22.882809
b 47.499852
c 86.466393
d 86.140909
Name: 1, dtype: float64
单标签索引
-----
a b c d
two 34.025462 77.849955 96.160170 55.159017
three 27.897582 39.595687 69.280955 49.477429
five NaN NaN NaN NaN
a b c d
3 59.695834 1.478707 15.069485 48.775008
2 80.840336 98.120735 84.495414 8.413039
1 22.882809 47.499852 86.466393 86.140909
多标签索引
-----
a b c d
one 73.070679 7.169884 80.820532 62.299367
two 34.025462 77.849955 96.160170 55.159017
three 27.897582 39.595687 69.280955 49.477429
a b c d
1 22.882809 47.499852 86.466393 86.140909
2 80.840336 98.120735 84.495414 8.413039
3 59.695834 1.478707 15.069485 48.775008
切片索引
df.iloc用法
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('------')
print(df.iloc[0])
print(df.iloc[-1])
print('单位置索引\n-----')
print(df.iloc[[0,2]])
print(df.iloc[[3,2,1]])
print('多位置索引\n-----')
print(df.iloc[1:3])
print(df.iloc[::2])
print('切片索引')
a b c d
one 21.848926 2.482328 17.338355 73.014166
two 99.092794 0.601173 18.598736 61.166478
three 87.183015 85.973426 48.839267 99.930097
four 75.007726 84.208576 69.445779 75.546038
------
a 21.848926
b 2.482328
c 17.338355
d 73.014166
Name: one, dtype: float64
a 75.007726
b 84.208576
c 69.445779
d 75.546038
Name: four, dtype: float64
单位置索引
-----
a b c d
one 21.848926 2.482328 17.338355 73.014166
three 87.183015 85.973426 48.839267 99.930097
a b c d
four 75.007726 84.208576 69.445779 75.546038
three 87.183015 85.973426 48.839267 99.930097
two 99.092794 0.601173 18.598736 61.166478
多位置索引
-----
a b c d
two 99.092794 0.601173 18.598736 61.166478
three 87.183015 85.973426 48.839267 99.930097
a b c d
one 21.848926 2.482328 17.338355 73.014166
three 87.183015 85.973426 48.839267 99.930097
切片索引
布尔型索引
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('------')
b1 = df < 20
print(b1,type(b1))
print(df[b1])
print('------')
b2 = df['a'] > 50
print(b2,type(b2))
print(df[b2])
print('------')
b3 = df[['a','b']] > 50
print(b3,type(b3))
print(df[b3])
print('------')
b4 = df.loc[['one','three']] < 50
print(b4,type(b4))
print(df[b4])
print('------')
a b c d
one 19.185849 20.303217 21.800384 45.189534
two 50.105112 28.478878 93.669529 90.029489
three 35.496053 19.248457 74.811841 20.711431
four 24.604478 57.731456 49.682717 82.132866
------
a b c d
one True False False False
two False False False False
three False True False False
four False False False False <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
a b c d
one 19.185849 NaN NaN NaN
two NaN NaN NaN NaN
three NaN 19.248457 NaN NaN
four NaN NaN NaN NaN
------
one False
two True
three False
four False
Name: a, dtype: bool <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a b c d
two 50.105112 28.478878 93.669529 90.029489
------
a b
one False False
two True False
three False False
four False True <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
a b c d
one NaN NaN NaN NaN
two 50.105112 NaN NaN NaN
three NaN NaN NaN NaN
four NaN 57.731456 NaN NaN
------
a b c d
one True True True True
three True True False True <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
a b c d
one 19.185849 20.303217 21.800384 45.189534
two NaN NaN NaN NaN
three 35.496053 19.248457 NaN 20.711431
four NaN NaN NaN NaN
------
多重索引
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['one','two','three','four'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
print('------')
print(df['a'].loc[['one','three']])
print(df[['b','c','d']].iloc[::2])
print(df[df['a'] < 50].iloc[:2])
a b c d
one 50.660904 89.827374 51.096827 3.844736
two 70.699721 78.750014 52.988276 48.833037
three 33.653032 27.225202 24.864712 29.662736
four 21.792339 26.450939 6.122134 52.323963
------
one 50.660904
three 33.653032
Name: a, dtype: float64
b c d
one 89.827374 51.096827 3.844736
three 27.225202 24.864712 29.662736
a b c d
three 33.653032 27.225202 24.864712 29.662736
four 21.792339 26.450939 6.122134 52.323963
Pandas基本技巧
数据查看、转置
'''
数据查看、转置 / 添加、修改、删除值 / 对齐 / 排序
'''
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(8,2)*100,
columns = ['a','b'])
print(df.head(2))
print(df.tail())
print(df.T)
a b
0 5.777208 18.374283
1 85.961515 55.120036
a b
3 21.236577 15.902872
4 46.137564 29.350647
5 70.157709 58.972728
6 8.368292 42.011356
7 29.824574 87.062295
0 1 2 3 4 5 \
a 5.777208 85.961515 11.005284 21.236577 46.137564 70.157709
b 18.374283 55.120036 35.595598 15.902872 29.350647 58.972728
6 7
a 8.368292 29.824574
b 42.011356 87.062295
添加与修改
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
df['e'] = 10
df.loc[4] = 20
print(df)
df['e'] = 20
df[['a','c']] = 100
print(df)
a b c d
0 17.148791 73.833921 39.069417 5.675815
1 91.572695 66.851601 60.320698 92.071097
2 79.377105 24.314520 44.406357 57.313429
3 84.599206 61.310945 3.916679 30.076458
a b c d e
0 17.148791 73.833921 39.069417 5.675815 10
1 91.572695 66.851601 60.320698 92.071097 10
2 79.377105 24.314520 44.406357 57.313429 10
3 84.599206 61.310945 3.916679 30.076458 10
4 20.000000 20.000000 20.000000 20.000000 20
a b c d e
0 100 73.833921 100 5.675815 20
1 100 66.851601 100 92.071097 20
2 100 24.314520 100 57.313429 20
3 100 61.310945 100 30.076458 20
4 100 20.000000 100 20.000000 20
删除
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df)
del df['a']
print(df)
print('-----')
print(df.drop(0))
print(df.drop([1,2]))
print(df)
print('-----')
print(df.drop(['d'], axis = 1))
print(df)
a b c d
0 91.866806 88.753655 18.469852 71.651277
1 64.835568 33.844967 6.391246 54.916094
2 75.930985 19.169862 91.042457 43.648258
3 15.863853 24.788866 10.625684 82.135316
b c d
0 88.753655 18.469852 71.651277
1 33.844967 6.391246 54.916094
2 19.169862 91.042457 43.648258
3 24.788866 10.625684 82.135316
-----
b c d
1 33.844967 6.391246 54.916094
2 19.169862 91.042457 43.648258
3 24.788866 10.625684 82.135316
b c d
0 88.753655 18.469852 71.651277
3 24.788866 10.625684 82.135316
b c d
0 88.753655 18.469852 71.651277
1 33.844967 6.391246 54.916094
2 19.169862 91.042457 43.648258
3 24.788866 10.625684 82.135316
-----
b c
0 88.753655 18.469852
1 33.844967 6.391246
2 19.169862 91.042457
3 24.788866 10.625684
b c d
0 88.753655 18.469852 71.651277
1 33.844967 6.391246 54.916094
2 19.169862 91.042457 43.648258
3 24.788866 10.625684 82.135316
对齐
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 4), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(7, 3), columns=['A', 'B', 'C'])
print(df1 + df2)
A B C D
0 -0.281123 -2.529461 1.325663 NaN
1 -0.310514 -0.408225 -0.760986 NaN
2 -0.172169 -2.355042 1.521342 NaN
3 1.113505 0.325933 3.689586 NaN
4 0.107513 -0.503907 -1.010349 NaN
5 -0.845676 -2.410537 -1.406071 NaN
6 1.682854 -0.576620 -0.981622 NaN
7 NaN NaN NaN NaN
8 NaN NaN NaN NaN
9 NaN NaN NaN NaN
排序:sort_values
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df1)
print(df1.sort_values(['a'], ascending = True))
print(df1.sort_values(['a'], ascending = False))
print('------')
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'a':[1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2],
'b':list(range(8)),
'c':list(range(8,0,-1))})
print(df2)
print(df2.sort_values(['a','c']))
a b c d
0 16.519099 19.601879 35.464189 58.866972
1 34.506472 97.106578 96.308244 54.049359
2 87.177828 47.253416 92.098847 19.672678
3 66.673226 51.969534 71.789055 14.504191
a b c d
0 16.519099 19.601879 35.464189 58.866972
1 34.506472 97.106578 96.308244 54.049359
3 66.673226 51.969534 71.789055 14.504191
2 87.177828 47.253416 92.098847 19.672678
a b c d
2 87.177828 47.253416 92.098847 19.672678
3 66.673226 51.969534 71.789055 14.504191
1 34.506472 97.106578 96.308244 54.049359
0 16.519099 19.601879 35.464189 58.866972
------
a b c
0 1 0 8
1 1 1 7
2 1 2 6
3 1 3 5
4 2 4 4
5 2 5 3
6 2 6 2
7 2 7 1
a b c
3 1 3 5
2 1 2 6
1 1 1 7
0 1 0 8
7 2 7 1
6 2 6 2
5 2 5 3
4 2 4 4
排序:sort_index
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = [5,4,3,2],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(16).reshape(4,4)*100,
index = ['h','s','x','g'],
columns = ['a','b','c','d'])
print(df1)
print(df1.sort_index())
print(df2)
print(df2.sort_index())
a b c d
5 57.327269 87.623119 93.655538 5.859571
4 69.739134 80.084366 89.005538 56.825475
3 88.148296 6.211556 68.938504 41.542563
2 29.248036 72.005306 57.855365 45.931715
a b c d
2 29.248036 72.005306 57.855365 45.931715
3 88.148296 6.211556 68.938504 41.542563
4 69.739134 80.084366 89.005538 56.825475
5 57.327269 87.623119 93.655538 5.859571
a b c d
h 50.579469 80.239138 24.085110 39.443600
s 30.906725 39.175302 11.161542 81.010205
x 19.900056 18.421110 4.995141 12.605395
g 67.760755 72.573568 33.507090 69.854906
a b c d
g 67.760755 72.573568 33.507090 69.854906
h 50.579469 80.239138 24.085110 39.443600
s 30.906725 39.175302 11.161542 81.010205
x 19.900056 18.421110 4.995141 12.605395
课后作业
作业一:用四种不同的方法,创建以下Dataframe(保证columns和index一致,值不做要求)
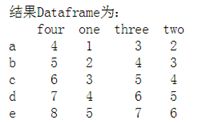
作业二:如图创建Dataframe(4*4,值为0-100的随机数),通过索引得到以下值① 索引得到b,c列的所有值② 索引得到第三第四行的数据③ 按顺序索引得到two,one行的值④ 索引得到大于50的值
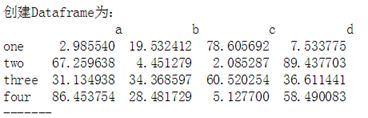
作业三:创建一个3*3,值在0-100区间随机值的Dataframe(如图),分别按照index和第二列值大小,降序排序

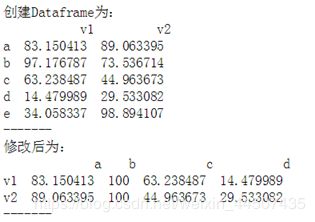
作业四:创建一个5*2,值在0-100区间随机值的Dataframe(如图)df1,通过修改得到df2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.array(np.random.rand(20).reshape(5,4))
,index = ['a','b','c','d','e']
,columns = ['four','onr','three','two']
)
print(df1)
print('-------------')
dt = {'four':np.random.rand(5)
,'one':np.random.rand(5)
,'three':np.random.rand(5)
,'two':np.random.rand(5)
}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(dt
,index = ['a','b','c','d','e']
)
print(df2)
print('-------------')
dt2 = {'four':{'a':np.random.rand(),'b':np.random.rand(),'c':np.random.rand(),'d':np.random.rand(),'e':np.random.rand()}
,'one':{'a':np.random.rand(),'b':np.random.rand(),'c':np.random.rand(),'d':np.random.rand(),'e':np.random.rand()}
,'three':{'a':np.random.rand(),'b':np.random.rand(),'c':np.random.rand(),'d':np.random.rand(),'e':np.random.rand()}
,'two':{'a':np.random.rand(),'b':np.random.rand(),'c':np.random.rand(),'d':np.random.rand(),'e':np.random.rand()}
}
df3 = pd.DataFrame(dt2)
print(df3)
print('-------------')
dt3 = {'four':pd.Series(np.random.rand(5),index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
,'one':pd.Series(np.random.rand(5),index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
,'three':pd.Series(np.random.rand(5),index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
,'two':pd.Series(np.random.rand(5),index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
}
df4 = pd.DataFrame(dt3)
print(df4)
print('-------------')
df5 = pd.DataFrame(np.array(np.random.rand(16)*100).reshape(4,4)
,index = ['one','two','three','four']
,columns = ['a','b','c','d']
)
print(df5)
print('-------------')
print(df5[['b','c']])
print('-------------')
print(df5.iloc[2:])
print('-------------')
print(df5.loc[['two','one']])
print('-------------')
print(df5[df5>50])
print('-------------')
df6 = pd.DataFrame(np.array(np.random.rand(9)*100).reshape(3,3)
,index = ['a','b','c']
,columns = ['v1','v2','v3']
)
print(df6)
print('-------------')
print(df6.sort_index(ascending = False))
print('-------------')
print(df6.sort_values('v2',ascending = False))
print('-------------')
df7 = pd.DataFrame(np.array(np.random.rand(10)*100).reshape(5,2)
,index = ['a','b','c','d','e']
,columns = ['v1','v2']
)
df8 = df7.T.drop(['e'],axis = 1)
df8['b'] = 100
print(df8)
print('-------------')
four onr three two
a 0.134831 0.048260 0.188670 0.481096
b 0.097001 0.029168 0.182705 0.124464
c 0.212457 0.746511 0.688974 0.859066
d 0.834185 0.005343 0.345565 0.212240
e 0.422503 0.556925 0.538528 0.628125
-------------
four one three two
a 0.474251 0.710641 0.086072 0.140992
b 0.576864 0.321785 0.069577 0.778031
c 0.080419 0.903965 0.436445 0.874909
d 0.086675 0.236333 0.633163 0.135534
e 0.289439 0.557750 0.629339 0.122334
-------------
four one three two
a 0.991070 0.721513 0.215028 0.953240
b 0.036697 0.253396 0.972485 0.826361
c 0.604048 0.824928 0.717234 0.886581
d 0.114709 0.903193 0.348327 0.284682
e 0.915651 0.839623 0.370719 0.697546
-------------
four one three two
a 0.378297 0.876233 0.152865 0.043542
b 0.642053 0.273930 0.552495 0.877918
c 0.113153 0.319127 0.192093 0.912887
d 0.822514 0.538863 0.950447 0.058296
e 0.077444 0.440550 0.776179 0.020215
-------------
a b c d
one 27.265654 89.931155 17.326695 80.346985
two 37.207292 54.426722 50.557111 87.842961
three 55.818562 51.156687 47.936648 48.377791
four 21.980787 19.015164 7.965595 49.234846
-------------
b c
one 89.931155 17.326695
two 54.426722 50.557111
three 51.156687 47.936648
four 19.015164 7.965595
-------------
a b c d
three 55.818562 51.156687 47.936648 48.377791
four 21.980787 19.015164 7.965595 49.234846
-------------
a b c d
two 37.207292 54.426722 50.557111 87.842961
one 27.265654 89.931155 17.326695 80.346985
-------------
a b c d
one NaN 89.931155 NaN 80.346985
two NaN 54.426722 50.557111 87.842961
three 55.818562 51.156687 NaN NaN
four NaN NaN NaN NaN
-------------
v1 v2 v3
a 47.910054 74.434013 6.522040
b 60.657311 15.013484 45.261134
c 12.485108 34.552472 18.666264
-------------
v1 v2 v3
c 12.485108 34.552472 18.666264
b 60.657311 15.013484 45.261134
a 47.910054 74.434013 6.522040
-------------
v1 v2 v3
a 47.910054 74.434013 6.522040
c 12.485108 34.552472 18.666264
b 60.657311 15.013484 45.261134
-------------
a b c d
v1 72.121111 100 39.199590 42.410840
v2 43.098583 100 9.776559 72.385025
-------------



