医学图像分割多目标分割(多分类)实践
文章目录
- 1. 数据集
- 2. 数据预处理
- 3. 代码部分
- 3.1 训练集和验证集划分
- 3.2 数据加载和处理
- 3.3 One-hot 工具函数
- 3.4 网络模型
- 3.5 模型权重初始化
- 3.6 损失函数
- 3.7 模型评价指标
- 3.8 训练
- 3.9 模型验证
- 3.10 实验结果
1. 数据集
来自ISICDM 2019 临床数据分析挑战赛的基于磁共振成像的膀胱内外壁分割与肿瘤检测数据集。

灰度值:灰色128为膀胱内外壁,白色255为肿瘤。
任务是要同时分割出膀胱内外壁和肿瘤部分,加上背景,最后构成一个三分类问题。
2. 数据预处理
数据预处理最重要的一步就是要对gt进行one-hot编码,如果对one-hot编码不太清楚可以看下这篇文章(数据预处理 One-hot 编码的两种实现方式)。
由于笔记本性能较差,为了代码能够在笔记本上跑起来。在对数据预处理的时候进行了缩放(scale)和中心裁剪(center crop)。原始数据大小为512,首先将数据缩放到256,再裁剪到128的大小。
3. 代码部分
3.1 训练集和验证集划分
按照训练集80%,验证集20%的策略进行重新分配数据集。直接运行当前文件进行数据重新划分,
仅供参考,当然这一部分代码可根据自己的需求随意设计。
# repartition_dataset.py
import os
import math
import random
def partition_data(dataset_dir, ouput_root):
"""
Divide the raw data into training sets and validation sets
:param dataset_dir: path root of dataset
:param ouput_root: the root path to the output file
:return:
"""
image_names = []
mask_names = []
val_size = 0.2
train_names = []
val_names = []
for file in os.listdir(os.path.join(dataset_dir, "Images")):
image_names.append(file)
image_names.sort()
for file in os.listdir(os.path.join(dataset_dir, "Labels")):
mask_names.append(file)
mask_names.sort()
rawdata_size = len(image_names)
random.seed(361)
val_indices = random.sample(range(0, rawdata_size), math.floor(rawdata_size * val_size))
train_indices = []
for i in range(0, rawdata_size):
if i not in val_indices:
train_indices.append(i)
with open(os.path.join(ouput_root, 'val.txt'), 'w') as f:
for i in val_indices:
val_names.append(image_names[i])
f.write(image_names[i])
f.write('\n')
with open(os.path.join(ouput_root, 'train.txt'), 'w') as f:
for i in train_indices:
train_names.append(image_names[i])
f.write(image_names[i])
f.write('\n')
train_names.sort(), val_names.sort()
return train_names, val_names
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset_dir = '../media/LIBRARY/Datasets/Bladder/'
output_root = '../media/LIBRARY/Datasets/Bladder/'
train_names, val_names = partition_data(dataset_dir, output_root)
print(len(train_names))
print(train_names)
print(len(val_names))
print(val_names)
3.2 数据加载和处理
数据加载写一个专门的数据类来做就可以了,最核心的其实就是实现里面的__getitem__()方法。make_dataset方法用来加载数据的文件名,真正加载数据是在__getitem__()里面,在DataLoder的时候自动调用。
# baldder.py
import os
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from torch.utils import data
from torchvision import transforms
from utils import helpers
'''
128= bladder
255 = tumor
0 = background
'''
palette = [[128], [255], [0]]
num_classes = 3
def make_dataset(root, mode):
assert mode in ['train', 'val', 'test']
items = []
if mode == 'train':
img_path = os.path.join(root, 'Images')
mask_path = os.path.join(root, 'Labels')
if 'Augdata' in root:
data_list = os.listdir(os.path.join(root, 'Images'))
else:
data_list = [l.strip('\n') for l in open(os.path.join(root, 'train.txt')).readlines()]
for it in data_list:
item = (os.path.join(img_path, it), os.path.join(mask_path, it))
items.append(item)
elif mode == 'val':
img_path = os.path.join(root, 'Images')
mask_path = os.path.join(root, 'Labels')
data_list = [l.strip('\n') for l in open(os.path.join(
root, 'val.txt')).readlines()]
for it in data_list:
item = (os.path.join(img_path, it), os.path.join(mask_path, it))
items.append(item)
else:
pass
return items
class Bladder(data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, root, mode, joint_transform=None, center_crop=None, transform=None, target_transform=None):
self.imgs = make_dataset(root, mode)
self.palette = palette
self.mode = mode
if len(self.imgs) == 0:
raise RuntimeError('Found 0 images, please check the data set')
self.mode = mode
self.joint_transform = joint_transform
self.center_crop = center_crop
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
def __getitem__(self, index):
img_path, mask_path = self.imgs[index]
img = Image.open(img_path)
mask = Image.open(mask_path)
if self.joint_transform is not None:
img, mask = self.joint_transform(img, mask)
if self.center_crop is not None:
img, mask = self.center_crop(img, mask)
img = np.array(img)
mask = np.array(mask)
# Image.open读取灰度图像时shape=(H, W) 而非(H, W, 1)
# 因此先扩展出通道维度,以便在通道维度上进行one-hot映射
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2)
mask = np.expand_dims(mask, axis=2)
mask = helpers.mask_to_onehot(mask, self.palette)
# shape from (H, W, C) to (C, H, W)
img = img.transpose([2, 0, 1])
mask = mask.transpose([2, 0, 1])
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img)
if self.target_transform is not None:
mask = self.target_transform(mask)
return img, mask
def __len__(self):
return len(self.imgs)
3.3 One-hot 工具函数
# helpers.py
import os
import csv
import numpy as np
def mask_to_onehot(mask, palette):
"""
Converts a segmentation mask (H, W, C) to (H, W, K) where the last dim is a one
hot encoding vector, C is usually 1 or 3, and K is the number of class.
"""
semantic_map = []
for colour in palette:
equality = np.equal(mask, colour)
class_map = np.all(equality, axis=-1)
semantic_map.append(class_map)
semantic_map = np.stack(semantic_map, axis=-1).astype(np.float32)
return semantic_map
def onehot_to_mask(mask, palette):
"""
Converts a mask (H, W, K) to (H, W, C)
"""
x = np.argmax(mask, axis=-1)
colour_codes = np.array(palette)
x = np.uint8(colour_codes[x.astype(np.uint8)])
return x
3.4 网络模型
原始数据:shape = [N, 1, H, W]
GT: shape = [N, 3, H, W]
模型输出:shape = [N, 3, H, W]
(其中N为batch size的大小,H和W分别是图像的高和宽)
使用医学图像分割里面经典的U-Net网络。
# u_net.py
from torch import nn
from utils import initialize_weights
class conv_block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out):
super(conv_block, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(ch_out, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
return x
class up_conv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out):
super(up_conv, self).__init__()
self.up = nn.Sequential(
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2),
nn.Conv2d(ch_in, ch_out, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ch_out),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.up(x)
return x
class U_Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_ch=1, num_classes=3):
super(U_Net, self).__init__()
self.Maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.Conv1 = conv_block(ch_in=img_ch, ch_out=64)
self.Conv2 = conv_block(ch_in=64, ch_out=128)
self.Conv3 = conv_block(ch_in=128, ch_out=256)
self.Conv4 = conv_block(ch_in=256, ch_out=512)
self.Conv5 = conv_block(ch_in=512, ch_out=1024)
self.Up5 = up_conv(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
self.Up_conv5 = conv_block(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
self.Up4 = up_conv(ch_in=512, ch_out=256)
self.Up_conv4 = conv_block(ch_in=512, ch_out=256)
self.Up3 = up_conv(ch_in=256, ch_out=128)
self.Up_conv3 = conv_block(ch_in=256, ch_out=128)
self.Up2 = up_conv(ch_in=128, ch_out=64)
self.Up_conv2 = conv_block(ch_in=128, ch_out=64)
self.Conv_1x1 = nn.Conv2d(64, num_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
initialize_weights(self)
def forward(self, x):
# encoding path
x1 = self.Conv1(x)
x2 = self.Maxpool(x1)
x2 = self.Conv2(x2)
x3 = self.Maxpool(x2)
x3 = self.Conv3(x3)
x4 = self.Maxpool(x3)
x4 = self.Conv4(x4)
x5 = self.Maxpool(x4)
x5 = self.Conv5(x5)
# decoding + concat path
d5 = self.Up5(x5)
d5 = torch.cat((x4, d5), dim=1)
d5 = self.Up_conv5(d5)
d4 = self.Up4(d5)
d4 = torch.cat((x3, d4), dim=1)
d4 = self.Up_conv4(d4)
d3 = self.Up3(d4)
d3 = torch.cat((x2, d3), dim=1)
d3 = self.Up_conv3(d3)
d2 = self.Up2(d3)
d2 = torch.cat((x1, d2), dim=1)
d2 = self.Up_conv2(d2)
d1 = self.Conv_1x1(d2)
return d1
3.5 模型权重初始化
# utils.py
def initialize_weights(*models):
for model in models:
for module in model.modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d) or isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(module.weight)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d):
module.weight.data.fill_(1)
module.bias.data.zero_()
3.6 损失函数
采用dice loss,实现思路可参考【Pytorch】 Dice系数与Dice Loss损失函数实现。
# loss.py
import torch.nn as nn
from .metrics import *
class SoftDiceLoss(_Loss):
__name__ = 'dice_loss'
def __init__(self, num_classes, activation=None, reduction='mean'):
super(SoftDiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.activation = activation
self.num_classes = num_classes
def forward(self, y_pred, y_true):
class_dice = []
for i in range(1, self.num_classes):
class_dice.append(diceCoeff(y_pred[:, i:i + 1, :], y_true[:, i:i + 1, :], activation=self.activation))
mean_dice = sum(class_dice) / len(class_dice)
return 1 - mean_dice
3.7 模型评价指标
Dice 系数。
# metircs.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
def diceCoeff(pred, gt, eps=1e-5, activation='sigmoid'):
r""" computational formula:
dice = (2 * (pred ∩ gt)) / (pred ∪ gt)
"""
if activation is None or activation == "none":
activation_fn = lambda x: x
elif activation == "sigmoid":
activation_fn = nn.Sigmoid()
elif activation == "softmax2d":
activation_fn = nn.Softmax2d()
else:
raise NotImplementedError("Activation implemented for sigmoid and softmax2d")
pred = activation_fn(pred)
N = gt.size(0)
pred_flat = pred.view(N, -1)
gt_flat = gt.view(N, -1)
intersection = (pred_flat * gt_flat).sum(1)
unionset = pred_flat.sum(1) + gt_flat.sum(1)
loss = (2 * intersection + eps) / (unionset + eps)
return loss.sum() / N
def diceCoeffv2(pred, gt, eps=1e-5, activation='sigmoid'):
r""" computational formula:
dice = (2 * tp) / (2 * tp + fp + fn)
"""
if activation is None or activation == "none":
activation_fn = lambda x: x
elif activation == "sigmoid":
activation_fn = nn.Sigmoid()
elif activation == "softmax2d":
activation_fn = nn.Softmax2d()
else:
raise NotImplementedError("Activation implemented for sigmoid and softmax2d")
pred = activation_fn(pred)
N = gt.size(0)
pred_flat = pred.view(N, -1)
gt_flat = gt.view(N, -1)
tp = torch.sum(gt_flat * pred_flat, dim=1)
fp = torch.sum(pred_flat, dim=1) - tp
fn = torch.sum(gt_flat, dim=1) - tp
loss = (2 * tp + eps) / (2 * tp + fp + fn + eps)
return loss.sum() / N
3.8 训练
# train.py
import time
import os
from torch import optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
# from datasets import bladder
from utils.loss import *
from utils import tools
from utils.metrics import diceCoeffv2
import utils.joint_transforms as joint_transforms
import utils.transforms as extended_transforms
from networks.u_net import *
crop_size = 128
batch_size = 2
n_epoch = 10
model_name = 'U_Net_'
loss_name = 'dice_'
times = 'no1_'
extra_description = ''
writer = SummaryWriter(os.path.join('../../log/bladder_trainlog', 'bladder_exp', model_name+loss_name+times+extra_description))
def main():
net = U_Net(img_ch=1, num_classes=3).cuda()
train_joint_transform = joint_transforms.Compose([
joint_transforms.Scale(256),
# joint_transforms.RandomRotate(10),
# joint_transforms.RandomHorizontallyFlip()
])
center_crop = joint_transforms.CenterCrop(crop_size)
train_input_transform = extended_transforms.ImgToTensor()
target_transform = extended_transforms.MaskToTensor()
train_set = bladder.Bladder('../../media/LIBRARY/Datasets/Bladder', 'train',
joint_transform=train_joint_transform, center_crop=center_crop,
transform=train_input_transform, target_transform=target_transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
if loss_name == 'dice_':
criterion = SoftDiceLoss(activation='sigmoid').cuda()
elif loss_name == 'bce_':
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss().cuda()
elif loss_name == 'wbce_':
criterion = WeightedBCELossWithSigmoid().cuda()
elif loss_name == 'er_':
criterion = EdgeRefinementLoss().cuda()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
train(train_loader, net, criterion, optimizer, n_epoch, 0)
def train(train_loader, net, criterion, optimizer, num_epoches , iters):
for epoch in range(1, num_epoches + 1):
st = time.time()
b_dice = 0.0
t_dice = 0.0
d_len = 0
for inputs, mask in train_loader:
X = inputs.cuda()
y = mask.cuda()
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = net(X)
loss = criterion(output, y)
# CrossEntropyLoss
# loss = criterion(output, torch.argmax(y, dim=1))
output = torch.sigmoid(output)
output[output < 0.5] = 0
output[output > 0.5] = 1
bladder_dice = diceCoeffv2(output[:, 0:1, :], y[:, 0:1, :], activation=None).cpu().item()
tumor_dice = diceCoeffv2(output[:, 1:2, :], y[:, 1:2, :], activation=None).cpu().item()
mean_dice = (bladder_dice + tumor_dice) / 2
d_len += 1
b_dice += bladder_dice
t_dice += tumor_dice
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
iters += batch_size
string_print = "Epoch = %d iters = %d Current_Loss = %.4f Mean Dice=%.4f Bladder Dice=%.4f Tumor Dice=%.4f Time = %.2f"\
% (epoch, iters, loss.item(), mean_dice,
bladder_dice, tumor_dice, time.time() - st)
tools.log(string_print)
st = time.time()
writer.add_scalar('train_main_loss', loss.item(), iters)
b_dice = b_dice / d_len
t_dice = t_dice / d_len
m_dice = (b_dice + t_dice) / 2
print('Epoch {}/{},Train Mean Dice {:.4}, Bladder Dice {:.4}, Tumor Dice {:.4}'.format(
epoch, num_epoches, m_dice, b_dice, t_dice
))
if epoch == num_epoches:
torch.save(net, '../../checkpoint/exp/{}.pth'.format(model_name + loss_name + times + extra_description))
writer.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3.9 模型验证
# validate.py
import os
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import utils.joint_transforms as joint_transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
from utils import helpers
import utils.transforms as extended_transforms
from utils.metrics import *
from datasets import bladder
from utils.loss import *
import train
LOSS = False
# numpy 高维数组打印不显示...
np.set_printoptions(threshold=9999999)
batch_size = 1
val_input_transform = extended_transforms.ImgToTensor()
center_crop = joint_transforms.Compose([
joint_transforms.Scale(256),
joint_transforms.CenterCrop(128)]
)
target_transform = extended_transforms.MaskToTensor()
val_set = bladder.Bladder('../../media/LIBRARY/Datasets/Bladder/', 'val',
transform=val_input_transform, center_crop=center_crop,
target_transform=target_transform)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
# 验证用的模型名称
model_name = train.model_name
loss_name = train.loss_name
times = train.times
extra_description = train.extra_description
model = torch.load("../../checkpoint/exp/{}.pth".format(model_name + loss_name + times + extra_description))
# model = torch.load("../../checkpoint/exp/{}.pth".format('U_Net_bce_no1_'))
model.eval()
if LOSS:
writer = SummaryWriter(os.path.join('../../log/vallog', 'bladder_exp', model_name+loss_name+times+extra_description))
if loss_name == 'dice_':
criterion = SoftDiceLoss(activation='sigmoid').cuda()
elif loss_name == 'bce_':
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss().cuda()
elif loss_name == 'wbce_':
criterion = WeightedBCELossWithSigmoid().cuda()
elif loss_name == 'er_':
criterion = EdgeRefinementLoss().cuda()
def val(model):
imname = '2-IM131'
# imname = '2-IM107'
img = Image.open('D:\\Learning\\datasets\\基于磁共振成像的膀胱内外壁分割与肿瘤检测\\Images\\{}.png'.format(imname))
mask = Image.open('D:\\Learning\\datasets\\基于磁共振成像的膀胱内外壁分割与肿瘤检测\\Labels\\{}.png'.format(imname))
img, mask = center_crop(img, mask)
img = np.asarray(img)
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2)
mri = img
mask = np.asarray(mask)
mask = np.expand_dims(mask, axis=2)
gt = np.float32(helpers.mask_to_onehot(mask, bladder.palette))
# 用来看gt的像素值
gt_showval = gt
gt = np.expand_dims(gt, axis=3)
gt = gt.transpose([3, 2, 0, 1])
gt = torch.from_numpy(gt)
img = img.transpose([2, 0, 1])
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=3)
img = img.transpose([3, 0, 1, 2])
img = val_input_transform(img)
img = img.cuda()
model = model.cuda()
pred = model(img)
pred = torch.sigmoid(pred)
pred[pred < 0.5] = 0
pred[pred > 0.5] = 1
bladder_dice = diceCoeffv2(pred[:, 0:1, :], gt.cuda()[:, 0:1, :], activation=None)
tumor_dice = diceCoeffv2(pred[:, 1:2, :], gt.cuda()[:, 1:2, :], activation=None)
mean_dice = (bladder_dice + tumor_dice) / 2
acc = accuracy(pred, gt.cuda())
p = precision(pred, gt.cuda())
r = recall(pred, gt.cuda())
print('mean_dice={:.4}, bladder_dice={:.4}, tumor_dice={:.4}, acc={:.4}, p={:.4}, r={:.4}'
.format(mean_dice.item(), bladder_dice.item(), tumor_dice.item(),
acc.item(), p.item(), r.item()))
pred = pred.cpu().detach().numpy()[0].transpose([1, 2, 0])
# 用来看预测的像素值
pred_showval = pred
pred = helpers.onehot_to_mask(pred, bladder.palette)
# np.uint8()反归一化到[0, 255]
imgs = np.uint8(np.hstack([mri, pred, mask]))
cv2.imshow("mri pred gt", imgs)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def auto_val(model):
# 效果展示图片数
iters = 0
SIZES = 8
imgs = []
preds = []
gts = []
dices = 0
tumor_dices = 0
bladder_dices = 0
for i, (img, mask) in enumerate(val_loader):
im = img
img = img.cuda()
model = model.cuda()
pred = model(img)
if LOSS:
loss = criterion(pred, mask.cuda()).item()
pred = torch.sigmoid(pred)
pred = pred.cpu().detach()
iters += batch_size
pred[pred < 0.5] = 0
pred[pred > 0.5] = 1
bladder_dice = diceCoeff(pred[:, 0:1, :], mask[:, 0:1, :], activation=None)
tumor_dice = diceCoeff(pred[:, 1:2, :], mask[:, 1:2, :], activation=None)
mean_dice = (bladder_dice + tumor_dice) / 2
dices += mean_dice
tumor_dices += tumor_dice
bladder_dices += bladder_dice
acc = accuracy(pred, mask)
p = precision(pred, mask)
r = recall(pred, mask)
print('mean_dice={:.4}, bladder_dice={:.4}, tumor_dice={:.4}, acc={:.4}, p={:.4}, r={:.4}'
.format(mean_dice.item(), bladder_dice.item(), tumor_dice.item(),
acc, p, r))
gt = mask.numpy()[0].transpose([1, 2, 0])
gt = helpers.onehot_to_mask(gt, bladder.palette)
pred = pred.cpu().detach().numpy()[0].transpose([1, 2, 0])
pred = helpers.onehot_to_mask(pred, bladder.palette)
im = im[0].numpy().transpose([1, 2, 0])
if LOSS:
writer.add_scalar('val_main_loss', loss, iters)
if len(imgs) < SIZES:
imgs.append(im * 255)
preds.append(pred)
gts.append(gt)
val_mean_dice = dices / (len(val_loader) / batch_size)
val_tumor_dice = tumor_dices / (len(val_loader) / batch_size)
val_bladder_dice = bladder_dices / (len(val_loader) / batch_size)
print('Val Mean Dice = {:.4}, Val Bladder Dice = {:.4}, Val Tumor Dice = {:.4}'
.format(val_mean_dice, val_bladder_dice, val_tumor_dice))
imgs = np.hstack([*imgs])
preds = np.hstack([*preds])
gts = np.hstack([*gts])
show_res = np.vstack(np.uint8([imgs, preds, gts]))
cv2.imshow("top is mri , middle is pred, bottom is gt", show_res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# val(model)
auto_val(model)
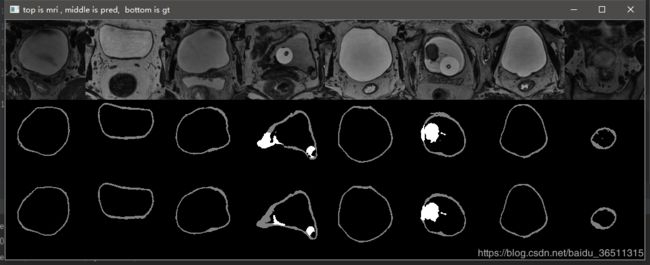
3.10 实验结果
这是笔记本跑了10个epoch的结果,仅仅是测试代码有没有问题。从结果可以看到,代码目前应该是没有问题的,后期只需调参数再训练提升效果即可。
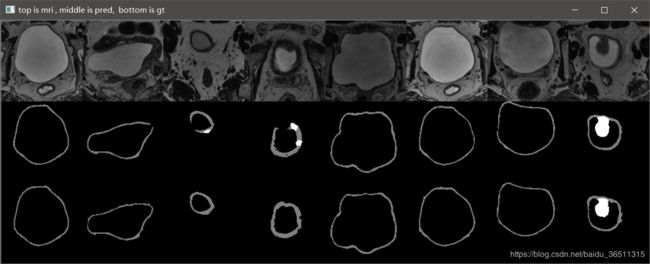
GTX2080TI 跑120个epoch的测试效果:
Val Mean Dice = 0.9051, Val Bladder Dice = 0.9012, Val Tumor Dice = 0.9091