【MaxCompute】实现自定义UDF、UDTF详解
背景及目的
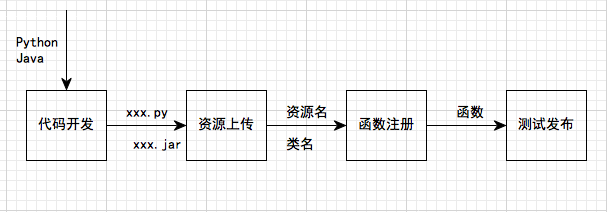
本文简单地介绍了一下如何新建工程,添加代码,打包,上传资源包和注册方法,对初次接触的用户提供帮助。
另外,详解介绍通过UDF来满足不同的计算需求。
UDF概述
UDF全称为User Defined Function,即用户自定义函数。MaxCompute提供很多内建函数来满足您的计算需求,同时您还可以通过创建自定义函数来满足不同的计算需求。
UDF在使用上与普通的 内建函数类似,Java和MaxCompute的数据类型的对应关系,请参见 参数与返回值类型。
如果您使用Maven,可以从 Maven 库中搜索odps-sdk-udf,从而获取不同版本的Java SDK,相关配置信息如下所示:
com.aliyun.odps
odps-sdk-udf
0.29.10-public
MaxCompute支持的UDF有三种:
User Defined Scalar Function(通常也称之为UDF)
用户自定义标量值函数(User Defined Scalar Function)。其输入与输出是一对一的关系,即读入一行数据,写出一条输出值。
UDTF(User Defined Table Valued Function)
自定义表值函数,是用来解决一次函数调用输出多行数据场景的,也是唯一能返回多个字段的自定义函数。而UDF只能一次计算输出一条返回值。
UDAF(User Defined Aggregation Function)
自定义聚合函数,其输入与输出是多对一的关系, 即将多条输入记录聚合成一条输出值。可以与SQL中的Group By语句联用。具体语法请参见 聚合函数。
Java UDF
数据类型对应关系
| MaxCompute Type | Java Type |
|---|---|
| Tinyint | java.lang.Byte |
| Smallint | java.lang.Short |
| Int | java.lang.Integer |
| Bigint | java.lang.Long |
| Float | java.lang.Float |
| Double | java.lang.Double |
| Decimal | java.math.BigDecimal |
| Boolean | java.lang.Boolean |
| String | java.lang.String |
| Varchar | com.aliyun.odps.data.Varchar |
| Binary | com.aliyun.odps.data.Binary |
| Datetime | java.util.Date |
| Timestamp | java.sql.Timestamp |
| Array | java.util.List |
| Map | java.util.Map |
| Struct | com.aliyun.odps.data.Struct |
UDF
实现UDF需要继承com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDF类,并实现evaluate方法。evaluate方法必须是非static的public方法 。Evaluate方法的参数和返回值类型将作为SQL中UDF的函数签名。这意味着您可以在UDF中实现多个evaluate方法,在调用UDF时,框架会依据UDF调用的参数类型匹配正确的evaluate方法 。
UDF的示例如下:
package org.alidata.odps.udf.examples;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDF;
public final class Lower extends UDF {
public String evaluate(String s) {
if (s == null) {
return null;
}
return s.toLowerCase();
}
}
可以通过实现void setup(ExecutionContext ctx)和void close()来分别实现UDF的初始化和结束代码。
如以下代码,定义了一个有三个overloads的UDF,其中第一个用了array作为参数,第二个用了map作为参数,第三个用了struct。由于第三个overloads了struct作为参数或者返回值,因此要求必须要对UDF class打上 @Resolve annotation,来指定struct的具体类型。
@Resolve("struct,string->string")
public class UdfArray extends UDF {
public String evaluate(List vals, Long len) {
return vals.get(len.intValue());
}
public String evaluate(Map map, String key) {
return map.get(key);
}
public String evaluate(Struct struct, String key) {
return struct.getFieldValue("a") + key;
}
}用户可以直接将复杂类型传入UDF中:
create function my_index as 'UdfArray' using 'myjar.jar';
select id, my_index(array('red', 'yellow', 'green'), colorOrdinal) as color_name from coUDAF
实现Java UDAF类需要继承 com.aliyun.odps.udf.Aggregator,并实现如下几个接口:
public abstract class Aggregator implements ContextFunction {
@Override
public void setup(ExecutionContext ctx) throws UDFException {
}
@Override
public void close() throws UDFException {
}
/**
* 创建聚合Buffer
* @return Writable 聚合buffer
*/
abstract public Writable newBuffer();
/**
* @param buffer 聚合buffer
* @param args SQL中调用UDAF时指定的参数,不能为null,但是args里面的元素可以为null,代表对应的输入数据是null
* @throws UDFException
*/
abstract public void iterate(Writable buffer, Writable[] args) throws UDFException;
/**
* 生成最终结果
* @param buffer
* @return Object UDAF的最终结果
* @throws UDFException
*/
abstract public Writable terminate(Writable buffer) throws UDFException;
abstract public void merge(Writable buffer, Writable partial) throws UDFException;
}其中最重要的是iterate,merge和terminate三个接口,UDAF的主要逻辑依赖于这三个接口的实现。此外,还需要您实现自定义的Writable buffer。
以实现求平均值avg为例,下图简要说明了在MaxCompute UDAF中这一函数的实现逻辑及计算流程: 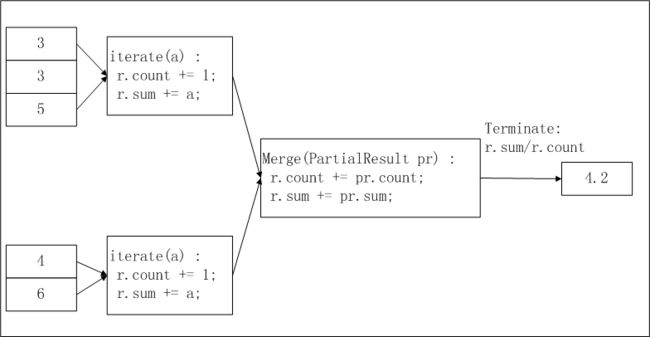
在上图中,输入数据被按照一定的大小进行分片(有关分片的描述请参见 MapReduce),每片的大小适合一个worker在适当的时间内完成。这个分片大小的设置需要您手动配置完成。
UDAF的计算过程分为两个阶段:
第一阶段:每个worker统计分片内数据的个数及汇总值,您可以将每个分片内的数据个数及汇总值视为一个中间结果。
第二阶段:worker汇总上一个阶段中每个分片内的信息。在最终输出时,r.sum / r.count即是所有输入数据的平均值。
计算平均值的UDAF的代码示例,如下所示:
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import com.aliyun.odps.io.DoubleWritable;
import com.aliyun.odps.io.Writable;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.Aggregator;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDFException;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.annotation.Resolve;
@Resolve("double->double")
public class AggrAvg extends Aggregator {
private static class AvgBuffer implements Writable {
private double sum = 0;
private long count = 0;
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeDouble(sum);
out.writeLong(count);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
sum = in.readDouble();
count = in.readLong();
}
}
private DoubleWritable ret = new DoubleWritable();
@Override
public Writable newBuffer() {
return new AvgBuffer();
}
@Override
public void iterate(Writable buffer, Writable[] args) throws UDFException {
DoubleWritable arg = (DoubleWritable) args[0];
AvgBuffer buf = (AvgBuffer) buffer;
if (arg != null) {
buf.count += 1;
buf.sum += arg.get();
}
}
@Override
public Writable terminate(Writable buffer) throws UDFException {
AvgBuffer buf = (AvgBuffer) buffer;
if (buf.count == 0) {
ret.set(0);
} else {
ret.set(buf.sum / buf.count);
}
return ret;
}
@Override
public void merge(Writable buffer, Writable partial) throws UDFException {
AvgBuffer buf = (AvgBuffer) buffer;
AvgBuffer p = (AvgBuffer) partial;
buf.sum += p.sum;
buf.count += p.count;
}
}使用Writable类型实现Concat的示例如下:
package com.aliyun.odps.udf.example;
import com.aliyun.odps.io.Text;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDF;
public class MyConcat extends UDF {
private Text ret = new Text();
public Text evaluate(Text a, Text b) {
if (a == null || b == null) {
return null;
}
ret.clear();
ret.append(a.getBytes(), 0, a.getLength());
ret.append(b.getBytes(), 0, b.getLength());
return ret;
}
}UDTF
Java UDTF需要继承 com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTF类。这个类需要实现4个接口,如下表所示:
| 接口定义 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| public void setup(ExecutionContext ctx) throws UDFException | 初始化方法,在UDTF处理输入数据前,调用用户自定义的初始化行为。在每个Worker内setup会被先调用一次。 |
| public void process(Object[] args) throws UDFException | 这个方法由框架调用,SQL中每一条记录都会对应调用一次process,process的参数为SQL语句中指定的UDTF输入参数。输入参数以Object[]的形式传入,输出结果通过forward函数输出。用户需要在process函数内自行调用forward,以决定输出数据。 |
| public void close() throws UDFException | UDTF的结束方法,此方法由框架调用,并且只会被调用一次,即在处理完最后一条记录之后。 |
| public void forward(Object …o) throws UDFException | 用户调用forward方法输出数据,每次forward代表输出一条记录。对应SQL语句UDTF的as子句指定的列。 |
UDTF 的程序示例,如下所示:
package org.alidata.odps.udtf.examples;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTF;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTFCollector;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.annotation.Resolve;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDFException;
// TODO define input and output types, e.g., "string,string->string,bigint".
@Resolve("string,bigint->string,bigint")
public class MyUDTF extends UDTF {
@Override
public void process(Object[] args) throws UDFException {
String a = (String) args[0];
Long b = (Long) args[1];
for (String t: a.split("\\s+")) {
forward(t, b);
}
}
}在SQL中可以这样使用这个UDTF,假设在MaxCompute上创建UDTF时注册函数名为 user_udtf:
select user_udtf(col0, col1) as (c0, c1) from my_table;假设my_table的col0,col1的值如下所示:
+------+------+
| col0 | col1 |
+------+------+
| A B | 1 |
| C D | 2 |
+------+------+则 select 出的结果,如下所示:
+----+----+
| c0 | c1 |
+----+----+
| A | 1 |
| B | 1 |
| C | 2 |
| D | 2 |
+----+----+UDTF使用说明
在SQL中的常用方式如下:
select user_udtf(col0, col1, col2) as (c0, c1) from my_table;
select user_udtf(col0, col1, col2) as (c0, c1) from (select * from my_table distribute by key sort by key) t;
select reduce_udtf(col0, col1, col2) as (c0, c1) from (select col0, col1, col2 from (select map_udtf(a0, a1, a2, a3) as (col0, col1, col2) from my_table) t1 distribute by col0 sort by col0, col1) t2;但使用UDTF有如下使用限制:
同一个SELECT子句中不允许有其他表达式。
select value, user_udtf(key) as mycol ...UDTF不能嵌套使用。
select user_udtf1(user_udtf2(key)) as mycol...不支持在同一个select子句中与group by / distribute by / sort by联用。
select user_udtf(key) as mycol ... group by mycol其他UDTF示例
在UDTF中,您可以读取MaxCompute的 资源。利用UDTF读取MaxCompute资源的示例,如下所示。
编写UDTF程序,编译成功后导出jar包(udtfexample1.jar)。
package com.aliyun.odps.examples.udf;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Iterator;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.ExecutionContext;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDFException;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDTF;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.annotation.Resolve;
/**
* project: example_project
* table: wc_in2
* partitions: p2=1,p1=2
* columns: colc,colb
*/
@Resolve("string,string->string,bigint,string")
public class UDTFResource extends UDTF {
ExecutionContext ctx;
long fileResourceLineCount;
long tableResource1RecordCount;
long tableResource2RecordCount;
@Override
public void setup(ExecutionContext ctx) throws UDFException {
this.ctx = ctx;
try {
InputStream in = ctx.readResourceFileAsStream("file_resource.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String line;
fileResourceLineCount = 0;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
fileResourceLineCount++;
}
br.close();
Iterator iterator = ctx.readResourceTable("table_resource1").iterator();
tableResource1RecordCount = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
tableResource1RecordCount++;
iterator.next();
}
iterator = ctx.readResourceTable("table_resource2").iterator();
tableResource2RecordCount = 0;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
tableResource2RecordCount++;
iterator.next();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new UDFException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void process(Object[] args) throws UDFException {
String a = (String) args[0];
long b = args[1] == null ? 0 : ((String) args[1]).length();
forward(a, b, "fileResourceLineCount=" + fileResourceLineCount + "|tableResource1RecordCount="
+ tableResource1RecordCount + "|tableResource2RecordCount=" + tableResource2RecordCount);
}
} 添加资源到MaxCompute。
Add file file_resource.txt;
Add jar udtfexample1.jar;
Add table table_resource1 as table_resource1;
Add table table_resource2 as table_resource2;在MaxCompute中创建UDTF函数(my_udtf)。
create function mp_udtf as com.aliyun.odps.examples.udf.UDTFResource using
'udtfexample1.jar, file_resource.txt, table_resource1, table_resource2';在MaxCompute创建资源表table_resource1、table_resource2和物理表tmp1,并插入相应的数据。
运行该UDTF。
select mp_udtf("10","20") as (a, b, fileResourceLineCount) from tmp1;
返回:
+-------+------------+-------+
| a | b | fileResourceLineCount |
+-------+------------+-------+
| 10 | 2 | fileResourceLineCount=3|tableResource1RecordCount=0|tableResource2RecordCount=0 |
| 10 | 2 | fileResourceLineCount=3|tableResource1RecordCount=0|tableResource2RecordCount=0 |
+-------+------------+-------+创建 UDF 简单介绍
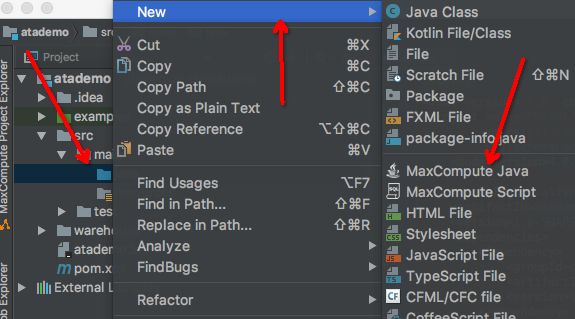
- 在IntelliJ IDEA中安装MaxCompute Studio的插件, 过程不多重复了, 基本方法就是去插件中心搜索MaxCompute studio,然后安装一下就好了。具体如何安装查看MaxCompute官方文档。
- 插件安装完毕后,需要将自己所在的package的信息加进来:
- 接下来,创建新工程,选择"MaxCompute Java",如下图所示:
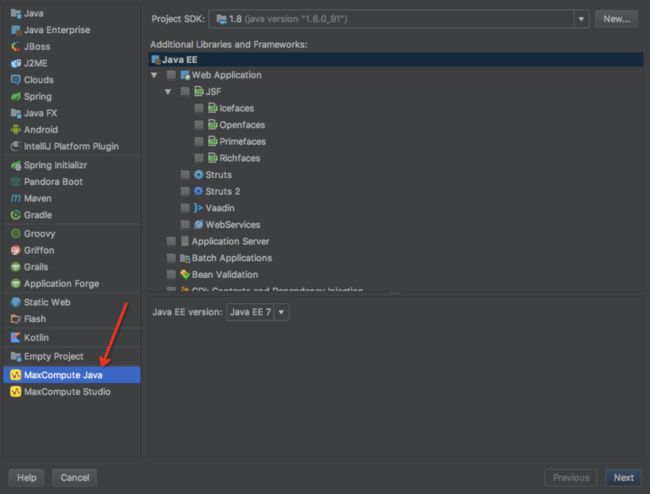
- 新建成功后,查看pom文件,发现相关依赖已经加进来了,如图:
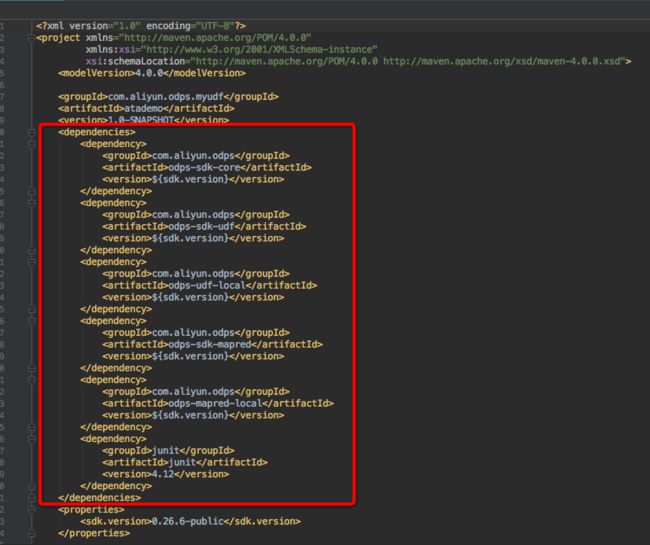
- 新建UDF的Java类
注意:请去src->main-Java里新建,不要在example里新建,否则下一步注册方法的时候找不到main class
- 编写代码吧,比如:

- 打包,在这个Java类文件上,右键,选择Run Maven,选择clean install,如图:
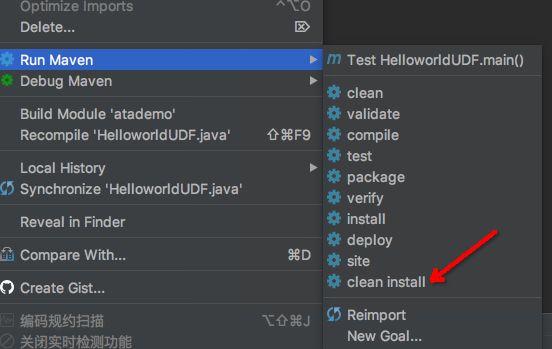
- 查看打出的包,如图所示:
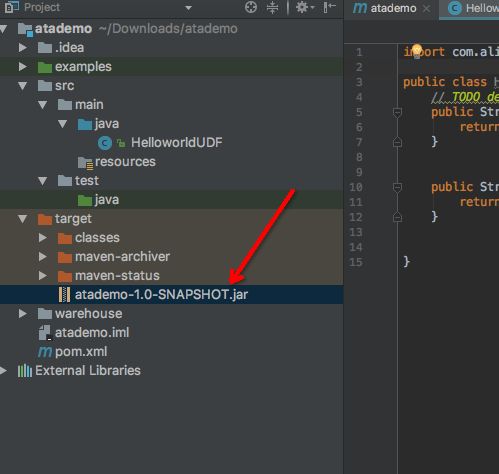
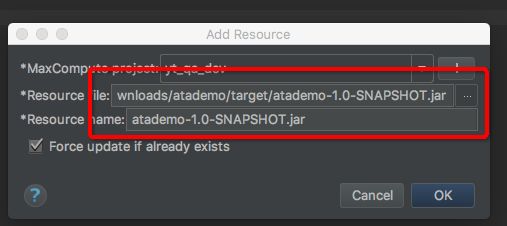
- 下一步就是降这个包上传到服务端了,在IntelliJ IDEA中,MaxCompute->add Resource,如图:
- 确定要上传的包,点击OK上传。
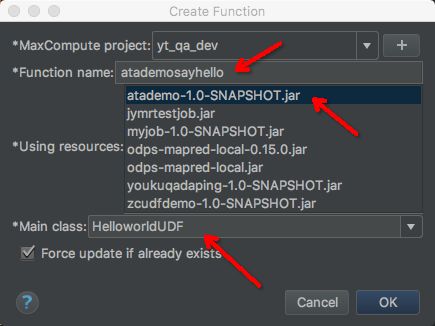
- 接下来就是注册方法了,在IntelliJ IDEA中,MaxCompute->Create function,如图:
- 选择Resource并确定Main class的名称(这就是上面说为什么要在main下面写Java类的原因了,如果写在example里,main class这是无法加载出来的),输入方法的名字,并点击OK进行确认,如下图:
- 注册方法成功后,会有提示框,如下图:
- 最后一步,去DataWorks控制台,跑起来吧:

- 总结
使得MaxCompute Studio,使我们创建UDF变得简单和方便了很多,本文只是简单的介绍了一下最基础的使用,如果您第一次接触UDF,可以照着以上的步骤跑起来。
通过 UDF 实现JSON解析
需求
大家在做数据分析时,有JSON数据解析的需求。输入数据是一个字段,如:
[{"id":"123","name":"jack","owner":"yixiu"},{"id":"456","name":" daniel","owner":"sixiang"}]
输入数据是一个json数组,需要解析成如下的两行数据(关系为1对多):
| id | name | owner |
|---|---|---|
| 123 | jack | yixiu |
| 456 | daniel | sixiang |
实现
这个需求可以通过UDTF实现,但是UDTF中不能通过fastjson完成数据解析,因为json、protobuf 类的包经常免不了要用反射的,会被沙箱挡住。解决方案是使用ODPS内置的gson完成json数据解析。
Gson gson = new Gson();
List projectList = gson.fromJson(projectListString, new TypeToken>(){}.getType()); 使用 UDJ 自定义SQL的Join操作
简介
目前MaxCompute内置了多种Join操作,包括inner/right outer/left outer/full outer/semi/anti-semi join等。对于普通用户而言,这些内置的join操作功能已经相当强大,能够满足很大一部分需求,但是其标准的join实现,依然无法满足很多跨表操作的需求。
本文通过一个样例场景,介绍了UDF框架中新近引入的一种新扩展机制:UDJ(User Defined Join),来实现灵活的跨表操作。这也是基于MaxCompute新一代体系机构发展NewSQL数据处理框架的重要一步。
背景
广义上我们通常用UDF(User Defined Function)来描述用户代码框架。现有的UDF/UDTF/UDAF接口主要是针对在单个数据表上的操作而设计。但是一旦涉及多表的用户自定义操作,用户经常需要依赖于内置join + 各种UDF/UDTF, 并且配合比较复杂的SQL语句来完成。甚至在一些多表操作的场景上,用户不得不放弃SQL而转向传统的完全自定义MR,才能完成所需的计算。
这两种方式对于用户的门槛都比较高。而且对于计算平台而言,多个复杂的join和散布在SQL语言各处的用户代码揉合在一起,带来的是多处的“逻辑黑盒”,并不利于产生最优的执行计划。而使用MR,不仅更大程度上剥夺了系统进行执行优化的可能性,而且由于MR绝大部分代码由Java完成,在执行效率上会远低于MaxCompute基于LLVM 代码生成器产生的深度优化native运行时。
MaxCompute 2.0的全面上线,为计算平台框架的发展提供了更大的灵活度,在这个基础上,我们提出了建设NewSQL生态的目标。NewSQL通过一个扩展的SQL框架,让用户能使用描述性的语言表达其主体逻辑流程,而仅在与分布系统执行流程无关的地方,才引入用户代码。这样的设计,能让用户对计算逻辑从“HOW”(怎样具体完成一个分布式计算流程),转变成“WHAT”(用户从逻辑上描述其想完成的事情和数据操作)。这样的转变,能让用户把更多的精力集中在“WHAT”上面,优化自己的商业处理逻辑上,而把“HOW”交给计算平台,让计算平台进行复杂的系统优化,产生最优的执行计划来完成具体流程。
在这个大背景下,我们在UDF框架中引入了UDJ这种全新的,针对多表数据操作的扩展机制。希望借由这种新的机制,减少用户之前不得不通过MR等方式对分布式系统底层细节的操作,从而达到用户可用性以及系统优化的双赢。
样例场景定义
有这样两个日志表,分别是payment和user_client_log。payment表中保存了用户的支付记录,一笔支付记录包含用户ID、支付时间和支付内容。另一个表user_client_log保存了用户的客户端日志,每一条日志包含了用户ID、日志时间和日志内容。
现要求对于每一条客户端日志,找出该用户在payment表里时间最接近的一条支付记录,将其中的支付内容和日志内容合并输出。举个例子,对于下面的数据:
payment
| user_id | time | content |
|---|---|---|
| 2656199 | 2018-2019-01-23 22:30:00 | gZhvdySOQb |
| 8881237 | 2018-2019-01-23 08:30:00 | pYvotuLDIT |
| 8881237 | 2018-2019-01-23 10:32:00 | KBuMzRpsko |
user_client_log
| user_id | time | content |
|---|---|---|
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 00:30:00 | click MpkvilgWSmhUuPn |
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 06:14:00 | click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL |
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 10:30:00 | click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL |
其中user_client_log的一条记录
| user_id | time | content |
|---|---|---|
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 00:30:00 | click MpkvilgWSmhUuPn |
和payment中时间最接近的一条是
| user_id | time | content |
|---|---|---|
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 08:30:00 | pYvotuLDIT |
因此,这两条记录合并为:
| user_id | time | content |
|---|---|---|
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 00:30:00 | click MpkvilgWSmhUuPn, pay pYvotuLDIT |
上面样例数据全部合并的结果如下:
| user_id | time | content |
|---|---|---|
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 00:30:00 | click MpkvilgWSmhUuPn, pay pYvotuLDIT |
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 06:14:00 | click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL, pay pYvotuLDIT |
| 8881237 | 2019-01-23 10:30:00 | click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL, pay KBuMzRpsko |
在使用UDJ解决这个问题之前,先看一下使用标准join能否解决这个问题。
答案是不能,因为这个问题除了要求按照user_id进行关联以外,还需要知道payment中哪一条记录和user_client_log中的记录的时间差异值最小,如果勉强写SQL伪代码的话类似于:
SELECT
p.user_id,
p.time,
merge(p.pay_info, u.content)
FROM
payment p RIGHT OUTER JOIN user_client_log u
ON p.user_id = u.user_id and abs(p.time - u.time) = min(abs(p.time - u.time))这就要求关联时需要知道相同user_id下的p.time与u.time差异最小的值,而聚合函数是不能出现在关联条件上的。因此,这个看似简单的问题,如果使用标准的关联操作是无法实现的。但在分布式系统中,Join操作实际上是将两个表按照某个(或多个)字段进行分组,并将同组数据集中到一个地方,关键在于标准SQL中的Join对于关联后的操作是有限的,这个时候,如果能提供一个通用编程语言接口,用户通过插件式的方式实现这个接口,在这个接口中将关联后的分组数据进行自定义处理并输出就能解决这个问题了。这个就是UDJ要解决的问题。
使用Java编写UDJ代码
下面,我将按步骤来演示如何用UDJ解决这个问题。首先这是一个新功能,我们需要一个比较新的SDK:
com.aliyun.odps
odps-sdk-udf
0.30.0
provided
新的SDK中包含了一个新的抽象类UDJ,我们通过继承这个类,来实现UDJ的功能:
package com.aliyun.odps.udf.example.udj;
import com.aliyun.odps.Column;
import com.aliyun.odps.OdpsType;
import com.aliyun.odps.Yieldable;
import com.aliyun.odps.data.ArrayRecord;
import com.aliyun.odps.data.Record;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.DataAttributes;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.ExecutionContext;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDJ;
import com.aliyun.odps.udf.annotation.Resolve;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
/** For each record of right table, find the nearest record of left table and
* merge two records.
*/
@Resolve("->string,bigint,string")
public class PayUserLogMergeJoin extends UDJ {
private Record outputRecord;
/** Will be called prior to the data processing phase. User could implement
* this method to do initialization work.
*/
@Override
public void setup(ExecutionContext executionContext, DataAttributes dataAttributes) {
//
outputRecord = new ArrayRecord(new Column[]{
new Column("user_id", OdpsType.STRING),
new Column("time", OdpsType.BIGINT),
new Column("content", OdpsType.STRING)
});
}
/** Override this method to implement join logic.
* @param key Current join key
* @param left Group of records of left table corresponding to the current key
* @param right Group of records of right table corresponding to the current key
* @param output Used to output the result of UDJ
*/
@Override
public void join(Record key, Iterator left, Iterator right, Yieldable output) {
outputRecord.setString(0, key.getString(0));
if (!right.hasNext()) {
// Empty right group, do nothing.
return;
} else if (!left.hasNext()) {
// Empty left group. Output all records of right group without merge.
while (right.hasNext()) {
Record logRecord = right.next();
outputRecord.setBigint(1, logRecord.getDatetime(0).getTime());
outputRecord.setString(2, logRecord.getString(1));
output.yield(outputRecord);
}
return;
}
ArrayList pays = new ArrayList<>();
// The left group of records will be iterated from the start to the end
// for each record of right group, but the iterator cannot be reset.
// So we save every records of left to an ArrayList.
left.forEachRemaining(pay -> pays.add(pay.clone()));
while (right.hasNext()) {
Record log = right.next();
long logTime = log.getDatetime(0).getTime();
long minDelta = Long.MAX_VALUE;
Record nearestPay = null;
// Iterate through all records of left, and find the pay record that has
// the minimal difference in terms of time.
for (Record pay: pays) {
long delta = Math.abs(logTime - pay.getDatetime(0).getTime());
if (delta < minDelta) {
minDelta = delta;
nearestPay = pay;
}
}
// Merge the log record with nearest pay record and output to the result.
outputRecord.setBigint(1, log.getDatetime(0).getTime());
outputRecord.setString(2, mergeLog(nearestPay.getString(1), log.getString(1)));
output.yield(outputRecord);
}
}
String mergeLog(String payInfo, String logContent) {
return logContent + ", pay " + payInfo;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
} 注解:在本例中没有处理记录中的NULL值,为了使程序简洁便于演示,我们这里假设数据中没有NULL值。
从代码中可以看到,在每次调用UDJ的join方法时,两张表中各有一组对应着同一个key数据,提供给了我们。因此,只需遍历右表(user_client_log)的分组,对于每一个log记录,遍历一遍左表(payment)的分组,找出时间相差最小的记录,将日志内容合并然后输出即可。
这里我们假设同一个用户的支付记录数是比较少的,所以我们可以预先将左表分组全部加载到内存(一般情况下不会有人一天产生的支付数连内存里都放不下)。但是这个假设不成立时怎么办?这里先放下不表,文章后面一节“使用SORT BY预排序”会解决这个问题。
在MaxCompute中创建UDJ
编写完UDJ的Java代码以后,还需要将这部分代码插件式的嵌入到MaxCompute SQL中进行执行。再此之前,需要将代码注册到MaxCompute。假设上述代码打包成了odps-udf-example.jar,我们通过add jar命令将其当做jar资源上传到MaxCompute:
add jar odps-udf-example.jar;然后通过create function语句注册UDJ函数,指定UDJ在SQL中的函数名pay_user_log_merge_join,以及关联上它对应的jar资源odps-udf-example.jar和在jar包中的类名com.aliyun.odps.udf.example.udj.PayUserLogMergeJoin:
create function pay_user_log_merge_join
as 'com.aliyun.odps.udf.example.udj.PayUserLogMergeJoin'
using 'odps-udf-example.jar';使用MaxCompute SQL进行UDJ查询
UDJ注册好了以后,就可以在MaxCompute SQL中使用了。
首先为了便于演示,我们先创建源表:
CREATE TABLE payment (
user_id string,
time datetime,
pay_info string
);
CREATE TABLE user_client_log (
user_id string,
time datetime,
content string
);然后制造一些演示数据:
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE payment VALUES
('1335656', datetime '2018-02-13 19:54:00', 'PEqMSHyktn'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 12:21:00', 'pYvotuLDIT'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 20:50:00', 'PEqMSHyktn'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 22:30:00', 'gZhvdySOQb'),
('8881237', datetime '2018-02-13 08:30:00', 'pYvotuLDIT'),
('8881237', datetime '2018-02-13 10:32:00', 'KBuMzRpsko'),
('9890100', datetime '2018-02-13 16:01:00', 'gZhvdySOQb'),
('9890100', datetime '2018-02-13 16:26:00', 'MxONdLckwa')
;
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE user_client_log VALUES
('1000235', datetime '2018-02-13 00:25:36', 'click FNOXAibRjkIaQPB'),
('1000235', datetime '2018-02-13 22:30:00', 'click GczrYaxvkiPultZ'),
('1335656', datetime '2018-02-13 18:30:00', 'click MxONdLckpAFUHRS'),
('1335656', datetime '2018-02-13 19:54:00', 'click mKRPGOciFDyzTgM'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 08:30:00', 'click CZwafHsbJOPNitL'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 09:14:00', 'click nYHJqIpjevkKToy'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 21:05:00', 'click gbAfPCwrGXvEjpI'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 21:08:00', 'click dhpZyWMuGjBOTJP'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 22:29:00', 'click bAsxnUdDhvfqaBr'),
('2656199', datetime '2018-02-13 22:30:00', 'click XIhZdLaOocQRmrY'),
('4356142', datetime '2018-02-13 18:30:00', 'click DYqShmGbIoWKier'),
('4356142', datetime '2018-02-13 19:54:00', 'click DYqShmGbIoWKier'),
('8881237', datetime '2018-02-13 00:30:00', 'click MpkvilgWSmhUuPn'),
('8881237', datetime '2018-02-13 06:14:00', 'click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL'),
('8881237', datetime '2018-02-13 10:30:00', 'click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL'),
('9890100', datetime '2018-02-13 16:01:00', 'click vOTQfBFjcgXisYU'),
('9890100', datetime '2018-02-13 16:20:00', 'click WxaLgOCcVEvhiFJ')
;在MaxCompute SQL中使用刚刚创建好的UDJ函数:
SELECT r.user_id, from_unixtime(time/1000) as time, content FROM (
SELECT user_id, time as time, pay_info FROM payment
) p JOIN (
SELECT user_id, time as time, content FROM user_client_log
) u
ON p.user_id = u.user_id
USING pay_user_log_merge_join(p.time, p.pay_info, u.time, u.content)
r
AS (user_id, time, content);UDJ的语法与标准Join语法类似,这里多了一个USING子句,其中pay_user_log_merge_join是注册的UDJ在SQL中的函数名;后面的(p.time, p.pay_info, u.time, u.content)是UDJ中分别用到的左右表的列;r是UDJ结果的别名,用于其他地方引用UDJ的结果;(user_id, time, content)是UDJ产生的结果的列名。
运行上面这条SQL,可以看到,我们通过使用UDJ完美的解决了这个问题。结果为:
+---------+------------+---------+
| user_id | time | content |
+---------+------------+---------+
| 1000235 | 2018-02-13 00:25:36 | click FNOXAibRjkIaQPB |
| 1000235 | 2018-02-13 22:30:00 | click GczrYaxvkiPultZ |
| 1335656 | 2018-02-13 18:30:00 | click MxONdLckpAFUHRS, pay PEqMSHyktn |
| 1335656 | 2018-02-13 19:54:00 | click mKRPGOciFDyzTgM, pay PEqMSHyktn |
| 2656199 | 2018-02-13 08:30:00 | click CZwafHsbJOPNitL, pay pYvotuLDIT |
| 2656199 | 2018-02-13 09:14:00 | click nYHJqIpjevkKToy, pay pYvotuLDIT |
| 2656199 | 2018-02-13 21:05:00 | click gbAfPCwrGXvEjpI, pay PEqMSHyktn |
| 2656199 | 2018-02-13 21:08:00 | click dhpZyWMuGjBOTJP, pay PEqMSHyktn |
| 2656199 | 2018-02-13 22:29:00 | click bAsxnUdDhvfqaBr, pay gZhvdySOQb |
| 2656199 | 2018-02-13 22:30:00 | click XIhZdLaOocQRmrY, pay gZhvdySOQb |
| 4356142 | 2018-02-13 18:30:00 | click DYqShmGbIoWKier |
| 4356142 | 2018-02-13 19:54:00 | click DYqShmGbIoWKier |
| 8881237 | 2018-02-13 00:30:00 | click MpkvilgWSmhUuPn, pay pYvotuLDIT |
| 8881237 | 2018-02-13 06:14:00 | click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL, pay pYvotuLDIT |
| 8881237 | 2018-02-13 10:30:00 | click OkTYNUHMqZzlDyL, pay KBuMzRpsko |
| 9890100 | 2018-02-13 16:01:00 | click vOTQfBFjcgXisYU, pay gZhvdySOQb |
| 9890100 | 2018-02-13 16:20:00 | click WxaLgOCcVEvhiFJ, pay MxONdLckwa |
+---------+------------+---------+使用SORT BY预排序
前面的UDJ代码我们提过一笔,为了找到payment中相差最小的一条记录,我们需要反复对payment表的iterator进行遍历,所以事先我们将相同user_id的payment记录全部加载到了ArrayList。当同一个用户的支付行为比较少时,这方式是没有问题的。但在其它场景中,有时候同组内的数据可能非常大,大到无法在内存中放下,这个时候我们可以利用UDJ的预排序功能。回到这个样例,但是假设一个土豪用户产生了巨量的支付, 导致我们无法将payment放在内存中。仔细想一下这个问题,发现组内所有数据如果已经按照time排好了序,那么这个问题就好解了,我们只需要比较两边iterator最"顶端"的数据,就可以实现这个功能。
@Override
public void join(Record key, Iterator left, Iterator right, Yieldable output) {
outputRecord.setString(0, key.getString(0));
if (!right.hasNext()) {
return;
} else if (!left.hasNext()) {
while (right.hasNext()) {
Record logRecord = right.next();
outputRecord.setBigint(1, logRecord.getDatetime(0).getTime());
outputRecord.setString(2, logRecord.getString(1));
output.yield(outputRecord);
}
return;
}
long prevDelta = Long.MAX_VALUE;
Record logRecord = right.next();
Record payRecord = left.next();
Record lastPayRecord = payRecord.clone();
while (true) {
long delta = logRecord.getDatetime(0).getTime() - payRecord.getDatetime(0).getTime();
if (left.hasNext() && delta > 0) {
// The delta of time between two records is decreasing, we can still
// explore the left group to try to gain a smaller delta.
lastPayRecord = payRecord.clone();
prevDelta = delta;
payRecord = left.next();
} else {
// Hit to the point of minimal delta. Check with the last pay record,
// output the merge result and prepare to process the next record of
// right group.
Record nearestPay = Math.abs(delta) < prevDelta ? payRecord : lastPayRecord;
outputRecord.setBigint(1, logRecord.getDatetime(0).getTime());
String mergedString = mergeLog(nearestPay.getString(1), logRecord.getString(1));
outputRecord.setString(2, mergedString);
output.yield(outputRecord);
if (right.hasNext()) {
logRecord = right.next();
prevDelta = Math.abs(
logRecord.getDatetime(0).getTime() - lastPayRecord.getDatetime(0).getTime()
);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
} SQL语句中,我们只需要对之前的例子稍作修改,在UDJ语句尾部增加SORT BY子句,指定UDJ组内左右表分别都按照各自的time字段进行排序(如果你跟着样例在运行,UDJ代码由于也进行了修改,所以请不要忘了更新UDJ的jar包)
SELECT r.user_id, from_unixtime(time/1000) as time, content FROM (
SELECT user_id, time as time, pay_info FROM payment
) p JOIN (
SELECT user_id, time as time, content FROM user_client_log
) u
ON p.user_id = u.user_id
USING pay_user_log_merge_join(p.time, p.pay_info, u.time, u.content)
r
AS (user_id, time, content)
SORT BY p.time, u.time;可以看到,使用SORT BY子句对UDJ的数据进行预排序后,在这个问题中最多只需要同时缓存3条记录,就可以实现和之前算法的相同的功能。
Python UDF
受限环境
MaxCompute UDF的Python版本为2.7,并以沙箱模式执行用户代码,即代码是在一个受限的运行环境中执行的,在这个环境中,以下行为会被禁止:
- 读写本地文件
- 启动子进程
- 启动线程
- 使用socket通信
- 其他系统调用
基于上述原因,您上传的代码必须都是纯Python实现,C扩展模块是被禁止的。
此外,Python的标准库中也不是所有模块都可用,涉及到上述功能的模块都会被禁止。具体标准库可用模块说明如下:
- 所有纯Python实现(不依赖扩展模块)的模块都可用。
- C实现的扩展模块中下列模块可用:
array、audioop、binascii
、_bisect、cmath、_codecs_cn、_codecs_hk、_codecs_iso2022、_codecs_jp、_codecs_kr、_codecs_tw、_collections、cStringIO、datetime、_functools、future_builtins、_hashlib、_heapq、itertools、_json、_locale、_lsprof、math、_md5、_multibytecodec、operator、_random、_sha256、_sha512、_sha、_struct、strop、time、unicodedata、_weakref、cPickle
- 部分模块功能受限。比如沙箱限制了您的代码最多可往标准输出和标准错误输出写出数据的大小,即sys.stdout/sys.stderr最多能写20Kb,多余的字符会被忽略。
第三方库
运行环境中还安装了除标准库以外比较常用的三方库,做为标准库的补充。支持的三方库还包括numpy。
Python UDF使用第三方库的详细介绍请参见使用第三方库。
参数与返回值类型
参数与返回值的指定方式,如下所示:
@odps.udf.annotate(signature)Python UDF目前支持的MaxCompute SQL数据类型包括Bigint、String、Double、Boolean和Datetime。SQL语句在执行之前,必须确定所有函数的参数类型和返回值类型。因此对于Python这一动态类型语言,需要通过对UDF类加decorator的方式指定函数签名。
函数签名signature通过字符串指定,命令格式如下:
arg_type_list '->' type_list
arg_type_list: type_list | '*' | ''
type_list: [type_list ','] type
type: 'bigint' | 'string' | 'double' | 'boolean' | 'datetime'- 箭头左边表示参数类型,右边表示返回值类型。
- 只有UDTF的返回值可以是多列,UDF和UDAF只能返回一列。
- *代表变长参数,使用变长参数,UDF/UDTF/UDAF可以匹配任意输入参数。
合法的signature示例如下:
'bigint,double->string' # 参数为bigint、double,返回值为string
'bigint,boolean->string,datetime' # UDTF参数为bigint、boolean,返回值为string,datetime
'*->string' # 变长参数,输入参数任意,返回值为string
'->double' # 参数为空,返回值为doubleQuery语义解析阶段会检查到不符合函数签名的用法,抛出错误禁止执行。执行时,UDF函数的参数会以函数签名指定的类型传给您。您的返回值类型也要与函数签名指定的类型一致,否则检查到类型不匹配时也会报错。MaxCompute SQL数据类型对应Python类型如下:
| MaxCompute SQL Type | Bigint | String | Double | Boolean | Datetime | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Python | Type | int | str | float | bool | int |
此外,odps.udf.int(value,[silent=True])的参数也做了调整。增加了参数silent 。当silent为True时,如果value无法转为Int ,不会抛出异常,而是返回None 。
UDF
实现Python UDF非常简单,只需要定义一个 new-style class,并实现 evaluate方法。示例如下:
from odps.udf import annotate
@annotate("bigint,bigint->bigint")
class MyPlus(object):
def evaluate(self, arg0, arg1):
if None in (arg0, arg1):
return None
return arg0 + arg1UDAF
- class odps.udf.BaseUDAF:继承此类实现Python UDAF。
- BaseUDAF.new_buffer():实现此方法返回聚合函数的中间值的buffer。buffer必须是marshallable object(比如list、dict),并且buffer的大小不应该随数据量递增。在极限情况下,buffer marshal过后的大小不应该超过2Mb。
- BaseUDAF.iterate(buffer[, args, ...]):实现此方法将args聚合到中间值buffer中。
- BaseUDAF.merge(buffer, pbuffer):实现此方法将两个中间值buffer聚合到一起,即将pbuffer merge到buffer中。
- BaseUDAF.terminate(buffer):实现此方法将中间值buffer转换为MaxCompute SQL的基本类型。
UDAF求平均值的示例如下:
@annotate('double->double') class Average(BaseUDAF):def new_buffer(self): return [0, 0] def iterate(self, buffer, number): if number is not None: buffer[0] += number buffer[1] += 1 def merge(self, buffer, pbuffer): buffer[0] += pbuffer[0] buffer[1] += pbuffer[1] def terminate(self, buffer): if buffer[1] == 0: return 0.0 return buffer[0] / buffer[1]
UDTF
- class odps.udf.BaseUDTF:Python UDTF的基类,用户继承此类,并实现process、close等方法。
- BaseUDTF.__init__():初始化方法,继承类如果实现这个方法,则必须在一开始调用基类的初始化方法 super(BaseUDTF, self).__init__() 。
init方法在整个UDTF生命周期中只会被调用一次,即在处理第一条记录之前。当UDTF需要保存内部状态时,可以在这个方法中初始化所有状态。 - BaseUDTF.process([args, ...]):这个方法由MaxCompute SQL框架调用,SQL中每一条记录都会对应调用一次process,process的参数为SQL语句中指定的UDTF输入参数。
- BaseUDTF.forward([args, ...]):UDTF的输出方法,此方法由用户代码调用。每调用一次forward,便会输出一条记录。 forward的参数为SQL语句中指定的UDTF的输出参数。
- BaseUDTF.close():UDTF的结束方法,此方法由MaxCompute SQL框架调用,并且只会被调用一次,即在处理完最后一条记录之后。
UDTF的示例如下:
#coding:utf-8
# explode.py
from odps.udf import annotate
from odps.udf import BaseUDTF
@annotate('string -> string')
class Explode(BaseUDTF):
"""将string按逗号分隔输出成多条记录
"""
def process(self, arg):
props = arg.split(',')
for p in props:
self.forward(p)引用资源
Python UDF可以通过odps.distcache模块引用资源文件,目前支持引用文件资源和表资源。
- odps.distcache.get_cache_file(resource_name):
** 返回指定名字的资源内容。resource_name为Str类型,对应当前Project中已存在的资源名。如果资源名非法或者没有相应的资源,会抛出异常。
** 返回值为file-like object ,在使用完这个object后,调用者有义务调用close方法释放打开的资源文件。
使用get_cache_file的示例如下:
@annotate('bigint->string')
class DistCacheExample(object):
def __init__(self):
cache_file = get_cache_file('test_distcache.txt')
kv = {}
for line in cache_file:
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
k, v = line.split()
kv[int(k)] = v
cache_file.close()
self.kv = kv
def evaluate(self, arg):
return self.kv.get(arg)- odps.distcache.get_cache_table(resource_name):
** 返回指定资源表的内容。resource_name为Str类型,对应当前Project中已存在的资源表名。如果资源名非法或者没有相应的资源,会抛出异常。
** 返回值为generator类型,调用者通过遍历获取表的内容,每次遍历得到的是以tuple形式存在的表中的一条记录。
使用get_cache_table的示例如下:
from odps.udf import annotate
from odps.distcache import get_cache_table
@annotate('->string')
class DistCacheTableExample(object):
def __init__(self):
self.records = list(get_cache_table('udf_test'))
self.counter = 0
self.ln = len(self.records)
def evaluate(self):
if self.counter > self.ln - 1:
return None
ret = self.records[self.counter]
self.counter += 1
return str(ret)UDF示例程序
UDF实例程序大全:
- JSON字符串获取示例
- JSON字符串值判断示例
- 不同类型数据转换JSONString示例
- 获取URL中指定位置的字符示例
- JSON字符串增加键值示例
- 取余函数示例
- 使用正则表达式替换字符串示例
- 获取字符串(含有分隔符)value示例
- 获取字符串(不含分隔符)value示例
- 获取指定日期格式的时间示例
更多详细的程序,请参考MaxCompute文档。