哈夫曼树的应用——课程设计
这个是我去年的课程设计报告,因为有学弟要我就整理了下,功能很简单,就一个加密解密还有求哈夫曼编码,但足够满足老师的要求,现在传给有需要的童鞋参考~
完整的代码及报告
以下是实验报告内容
哈夫曼树的应用——对文件进行解码和译码
一、 需求分析说明
随着信息时代的到来,信息越来越多,如何压缩信息已经是重要课题。特别是多媒体技术的发展,使得信息量大的问题凸显。
哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding)是一种无损压缩编码方式,以哈夫曼树—即最优二叉树,带权路径长度最小的二叉树,经常应用于数据压缩。在计算机信息处理中,“哈夫曼编码”是一种一致性编码法(又称"熵编码法"),用于数据的无损耗压缩。这一术语是指使用一张特殊的编码表将源字符(例如某文件中的一个符号)进行编码。这张编码表的特殊之处在于,它是根据每一个源字符出现的估算概率而建立起来的(出现概率高的字符使用较短的编码,反之出现概率低的则使用较长的编码,这便使编码之后的字符串的平均期望长度降低,从而达到无损压缩数据的目的)。这种方法是由David.A.Huffman发展起来的。例如,在英文中,e的出现概率很高,而z的出现概率则最低。当利用哈夫曼编码对一篇英文进行压缩时,e极有可能用一个位(bit)来表示,而z则可能花去 25个位(不是26)。用普通的表示方法时,每个英文字母均占用一个字节(byte),即8个位。二者相比,e使用了一般编码的1/8的长度,z则使用了 3倍多。倘若我们能实现对于英文中各个字母出现概率的较准确的估算,就可以大幅度提高无损压缩的比例。
当然本软件的目的不在于如何去压缩一个文件信息,而是通过建立哈夫曼树,由哈夫曼树编得二进制码,再译码,来了解哈夫曼树编码实现过程。(庞大的翻译内容会进行报错)
二、 主要功能
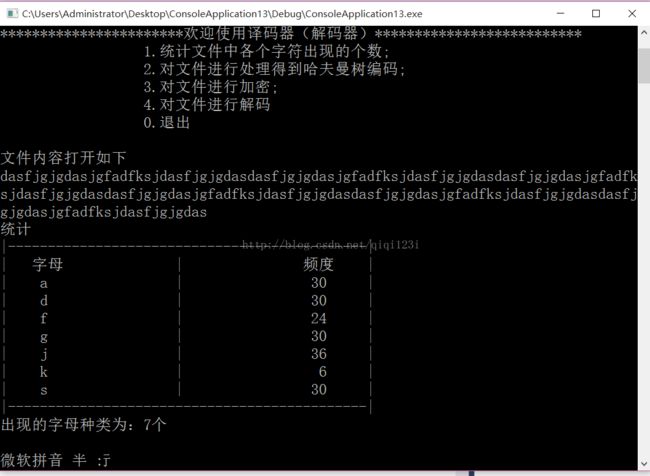
1.统计文件中各个字符出现的个数;
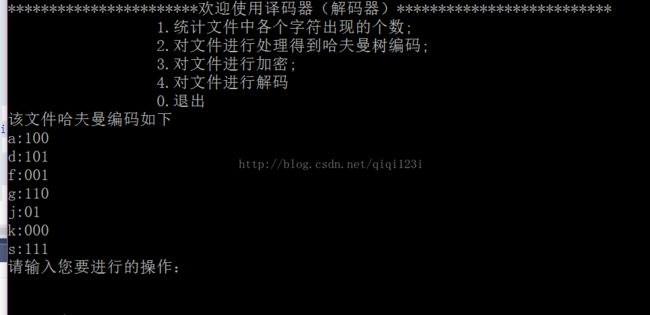
2.对文件进行处理得到哈夫曼树编码;
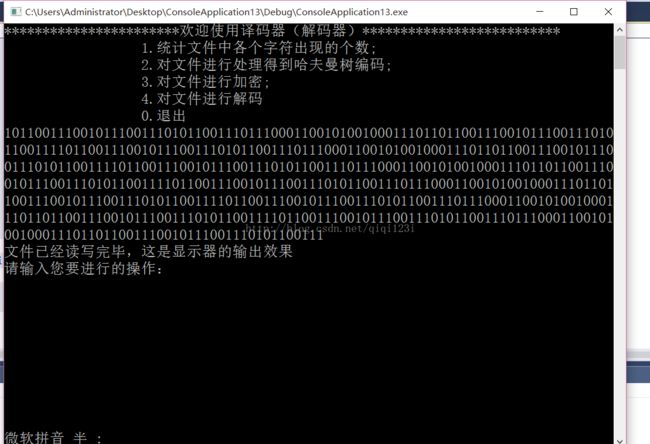
3.对文件进行加密;
4.对文件进行解码
三、 所运用到的知识点
(1)链式存储结构(用来从文件中读取数据,构造哈夫曼编码)
(2)队列的应用(主要用在解码那一块,从文件中逐个读取字符,进入队列,再一个一个判断是否是哪个编码值)
(3)构造最优二叉树,对树的基本操作
(4)对文件的操作(打开文件,读写文件)
四、核心代码实现
(一) 菜单块
while (i != 0)
{
cout << "***********************欢迎使用译码器(解码器)**************************" << endl;
cout << " 1.统计文件中各个字符出现的个数; " << endl;
cout << " 2.对文件进行处理得到哈夫曼树编码; " << endl;
cout << " 3.对文件进行加密; " << endl;
cout << " 4.对文件进行解码 " << endl;
cout << " 0.退出 " << endl;
switch (i)
{
case 1:
List.creatlist();
List.disp();
List.total(); break;
case 2:
L.CreateHT();
L.CreateHCode();
L.DispHCode(); break;
case 3:
L.CreateHT();
L.CreateHCode();
L.Revertext(); break;
/* case 0:
exit(0);*/
case 4: /*将二进制转化为字母*/
L.CreateHT();
L.CreateHCode();
L.decode(); break;
case 0:
cout << "欢迎下次使用译码器(解码器)" << endl;
break;
}
cout << "请输入您要进行的操作:";
cin >> i;
system("cls");
}
(二) 统计字符
void total() //利用一个数组,统计字母出现次数
{
linklist *s;
int j = 0;
int count[127] = { 0 }; //设置初始化
s = head->next;
int num;
while (s)
{
num = s->data;
if (num != 32) //不计算空格出现的频度
{
count[num - 0]++;
}
s = s->next;
}
cout << "统计" << endl;
cout << "|---------------------------------------------|" << endl;
cout << "| 字母 | 频度 |" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 127; i++)
{
if (count[i])
{
aa[j].data = i;
aa[j].weight = count[i];
j++;
cout << "| " << char(i) << " | " << setw(6) << count[i] << " |" << endl;
}
}
Count = j;
cout << "|---------------------------------------------|" << endl;
cout << "出现的字母种类为:" << Count << "个" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
};
(三) 创建哈夫曼树
void HuffmanClass::CreateHT() //构造哈夫曼树
{
int i, k, lnode, rnode;
double min1, min2;
for (i = 0; i < (2 * no - 1); i++) //所有结点的相关域置初值-1
{
ht[i].parent = -1;
ht[i].lchild = -1;
ht[i].rchild = -1;
}
for (i = no; i < (2 * no - 1); i++) //构造哈夫曼树,仅求非叶子结点
{
min1 = min2 = 32767.0; //初始时置最大权值
lnode = rnode = -1; //lnode和rnode为两个权重最小的节点位置
for (k = 0; k <= (i - 1); k++) //在ht数组中找权值最小的两个结点
if (ht[k].parent == -1) //只在二叉树的根节点中寻找
{
if (ht[k].weight < min1)
{
min2 = min1;
rnode = lnode;
min1 = ht[k].weight;
lnode = k;
}
else if (ht[k].weight < min2)
{
min2 = ht[k].weight;
rnode = k;
}
}
ht[lnode].parent = i; //把后面的no-1个非叶子结点处理完毕
ht[rnode].parent = i;
ht[i].weight = ht[lnode].weight + ht[rnode].weight;
ht[i].lchild = lnode; //ht[i]作为双亲结点
ht[i].rchild = rnode;
}
}
(四) 得到哈夫曼编码
void HuffmanClass::CreateHCode() //根据哈夫曼树求哈夫曼编码
{
int i, f, c;
for (i = 0; i < no; i++) //遍历下标从0到no-1的叶子结点
{
hcd[i].start = no; //从hcd[i].cd[no]开始放置哈夫曼编码
c = i;
f = ht[i].parent; //找其双亲结点
while (f != -1) //循环直至无双亲结点即到达树根结点
{
if (ht[f].lchild == c) //当前结点是双亲结点的左孩子结点
{
hcd[i].cd[hcd[i].start] = '0';
/*cout << hcd[i].cd[hcd[i].start]< (五) 对文件进行加密
void HuffmanClass::Revertext()
{
SqQueueClass L;
L.initQueue();
FILE *fin, *fout;
char ch;
if ((fin = fopen("D:\\test.txt", "r")) == NULL)
{
cout << "无法打开此文件" << endl;
exit(0);
}
if ((fout = fopen("D:\\tex.txt", "w")) == NULL)
{
cout << "无法打开此文件" << endl;
exit(0);
}
ch = fgetc(fin);//一个一个读出来
while (!feof(fin))
{
for (int i = 0; i < no; i++)
{
if (ch == ht[i].data)
{
for (int j = hcd[i].start; j <= no; j++)
{
cout << hcd[i].cd[j];
fputc(hcd[i].cd[j], fout);
}
}
}
ch = fgetc(fin); //从fin 文件中打开,再次读
}
cout << endl << "文件已经读写完毕,这是显示器的输出效果" << endl;
fclose(fin);
fclose(fout);
}
(六) 对文件进行解码
void HuffmanClass::decode()//解码
{
cout << "文件解码为:" << endl;
int mark = 0;//设置标志
int q, j, ii, jj, k, tt;
int kk = 0;
char temp[MaxQueue][MaxQueue];
char temp1[MaxQueue][MaxQueue];
SqQueueClass L;
L.initQueue();
FILE *fin;
char ch;
if ((fin = fopen("D:\\test1.txt", "r")) == NULL)
{
cout << "无法打开此文件" << endl;
exit(0);
}
for (int aa = 0; aa < no; aa++)
{
for (int bb = hcd[aa].start; bb <= no; bb++)
{
temp1[aa][(bb - hcd[aa].start)] = hcd[aa].cd[bb];
/*cout << temp1[aa][(bb - hcd[aa].start)] << " ";*/ /*保留*/
}
}
ch = fgetc(fin);//一个一个读出来
while (!feof(fin))
{
mark = 0;
L.enQueue(ch);//进队
for (j = 0, q = L.getfront() + 1; q != L.getrear() + 1; j++, q++) //一个个获得临时的01(temp)序列,以便和哈夫曼编码比较
{
temp[kk][j] = L.data[q];
}
for (ii = 0; ii < no; ii++)//哈弗曼编码放到二维数组里了
{
int zz;
zz = 0;
for (jj = 0; jj <= no - hcd[ii].start; jj++)
{
if (temp[kk][jj] == temp1[ii][jj])//若两个相等
{
zz = zz + 1;
}
}
if (zz == no - hcd[ii].start + 1)
{
cout << ht[ii].data;
mark = 1; break;
}
}
if (mark == 1)
{
L.destory();//清空队列
/*cout << "清空" << endl;*/
}
ch = fgetc(fin); //从fin 文件中打开,再次读
kk = kk + 1;
}
if (L.getfront() != L.getrear())
{
cout << "\n以下二进制串输入有错误:";
for (int j = L.getfront() + 1; j != L.getrear() + 1; j++)
cout << L.data[j];
}
else
cout << endl;
cout << endl << "文件已经读写完毕,这是显示器的输出效果" << endl;
fclose(fin);
}
五、 结果展示
菜单:
计算字符出现的频度:
得到哈夫曼编码:
加密:
解码:
六、 总结
做这个课程设计是熬了两个晚上做出来的,其中有一个如何解密,如何判断从文件读取的数据构成的数组与我的每一个哈夫曼编码值是否相等,因为哈夫曼编码的存储方式是存在数组,且从start元素到no元素才是正确的值,所以非常麻烦。我一直在不停地用循环判断,甚至要重新写我如何得到哈夫曼的编码,因为实在太困难了。索性,学到了一个好方法,就是中断,通过中断可以查看自己的程序走到哪一步了,再跟着步骤和本应该有的步骤进行对比,就很容易发现错误,这一次最大的收获就是学会熟练使用中断。还有可以用到之前学到的知识点,比如这里用了队列进行读取数据,以前从没有想过队列可以这样用。还有要集思广益,不一定去网上找代码就是不好的,因为适合别人的代码不一定适合自己,还是要自己写,主要是学习他们的思路,然后用自己的方法做出来。这个.cpp的功能其实还有缺陷,就是如果我对非常多的‘0’‘1’进行译码是会出现错误,我不知道是什么问题,不过会继续深入,另外还有一个可以提升的地方是对文件的操作应该是让用户自己选择文件而不是固定文件,不过,因为自己的代码太冗余,很难实现这个操作,不过会继续学习如何写出漂亮的代码。
完整的代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#include
#include
#define MaxSize 100
#define MaxQueue 100
struct linklist //单链表结点类型
{
char data;
linklist *next;
};
struct pindu //每个字母出现的频度结点类型
{
char data; //字母
int weight; //权值
};
template
struct HTNode //哈夫曼结点类型
{
T data;//结点值
double weight;//权值
int parent;//双亲结点
int lchild;//左孩子结点
int rchild;//右孩子结点
};
struct HCode //哈夫曼编码类型
{
char cd[MaxSize]; //存放当前结点的哈夫曼编码
int start; //用cd[start..no]存放哈夫曼编码,包括start和no
};
class sqlist
{
private:
linklist *head;
int Count; //计算个数
public:
pindu aa[100]; //存放频度的信息
sqlist()
{
head = new linklist[100];
head->next = NULL;
Count = 0;
}
void destorysqlist() //删除单链表,不能用析构,因为随时不用,会对哈夫曼数的构造造成影响
{
linklist *pre, *p;
pre = head;
p = pre->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
delete pre;
pre = p; p = p->next;
}
delete pre;
}
int getCount() //得到权值个数
{
linklist *s;
int j = 0;
int count[127] = { 0 }; //设置初始化
s = head->next;
int num;
while (s)
{
num = s->data;
if (num != 32) //不计算空格出现的频度
{
count[num - 0]++;
}
s = s->next;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 127; i++)
{
if (count[i])
{
aa[j].data = i;
aa[j].weight = count[i];
j++;
}
}
Count = j;
return Count;
}
void creatlist() //创建单链表,把文件中的字母写进单链表中
{
linklist *s, *r;
r = head;
FILE *fin;
char ch;
/*char filename[100] = { 0 };
cout << "请输入文件路径:";
cin >> filename;*/
if ((fin = fopen("H:\\test.txt", "r")) == NULL)
{
cout << "无法打开此文件" << endl;
exit(0);
}
ch = fgetc(fin);
while (!feof(fin))
{
s = new linklist;
s->data = ch;
r->next = s;
r = s;
ch = fgetc(fin); //从fin 文件中打开
}
r->next = NULL;
fclose(fin);
/* cout << endl;
cout << endl;*/
}
void disp() //输出单链表内容,即文章内容
{
cout << endl << "文件内容打开如下" << endl;
linklist *s;
s = head->next;
int count[257] = { 0 };
while (s)
{
cout << s->data;
s = s->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
void total() //利用一个数组,统计字母出现次数
{
linklist *s;
int j = 0;
int count[127] = { 0 }; //设置初始化
s = head->next;
int num;
while (s)
{
num = s->data;
if (num != 32) //不计算空格出现的频度
{
count[num - 0]++;
}
s = s->next;
}
cout << "统计" << endl;
cout << "|---------------------------------------------|" << endl;
cout << "| 字母 | 频度 |" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 127; i++)
{
if (count[i])
{
aa[j].data = i;
aa[j].weight = count[i];
j++;
cout << "| " << char(i) << " | " << setw(6) << count[i] << " |" << endl;
}
}
Count = j;
cout << "|---------------------------------------------|" << endl;
cout << "出现的字母种类为:" << Count << "个" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
};
template
class SqQueueClass //队列进行解码操作
{
private:
int front;
int rear;
public:
T data[MaxQueue];
void initQueue()//初始化
{
front = rear = 0;
}
void destory()//清空队列
{
initQueue();
}
void enQueue(T e)//进队
{
//if ((rear + 1) % MaxQueue == front)//队满
// return false;
rear = (rear + 1) % MaxQueue;
data[rear] = e;
}
void deQueue(T &e)//出队
{
/*if (rear == front)
return false;*/
front = (front + 1) % MaxQueue;
e = data[front];
}
void disp()
{
for (int i = front + 1; i <= rear; i++)
{
cout << data[i] << " ";
}
}
int getfront()
{
return front;
}
int getrear()
{
return rear;
}
};
template
class HuffmanClass
{
private:
int no; //权值个数
HTNode ht[MaxSize]; //存放哈夫曼树
HCode hcd[MaxSize]; //存放哈夫曼编码
public:
HuffmanClass(); //Setvalue设置初值
void CreateHT(); //构造哈夫曼树
void CreateHCode(); //根据哈夫曼树求哈夫曼编码
void DispHCode(); //输出哈夫曼编码
void Revertext(); //将文本转化成二进制代码存入另一个文件中
void decode(); //解码,把二进制转化成文字
};
template
HuffmanClass::HuffmanClass() //设置初值
{
pindu str[100];
sqlist List;//
List.creatlist();//
for (int i = 0; i < List.getCount(); i++)
{
str[i].data = List.aa[i].data;
str[i].weight = List.aa[i].weight;
}
no = List.getCount(); //权值个数
for (int i = 0; i <(2 * no - 1); i++)
{
ht[i].data = str[i].data;
ht[i].weight = str[i].weight;
}
}
template
void HuffmanClass::CreateHT() //构造哈夫曼树
{
int i, k, lnode, rnode;
double min1, min2;
for (i = 0; i < (2 * no - 1); i++) //所有结点的相关域置初值-1
{
ht[i].parent = -1;
ht[i].lchild = -1;
ht[i].rchild = -1;
}
for (i = no; i < (2 * no - 1); i++) //构造哈夫曼树,仅求非叶子结点
{
min1 = min2 = 32767.0; //初始时置最大权值
lnode = rnode = -1; //lnode和rnode为两个权重最小的节点位置
for (k = 0; k <= (i - 1); k++) //在ht数组中找权值最小的两个结点
if (ht[k].parent == -1) //只在二叉树的根节点中寻找
{
if (ht[k].weight < min1)
{
min2 = min1;
rnode = lnode;
min1 = ht[k].weight;
lnode = k;
}
else if (ht[k].weight < min2)
{
min2 = ht[k].weight;
rnode = k;
}
}
ht[lnode].parent = i; //把后面的no-1个非叶子结点处理完毕
ht[rnode].parent = i;
ht[i].weight = ht[lnode].weight + ht[rnode].weight;
ht[i].lchild = lnode; //ht[i]作为双亲结点
ht[i].rchild = rnode;
}
}
template
void HuffmanClass::CreateHCode() //根据哈夫曼树求哈夫曼编码
{
int i, f, c;
for (i = 0; i < no; i++) //遍历下标从0到no-1的叶子结点
{
hcd[i].start = no; //从hcd[i].cd[no]开始放置哈夫曼编码
c = i;
f = ht[i].parent; //找其双亲结点
while (f != -1) //循环直至无双亲结点即到达树根结点
{
if (ht[f].lchild == c) //当前结点是双亲结点的左孩子结点
{
hcd[i].cd[hcd[i].start] = '0';
/*cout << hcd[i].cd[hcd[i].start]<
void HuffmanClass::DispHCode()
{
cout << "该文件哈夫曼编码如下" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < no; i++)
{
cout << ht[i].data << ":";
for (int j = hcd[i].start; j <= no; j++) //因为start一直在变化,一直在减小,存的值是从下往上走的,就是start减小的顺序
{
cout << hcd[i].cd[j];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
template
void HuffmanClass::Revertext()
{
SqQueueClass L;
L.initQueue();
FILE *fin, *fout;
char ch;
if ((fin = fopen("H:\\test.txt", "r")) == NULL)
{
cout << "无法打开此文件" << endl;
exit(0);
}
if ((fout = fopen("H:\\tex.txt", "w")) == NULL)
{
cout << "无法打开此文件" << endl;
exit(0);
}
ch = fgetc(fin);//一个一个读出来
while (!feof(fin))
{
for (int i = 0; i < no; i++)
{
if (ch == ht[i].data)
{
for (int j = hcd[i].start; j <= no; j++)
{
cout << hcd[i].cd[j];
fputc(hcd[i].cd[j], fout);
}
}
}
ch = fgetc(fin); //从fin 文件中打开,再次读
}
cout << endl << "文件已经读写完毕,这是显示器的输出效果" << endl;
fclose(fin);
fclose(fout);
}
template
void HuffmanClass::decode()//解码
{
cout << "文件解码为:" << endl;
int mark = 0;//设置标志
int q, j, ii, jj, k, tt;
int kk = 0;
char temp[MaxQueue][MaxQueue];
char temp1[MaxQueue][MaxQueue];
SqQueueClass L;
L.initQueue();
FILE *fin;
char ch;
if ((fin = fopen("H:\\test1.txt", "r")) == NULL)
{
cout << "无法打开此文件" << endl;
exit(0);
}
for (int aa = 0; aa < no; aa++)
{
for (int bb = hcd[aa].start; bb <= no; bb++)
{
temp1[aa][(bb - hcd[aa].start)] = hcd[aa].cd[bb];
/*cout << temp1[aa][(bb - hcd[aa].start)] << " ";*/ /*保留*/
}
}
ch = fgetc(fin);//一个一个读出来
while (!feof(fin))
{
mark = 0;
L.enQueue(ch);//进队
for (j = 0, q = L.getfront() + 1; q != L.getrear() + 1; j++, q++) //一个个获得临时的01(temp)序列,以便和哈夫曼编码比较
{
temp[kk][j] = L.data[q];
}
for (ii = 0; ii < no; ii++)//哈弗曼编码放到二维数组里了
{
int zz;
zz = 0;
for (jj = 0; jj <= no - hcd[ii].start; jj++)
{
if (temp[kk][jj] == temp1[ii][jj])//若两个相等
{
zz = zz + 1;
}
}
if (zz == no - hcd[ii].start + 1)
{
cout << ht[ii].data;
mark = 1; break;
}
}
if (mark == 1)
{
L.destory();//清空队列
/*cout << "清空" << endl;*/
}
ch = fgetc(fin); //从fin 文件中打开,再次读
kk = kk + 1;
}
if (L.getfront() != L.getrear())
{
cout << "\n以下二进制串输入有错误:";
for (int j = L.getfront() + 1; j != L.getrear() + 1; j++)
cout << L.data[j];
}
else
cout << endl;
cout << endl << "文件已经读写完毕,这是显示器的输出效果" << endl;
fclose(fin);
}
void menu()
{
HuffmanClass L;
sqlist List;
int i;
cout << "***********************欢迎使用译码器(解码器)**************************" << endl;
cout << " 1.统计文件中各个字符出现的个数; " << endl;
cout << " 2.对文件进行处理得到哈夫曼树编码; " << endl;
cout << " 3.对文件进行加密; " << endl;
cout << " 4.对文件进行解码 " << endl;
cout << " 0.退出 " << endl;
cout << "请输入您要进行的操作:";
cin >> i;
while (i != 0)
{
cout << "***********************欢迎使用译码器(解码器)**************************" << endl;
cout << " 1.统计文件中各个字符出现的个数; " << endl;
cout << " 2.对文件进行处理得到哈夫曼树编码; " << endl;
cout << " 3.对文件进行加密; " << endl;
cout << " 4.对文件进行解码 " << endl;
cout << " 0.退出 " << endl;
switch (i)
{
case 1:
List.creatlist();
List.disp();
List.total(); break;
case 2:
L.CreateHT();
L.CreateHCode();
L.DispHCode(); break;
case 3:
L.CreateHT();
L.CreateHCode();
L.Revertext(); break;
/* case 0:
exit(0);*/
case 4: /*将二进制转化为字母*/
L.CreateHT();
L.CreateHCode();
L.decode(); break;
case 0:
cout << "欢迎下次使用译码器(解码器)" << endl;
break;
}
cout << "请输入您要进行的操作:";
cin >> i;
system("cls");
}
}
int main()
{
menu();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 代码注意事项:
1.统计文件中各个字符出现的个数;
2.对文件进行处理得到哈夫曼树编码;
3.对文件进行加密;
4.对文件进行解码
2.在H盘创建一个名为test1.txt的文件,存放01字符;
3.在H盘创建一个名为tex.txt的文件(可以什么都不放);
(可自行换盘,代码要改)
功能一:求test.txt的各个字符出现的频度;
功能二:求出哈夫曼编码(根据test.txt中的字符);
功能三:对test.txt的文件进行加密(根据求得的哈夫曼编码来),然后把结果存放到tex.txt中;
功能四:是对test1中的01字符进行解码,翻译成对应的字符,将结果输出到屏幕;(就是根据功能二得到的哈夫曼树,对test1.txt的内容进行解码)