AGC019F YES or NO
题意
有n+m个问题,其中n个的答案是YES,m个的答案是NO,你现在从前往后回答问题,按照最优策略猜答案,回答完当前问题后你会知道这个问题的答案,问期望答对的题目的数量
n,m<=500000
题解
假设当前还剩a个问题答案是YES,b个问题答案是NO,那么显然最优策略是答更大的那个,即答对的概率是max(a,b)/(a+b)
将回答的所有情况画成一个图得到:
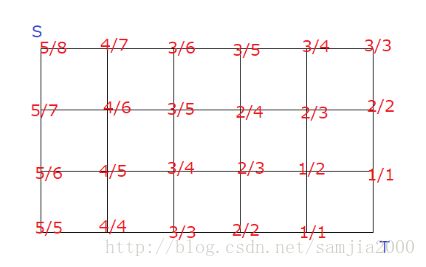
答案就是从S走到T的路径的权值和的期望值
将相邻有差值的边画出来可以得到:
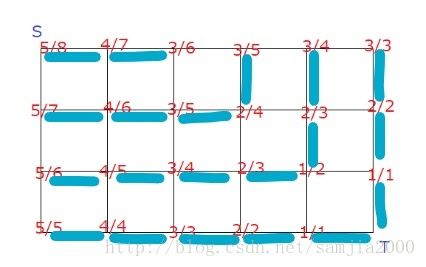
那么,对于一条路径来说,如果经过了蓝色的边,他的权值就会减一。
考虑处理一条斜对角线上,所有路径的权值和,要维护这个东西就要计算这条对角线上经过竖蓝边的方案数和横蓝边的方案数,移动对角线的时候就减一下。
由于横竖有很好的对称性,这里只讨论横边的情况。
考虑一条横边(x,y)–>(x,y-1),经过他的方案数就等于从(n,m)到(x,y)的方案数乘上从(x,y-1)到(0,0)的方案数,就等于从(n,m)到(x,y)的方案数乘上从(x,y)到(0,1)的方案数,即我们可以把一条横边变成点来处理。
这样就有两种情况:
1、
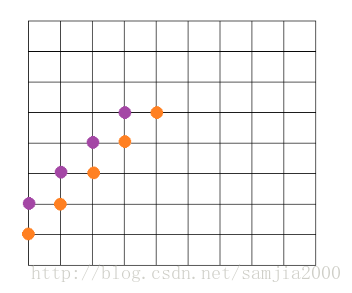
最右边的橙点上没有紫点
从紫色转移到橙色,经过这些点的方案数要加上经过最右边的橙色点上面那条边的方案数
2、
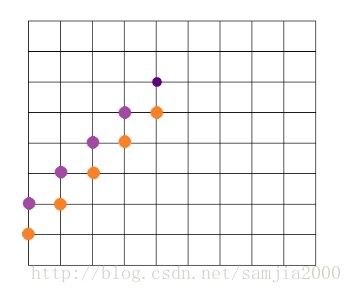
最右边的橙点上有紫点
这样就需要减掉经过最右边的紫点右边那条边的方案数
对于竖边类似处理
Code
#include1]+mo-comb(n-(w+1),m-(i-w+1))*comb(i-w+1,w-1)%mo)%mo;
printf("%d\n",w);
}
LL now=comb(n,m)*m%mo,ans=now*inv[n+m]%mo;
fd(i,n+m-1,1){
now=(now+mo-v0[i])%mo;
now=(now+mo-v1[i])%mo;
ans=(ans+now*inv[i]%mo)%mo;
}
ans=ans*nycomb(n,m)%mo;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}