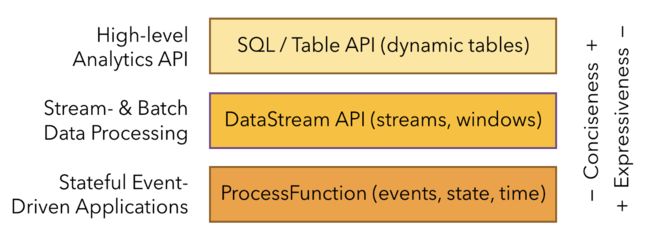
Flink提供了三层API,每层API针对不同的用例,在简洁性和表达性之间提供了不同的权衡。
下面我们简要的介绍每一个API,讨论他的应用程序并且展示代码示例。
1、处理函数(ProcessFunctions)
处理函数 是Flink提供的最具有表现力的接口。Flink 提供的ProcessFuntion是用来处理来自于一个或者两个输入流或者一段时间窗内的聚合的独立event。ProcessFunction提供了对时间和状态的细粒度控制。一个ProcessFunction可以任意的修改它的状态,并且也可以注册定时器在将来触发一个回调函数。因此,ProcessFunction可以根据需要为有很多有状态的事件驱动的应用实现复杂的单事件业务逻辑。
下面的例子展示了用来操作KeyedStream并且可以匹配START 和 END 的KeyedProcessFunction,这个函数会记录他的状态的时间戳,并且在四小时之内注册一个定时器。如果在定时器执行之前接收到END event,这个函数会计算END和START这段区间,清空状态并且返回值。另外,这个定时器仅仅触发来清空状态。
/**
* Matches keyed START and END events and computes the difference between
* both elements' timestamps. The first String field is the key attribute,
* the second String attribute marks START and END events.
*/
public static class StartEndDuration
extends KeyedProcessFunction, Tuple2> {
private ValueState startTime;
@Override
public void open(Configuration conf) {
// obtain state handle
startTime = getRuntimeContext()
.getState(new ValueStateDescriptor("startTime", Long.class));
}
/** Called for each processed event. */
@Override
public void processElement(
Tuple2 in,
Context ctx,
Collector> out) throws Exception {
switch (in.f1) {
case "START":
// set the start time if we receive a start event.
startTime.update(ctx.timestamp());
// register a timer in four hours from the start event.
ctx.timerService()
.registerEventTimeTimer(ctx.timestamp() + 4 * 60 * 60 * 1000);
break;
case "END":
// emit the duration between start and end event
Long sTime = startTime.value();
if (sTime != null) {
out.collect(Tuple2.of(in.f0, ctx.timestamp() - sTime));
// clear the state
startTime.clear();
}
default:
// do nothing
}
}
/** Called when a timer fires. */
@Override
public void onTimer(
long timestamp,
OnTimerContext ctx,
Collector> out) {
// Timeout interval exceeded. Cleaning up the state.
startTime.clear();
}
}
这个例子说明了KeyedProcessFunction的表现力,但是也强调了它是一个相当冗长的接口。
2、DataStream API
DataStream API为很多常用的流式计算操作提供了基元,比如窗口(windowing)、记录的转换(record-at-a-time transformations),并且通过查询外部存储来丰富event。DataStream API对于Java和Scala都是可用的,并且它是基于函数的,比如map()、reduce()以及aggregate()。函数可以通过扩展接口或者Java或Scala的lambda表达式来定义。
下例展示了如果对点击流进行会话处理,并且计算每个会话的点击次数。
DataStream clicks = ...
DataStream> result = clicks
// project clicks to userId and add a 1 for counting
.map(
// define function by implementing the MapFunction interface.
new MapFunction>() {
@Override
public Tuple2 map(Click click) {
return Tuple2.of(click.userId, 1L);
}
})
// key by userId (field 0)
.keyBy(0)
// define session window with 30 minute gap
.window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.minutes(30L)))
// count clicks per session. Define function as lambda function.
.reduce((a, b) -> Tuple2.of(a.f0, a.f1 + b.f1));
3、SQL & Table API
Flink提供了两种关系型的API,Table API 和 SQL 。对于批处理和流处理来说,这两种API是一致的,比如无边界的实时的流或者有边界的记录好的流产生相同的结果,都是使用相同的语义来执行查询。Table API 和 SQL 使用 Apache Calcite 进行转换、校验和查询优化。他们可以无缝的与DataStream和DataSet API结合,并且支持用户定义的分层级的(scalar)、聚合的、表值(table-value)类型的函数。
Flink的关系型API目的是为了简化数据分析、数据流水(data pipeline)以及ETL应用的定义。
下面的例子展示了会话处理点击流并且计算每个会话的点击数量的SQL 查询语句。这是与DataStream API例子中相同的场景。
SELECT userId, COUNT(*)
FROM clicks
GROUP BY SESSION(clicktime, INTERVAL '30' MINUTE), userId