1. 绘制矩形
1.1 直线方式绘制矩形代码
int i;
HDC hdc;
hdc = GetWindowDC(hWnd);
POINT apt[5] = { 200, 200, 400, 200, 400, 400, 200, 400, 200, 200 };
MoveToEx(hdc, apt[0].x, apt[0].y, NULL);
for (i = 1; i < 5; i++)
{
LineTo(hdc, apt[i].x, apt[i].y);
}
1.2 连接点的方式绘制矩形代码
HDC hdc;
hdc = GetWindowDC(hWnd);
POINT apt[5] = { 200, 200, 400, 200, 400, 400, 200, 400, 200, 200 };
Polyline(hdc, apt, 5);
1.3 直接 Rectangle 绘制
HDC hdc;
hdc = GetWindowDC(hWnd);
Rectangle(hdc, 200, 200, 400, 400);
1.4 矩形示意图
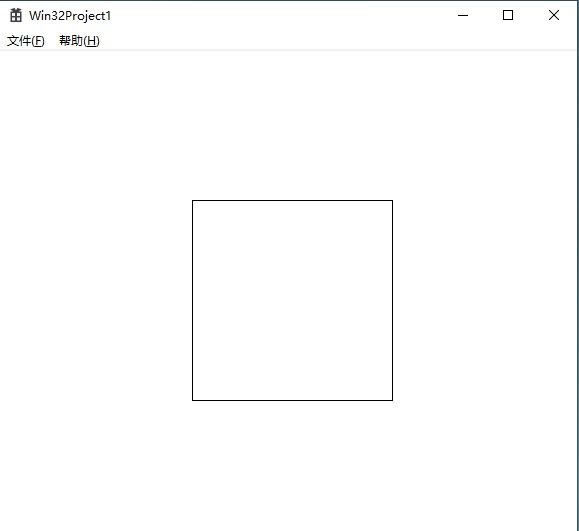
2. 绘制正弦波
2.1 正弦波代码
#define NUM 1000
#define TWOPI (2 * 3.1415926535)
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
static int cxClient, cyClient;
HDC hdc;
int i;
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
POINT apt[NUM];
switch (message)
{
case WM_SIZE:
cxClient = LOWORD(lParam);
cyClient = HIWORD(lParam);
return 0;
case WM_PAINT:
hdc = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2, NULL);
LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2);
for (i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
{
apt[i].x = i * cxClient / NUM;
apt[i].y = (int)(cyClient / 2 * (1 - sin(TWOPI * i / NUM)));
}
Polyline(hdc, apt, NUM);
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
return 0;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
}
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
2.2 正弦波示意图

参考资料

