并查集 Union Find
在计算机科学中,并查集是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不交集(Disjoint Sets)的合并及查询问题。有一个联合-查找算法(Union-find Algorithm)定义了两个用于此数据结构的操作:
Find:确定元素属于哪一个子集。它可以被用来确定两个元素是否属于同一子集。
Union:将两个子集合并成同一个集合。
由于支持这两种操作,一个不相交集也常被称为联合-查找数据结构(Union-find Data Structure)或合并-查找集合(Merge-find Set)。
为了更加精确的定义这些方法,需要定义如何表示集合。一种常用的策略是为每个集合选定一个固定的元素,称为代表,以表示整个集合。接着,Find(x) 返回 xx 所属集合的代表,而 Union 使用两个集合的代表作为参数。https://leetcode-cn.com/tag/union-find/
- 最小生成树问题 Kruskal:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40794973/article/details/103037329
- 200. 岛屿数量:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40794973/article/details/102972631
- 130. 被围绕的区域:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40794973/article/details/102975239
- Bridges:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40794973/article/details/103068130
一种很不一样的树形结构
连接问题 Connectivity Problem
网络中节点间的连接状态
- 网络是个抽象的概念:用户之间形成的网络
数学中的集合类实现
连接问题和路径问题
比路径问题要回答的问题少
- 和二分查找作比较
- 和select作比较
- 和堆作比较
1 并查集主要的操作
2 并查集的基本数据表示
2 实现 Union Find
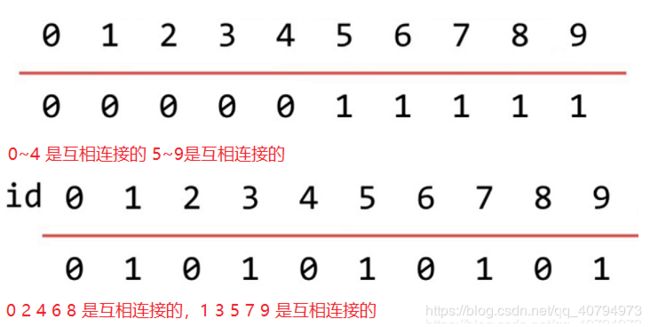
2.1 第一版Quick Find
Quick Find
Quick Find 下的 Union
// 第一版Union-Find
public class UnionFind1 {
private int[] id; // 第一版Union-Find本质就是一个数组
private int count; // 数据个数
public UnionFind1(int n) {
count = n;
id = new int[n];
// 初始化, 每一个id[i]指向自己, 没有合并的元素
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
id[i] = i;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(1)复杂度
private int find(int p) {
assert p >= 0 && p < count;
return id[p];
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(1)复杂度
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(n) 复杂度
public void unionElements(int p, int q) {
int pID = find(p);
int qID = find(q);
if (pID == qID) {
return;
}
// 合并过程需要遍历一遍所有元素, 将两个元素的所属集合编号合并
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (id[i] == pID) {
id[i] = qID;
}
}
}
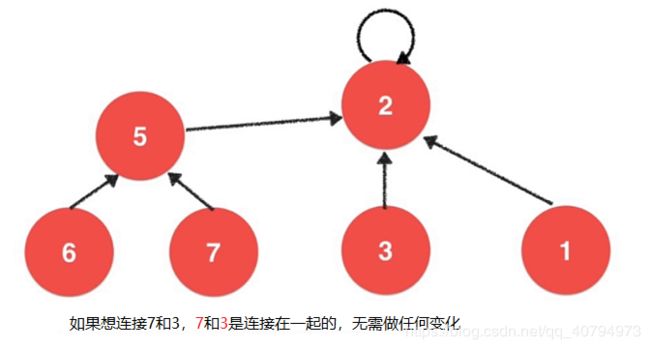
}2.2 第二版Quick-Union
将每一个元素,看做是一个节点
Quick Union 下的数据表示
Quick Union 演示
// 第二版Union-Find
public class UnionFind2 {
// 第二版Union-Find, 使用一个数组构建一棵指向父节点的树
// parent[i]表示第一个元素所指向的父节点
private int[] parent;
private int count; // 数据个数
// 构造函数
public UnionFind2(int count) {
parent = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
private int find(int p) {
assert (p >= 0 && p < count);
// 不断去查询自己的父亲节点, 直到到达根节点
// 根节点的特点: parent[p] == p
while (p != parent[p]) {
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public void unionElements(int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if (pRoot == qRoot) {
return;
}
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
}
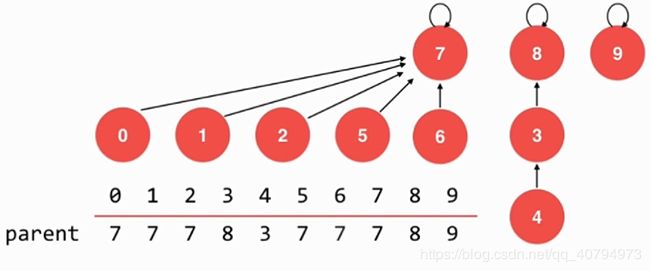
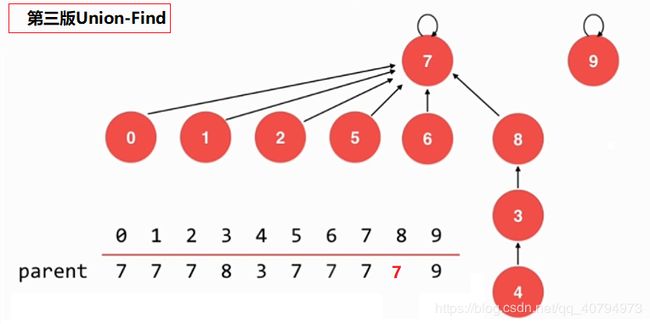
}2.3 第三版基于size的优化
// 第三版Union-Find
public class UnionFind3 {
private int[] parent; // parent[i]表示第一个元素所指向的父节点
private int[] sz; // sz[i]表示以i为根的集合中元素个数
private int count; // 数据个数
// 构造函数
public UnionFind3(int count) {
parent = new int[count];
sz = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
private int find(int p) {
assert (p >= 0 && p < count);
// 不断去查询自己的父亲节点, 直到到达根节点
// 根节点的特点: parent[p] == p
while (p != parent[p]) {
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public void unionElements(int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if (pRoot == qRoot) {
return;
}
// 根据两个元素所在树的元素个数不同判断合并方向
// 将元素个数少的集合合并到元素个数多的集合上
if (sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot]) {
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
} else {
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
}
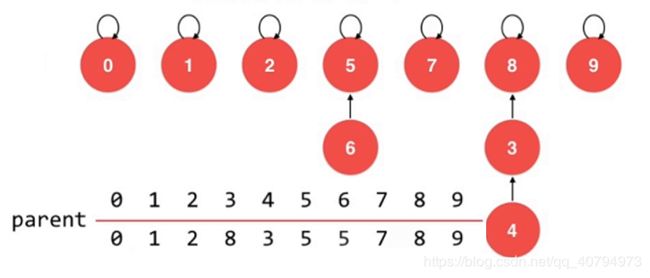
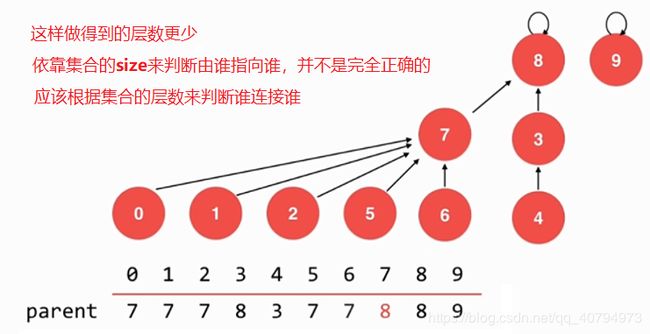
}2.4 第四版基于rank的优化
rank[i] 表示根节点为i的树的高度
union 4,2
// 第四版Union-Find
public class UnionFind4 {
private int[] rank; // rank[i]表示以i为根的集合所表示的树的层数
private int[] parent; // parent[i]表示第i个元素所指向的父节点
private int count; // 数据个数
// 构造函数
public UnionFind4(int count) {
rank = new int[count];
parent = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
private int find(int p) {
assert (p >= 0 && p < count);
// 不断去查询自己的父亲节点, 直到到达根节点
// 根节点的特点: parent[p] == p
while (p != parent[p]) {
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public void unionElements(int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if (pRoot == qRoot) {
return;
}
// 根据两个元素所在树的层数不同判断合并方向
// 将层数少的集合合并到层数多的集合上
if (rank[pRoot] < rank[qRoot]) {
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
} else if (rank[qRoot] < rank[pRoot]) {
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
} else { // rank[pRoot] == rank[qRoot]
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
rank[qRoot] += 1; // 此时才维护rank的值
}
}
}
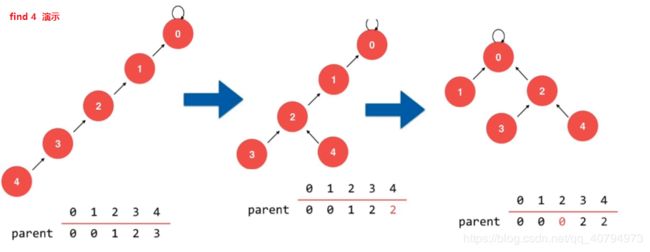
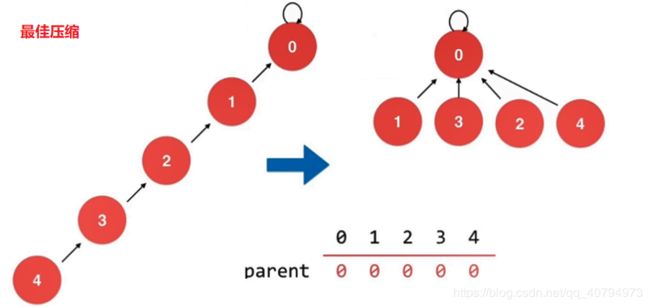
2.5 第五版路径压缩迭代实现
路径压缩 Path Compression
// 我们设计一个UF的接口,让不同的UF实现具体实现这个接口
public interface UF {
boolean isConnected(int p, int q);
void unionElements(int p, int q);
}// 第五版Union-Find, 路径压缩使用迭代实现
public class UnionFind5 implements UF {
// rank[i]表示以i为根的集合所表示的树的层数
// 在后续的代码中, 我们并不会维护rank的语意, 也就是rank的值在路径压缩的过程中, 有可能不在是树的层数值
// 这也是我们的rank不叫height或者depth的原因, 他只是作为比较的一个标准
// http://coding.imooc.com/learn/questiondetail/7287.html
private int[] rank;
public int[] parent; // parent[i]表示第i个元素所指向的父节点 后续, 我们要在外部操控并查集的数据, 在这里使用public
private int count; // 数据个数
// 构造函数
public UnionFind5(int count){
rank = new int[count];
parent = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public int find(int p){
assert( p >= 0 && p < count );
// path compression 1
while( p != parent[p] ){
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
@Override
public boolean isConnected(int p , int q ){
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
@Override
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot ) {
return;
}
// 根据两个元素所在树的元素个数不同判断合并方向
// 将元素个数少的集合合并到元素个数多的集合上
if( rank[pRoot] < rank[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
}
else if( rank[qRoot] < rank[pRoot]){
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
}
else{ // rank[pRoot] == rank[qRoot]
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
rank[qRoot] += 1; // 此时, 我维护rank的值
}
}
// 打印输出并查集中的parent数据
public void show(){
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ) {
System.out.print( parent[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}2.6 第六版路径压缩递归实现
// 我们的第六版Union-Find, 路径压缩使用递归实现
public class UnionFind6 implements UF {
private int[] rank;
public int[] parent; // parent[i]表示第i个元素所指向的父节点 后续, 我们要在外部操控并查集的数据, 在这里使用public
private int count; // 数据个数
// 构造函数
public UnionFind6(int count){
rank = new int[count];
parent = new int[count];
this.count = count;
// 初始化, 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ){
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
public int find(int p){
assert( p >= 0 && p < count );
// path compression 2, 递归算法
if( p != parent[p] ) {
parent[p] = find( parent[p] );
}
return parent[p];
}
// 查看元素p和元素q是否所属一个集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
@Override
public boolean isConnected(int p , int q ){
return find(p) == find(q);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
// O(h)复杂度, h为树的高度
@Override
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot ) {
return;
}
// 根据两个元素所在树的元素个数不同判断合并方向
// 将元素个数少的集合合并到元素个数多的集合上
if( rank[pRoot] < rank[qRoot] ){
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
}
else if( rank[qRoot] < rank[pRoot]){
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
}
else{ // rank[pRoot] == rank[qRoot]
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
rank[qRoot] += 1; // 此时, 我维护rank的值
}
}
// 打印输出并查集中的parent数据
public void show(){
for( int i = 0 ; i < count ; i ++ ) {
System.out.print( parent[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}//// 为了能够方便地看出两种路径压缩算法的不同,我们只使用有5个元素的并查集进行试验
//int n = 5;
//UnionFind5 uf5 = new UnionFind5(n);
//UnionFind6 uf6 = new UnionFind6(n);
//// 我们将我们的并查集初始设置成如下的样子
//// 0
//// /
//// 1
//// /
//// 2
//// /
//// 3
//// /
//// 4
//for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++){
// uf5.parent[i] = i-1;
// uf6.parent[i] = i-1;
//}
//// 现在, 我们对两个并查集调用find(4)操作
//uf5.find(n-1);
//uf6.find(n-1);
//// 通过show, 我们可以看出, 使用迭代的路径压缩, 我们的并查集变成这个样子:
//// 0
//// / \
//// 1 2
//// / \
//// 3 4
//System.out.println("UF implements Path Compression by recursion:");
//uf5.show();
//System.out.println();
//// 使用递归的路径压缩, 我们的并查集变成这个样子:
//// 0
//// / / \ \
//// 1 2 3 4
//System.out.println("UF implements Path Compression without recursion:");
//uf6.show();
//// 大家也可以调大n的值, 看看结果的不同3 时间复杂度
并查集的操作,时间复杂度近乎是O(1)的