oracle的安装及查询
1. Oracle简介
1.1. Oracle数据库是什么?
- Oracle Database,又名Oracle RDBMS,简称Oracle。是甲骨文公司推出的一款关系数据库管理系统。
- Oracle数据库系统是目前世界上流行的关系数据库管理系统,拥有可移植性好、使用方便、功能强等优点,在各类大、中、小、微机环境中都适用。
- Oracle是一种高效率、可靠性好的、适应高吞吐量的数据库解决方案。
1.2. 数据库和实例
Oracle数据库服务器由一个数据库和至少一个数据库实例组成。 数据库是一组存储数据的文件,而数据库实例则是管理数据库文件的内存结构。此外,数据库是由后台进程组成。
数据库和实例是紧密相连的,所以我们一般说的Oracle数据库,通常指的就是实例和数据库。
下图说明了Oracle数据库服务器体系结构:

在这种体系结构中,Oracle数据库服务器包括两个主要部分:文件(Oracle数据库)和内存(Oracle实例)。
1.3. 表空间
2. Oracle的安装和卸载
下载地址:
https://www.oracle.com/database/technologies/112010-win64soft.html
https://www.oracle.com/database/technologies/instant-client/downloads.html
2.1. Oracle的安装
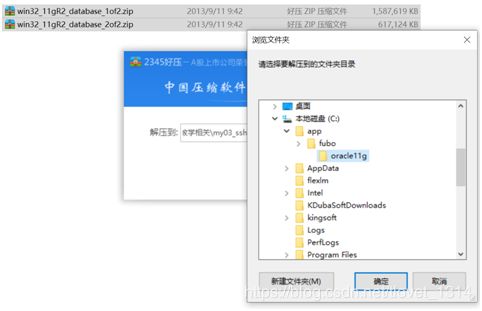
- 有一点需要注意,Oracle11g的安装程序分成2个文件,下载后将2个文件解压到同一目录即可。将2个压缩文件一起选中,鼠标右键—解压文件,如下图所示。两个压缩文件解压到同一目录下。需要注意的是,路径名称中最好不要出现中文、空格等不规则字符。
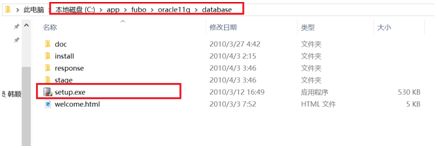
- 打开相应的解压路径,找到安装文件“setup.exe”,双击进行安装,如下图所示:
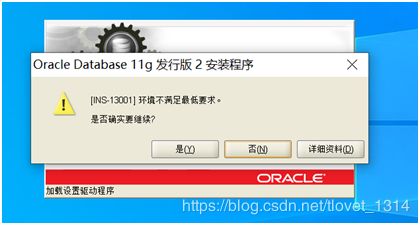
也许会出现上图提示,我们点击是即可。 - 配置安全更新。电子邮件可写可不写,取消下面的“我希望通过My Oracle Support接受安全更新(W)”,如下图所示,单击下一步。


- 安装选项。直接选择默认的“创建和配置数据库”,如下图所示,单击下一步。

- 系统类。由于咱们安装的是桌面类,所以选择“桌面类”,如下图所示,单击下一步

- 典型安装。
- 数据库版本。选择“企业版”,如下图所示,单击下一步。
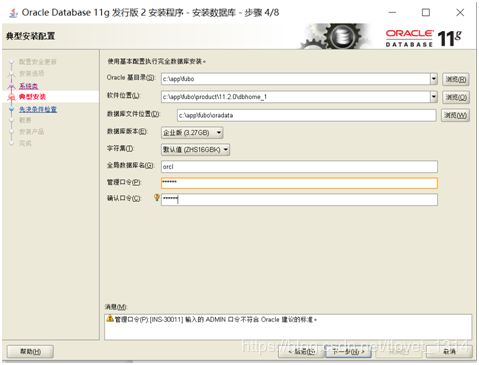
- 安装位置。填入安装路径(只需要填“Oracle基目录”即可,“软件位置”会自动生成),如下图所示,单击下一步。
- 数据库标识符。填入全局数据库名和SID,如下图所示,单击下一步。
- 配置选项。切换到“字符集”选项卡,选择“使用Unicode(AL32UTF8)”,如下图所示,单击下一步。

- 概要。完成先决条件检查后,单击完成就可以正式开始安装了,如下图所示,单击完成。

- 安装产品。安装完成后,会列出相关数据库配置清单,这个最好截图保存,如下图所示,单击确定
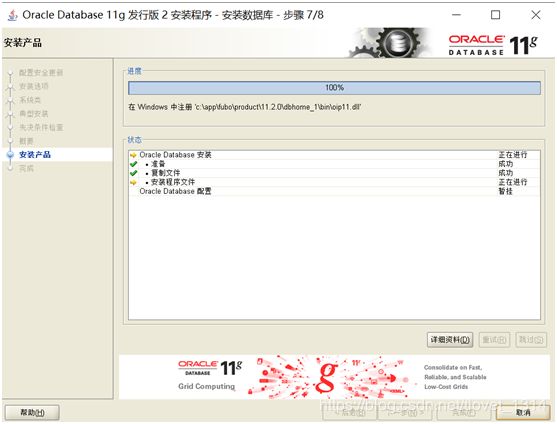
- 完成。这时安装已完成,单击关闭即可。
- 测试一下。打开Oracle自带的SQL PLUS,如下图所示。
- 输入用户名、密码(就是第18步设置的密码),测试成功!可以直接输入SQL语句了!需要注意的是,这里Oracle输入的口令是不显示的
2.2. Oracle的卸载
- 停用oracle服务:进入计算机管理,在服务中,找到oracle开头的所有服务,右击选择停止

- 在开始菜单中,找到Universal Installer,运行Oracle Universal Installer,单击卸载产品

- 在产品清单窗口中,单击全部展开,除了OraDb11g_home1外,勾选其他项目,单击删除

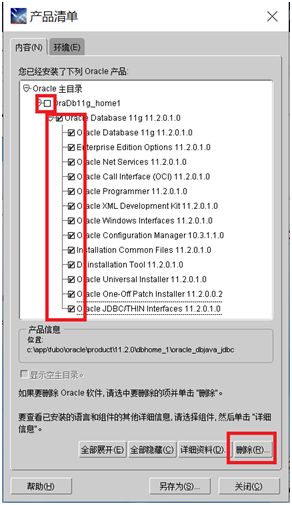
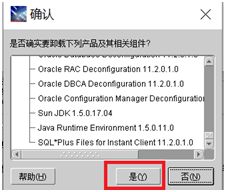

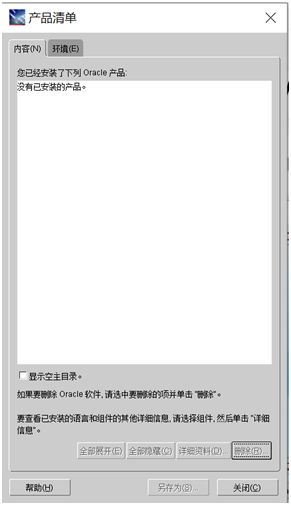
- 按Windows徽标键和R键,打开运行窗口,输入regedit,打开注册表,依次展开HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE,找到oracle,删除之
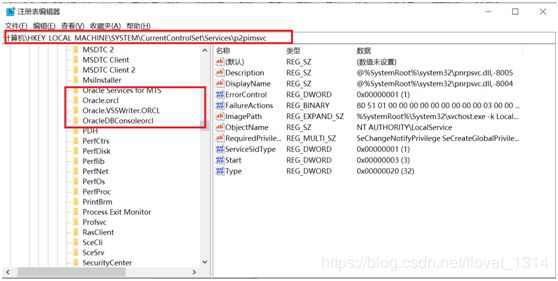
- 依次展开HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services中,删除所有oracle开头的项

- 依次展开HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Eventlog\Application,删除所有oracle开头的项;
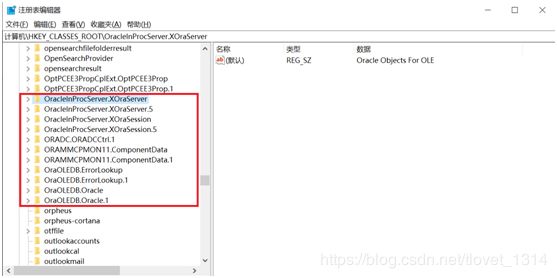
- 在HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT,删除以ora开头的项
- 重启电脑,删除oracle目录,删除Oracle的安装目录app等
3. Oracle和MySQL的区别
都遵循SQL标准,都有自己的方言
- Oracle是以用户为单位
- MySQL是数据库为单位
Eg:开发一个系统,使用Oracle和MySql
Oralce------->表空间------->用户------>表
MySQL------->数据库------>表 - Oracle是多用户的
- MySQL是多数据库的
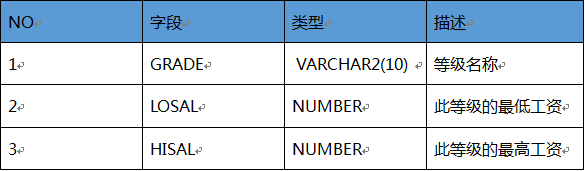
4. Oracle测试账号scott
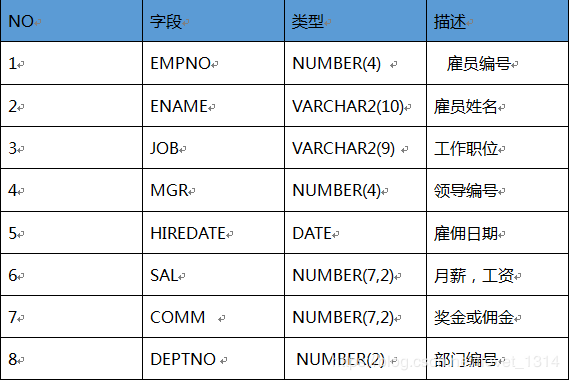
EMP(雇员表)
DEPT(部门表)
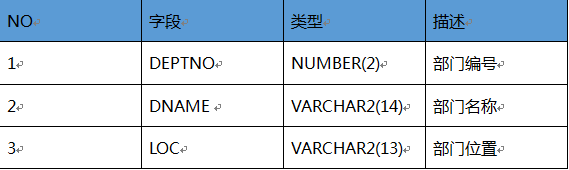
BOUNS(奖金表)
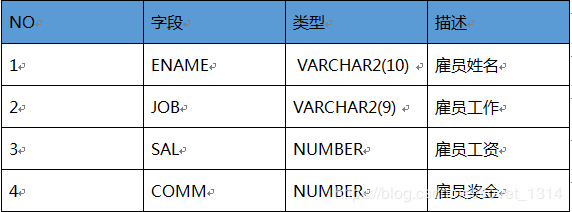
SALGRADE(工资等级表)
5. dual表
该表是oracle系统提供的一个虚表(伪表),主要用来补齐语法结构,用来构成select的语法规则。
- 查看当前用户,可以在 SQL Plus中执行下面语句 select user from dual;
- 用来调用系统函数
- select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’) from dual;–获得当前系统时间
- select SYS_CONTEXT(‘USERENV’,‘TERMINAL’) from dual;–获得主机名
- select SYS_CONTEXT(‘USERENV’,‘language’) from dual;–获得当前 locale
+select dbms_random.random from dual;–获得一个随机数
- 得到序列的下一个值或当前值,用下面语句
- select your_sequence.nextval from dual;–获得序列your_sequence的下一个值
- select your_sequence.currval from dual;–获得序列your_sequence的当前值
- 可以用做计算器 select 7*9 from dual;
6. SQL基本查询
SQL:structured query language 结构查询语言
6.1. SQL分类面试题
请说一下SQL的分类,及各类的常用操作符
DDL:数据库定义语言,create、drop、alter、truncate
DML:数据库操作语言,insert、delete、update
DCL:数据库控制语言,grant(授权)、 revoke(回收)
DQL:数据库查询语言,select … from… where… group by… having… order by…limit…
6.2. 最基本查询
select * from emp;
6.3. 别名查询
– as 别名 as可以省略
– 如果别名中有空格等特殊符号,需要把别名使用“”
select ENAME as “雇 员”,HIREDATE “入职时间%” from emp;
6.4. 去除重复数据
– 涉及关键字distinct
–单列去除
select distinct job from emp;
–多列去除,多列都相同才认为重复
select distinct job,deptno from emp;
6.5. 查询中的四则运算
加减乘除
select 1+1 from dual;
select 1*2 from dual;
select 2/2.5 from dual;
select 2-3 from dual;
案例:获取员工年薪(月薪*12+奖金)
–null值,代表不确定,不可以进行四则运算
select sal*12+comm from emp;
–解决null值问题,nvl(comm,0)
select sal*12+nvl(comm,0) from emp;
6.6. 字符串拼接
使用||进行拼接
–java中使用+拼接
–oracle中使用,||或concat(str1,str2)
–mysql中使用, concat(str,str2)
–oracle中“”主要用来取别名,‘’用来表示字符串
–oracle 中 select “姓名:”||ename from emp,是会报错的
select ename||hiredate from emp;
6.7. Oracle和Mysql方言测试
select 1+1; --oracle报错
select 1+1 from dual; --oracle需要指定dual表
select 1+1; --mysql结果为2
7. 条件查询
sql查询中where后面的条件
7.1. 关系运算符
> >= < <= != <>
7.2. 逻辑运算符
and or not
7.3. 其他运算符
- like模糊查询
- in(set) 在某个集合内
- between…and在某个区间范围内
- is null判断为空is not null 判断不为空
7.4. 案例
- 查询每个月能得到奖金的员工信息
select * from emp where comm is not null
- 查询工资在1500-3000的员工信息
select * from emp where sal between 1500 and 3000
select * from emp where sal>=1500 and sal<=3000
- 查询名字在某个范围的员工信息,eg:范围:ALLEN、JONES、TY
select * from emp where ename in (‘ALLEN’,‘JONES’,‘TY’)
- 查询员工姓名中第三个字符是O的员工信息
使用like关键字,like后的表达式中特色字符
%:匹配多个字符
_:匹配一个字符
如果表达式中需要把%或_当作字符,需要使用进行转义,需要使用escape声明转义字符
select * from emp where ename like ‘__O%’;
update emp set ename=‘ALL_EN’ where ename=‘ALLEN’;
select * from emp where ename like ‘%_%’ escape ‘’;
8. 排序查询
涉及关键字 order by asc[desc]
asc:升序,默认为升序,desc:降序
注:排序中空值处理,默认为nulls first|last(默认为null值排在最后)
select * from emp order by comm nulls first;
查询员工信息,按照部门编号升序,工资降序
select * from emp order by deptno asc,sal desc;
9. 分组查询
select 分组条件,分组后的操作 from 表名 group by 分组条件 having 条件过滤
案例:
统计员工平均工资,并查询平均工资大于1500的员工
select empno,avg(sal) from emp group by empno having avg(sal)>1500 ;
注:
SQL编写顺序
Select … from … where … group by … having … order by …
SQL执行顺序
from…where… group by … having … select … order by …
where和having的区别
- where后面不能接聚合函数,可以接单行函数
- having后可以接聚合函数
10. Oracle中的函数
注:数据库中的函数必须有返回值。
函数分类:单行函数和多行函数
10.1. 多行函数
特点:对某一列的所有符合条件的行都进行处理
多行函数也就是我们的聚合函数。聚合函数会忽略空值。
max(), min(), count(), avg(), sum()
- 统计员工的奖金总和(2200)
select sum(comm) from emp;
- 统计员工的平均工资
select avg(sal) from emp;
- 统计员工的平均奖金(2200/14)
–以下查询时错误的,null值影响了
select avg(comm) from emp;
–以下查询才正确
select sum(comm)/count(1) from emp;
10.2. 单行函数
特点:对某一行的某个值进行处理
单行函数分类:
10.2.1. 数值函数
select ceil(45.926) from dual; --46
select floor(45.926) from dual; --45
Select abs(-12) from dual; --12
–四舍五入
select round(45.926,2) from dual; --45.93
select round(45.926,1) from dual; --45.9
select round(45.926,0) from dual; --46
select round(45.926,-1) from dual; --50
select round(45.926,-2) from dual; --0
select round(65.926,-2) from dual; --100
–截断
select trunc(45.926,2) from dual; --45.92
select trunc(45.926,1) from dual; --45.9
select trunc(45.926,0) from dual; --45
select trunc(45.926,-1) from dual; --40
select trunc(45.926,-2) from dual; --0
select trunc(65.926,-2) from dual; --0
–取余
select mod(10,2) from dual; --0
select mod(10,3) from dual; --1
select mod(10,3.3) from dual;–0.1
10.2.2. 字符函数
- 截取字符串函数:substr(str,start,len)
str:要截取的字符串
start:开始索引0或1都是从第一个字符开始截取,包含第一个字符
len:截取到字符的长度
select substr(‘abcdefg’,0,3) from dual; --abc
select substr(‘abcdefg’,1,3) from dual; --abc
select substr(‘abcdefg’,2,3) from dual; --bcd
- 获取字符串长度函数:length(str)
select length(‘abcdefg’) from dual;
- 去除字符串左右两边的空白:trim(str)
select trim(’ abcdef ') from dual;
- 替换字符中指定字符:replace(str,oldstr,newstr)
select replace(‘ababcccabdd’,‘ab’,‘A’) from dual;–AAcccAdd
10.2.3. 日期函数
- 获取当前日期
select sysdate from dual;
- 查询x个月后的日期add_months(sysdate,x)
select add_months(sysdate,4) from dual;
- 查询x天后的日期sysdate+x
select sysdate+3 from dual;
- 查询两个日期之间的间隔月数
select months_between(sysdate+32,sysdate) from dual;
案例:
- 查询员工的入职的天数
select ceil(sysdate-hiredate) from emp;
- 查询员工的入职周数
select (sysdate-hiredate)/7 from emp;
- 查询员工的入职月数
select months_between(sysdate,hiredate) from emp;
- 查询员工的入职年份
select months_between(sysdate,hiredate)/12 from emp;
10.2.4. 转换函数
- 字符转数值
to_number(str),其实可以自动转换
select 119+‘110’ from dual; --229
select 119+to_number(‘110’) from dual; --229
- 数值转字符
to_char(number,’格式’)
select to_char(sal,’$9999,9.99’) from emp;
- 日期转字符
to_char(date,’格式’)
–to_char(sysdate,‘d’) 每周第几天
select to_char(sysdate,‘d’) from dual;
–to_char(sysdate,‘dd’) 每月第几天
select to_char(sysdate,‘dd’) from dual;
–to_char(sysdate,‘ddd’) 每年第几天
select to_char(sysdate,‘ddd’) from dual;
–to_char(sysdate,‘ww’) 每年第几周
select to_char(sysdate,‘ww’) from dual;
–to_char(sysdate,‘mm’) 每年第几月
select to_char(sysdate,‘mm’) from dual;
–to_char(sysdate,‘q’) 每年第几季
select to_char(sysdate,‘q’) from dual;
–to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy’) 年
select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy’) from dual;
select to_char(sysdate,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss’) from dual;
- 字符串转日期
select to_date(‘2019/09/02’,‘yyyy/mm/dd’) from dual;
–查询1981年-1985年入职的员工
select * from emp where to_char(emp.hiredate,‘yyyy’)>=1980 and to_char(emp.hiredate,‘yyyy’)<=1985
select * from emp where emp.hiredate between to_date(‘1980’,‘yyyy’) and to_date(‘1985’,‘yyyy’)
10.2.5. 通用函数
【语法】NVL (expr1, expr2)
【功能】若expr1为NULL,返回expr2;expr1不为NULL,返回expr1。
注意两者的类型要一致
select nvl(null,‘s2’) from dual;
select nvl(‘s1’,‘s2’) from dual;
【语法】NVL2 (expr1, expr2, expr3)
【功能】expr1不为NULL,返回expr2;
expr1为NULL,返回expr3。
expr2和expr3类型不同的话,expr3会转换为expr2的类型
select nvl2(null,‘s1’,‘s2’) from dual; --s2
select nvl2(‘s0’,‘s1’,‘s2’) from dual; --s1
【语法】NULLIF (expr1, expr2)
【功能】expr1和expr2相等返回NULL,不相等返回expr1
select nullif(‘s1’,‘s2’) from dual; --s1
select nullif(‘s1’,‘s1’) from dual; --null
select nullif(3,3) from dual; -null
【语法】COALESCE(c1, c2, …,cn)
【功能】返回列表中第一个非空的表达式,如果所有表达式都为空值则返回1个空值
【参数】c1, c2, …,cn,字符型/数值型/日期型,必须类型相同或null
select coalesce(2,3) from dual;
select coalesce(’’,‘aa’,‘bb’) from dual;
11. 条件表达式
- case 字段 when 值1 then 新值1 when 值2 then 新值2 else 默认值 end
select
case ename
when ‘SCOTT’ then ‘考斯特’
when ‘SMITH’ then ‘斯密斯’
else ‘路人’
end
from emp;
- decode(字段,if,then,if,then,else) oracle特有
select decode(ename,‘SMITH’,‘斯密斯’,‘SCOTT’,‘考斯特’,‘路人’) from emp;
12. 多表查询
12.1. 笛卡尔积(全连接)
没有where条件的交叉连接将产生连接表所涉及的笛卡尔积。即table_a的行数*table_b的行数的结果集。
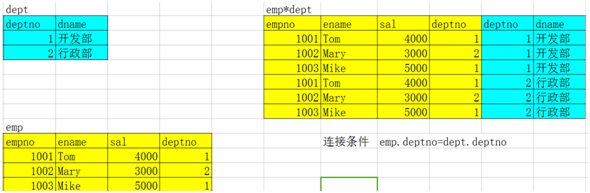
注:结果没有实际意义
12.2. 内连接
12.2.1. 等值连接
- 显式连接
select a.,b. from a inner join b on a.id=b.id
- 隐式连接
select a.,b. from a,b where a.id=b.id
案例:
查询员工的编号、姓名、部门名称
select e.empno,e.ename,t.dname from emp e join dept t on e.deptno=t.deptno;
12.2.2. 不等值连接
不等值连接查询就是无条件判断,若查询多个表内的数据,其中的数据不会同步,各自把各自的展现出来,没有任何关联。笛卡儿积数据除了等值连接后的数据。
12.2.3. 自连接
自连接的连接的两种表是同一张表
案例:
查询拥有上司的员工的编号、姓名、上司编号、上司姓名
select * from emp e1 ,emp e2 where e1.mgr=e2.empno
查询拥有上司的员工的编号、姓名、员工部门名称、员工工资等级、上司编号、上司姓名、上司部门名称
–查询拥有上司的员工的编号、姓名、员工部门名称、员工工资等级、上司编号、上司姓名、上司部门名称
–1.查询拥有上司的员工的编号、姓名、上司编号、上司姓名
select e.ename,e.empno,e.mgr from emp e,emp e2 where e.mgr=e2.empno;
–2.给符合的员工找部门
select e.ename,e.empno,e.mgr,d1.dname from emp e,emp e2,dept d1 where e.mgr=e2.empno and e.deptno=d1.deptno
–3.给上司找部门
select e.ename,e.empno,e.mgr, d1.dname “员工部门”,e2.ename “上司名称”,d2.dname “上司部门” from emp e,emp e2,dept d1,dept d2 where e.mgr=e2.empno and e.deptno=d1.deptno and e2.deptno=d2.deptno
–4.获取员工工资等级,还需进行连表,和工资表进行连接
select e.ename,
e.empno,
e.mgr,
s.grade “员工工资等级”,
d1.dname “员工部门”,
e2.ename “上司名称”,
d2.dname “上司部门”
from emp e, emp e2, dept d1, dept d2,salgrade s
where e.mgr = e2.empno
and e.deptno = d1.deptno
and e2.deptno = d2.deptno
and e.sal>=s.losal and e.sal<=s.hisal;
12.3. 外连接
12.3.1. 左外连接
left outer join
查询数据:左表中的所有数据, 如果右表中没有对应的数据则置为空 outer 关键字可以省略
案例:
查询员工编号,及其上司的编号,上司名称
select * from emp e1 left join emp e2 on e1.mgr= e2.empno
12.3.2. 右外连接
right outer join
查询数据:右表中的所有数据, 如果左表中没有对应的数据则置为空outer 关键字可以省略
select * from emp e1 right join dept d on e1.deptno=d.deptno
13. 子查询
子查询是一个嵌套在 SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE 或 DELETE 语句或其他子查询中的查询,子查询(内查询)在主查询之前一次执行完成,子查询的结果被主查询(外查询)使用,子查询要包含在括号内,将子查询放在比较条件的右侧,多行操作符对应多行子查询。
子查询作用:
1)可以作为另一个查询的条件
2)可以作为一张表
子查询注意的问题:
- 子查询需要添加括号
- 可以在where select having from后面 都可以使用子查询
- 不可以在group by后面使用子查询
- 主查询和子查询可以不是同一张表;只要子查询返回的结果 主查询可以使用即可
- 单行子查询只能使用单行操作符;多行子查询只能使用多行操作符
案例:
查询员工中最高工资的人员信息
–查询员工中最高工资的人员信息
–1.查询最高工资
select max(sal) from emp;
–2.查询工资为5000的员工信息
select * from emp where sal=(select max(sal) from emp);
查询每个部门最低员工的信息和它所在部门的信息
–1.查询各个部门最低工资
select deptno,min(sal) minsal from emp group by deptno;
–2.查询各个部门最低工资的员工
select e.* from emp e ,
(select deptno,min(sal) minsal from emp group by deptno) t
where e.deptno=t.deptno and e.sal=t.minsal
–3.查询各个部门最低工资的员工信息和部门信息
select e.*,d.dname,d.loc from emp e ,
(select deptno,min(sal) minsal from emp group by deptno) t,dept d
where e.deptno=e.deptno and e.sal=t.minsal and e.deptno=d.deptno
13.1. 单行子查询
将子查询和比较运算符联合使用,必须保证子查询返回的值不能多于一个
案例:
查询出比雇员7654工资高,同时和7788从事相同工作的员工信息
select * from emp where sal>(select sal from emp where empno=7654) and job = (select job from emp where empno=7788)
13.2. 多行子查询
多行子查询,子查询的结果是多行,选择的比较运算符要使用多行比较运算符。
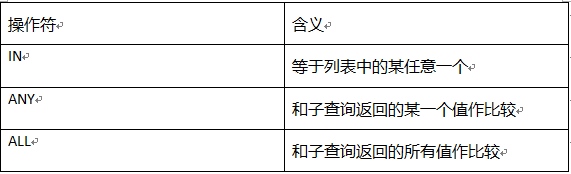
案例:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44545511/article/details/89080333
查询领导信息
select * from emp where empno in(select distinct mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
查询比任意领导编号小的员工信息
select * from emp where empno
查询比所有领导编号大的员工信息
select * from emp where empno >all (select distinct mgr from emp where mgr is not null);
13.3. exists子查询
exists子查找如果有数据,则进行主查询
exists子查询无数据,则不进行
案例:
查询有员工的部门信息
–查询有员工的部门信息
select * from dept where deptno in (select distinct deptno from emp )
select d.* from dept d where exists (select empno from emp e where e.deptno=d.deptno );
14. 补充知识rownum和rowid
14.1. rownum
rownum:oracle的关键字,表示伪列,系统自动生成的一列,用来标识行号。是Oracle中特有的,启始值为1,查询出一条记录,值增1。
数据库查询数据,是一条一条查询,而不是一次性都查询出来。
select e.,rownum from emp e where rownum>2; --查询不出数据,默认rownum值1,不符合条件查询不出数据
select e.,rownum from emp e where rownum>=1; --查询出所有数据
select e.*,rownum from emp e where rownum<=3; --查询前三条数据
总结:rownum不用做大于运算。
14.2. rowid
rowid表示每行记录的物理地址。
案例:
create table p(
name nvarchar2(50)
);
insert into p values (‘阿狗’);
select * from p;
去除重复列
delete from p p1 where p1.rowid>(select min(rowid) from p p2 where p1.name=p2.name )
15. 集合运算
15.1. 并集
将两个查询结果进行合并。关键字为union/union all
union:合并会去重,并且会根据第一个字段进行排序
union all:只合并不去重
案例:
工资大于1500,或者20号部门下的员工
select * from emp where sal>1500 or deptno=20
select * from emp where sal>1500 union select * from emp where deptno=20
–由于我们的数据可能来自不同的表,如果是不同表第一种就查询不正确了
15.2. 交集
将两边的查询结果进行交集运算。关键字为intersect
案例:
工资大于1500,且在20号部门下的员工
select * from emp where sal>1500 intersect select * from emp where deptno=20
15.3. 差集
返回第一个查询结果,且不属于第二个查询的结果。关键字minus
案例:
查询1981年入职的,且不是总裁和经理的员工信息
–查询1981年入职的,且不是总裁和经理的员工信息
–1.查询1981年入职的
select * from emp where to_char(hiredate,‘yyyy’)=1981
minus
–2.查询1981年入职的总裁和经理
select * from emp where (job=‘PRESIDENT’ or job =‘MANAGER’) and to_char(hiredate,‘yyyy’)=1981
15.4. 集合运算注意
- 列的查询顺序要一致
- 列的查询数量要一致,如果没有使用null进行填充
–查询1981年入职的,且不是总裁和经理的员工信息
–1.查询1981年入职的
select deptno,ename,null from emp where to_char(hiredate,‘yyyy’)=1981
minus
–2.查询1981年入职的总裁和经理
select deptno,ename,empno from emp where (job=‘PRESIDENT’ or job =‘MANAGER’) and to_char(hiredate,‘yyyy’)=1981

