KdTree理解与实现(Java)
KdTree理解与实现(Java)
- 抛出问题
- KdTree简介
- 原理简介
- 代码实现
- Point.java
- Rect.java
- KdTree.java
- 复杂度比较
- 结语
抛出问题
如果让你设计一个外卖系统,你的数据库中有所有外卖商家所在的经纬度,那么如何能有效地根据用户的位置筛选出所有附近的商家?
最直接的方法是根据城市或者城市的每个区(如崂山区,市南区…)来对商家进行分类,然后根据用户所在的区返回同一区域下的所有商家。这个方法可以解决大部分问题,但是如果用户位于两个区的分界线周围怎么办?
KdTree简介
KdTree 是以二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)为原型的用于空间检索的数据结构,能够在随机分布的空间内以 O(log2N) 的时间复杂度实现对平面内点的搜索以及 O(log2N) + R 的复杂度查询平面内任意矩形内的所有点(R为矩形内点的个数)。 KdTree的应用十分广泛,包括且不限于范围搜索,最邻近点搜索,物理引擎中的碰撞检测以及地理节点(如外卖商家)数据库等。
原理简介
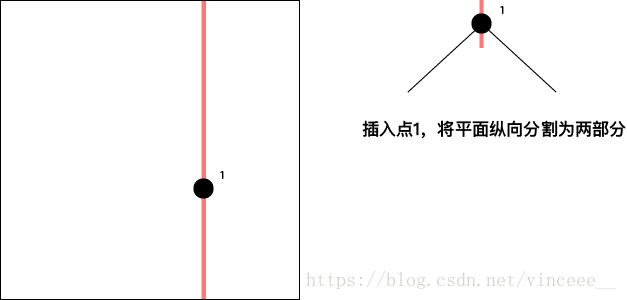
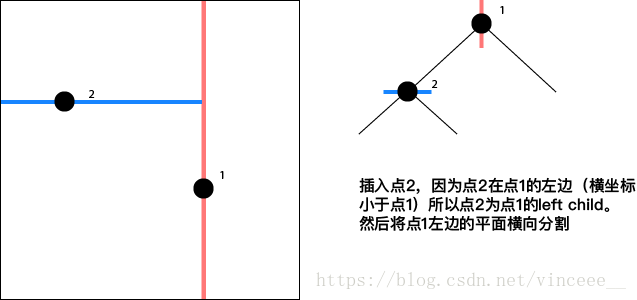
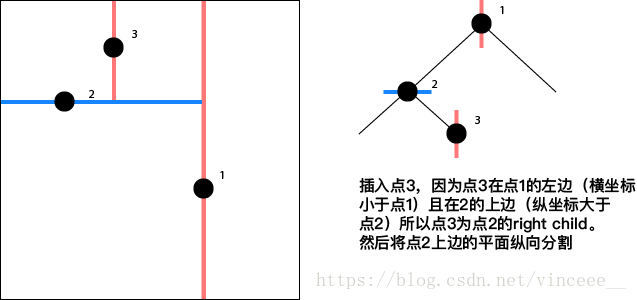
KdTree的实现方法与BST十分相似,以最常用的二维平面的KdTree为例,其每个节点存储一个二维的坐标点,并将平面空间以该点所在的横线/竖线递归地分割成两个子空间。
以width = 1.0, height = 1.0的单位平面为例,依次插入下列点
Note:
- 点对平面的分割方式是横向/纵向按照层次交替出现(根节点是哪个方向都可以)。
- 插入节点的方法类似于BST,即从根节点开始,(设要插入的节点为Pinsert,当前遍历的节点为Pcurrent)如果Pinsert在Pcurrent的左边或者下边,那么就访问Pcurrent的left child, 反之访问right child直到成为叶子节点。
- 本KdTree不支持删除操作。
代码实现
在介绍KdTree实现之前先定义两个辅助类Point(用来表示点)和Rect(用来表示矩形)
Point.java
用来表示一个坐标点,在本博客的语境下只需要两个方法:计算与另一点的距离(以平方和的形式) 和 判断两点是否相等。
// @file Point.java
// @author 王成昊
// @date 2018.10.14
public class Point {
public final double x;
public final double y;
// Point类是 immutable datatype
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// 为了减少计算量,一般使用平方和来表示距离
public double distanceSquareTo(Point that) {
double dx = that.x - this.x;
double dy = that.y - this.y;
return dx * dx + dy * dy;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object that) {
if (this == that) return true;
if (that == null) return false;
if (that.getClass() != this.getClass()) return false;
Point point = (Point) that;
return (x == point.x) && (y == point.y);
}
}
Rect.java
用来表示一个矩形,在本例中使用四个坐标值来表示一个矩形。需要的方法是 判断矩形是否包含一个点 和 计算矩形和某点的距离(平方和的形式)
// @file Rect.java
// @author 王成昊
// @date 2018.10.14
public class Rect {
// 分别表示左下顶点和右上顶点
public final double minX;
public final double minY;
public final double maxX;
public final double maxY;
// Rect类是 immutable datatype
public Rect(double x0, double y0, double x1, double y1) {
minX = x0;
minY = y0;
maxX = x1;
maxY = y1;
}
// 判断该点是否位于该矩形之内
public boolean contains(Point point) {
return (point.x >= minX) && (point.x <= maxX)
&& (point.y >= minY) && (point.y <= maxY);
}
// 计算矩形到某一点的最近距离(以平方和的形式)
public double distanceSquareToPoint(Point point) {
double dx = 0.0;
double dy = 0.0;
if (point.x < minX) dx = minX - point.x;
else if (point.x > maxX) dx = point.x - maxX;
if (point.y < minY) dy = minY - point.y;
else if (point.y > maxY) dy = point.y - maxY;
return dx * dx + dy * dy;
}
}
KdTree.java
本例中KdTree将实现4个功能:
- 插入
- 判断是否包含某点
- 查询任意矩形内的所有点
- 查询距离某一点最近的点
// @file KdTree.java
// @author 王成昊
// @date 2018.10.14
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class KdTree {
// 节点类,其中 rect 成员表示该节点所分割的平面,
// 即它的左右孩子所表示的空间之和,该成员用于判断
// 最邻近点
private class Node {
Point point;
Rect rect;
Node left;
Node right;
Node (Point p, Rect r) {
point = p;
rect = r;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
// 根节点
private Node root;
// 构造函数
public KdTree() {
root = null;
}
// 插入, 用同名私有方法递归实现, 默认根节点是纵向分割
public void insert(Point point) {
root = insert(point, root, false, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
private Node insert(Point point, Node node, boolean isVertical,
double x0, double y0, double x1, double y1) {
if (node == null) {
return new Node(point, new Rect(x0, y0, x1, y1));
}
// 改变分割方向
isVertical = !isVertical;
// 判断要插入的点在当前点的左/下还是右/上
double value0 = isVertical ? point.x : point.y;
double value1 = isVertical ? node.point.x : node.point.y;
if (value0 < value1) {
node.left = insert(point, node.left, isVertical,
x0, y0, isVertical ? node.point.x : x1, isVertical ? y1 : node.point.y);
} else {
node.right = insert(point, node.right, isVertical,
isVertical ? node.point.x : x0, isVertical ? y0 : node.point.y, x1, y1);
}
return node;
}
// 判断是否包含该点, 用同名私有方法递归实现
public boolean contains(Point point) {
return contains(point, root, false);
}
private boolean contains(Point point, Node node, boolean isVertical) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (node.point.equals(point)) return true;
// 改变分割方向
isVertical = !isVertical;
// 判断要查询的点在当前点的左/下还是右/上
double value1 = isVertical ? point.x : point.y;
double value2 = isVertical ? node.point.x : node.point.y;
if (value1 < value2) {
return contains(point, node.left, isVertical);
} else {
return contains(point, node.right, isVertical);
}
}
// 返回矩形范围内的所有点, 用同名私有方法递归实现
public Iterable<Point> range(Rect rect) {
LinkedList<Point> result = new LinkedList<Point>();
range(rect, root, false, result);
return result;
}
private void range(Rect rect, Node node, boolean isVertical, LinkedList<Point> bag) {
if (node == null) return;
// 改变分割方向
isVertical = !isVertical;
Point point = node.point;
if (rect.contains(point)) bag.add(point);
// 判断当前点所分割的两个空间是否与矩形相交
double value = isVertical ? point.x : point.y;
double min = isVertical ? rect.minX : rect.minY;
double max = isVertical ? rect.maxX : rect.maxY;
if (min < value) {
range(rect, node.left, isVertical, bag);
}
if (max >= value) {
range(rect, node.right, isVertical, bag);
}
}
// 返回距离该点最近的点, 用同名私有方法递归实现
public Point nearest(Point target) {
return nearest(target, root, null, false);
}
private Point nearest(Point target, Node node, Point currentBest, boolean isVertical) {
if (node == null) return currentBest;
isVertical = !isVertical;
double value1 = isVertical ? target.x : target.y;
double value2 = isVertical ? node.point.x : node.point.y;
// 继续搜索目标点所在的半区
Node next = value1 < value2 ? node.left : node.right;
Node other = value1 < value2 ? node.right : node.left;
Point nextBest = nearest(target, next, node.point, isVertical);
double currentDistance = 0;
double nextDistance = nextBest.distanceSquareTo(target);
if (currentBest == null) {
currentBest = nextBest;
currentDistance = nextDistance;
} else {
currentDistance = currentBest.distanceSquareTo(target);
if (nextDistance < currentDistance) {
currentBest = nextBest;
currentDistance = nextDistance;
}
}
// 判断另一半区是否可能包含更近的点
if ((other != null) && (other.rect.distanceSquareToPoint(target) < currentDistance)) {
currentBest = nearest(target, other, currentBest, isVertical);
}
return currentBest;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// unit test
}
}
Note:
比较难理解的是nearest()方法,该方法为深度优先搜索,逻辑是:
1.从根节点开始向下搜索,递归搜索优势半区 (定义 目标点 为
public Point nearest(Point target)
中的target, 目标点所在的半区为优势半区,另一半区为劣势半区 ) ,并将当前点作为currentBest 参数传递给下层,直到叶子节点。
2.此时开始回溯,返回 nextBest ,获得 {该节点优势半区中的所有点,以及parent点} 中距离目标点最近的点 ,其最优距离为currentDistance。 此时考虑是否需要搜索劣势半区。
3.如果劣势半区所在的矩形与目标点的距离小于currentDistance,则搜索劣势半区。换句话说,如果矩形到目标点的距离小于currentDistance,说明劣势半区中有存在更近的点的可能。
复杂度比较
KdTree在最坏情况下的复杂度与暴力求解(用集合遍历所有元素)一样都是O(n), 但在随机分布的情况下可以达到O(log2N)。
以下为两个数据结构在随机分布的空间中的算法复杂度 (其中R表示矩形范围内点的个数)
| 数据结构 | insert() | contains() | range() | nearest() |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Set | 1 | N/2 | N | N |
| KdTree | log2N | log2N | log2N + R | log2N |
结语
之前在学数据库的时候大作业是做一个类似饿了么的外卖网站,其中的一个难点是如何根据用户所在的位置检索出所有附近的商家。当时想了半天也想不出来怎么能有效的进行区间搜索,用的是暴力方法(因为是demo所以数据量很小),现在学到了KdTree之后真的是大彻大悟啊