Muduo网络库源码分析(一) EventLoop事件循环(Poller和Channel)
从这一篇博文起,我们开始剖析Muduo网络库的源码,主要结合《Linux多线程服务端编程》和网上的一些学习资料!
(一)TCP网络编程的本质:三个半事件
1. 连接的建立,包括服务端接受(accept) 新连接和客户端成功发起(connect) 连接。TCP 连接一旦建立,客户端和服务端是平等的,可以各自收发数据。
2. 连接的断开,包括主动断开(close 或shutdown) 和被动断开(read(2) 返回0)。
3. 消息到达,文件描述符可读。这是最为重要的一个事件,对它的处理方式决定了网络编程的风格(阻塞还是非阻塞,如何处理分包,应用层的缓冲如何设计等等)。
3.5 消息发送完毕,这算半个。对于低流量的服务,可以不必关心这个事件;另外,这里“发送完毕”是指将数据写入操作系统的缓冲区,将由TCP 协议栈负责数据的发送与重传,不代表对方已经收到数据。
这其中,最主要的便是第三点: 消息到达,文件描述符可读。下面我们来仔细分析(顺便分析消息发送完毕):
(1)消息到达,文件可读:
内核接收-> 网络库可读事件触发--> 将数据从内核转至应用缓冲区(并且回调函数OnMessage根据协议判断是否是完整的数据包,如果不是立即返回)-->如果完整就取出读走、解包、处理、发送(read decode compute encode write)
(2)消息发送完毕:
应用缓冲区-->内核缓冲区(可全填)--->触发发送完成的事件,回调Onwrite。如果内核缓冲区不足以容纳数据(高流量的服务),要把数据追加到应用层发送缓冲区中内核数据发送之后,触发socket可写事件,应用层-->内核;当全发送至内核时,又会回调Onwrite(可继续写)
(二)事件循环类图

EventLoop类:
EventLoop是对Reactor模式的封装,由于Muduo的并发原型是 Multiple reactors + threadpool (one loop per thread + threadpool),所以每个线程最多只能有一个EventLoop对象。EventLoop对象构造的时候,会检查当前线程是否已经创建了其他EventLoop对象,如果已创建,终止程序(LOG_FATAL),EventLoop类的构造函数会记录本对象所属线程(threadld_),创建了EventLoop对象的线程称为IO线程,其功能是运行事件循环(EventLoop:loop),啥也不干==
下面是简化版的EventLoop(内部的Poller尚未实现,只是一个框架)
EventLoop.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#define MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#include
#include
#include
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
/// Reactor, at most one per thread.
/// This is an interface class, so don't expose too much details.
class EventLoop : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
EventLoop();
~EventLoop(); // force out-line dtor, for scoped_ptr members.
/// Loops forever.
/// Must be called in the same thread as creation of the object.
void loop();
void assertInLoopThread()
{
if (!isInLoopThread())
{
abortNotInLoopThread();
}
}
bool isInLoopThread() const { return threadId_ == CurrentThread::tid(); }
static EventLoop* getEventLoopOfCurrentThread();
private:
void abortNotInLoopThread();
bool looping_; /* atomic */
const pid_t threadId_; // 当前对象所属线程ID
};
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_NET_EVENTLOOP_H
#include
#include
#include
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
namespace
{
// 当前线程EventLoop对象指针
// 线程局部存储
__thread EventLoop* t_loopInThisThread = 0;
}
EventLoop* EventLoop::getEventLoopOfCurrentThread()
{
return t_loopInThisThread;
}
EventLoop::EventLoop()
: looping_(false),
threadId_(CurrentThread::tid())
{
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop created " << this << " in thread " << threadId_;
// 如果当前线程已经创建了EventLoop对象,终止(LOG_FATAL)
if (t_loopInThisThread)
{
LOG_FATAL << "Another EventLoop " << t_loopInThisThread
<< " exists in this thread " << threadId_;
}
else
{
t_loopInThisThread = this;
}
}
EventLoop::~EventLoop()
{
t_loopInThisThread = NULL;
}
// 事件循环,该函数不能跨线程调用
// 只能在创建该对象的线程中调用
void EventLoop::loop()
{
assert(!looping_);
// 断言当前处于创建该对象的线程中
assertInLoopThread();
looping_ = true;
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " start looping";
::poll(NULL, 0, 5*1000);
LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " stop looping";
looping_ = false;
}
void EventLoop::abortNotInLoopThread()
{
LOG_FATAL << "EventLoop::abortNotInLoopThread - EventLoop " << this
<< " was created in threadId_ = " << threadId_
<< ", current thread id = " << CurrentThread::tid();
}
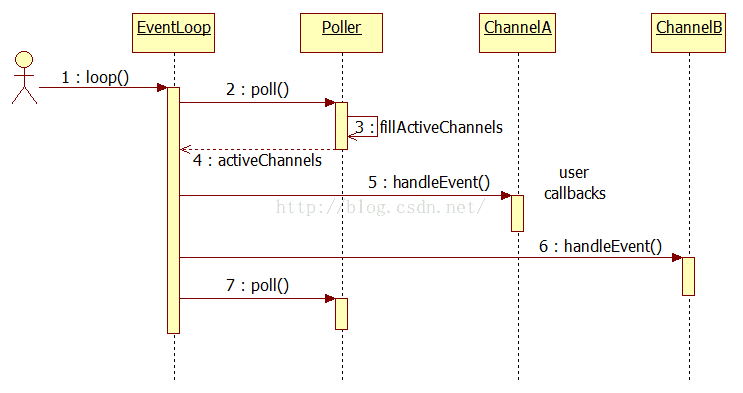
Poller类:
时序图:
Poller是个抽象类,具体可以是EPollPoller(默认) 或者PollPoller,需要去实现(唯一使用面向对象的一个类)
对于PollPoller来说,存在一个map,用来关联fd和channel的,我们可以根据fd快速找到对应的channel。一个fd对应一个struct pollfd(pollfd.fd),一个fd 对应一个channel*;这个fd 可以是socket, eventfd, timerfd, signalfd。Poller的作用是更新IO复用中的channel(IO事件),添加、删除Channel。我们看一下PollPoller的实现:
PollPoller.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_POLLER_POLLPOLLER_H
#define MUDUO_NET_POLLER_POLLPOLLER_H
#include
#include PollPoller.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
PollPoller::PollPoller(EventLoop* loop)
: Poller(loop)
{
}
PollPoller::~PollPoller()
{
}
Timestamp PollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels)
{
// XXX pollfds_ shouldn't change
int numEvents = ::poll(&*pollfds_.begin(), pollfds_.size(), timeoutMs);
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
if (numEvents > 0)
{
LOG_TRACE << numEvents << " events happended";
fillActiveChannels(numEvents, activeChannels);
}
else if (numEvents == 0)
{
LOG_TRACE << " nothing happended";
}
else
{
LOG_SYSERR << "PollPoller::poll()";
}
return now;
}
void PollPoller::fillActiveChannels(int numEvents,
ChannelList* activeChannels) const
{
for (PollFdList::const_iterator pfd = pollfds_.begin();
pfd != pollfds_.end() && numEvents > 0; ++pfd)
{
if (pfd->revents > 0)
{
--numEvents;
ChannelMap::const_iterator ch = channels_.find(pfd->fd);
assert(ch != channels_.end());
Channel* channel = ch->second;
assert(channel->fd() == pfd->fd);
channel->set_revents(pfd->revents);
// pfd->revents = 0;
activeChannels->push_back(channel);
}
}
}
void PollPoller::updateChannel(Channel* channel)
{
Poller::assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "fd = " << channel->fd() << " events = " << channel->events();
if (channel->index() < 0)
{
// index < 0说明是一个新的通道
// a new one, add to pollfds_
assert(channels_.find(channel->fd()) == channels_.end());
struct pollfd pfd;
pfd.fd = channel->fd();
pfd.events = static_cast(channel->events());
pfd.revents = 0;
pollfds_.push_back(pfd);
int idx = static_cast(pollfds_.size())-1;
channel->set_index(idx);
channels_[pfd.fd] = channel;
}
else
{
// update existing one
assert(channels_.find(channel->fd()) != channels_.end());
assert(channels_[channel->fd()] == channel);
int idx = channel->index();
assert(0 <= idx && idx < static_cast(pollfds_.size()));
struct pollfd& pfd = pollfds_[idx];
assert(pfd.fd == channel->fd() || pfd.fd == -channel->fd()-1);
pfd.events = static_cast(channel->events());
pfd.revents = 0;
// 将一个通道暂时更改为不关注事件,但不从Poller中移除该通道
if (channel->isNoneEvent())
{
// ignore this pollfd
// 暂时忽略该文件描述符的事件
// 这里pfd.fd 可以直接设置为-1
pfd.fd = -channel->fd()-1; // 这样子设置是为了removeChannel优化
}
}
}
void PollPoller::removeChannel(Channel* channel)
{
Poller::assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "fd = " << channel->fd();
assert(channels_.find(channel->fd()) != channels_.end());
assert(channels_[channel->fd()] == channel);
assert(channel->isNoneEvent());
int idx = channel->index();
assert(0 <= idx && idx < static_cast(pollfds_.size()));
const struct pollfd& pfd = pollfds_[idx]; (void)pfd;
assert(pfd.fd == -channel->fd()-1 && pfd.events == channel->events());
size_t n = channels_.erase(channel->fd());
assert(n == 1); (void)n;
if (implicit_cast(idx) == pollfds_.size()-1)
{
pollfds_.pop_back();
}
else
{
// 这里移除的算法复杂度是O(1),将待删除元素与最后一个元素交换再pop_back
int channelAtEnd = pollfds_.back().fd;
iter_swap(pollfds_.begin()+idx, pollfds_.end()-1);
if (channelAtEnd < 0)
{
channelAtEnd = -channelAtEnd-1;
}
channels_[channelAtEnd]->set_index(idx);
pollfds_.pop_back();
}
} Channel类:
Channel是selectable IO channel,负责注册与响应IO 事件,它不拥有file descriptor。
Channel是Reactor结构中的“事件”,它自始至终都属于一个EventLoop(一个EventLoop对应多个Channel,处理多个IO),负责一个文件描述符的IO事件,它包含又文件描述符fd_,但实际上它不拥有fd_,不用负责将其关闭。在Channel类中保存这IO事件的类型以及对应的回调函数,当IO事件发生时,最终会调用到Channel类中的回调函数。Channel类一般不单独使用,它常常包含在其他类中(Acceptor、Connector、EventLoop、TimerQueue、TcpConnection)使用。Channel类有EventLoop的指针 loop_,通过这个指针可以向EventLoop中添加当前Channel事件。事件类型用events_表示,不同事件类型对应不同回调函数。
以下两个都由Channel注册:
Acceptor是被动连接的抽象--->关注监听套接字的可读事件,回调handleRead。
Connector对主动连接的抽象。
时序图:
Channel.h
#ifndef MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H
#define MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
namespace muduo
{
namespace net
{
class EventLoop;
/// A selectable I/O channel.
/// This class doesn't own the file descriptor.
/// The file descriptor could be a socket,
/// an eventfd, a timerfd, or a signalfd
class Channel : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef boost::function EventCallback;
typedef boost::function ReadEventCallback;
Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd);
~Channel();
void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);
void setReadCallback(const ReadEventCallback& cb)
{ readCallback_ = cb; }
void setWriteCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ writeCallback_ = cb; }
void setCloseCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ closeCallback_ = cb; }
void setErrorCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ errorCallback_ = cb; }
/// Tie this channel to the owner object managed by shared_ptr,
/// prevent the owner object being destroyed in handleEvent.
void tie(const boost::shared_ptr&);
int fd() const { return fd_; }
int events() const { return events_; }
void set_revents(int revt) { revents_ = revt; } // used by pollers
// int revents() const { return revents_; }
bool isNoneEvent() const { return events_ == kNoneEvent; }
void enableReading() { events_ |= kReadEvent; update(); }
// void disableReading() { events_ &= ~kReadEvent; update(); }
void enableWriting() { events_ |= kWriteEvent; update(); }
void disableWriting() { events_ &= ~kWriteEvent; update(); }
void disableAll() { events_ = kNoneEvent; update(); }
bool isWriting() const { return events_ & kWriteEvent; }
// for Poller
int index() { return index_; }
void set_index(int idx) { index_ = idx; }
// for debug
string reventsToString() const;
void doNotLogHup() { logHup_ = false; }
EventLoop* ownerLoop() { return loop_; }
void remove();
private:
void update();
void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);
static const int kNoneEvent;
static const int kReadEvent;
static const int kWriteEvent;
EventLoop* loop_; // 所属EventLoop
const int fd_; // 文件描述符,但不负责关闭该文件描述符
int events_; // 关注的事件
int revents_; // poll/epoll返回的事件
int index_; // used by Poller.表示在poll的事件数组中的序号
bool logHup_; // for POLLHUP
boost::weak_ptr tie_;
bool tied_;
bool eventHandling_; // 是否处于处理事件中
ReadEventCallback readCallback_;
EventCallback writeCallback_;
EventCallback closeCallback_;
EventCallback errorCallback_;
};
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_NET_CHANNEL_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
const int Channel::kNoneEvent = 0;
const int Channel::kReadEvent = POLLIN | POLLPRI;
const int Channel::kWriteEvent = POLLOUT;
Channel::Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd__)
: loop_(loop),
fd_(fd__),
events_(0),
revents_(0),
index_(-1),
logHup_(true),
tied_(false),
eventHandling_(false)
{
}
Channel::~Channel()
{
assert(!eventHandling_);
}
void Channel::tie(const boost::shared_ptr& obj)
{
tie_ = obj;
tied_ = true;
}
void Channel::update()
{
loop_->updateChannel(this);
}
// 调用这个函数之前确保调用disableAll
void Channel::remove()
{
assert(isNoneEvent());
loop_->removeChannel(this);
}
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
boost::shared_ptr guard;
if (tied_)
{
guard = tie_.lock();
if (guard)
{
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
else
{
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime)
{
eventHandling_ = true;
if ((revents_ & POLLHUP) && !(revents_ & POLLIN))
{
if (logHup_)
{
LOG_WARN << "Channel::handle_event() POLLHUP";
}
if (closeCallback_) closeCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & POLLNVAL)
{
LOG_WARN << "Channel::handle_event() POLLNVAL";
}
if (revents_ & (POLLERR | POLLNVAL))
{
if (errorCallback_) errorCallback_();
}
if (revents_ & (POLLIN | POLLPRI | POLLRDHUP))
{
if (readCallback_) readCallback_(receiveTime);
}
if (revents_ & POLLOUT)
{
if (writeCallback_) writeCallback_();
}
eventHandling_ = false;
}
string Channel::reventsToString() const
{
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << fd_ << ": ";
if (revents_ & POLLIN)
oss << "IN ";
if (revents_ & POLLPRI)
oss << "PRI ";
if (revents_ & POLLOUT)
oss << "OUT ";
if (revents_ & POLLHUP)
oss << "HUP ";
if (revents_ & POLLRDHUP)
oss << "RDHUP ";
if (revents_ & POLLERR)
oss << "ERR ";
if (revents_ & POLLNVAL)
oss << "NVAL ";
return oss.str().c_str();
}
参考:
《Muduo使用手册》
《Linux多线程服务端编程》