OpenVINO整活(一) 输入分辨率
OpenVINO整活(一) 输入分辨率
OpenVINO分为转换与部署两个部分,如下图所示
在转换步中,需要将输入模型序列化后传入OpenVINO的MOModel Optimizer工具对模型进行优化,以得到IR
Intermediate Representation中间表示,详细的内部行为可以参考Model Optimizer Developer Guide。接着,在部署步中,我们使用OpenVINO提供的Python或者CPP的api,进行编程以达到我们想要的结果:1) 载入ir文件, 2) 建立ieInference Engine推理引擎, 3) 生成执行对象ExecutableNetwork, 载入不同的plugin,以支持特定的硬件(CPU、GPU等等),详细行为可参考Inference Engine Developer Guide。
对于转换步,针对"输入模型序列化"我就产生了疑问,OpenVINO所使用的序列化后进行ir转换的模型,它是一个类似静态图的东西,序列化后我再转换,那岂不就是我只能支持输入静态分辨率了?要使用OpenVINO化的模型进行推理,任意输入就得按照序列化时的分辨率来推理,岂不是很僵硬。难道,OpenVINO的推理,就得先插值,再推理,最后再插值回原分辨率?
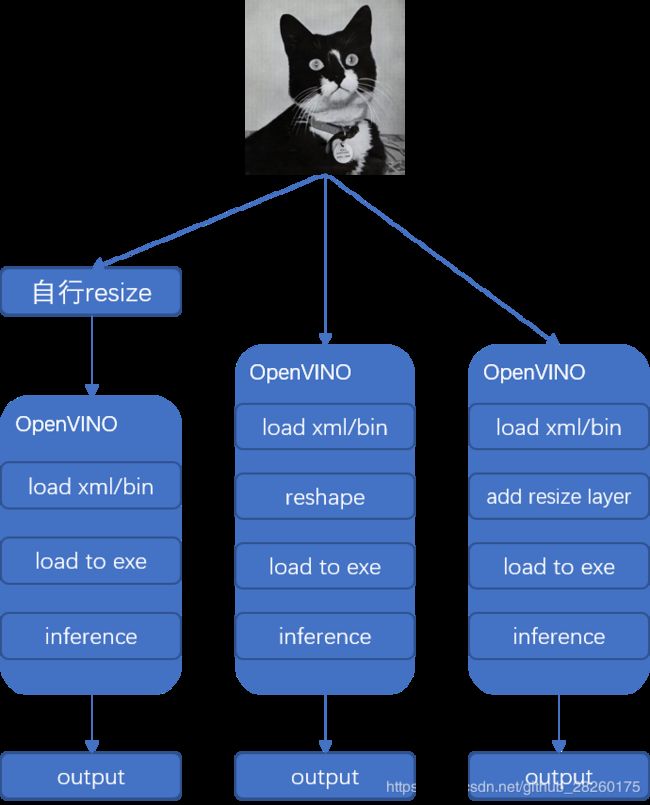
这里就直接给结论了,OpenVINO是支持动态输入的,并且在它的手册里,也有相应的段落Using Shape Inference,乍看起来很简单,但实则暗藏坑点,这里我也直接给出坑点来,CPP api是无法全面支持OpenVINO reshape操作的:
- Python api 全面支持reshape操作,不会出错
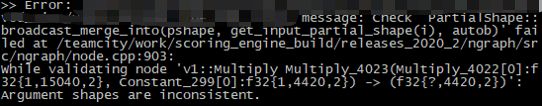
- CPP api 某些简单网络支持,我推测还是scale的精度问题,参考我之前的日志PyTorch转ONNX之F.interpolate,从4到9,python搞得定,cpp估计就搞不定了,例如就会报如下的错,也是网络内部的upsample的问题,所以可以在2) 建立ie引擎的时候,加入resize层,也就是在ir外部添加一个处理,而不是reshape整个ir
那么,下面就是两部分的详细说明
Python api
由于Python不像CPP,在精度和内存分配上,我们都不需要担心,所以完全可以使用OpenVINO自带的reshape操作,将整个ir调整到适合的输入分辨率。
这里需要注意两点,一是在使用mo工具进行ir转换的时候,需要使用--keep_shape_ops,二是在部署的时候,需要在"3) 生成ExecutableNetwork对象"前使用reshape。
一、使用mo转换ir
--keep_shape_ops
[ Experimental feature ] Enables `Shape` operation
with all children keeping. This feature makes model
reshapable in Inference Engine
详细地,可以参考When to Specify --keep_shape_ops Command Line Parameter,mo工具会保留内部的分辨率变化的图结构,实话说这部分保留了什么样的图结构,我不清楚,我猜是像onnx那样的scale值,onnx是通过scale值来计算输入与输出的分辨率大小,有可能,--keep_shape_ops取消了原本scale的const类型?
二、使用python api进行推理
这里我给一个示例代码,这里也是修改自OpenVINO提供的deployment_tools/inference_engine/samples/python里面的,我把注释和提示信息打印了出来,方便大家理解。
# model config
model_xml = 'your_model.xml'
model_bin = 'your_model.bin'
# Read IR
print("Creating Inference Engine...")
ie = IECore()
print("Loading network files:\n\t{}\n\t{}".format(model_xml, model_bin))
net = ie.read_network(model=model_xml, weights=model_bin)
# Check params in IR
# 检查IR模型是否是支持CPU硬件的
supported_layers = ie.query_network(net, "CPU")
not_supported_layers = [l for l in net.layers.keys() if l not in supported_layers]
if len(not_supported_layers) != 0:
print("Following layers are not supported by the plugin for specified device {}:\n {}".
format('CPU', ', '.join(not_supported_layers)))
print("Please try to specify cpu extensions library path in sample's command line parameters using -l "
"or --cpu_extension command line argument")
sys.exit(1)
# 检查输入层的维度,这里说明是一个输入
assert len(net.inputs.keys()) == 1, "Sample supports only 1 input topologies -> {}".format(len(net.inputs.keys()))
# xml里面“注册”的输入的名字
required_input_keys = {'input'}
assert required_input_keys == set(net.inputs.keys()), \
'Demo supports only topologies with the following input keys: {}'.format(', '.join(required_input_keys))
# 检查输出层的维度,这里有两个输出
assert len(net.outputs) == 2, "Sample supports only single output topologies"
# xml里面“注册”的输出的名字
required_output_keys = {'boxes', 'scores'}
assert required_output_keys.issubset(net.outputs.keys()), \
'Demo supports only topologies with the following output keys: {}'.format(', '.join(required_output_keys))
# Read and pre-process input images
n, c, h, w = net.inputs['input'].shape
print("input_blob NxCxHxW is {}x{}x{}x{}".format(n, c, h, w))
# Reshape IR
# 读入输入图像的分辨率
input_size = cv2.imread("your_input_image.png").shape[:-1]
net.reshape({'input': (1, 3, input_size[0], input_size[1])})
n, c, h, w = net.inputs['input'].shape
print("input_blob NxCxHxW is resized to {}x{}x{}x{}".format(n, c, h, w))
# Loading model to the plugin
# 生成执行对象ExecutableNetwork
print("Loading model to the plugin")
exec_net = ie.load_network(network=net, device_name='CPU')
# Inference
print("Starting inference in synchronous mode")
for j in range(len(img_list)):
img_path = img_list[j]
ori_img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(ori_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32)
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # Change data layout from HWC to CHW
img = img[np.newaxis, :, :, :] # 整成1CHW
# Start sync inference
print('[{}/{}]'.format(j, len(img_list)))
res = exec_net.infer(inputs={'input': img})
# Get results
boxes = res['boxes']
scores = res['scores']
# Post-processing
这里说明下“注册”是个啥意思,就是输入输出层的名字,实际上静态图里面,各层都是有类似“conv35”——“层类型-层的id”这样的名字,如果在IR转换的时候不规定,就是默认“conv35”的名称,规定层的名称,就是“注册”,我感觉这样来形容更加贴切一点。
CPP api
一、使用CPP api进行推理
模型转换那里是一样的,因此就不再赘述。
按理说,流程应该与“Python api推理”的流程是一致的,在文档Using Shape Inference的Usage of Reshape Method中提到CPP的流程如下所示:
InferenceEngine::Core core;
// ------------- 0. Read IR and image ----------------------------------------------
CNNNetwork network = core.ReadNetwork("path/to/IR/xml");
cv::Mat image = cv::imread("path/to/image");
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ------------- 1. Collect the map of input names and shapes from IR---------------
auto input_shapes = network.getInputShapes();
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ------------- 2. Set new input shapes -------------------------------------------
std::string input_name;
SizeVector input_shape;
std::tie(input_name, input_shape) = *input_shapes.begin(); // let's consider first input only
input_shape[0] = batch_size; // set batch size to the first input dimension
input_shape[2] = image.rows; // changes input height to the image one
input_shape[3] = image.cols; // changes input width to the image one
input_shapes[input_name] = input_shape;
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ------------- 3. Call reshape ---------------------------------------------------
network.reshape(input_shapes);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
...
// ------------- 4. Loading model to the device ------------------------------------
std::string device = "CPU";
ExecutableNetwork executable_network = core.LoadNetwork(network, device);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
虽然会报之前讲到的错,因此我觉得这条reshape路是不容易走通的,那么是不是就卡关了呢?实际上是有解的,OpenVINO提供在"3) 生成ExecutableNetwork对象"前添加一个类似resize层的东西,这样就不会变动IR结构,而且使用OpenVINO提供的内建的resize操作,比自己在输入OpenVINO前进行自己的resize操作,我感觉应该是要快一点,如果画成图的话,就如下图所示,我们可以使用OpenVINO优化后的resize操作。
using namespace InferenceEngine;
Core ie;
string cnnNetworkXmlPath;
// ------------- 0. Read IR ----------------------------------------------
// 读取xml与bin
// ie默认读入与xml文件同名同路径的bin文件
// 例如,你的xml路径为/data/your_model.xml,那么ie会默认读取/data/your_model.bin
auto cnnNetwork = ie.ReadNetwork(cnnNetworkXmlPath);
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// ------------- 1. Collect the map of input names and shapes from IR-----
// 获取网络的输入信息
InputsDataMap inputInfo(cnnNetwork.getInputsInfo());
for (const auto & inputInfoItem : inputInfo)
{
if (inputInfoItem.second->getTensorDesc().getDims().size() == 4)
{
// 确保输入一定是4维,包含N、C、H、W
imageInputName = inputInfoItem.first;
// 设置输入精度为uint8,这样CPU占用要小一些
inputInfoItem.second->setPrecision(Precision::U8);
// 设置输入的维度格式,为NCHW
inputInfoItem.second->getInputData()->setLayout(Layout::NCHW);
// 添加前处理resize操作,并且这个resize层是双线性插值的
inputInfoItem.second->getPreProcess().setResizeAlgorithm(ResizeAlgorithm::RESIZE_BILINEAR);
}
else
{
throw std::logic_error("Unsupported " +
std::to_string(inputInfoItem.second->getTensorDesc().getDims().size()) + "D "
"input layer '" + inputInfoItem.first + "'. "
"Only 4D input layers are supported");
}
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// ------------- 4. Loading model to the device --------------------------
std::string device = "CPU";
ExecutableNetwork executable_network = ie.LoadNetwork(network, device);
上述操作就是为前处理添加一个resize操作层,实际上这个PreProcess是支持很多操作的,例如归一化、减去均值等等,相当于就是在mo转ir的时候,插入的操作,大家可以查看相应的文档InferenceEngine::PreProcessInfo Class Reference看到它支持的各种操作。
好了,以上就是全部内容,在接下来的时间里,我应该会继续更新模型部署的内容,比如ssd的部署啊,trt的量化啊什么的,openvino的量化我也想试一试,奈何经历不够,又要吃饭,又想玩。