算法初级(三)—— 二叉树
文章目录
- 1、二叉树的遍历(递归/非递归)
- 2、打印二叉树
- 3、在一个二叉树中找一个节点的后继节点
- 4、序列化与反序列化
- 5、判断是否为平衡二叉树
- 6、判断是否为搜索二叉树和完全二叉树
- 7、已知一棵完全二叉树,求其节点数
1、二叉树的遍历(递归/非递归)
递归
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
public static void posOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
posOrderRecur(head.left);
posOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
}
非递归
先序:先压右后压左
//非递归先序遍历
//先将节点压栈,出栈后,先将该节点右节点压栈,再将左节点压栈
public static void preOrderUnrecur(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
//创建栈,将head压栈
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
//head出栈并打印
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
//先将右节点压栈
if (head.right != null) {
stack.push(head.right);
}
//再将左节点压栈
if (head.left != null) {
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
}
中序
当前节点为空,从栈中取出一个并打印,向右
当前节点不为空,当前节点压栈,向左
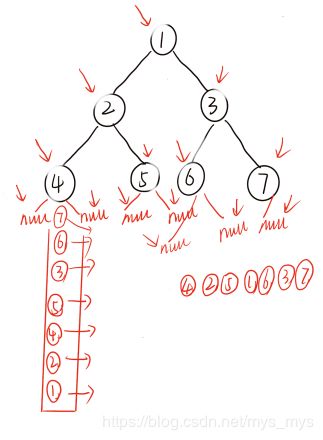
public static void inOrderUnrecur(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) {
//当前节点不为空,当前节点压栈,向左
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.left;
} else {
//当前节点为空,从栈中取出一个并打印,向右
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
}
}
后序
非递归后序(左右根)遍历:
先得到 根右左,放入栈中,再出栈得到左右根
根右左:与先序遍历的方法类似,先压左后压右
public static void posOrderUnprecur(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<>();//保存得到的 根左右
s1.push(head);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
head = s1.pop();
s2.push(head);
//先压左
if (head.left != null) {
s1.push(head.left);
}
//后压右
if (head.right != null) {
s1.push(head.right);
}
}
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
}
2、打印二叉树
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void printTree(Node head) {
System.out.println("Binary Tree:");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len);
String val = to + head.value + to;
int lenM = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2;
int lenR = len - lenM - lenL;
val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR);
System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val);
printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len);
}
public static String getSpace(int num) {
String space = " ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
3、在一个二叉树中找一个节点的后继节点
- 节点有右子树,则其后继节点就是右子树上最左节点
- 节点没有右子树,当前节点与其右节点往上走,直到当前节点是其父节点的左孩子停止,这个父节点就是原始结点的后继节点
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
//节点有右子树,则其后继节点就是右子树上最左节点
if (node.right != null) {
return getLeftMost(node);
} else {//节点没有右子树
Node parent = node.parent;
//当前节点与其父节点往上走,直到当前节点是其父节点的左孩子停止
while (parent != null && parent.left != node) {
node = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
//这个父节点就是原始结点的后继节点
return parent;
}
}
//找最左节点
public static Node getLeftMost(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
4、序列化与反序列化
//先序序列化
public static String serialByPre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return "#_";
}
String res = head.value + "_";//_结束标志
res += serialByPre(head.left);
res += serialByPre(head.right);
return res;
}
//先序反序列化
public static Node reconByPreString(String preStr) {
//以_划分,放入values中
String[] values = preStr.split("_");
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//将values的值加入queue
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i ++) {
queue.offer(values[i]);
}
//先序反序列化
return reconPreOrder(queue);
}
public static Node reconPreOrder(Queue<String> queue) {
//依次出队列,并通过str创建节点
String value = queue.poll();
if (value.equals("#")) {
//空使用#表示
return null;
}
Node head = new Node(Integer.valueOf(value));
head.left = reconPreOrder(queue);
head.right = reconPreOrder(queue);
return head;
}
按层序列化与反序列化
//按层序列化
public static String serialByLevel(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return "#_";
}
String res = head.value + "_";
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//先加入head
queue.offer(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
//再分别加入其左右节点
if (head.left != null) {
res += head.left.value + "_";
queue.offer(head.left);
} else {
res += "#_";
}
if (head.right != null) {
res += head.right.value + "_";
queue.offer(head.right);
} else {
res += "#_";
}
}
return res;
}
//按层反序列化
public static Node reconByLevelString(String levelStr) {
String[] values = levelStr.split("_");
int index = 0;
//生成头节点
Node head = generateNodeByString(values[index++]);
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//如果头节点不为空,加入queue
if (head != null) {
queue.offer(head);
}
Node node = null;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//当前节点出队列
node = queue.poll();
//生成当前节点的右节点
node.left = generateNodeByString(values[index++]);
//生成当前节点的左节点
node.right = generateNodeByString(values[index++]);
//如果不为空,入队列
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
return head;
}
//根据str生成节点
public static Node generateNodeByString(String val) {
if (val.equals("#")) {
return null;
}
return new Node(Integer.valueOf(val));
}
5、判断是否为平衡二叉树
左右子树高度差不超过1
public static boolean isBalance(Node head) {
boolean[] res = new boolean[1];
res[0] = true;
getHeight(head, 1, res);
return res[0];
}
public static int getHeight(Node head, int level, boolean[] res) {
if (head == null) {
return level;
}
//左子树的高度
int lH = getHeight(head.left, level+1, res);
if (!res[0]) {
return level;
}
//右子树的高度
int rH = getHeight(head.right, level+1, res);
if (!res[0]) {
return level;
}
//左右子树高度差不大于1
if (Math.abs(lH - rH) > 1) {
res[0] = false;
}
return Math.max(lH, rH);
}
6、判断是否为搜索二叉树和完全二叉树
搜索二叉树
判断是否为搜索二叉树 (一般不存在相同值):
任何一个节点,左子树比它小,右子树比它大
使用中序遍历,如果一次升序就是搜索二叉树
//与非递归中序遍历相似,只是将输出语句换成比较语句
public static boolean isBST(Node head) {
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
//比较
if (head.value < head.left.value) {
return false;
}
head = head.left;
} else {
head = stack.pop();
//比较
if (head.value > head.right.value ) {
return false;
}
head = head.right;
}
}
}
return true;
}
完全二叉树
- 有右孩子没有左孩子 = > false
- 有左孩子没有右孩子 OR 既没有左孩子也没有右孩子
如果节点其后所有节点都是叶子节点,说明进入leaf阶段
public static boolean isCBT(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean leaf = false;//标记是否进入leaf阶段
Node l = null;
Node r = null;
queue.offer(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
l = head.left;
r = head.right;
//有右孩子没有左孩子=>false
//到达leaf阶段,其所有节点不全是叶子节点=>false
if ((leaf && (l != null || r != null)) || (l == null && r != null)) {
return false;
}
//节点不是左右孩子都空
if (l != null) {
queue.offer(l);
}
if (r != null) {
queue.offer(r);
} else {
//进入leaf阶段,其后所有节点都是叶子节点
leaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
7、已知一棵完全二叉树,求其节点数
要求:时间复杂度低于O(N)
满二叉树 h=l : 节点数=(2^l) - 1
public static int nodeNum(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
return bs(head, 1, mostLeftLevel(head, 1));
}
/**
*
* @param node 当前节点
* @param level 当前节点在第几层
* @param h 整个树的层数
* 满二叉树 h=l :节点2^l - 1
* @return 节点数
*/
public static int bs(Node node, int level, int h) {
if (level == h) {
return 1;
}
//右子树左边界到了最后一层(左子树满树)
if (mostLeftLevel(node.right, level+1) == h) {
//(1<<(h-level))==2^(h-level):当前节点+左子树节点数 => 1+ 2^ (h-level)-1
//bs(node.right, level + 1, h):右子树节点数
return (1 << (h - level)) + bs(node.right, level + 1, h);
} else {//右子树左边界没到最后一层(左子树没满,右子树满(h-1))
//(1 << (h - level - 1)):当前节点+右子树节点数
return (1 << (h - level - 1)) + bs(node.left, level + 1, h);
}
}
public static int mostLeftLevel(Node head, int level) {
while (head != null) {
level ++;
head = head.left;
}
return level - 1;
}
