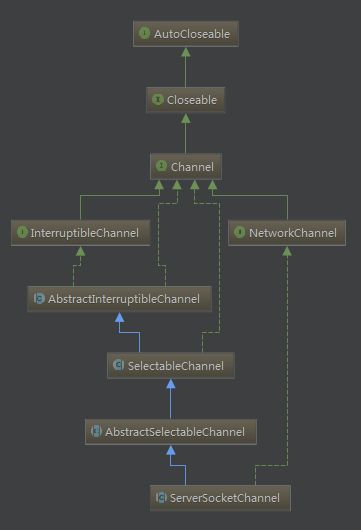
【NIO】解读 java.nio.channels.Channel
目录
Part 1. Define
Part 2. Implementation
1. Channel
2. FileChannel
3. ServerSocketChannel
4. SocketChannel
5. ServerSocket
Part 3. Demo
1. FileChannel
2. ServerSocketChannel
Part 1. Define
Difference between NIO's Channel and Stream:
1 NIO Channel can both read and write from / to channel, but the read and write of the stream is usually one-way.
2 Channels can be read and written asynchronously.
3 The data in the channel must always be read to a Buffer first, or always written from a Buffer.
A channel represents an open connection to an entity such as a hardware device, a file, a network socket, or a program component that is capable of performing one or more distinct I/O operations, for example reading or writing.
A channel is either open or closed. A channel is open upon creation, and once closed it remains closed. Once a channel is closed, any attempt to invoke an I/O operation upon it will cause a 'ClosedChannelException' to be thrown. Whether or not a channel is open may be tested by invoking its 'isOpen' method.
Channels are, in general, intended to be safe for multithreaded access as described in the specifications of the interfaces and classes that extend and implement this interface.
Part 2. Implementation
There are four main implementations of Channel in java like 'FileChannel', 'SocketChannel', 'ServerSocketChannel' and 'DatagramChannel':
* FileChannel read and write from/to file
* DatagramChannel read and write from/to file UDP
* SocketChannel read and write from/to TCP
* ServerSocketChannel Listen new tcp connect like Web Server. Every new connect will create a SocketChannel
1. Channel
1) What's Channel?
Channel is the super interface of 'channel in NIO' that define the common method.
2) What's the core method?
1. boolean isOpen();
return whether or not this channel is open.
2. void close()
1) Closes this channel.
1. After a channel is closed, any further attempt to invoke I/O operations upon it will cause a {@link ClosedChannelException} to be thrown.
2. If this channel is already closed then invoking this method has no effect.
3. This method may be invoked at any time. If some other thread has already invoked it, however, then another invocation will block until the first invocation is complete, after which it will return without effect.
2. FileChannel
1) What is FileChannel?
A channel for reading, writing, mapping, and manipulating a file.
A file channel is a 'SeekableByteChannel'(super class) that is connected to a file. It has a current position within its file which can be both position() queried and position(long) modified. The file itself contains a variable-length sequence of bytes that can be read and written and whose current size can be queried. The size of the file increases when bytes are written beyond its current size; the size of the file decreases when it is truncated. The file may also have some associated metadata such as access permissions, content type, and last-modification time; this class does not define methods for metadata access.
2) How to get a FileChannel and What feature does it support?
1. A file channel is created by invoking one of the open methods defined by this class. A file channel can also be obtained from an existing FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, or RandomAccessFile object by invoking that object's getChannel method, which returns a file channel that is connected to the same underlying file. Where the file channel is obtained from an existing stream or random access file then the state of the file channel is intimately connected to that of the object whose getChannel method returned the channel.
2. Changing the channel's position, whether explicitly or by reading or writing bytes, will change the file position of the originating object, and vice versa. Changing the file's length via the file channel will change the length seen via the originating object, and vice versa. Changing the file's content by writing bytes will change the content seen by the originating object, and vice versa.
3. "open-mode" - At various points this class specifies that an instance that is "open for reading," "open for writing," or "open for reading and writing" is required. A channel obtained via the getChannel method of a FileInputStream instance will be open for reading. A channel obtained via the getChannel method of a FileOutputStream instance will be open for writing. Finally, a channel obtained via the getChannel method of a RandomAccessFile instance will be open for reading if the instance was created with mode "r" and will be open for reading and writing if the instance was created with mode "rw".
4."append-mode" - A file channel that is open for writing may be in 'append mode', for example if it was obtained from a file-output stream that was created by invoking the FileOutputStream(java.io.File,boolean), FileOutputStream(File,boolean) constructor and passing 'true' for the second parameter. In this mode each invocation of a relative write operation first advances the position to the end of the file and then writes the requested data. Whether the advancement of the position and the writing of the data are done in a single atomic operation is system-dependent and therefore unspecified.
3) What operation does FileChannel support?
In addition to the familiar read, write, and close operations of byte channels, this class defines the following file-specific operations:
1. Bytes may be read(ByteBuffer, long) read or write(ByteBuffer, long) written at an absolute position in a file in a way that does not affect the channel's current position.
2. A region of a file may be mapped directly into memory; for large files this is often much more efficient than invoking the usual read or write methods.
3. Updates made to a file may be forced out to the underlying storage device, ensuring that data are not lost in the event of a system crash.
4. Bytes can be transferred from a file to some other channel, and vice versa, in a way that can be optimized by many operating systems into a very fast transfer directly to or from the filesystem cache.
5. A region of a file may be locked against access by other programs.
6. File channels are safe for use by multiple concurrent threads.
4) What's the Core Method?
// Opens or creates a file, returning a file channel to access the file.
FileChannel open(...);
// Reads a sequence of bytes from this channel into the given buffer.
int read(ByteBuffer dst);
// Writes a sequence of bytes to this channel from the given buffer.
int write(ByteBuffer src);
// Returns this channel's file position.
long position();
// Returns the current size of this channel's file.
long size();
3. ServerSocketChannel
1) What is ServerSocketChannel?
A selectable channel for stream-oriented listening sockets.
A server-socket channel is created by invoking the open() method of this class. It is not possible to create a channel for an arbitrary, pre-existing ServerSocket. A newly-created server-socket channel is open but not yet bound. An attempt to invoke the accept() method of an unbound server-socket channel will cause a 'NotYetBoundException' to be thrown. A server-socket channel can be bound by invoking one of the bind(java.net.SocketAddress,int) methods defined by this class.
Socket options are configured using the setOption(SocketOption,Object) method. Server-socket channels support the following options:
Socket options
Socket options are configured using the setOption(SocketOption,Object) method. Server-socket channels support the following options:
1 - java.net.StandardSocketOptions.SO_RCVBUF (The size of the socket receive buffer)
2 - java.net.StandardSocketOptions.SO_REUSEADDR (Re-use address)
2) What's the Core Method?
// Opens a server-socket channel.
ServerSocketChannel open();
// Binds the channel's socket to a local address and configures the socket to listen for connections.
ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local);
// set the socket Options
ServerSocketChannel setOption(SocketOption name, T value);
// (import) Retrieves a server socket associated with this channel.
ServerSocket socket();
/**
* (import)Accepts a connection made to this channel's socket.
*
* If this channel is in non-blocking mode then this method will
* immediately return null if there are no pending connections.
* Otherwise it will block indefinitely until a new connection is available
* or an I/O error occurs.
*
*
The socket channel returned by this method, if any, will be in
* blocking mode regardless of the blocking mode of this channel.
*/
SocketChannel accept() throws IOException;
4. SocketChannel
1) What is SocketChannel?
A socket channel is created by invoking one of the open methods of this class. It is not possible to create a channel for an arbitrary, pre-existing socket. A newly-created socket channel is open but not yet connected. An attempt to invoke an I/O operation upon an unconnected channel will cause a NotYetConnectedException to be thrown. A socket channel can be connected by invoking its connect method; once connected, a socket channel remains connected until it is closed. Whether or not a socket channel is connected may be determined by invoking its isConnected method.
2) What kind of feature does ServerSocketChannel support?
Socket channels support 'non-blocking connection':A socket channel may be created and the process of establishing the link to the remote socket may be initiated via the connect method for later completion by the finishConnect method. Whether or not a connection operation is in progress may be determined by invoking the isConnectionPending method.
Socket channels support 'asynchronous shutdown', which is similar to the asynchronous close operation specified in the Channel class. If the input side of a socket is shut down by one thread while another thread is blocked in a read operation on the socket's channel, then the read operation in the blocked thread will complete without reading any bytes and will return '-1'. If the output side of a socket is shut down by one thread while another thread is blocked in a write operation on the socket's channel, then the blocked thread will receive an 'AsynchronousCloseException'.
3) How to operate it?
1. Socket options are configured using the 'setOption(SocketOption,Object)' method. Socket channels support the following options:
1 java.net.StandardSocketOptions.SO_SNDBUF (The size of the socket send buffer)
2 java.net.StandardSocketOptions.SO_RCVBUF (The size of the socket receive buffer)
3 java.net.StandardSocketOptions.SO_KEEPALIVE (Keep connection alive)
4 java.net.StandardSocketOptions.SO_REUSEADDR (Re-use address)
5 java.net.StandardSocketOptions.SO_LINGER (Linger on close if data is present (when configured in blocking modeonly))
6 java.net.StandardSocketOptions.TCP_NODELAY (Disable the Nagle algorithm)
2. Two ways to create SocketChannel
1) Open the SocketChannel and then connect to server.
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("http://XXX.com", 8080));2) Created by ServerSocketChannel when receive a new connect.
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();3. Read from SocketChannel
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buf);4. Write to SocketChannel
String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
buf.clear();
buf.put(newData.getBytes());
buf.flip();
while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buf);
}
4) What are the core method of SocketChannel?
/**
* Opens a socket channel.
*/
public static SocketChannel open() throws IOException
/**
* Connects this channel's socket.
*
* If this channel is in non-blocking mode then an invocation of this
* method initiates a non-blocking connection operation. If the connection
* is established immediately, as can happen with a local connection, then
* this method returns true. Otherwise this method returns
* false and the connection operation must later be completed by
* invoking the {@link #finishConnect finishConnect} method.
*
*
If this channel is in blocking mode then an invocation of this
* method will block until the connection is established or an I/O error
* occurs.
*/
boolean connect(SocketAddress remote);
/**
* read data from channel to bytebuffer
*/
int read(ByteBuffer dst);
/**
* write data from buffer to channel
*/
int write(ByteBuffer src);
5. ServerSocket
1 What is ServerSocket?
A server socket waits for requests to come in over the network. It performs some operation based on that request, and then possibly returns a result to the requester.
2 What are the core method?
/**Binds the {@code ServerSocket} to a specific address
* (IP address and port number).
*
* If the address is {@code null}, then the system will pick up
* an ephemeral port and a valid local address to bind the socket.
*/
void bind(SocketAddress endpoint);
/**
* Listens for a connection to be made to this socket and accepts
* it. The method blocks until a connection is made.
*
*
A new Socket {@code s} is created and, if there
* is a security manager,
* the security manager's {@code checkAccept} method is called
* with {@code s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()} and
* {@code s.getPort()}
* as its arguments to ensure the operation is allowed.
* This could result in a SecurityException.
*/
Socket accept()
Part 3. Demo
1. FileChannel
public class FileChannelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 从文件中读取
FileInputStream stream = new FileInputStream("NioTest.txt");
FileChannel channel = stream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
channel.read(buffer);
// 输入、输出 转换
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
byte b = buffer.get();
System.out.println("Character:" + (char)b);
}
stream.close();
}
}public class FileChannelTest1{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileOutputStream stream = new FileOutputStream("NioTest1.txt");
FileChannel channel = stream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
byte[] bytes = "hello world!".getBytes();
// 读到buffer
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; ++i) {
buffer.put(bytes[i]);
}
// 输入、输出 转换
buffer.flip();
// 输出到 txt
channel.write(buffer);
stream.close();
}
}public class FileChannelTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("NioTest2.txt");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("NioTest3.txt");
FileChannel inputChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true) {
buffer.clear();
int read = inputChannel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(read);
if (-1 == read) {
break;
}
buffer.flip();
outputChannel.write(buffer);
}
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
}2. ServerSocketChannel
public class ScatterGatherTest {
/**
* Scattering 与 Gathering 的应用
*
*
* telnet 或 nc 测试
*
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// nio 监听端口
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(8899);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(address);
// 定义消息长度9,分散给3个buffer
int mesLength = 2 + 3 + 4;
ByteBuffer[] buffers = new ByteBuffer[3];
buffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(2);
buffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
buffers[2] = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
while (true) {
//读 buffer
int bytesRead = 0;
//读不够9个字节时,不执行后续流程
while (bytesRead < mesLength) {
long r = socketChannel.read(buffers);
bytesRead += r;
Arrays.asList(buffers).stream()
.map((buffer) -> "position:" + buffer.position() + ", limit:" + buffer.limit())
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//读写转换
Arrays.asList(buffers).forEach(buffer -> { buffer.flip(); });
//写 buffer
long bytesWritten = 0;
while (bytesWritten < mesLength) {
long r =socketChannel.write(buffers);
bytesWritten += r;
}
//buffer归位
Arrays.asList(buffers).forEach(buffer -> buffer.clear());
System.out.println("bytesRead:" + bytesRead + ", bytesWrite:" + bytesWritten + ",messageLength " + mesLength);
}
}
}public class NioServer {
private static HashMap clientMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* Server端
*
* 两次register,一次serverSocketChannel.register(),一次socketChannel.register(); 对应selectionKey.channel()强转类型不同。
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//开启serverSocketChannel,设置非阻塞,绑定8899端口
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ServerSocket socket = serverSocketChannel.socket();
socket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8899));
//开启选择器,注册accept事件
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
try {
int num = selector.select();
Set selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
selectionKeys.forEach(selectionKey -> {
final SocketChannel client;
try {
// 接受新建立的连接
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
client = server.accept();
client.configureBlocking(false);
//第一次连接成功后,注册 read事件
client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
String key = "【" + UUID.randomUUID().toString() + "】";
clientMap.put(key, client);
}
// 读取client内容
else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
client = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
//定义buffer,读取channel数据
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = client.read(readBuffer);
if (count > 0) {
//读写翻转
readBuffer.flip();
Charset charset = Charset.forName("utf-8");
String receiveMsg = String.valueOf(charset.decode(readBuffer).array());
System.out.println(client + ":" + receiveMsg);
String sendKey = null;
for (Map.Entry entry : clientMap.entrySet()) {
if (client == entry.getValue()) {
sendKey = entry.getKey();
break;
}
}
//向cahnnel中,写出数据
for (Map.Entry entry : clientMap.entrySet()) {
SocketChannel value = entry.getValue();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
writeBuffer.put((sendKey + ":" + receiveMsg).getBytes());
writeBuffer.flip();
value.write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
selectionKeys.clear();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} public class NioClient {
/**
* Client端
*
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
try {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8899));
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set keySets = selector.selectedKeys();
for (SelectionKey selectionKey : keySets) {
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {
SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
if (client.isConnectionPending()) {
client.finishConnect();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.put((LocalDateTime.now() + "连接成功").getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
client.write(byteBuffer);
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
executorService.submit(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
byteBuffer.clear();
InputStreamReader input = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(input);
String sendMessage = br.readLine();
byteBuffer.put(sendMessage.getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
client.write(byteBuffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}