- 开代理
- 网址:https://www.gurobi.com
- 注册
- My account的位置有register,点击注册,输入注册信息

-
- 登录,点击同样位置的login
- 申请licence(download&licence->academic license)
- 复制licence
- 下载软件
- download&licence->download center->Gurobi Optimizer
- 选择版本
- 安装gurobi
- 全都默认就可以,可以自己改安装路径
- 安装完了重启(安装默认修改了环境变量)
- 打开软件输入grbgetkey
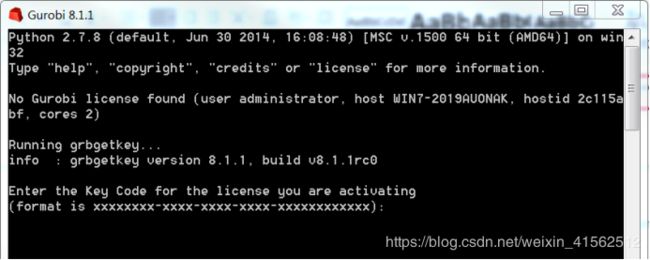
- 操作完软件会退出,再次打开

- 安装anaconda(网上很多,就不写了)
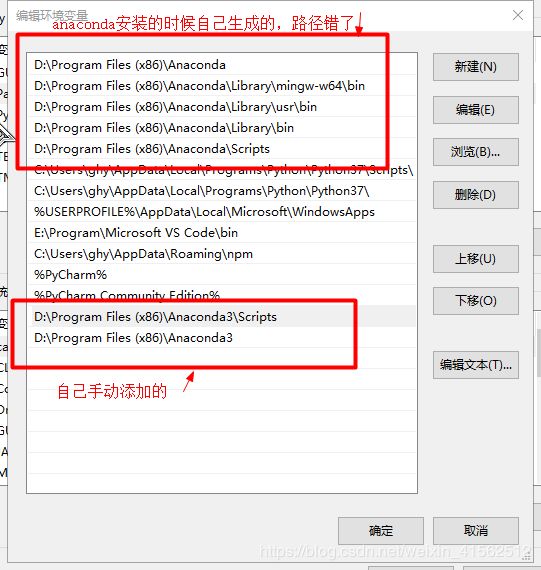
- 只说一点问题:conda不是内部或者外部命令
- 解决办法:手动修改path环境变量,自己添加下图的两个路径
- 使用anaconda下载gurobi package
- 打开anaconda prompt

- 输入指令
- conda config --add channels http://conda.anaconda.org/gurobi
- conda install gurobi
- 测试
- 在gurobi的安装路径下的examples文件夹找一个例子运行
- 也可以直接粘贴我的:
#!/usr/bin/python
# Copyright 2019, Gurobi Optimization, LLC
# Facility location: a company currently ships its product from 5 plants
# to 4 warehouses. It is considering closing some plants to reduce
# costs. What plant(s) should the company close, in order to minimize
# transportation and fixed costs?
#
# Note that this example uses lists instead of dictionaries. Since
# it does not work with sparse data, lists are a reasonable option.
#
# Based on an example from Frontline Systems:
# http://www.solver.com/disfacility.htm
# Used with permission.
from gurobipy import *
# Warehouse demand in thousands of units
demand = [15, 18, 14, 20]
# Plant capacity in thousands of units
capacity = [20, 22, 17, 19, 18]
# Fixed costs for each plant
fixedCosts = [12000, 15000, 17000, 13000, 16000]
# Transportation costs per thousand units
transCosts = [[4000, 2000, 3000, 2500, 4500],
[2500, 2600, 3400, 3000, 4000],
[1200, 1800, 2600, 4100, 3000],
[2200, 2600, 3100, 3700, 3200]]
# Range of plants and warehouses
plants = range(len(capacity))
warehouses = range(len(demand))
# Model
m = Model("facility")
# Plant open decision variables: open[p] == 1 if plant p is open.
open = m.addVars(plants,
vtype=GRB.BINARY,
obj=fixedCosts,
name="open")
# Transportation decision variables: transport[w,p] captures the
# optimal quantity to transport to warehouse w from plant p
transport = m.addVars(warehouses, plants, obj=transCosts, name="trans")
# You could use Python looping constructs and m.addVar() to create
# these decision variables instead. The following would be equivalent
# to the preceding two statements...
#
#open = []
#for p in plants:
# open.append(m.addVar(vtype=GRB.BINARY,
# obj=fixedCosts[p],
# name="open[%d]" % p))
#
#transport = []
#for w in warehouses:
# transport.append([])
# for p in plants:
# transport[w].append(m.addVar(obj=transCosts[w][p],
# name="trans[%d,%d]" % (w, p)))
# The objective is to minimize the total fixed and variable costs
m.modelSense = GRB.MINIMIZE
# Production constraints
# Note that the right-hand limit sets the production to zero if the plant
# is closed
m.addConstrs(
(transport.sum('*',p) <= capacity[p]*open[p] for p in plants),
"Capacity")
# Using Python looping constructs, the preceding would be...
#
#for p in plants:
# m.addConstr(sum(transport[w][p] for w in warehouses) <= capacity[p] * open[p],
# "Capacity[%d]" % p)
# Demand constraints
m.addConstrs(
(transport.sum(w) == demand[w] for w in warehouses),
"Demand")
# ... and the preceding would be ...
#for w in warehouses:
# m.addConstr(sum(transport[w][p] for p in plants) == demand[w], "Demand[%d]" % w)
# Save model
m.write('facilityPY.lp')
# Guess at the starting point: close the plant with the highest fixed costs;
# open all others
# First, open all plants
for p in plants:
open[p].start = 1.0
# Now close the plant with the highest fixed cost
print('Initial guess:')
maxFixed = max(fixedCosts)
for p in plants:
if fixedCosts[p] == maxFixed:
open[p].start = 0.0
print('Closing plant %s' % p)
break
print('')
# Use barrier to solve root relaxation
m.Params.method = 2
# Solve
m.optimize()
# Print solution
print('\nTOTAL COSTS: %g' % m.objVal)
print('SOLUTION:')
for p in plants:
if open[p].x > 0.99:
print('Plant %s open' % p)
for w in warehouses:
if transport[w,p].x > 0:
print(' Transport %g units to warehouse %s' % \
(transport[w,p].x, w))
else:
print('Plant %s closed!' % p)
-
- 发现失败了,没找到gurobipy,检查anaconda


- 检查file->settings->project interpreter->设置的符号->add

- 选择anaconda的安装路径下的python
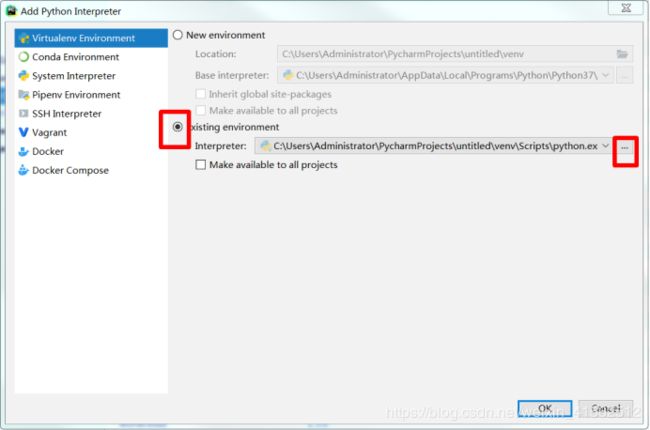
- 改完之后图标都会变
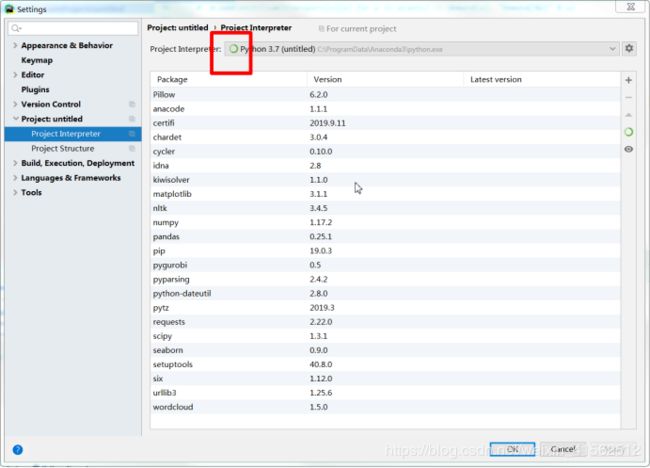
- 改完之后会很慢,要等一等
- 再次运行,就出结果了,测试成功

- 错误:
- 错误描述:anaconda安装的包在项目中无法使用
- 错误原因:可能是自己已经装了python,后装的anaconda,pycharm使用的python路径是自己装的那个版本的,而没使用anaconda中的python
- 问题:gurobipy.GurobiError: Version number is 9.0, license is for version 8.0
- 解决:使用conda prompt 输入命令:conda install gurobi==8.1.1
- 我的gurobi当时使用的就是这个版本,但是最近不小心更新了,导致版本不匹配,改回去就可以














