数据结构——栈——迷宫(c++)
迷宫旅行游戏
项目简介
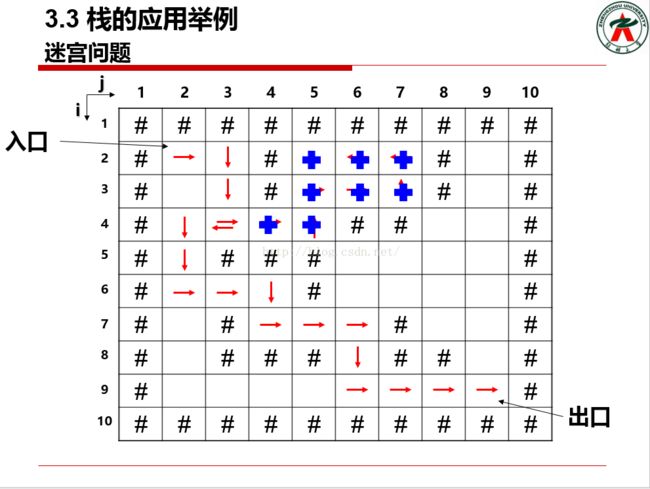
迷宫只有两个门,一个门叫入口,另一个门叫出口。一个骑士骑马从入口走进迷宫,迷宫中设置很多墙壁,对前进方向形成了多处障碍。骑士需要在迷宫中寻找通路以到达出口。
设计思路
迷宫问题的求解过程可以采用回溯法即在一定的约束条件下试探地搜索前进,若前进中受阻,则及时回头纠正错误另择通路继续搜索的方法。从入口出发,按某一方向向前探索,若能走通(未走过的),即某处可达,则到达新点,否则试探下一方向;若所有的方向均没有通路,则沿原路返回前一点,换下一个方向再继续试探,直到所有可能的通路都探索到,或找到一条通路,或无路可走又返回到入口点。
在求解过程中,为了保证在到达某一点后不能向前继续行走(无路)时,能正确返回前一点以便继续从下一个方向向前试探,则需要在试探过程中保存所能够到达的每一点的下标及从该点前进的方向,当找到出口时试探过程就结束了。
为了确保程序能够终止,调整时,必须保证曾被放弃过的填数序列不被再次试验,即要求按某种有序模型生成填数序列。给解的候选者设定一个被检验的顺序,按这个顺序逐一生成候选者并检验。
数据结构
迷宫问题是栈应用的一个典型例子。通过前面分析,我们知道在试探过程中为了能够沿着原路逆序回退,就需要一种数据结构来保存试探过程中曾走过的点的下标及从该点前进的方向,在不能继续走下去时就要退回前一点继续试探下一个方向,栈底元素是入口,栈顶元素是回退的第一站,也即后走过的点先退回,先走过的点后退回,与栈的“后进选出,先进后出”特点一致,故在该问题求解的程序中可以采用栈这种数据结构。在迷宫有通路时,栈中保存的点逆序连起来就是一条迷宫的通路,否则栈中没有通路。
demo.cpp
# include
#include "mStack.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
mPoint mpArray[10][10];
bool initArray[10][10] = {
{ false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false },
{ false,true ,true ,false,true ,true ,true ,false,true ,false },
{ false,true ,true ,false,true ,true ,true ,false,true ,false },
{ false,true ,true ,true ,true ,false,false,true ,true ,false },
{ false,true ,false,false,false,true ,true ,true ,true ,false },
{ false,true ,true ,true ,false,true ,true ,true ,true ,false },
{ false,true ,false,true ,true ,true ,false,true ,true ,false },
{ false,true ,false,false,false,true ,false,false,true ,false },
{ false,true,true ,true ,true ,true ,true ,true ,true ,false },
{ false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false,false } };//迷宫矩阵
for (int i = 0; i<10; i++)
for (int j = 0; j<10; j++)
{
mpArray[i][j].x = i;
mpArray[i][j].y = j;
mpArray[i][j].can_move_to = initArray[i][j];
}
mPoint startp(1, 1, true);//初始坐标(入口)
mPoint endp(8, 8, true); //结束坐标(出口)
mStack mpath;//定义对象
mpath.push(startp);//把初始坐标入栈
mPoint mp = startp;//记录当前坐标
while (true)
{
if (mp.x == endp.x && mp.y == endp.y)
break;//成功出迷宫
if (mpArray[mp.x + 1][mp.y].can_move_to)//向下
{
mpArray[mp.x + 1][mp.y].can_move_to = false;//将走过的路标记为false
mpath.push(mPoint(mp.x + 1, mp.y));
mp = mpArray[mp.x + 1][mp.y];
continue;
}
if (mpArray[mp.x - 1][mp.y].can_move_to)//向上
{
mpArray[mp.x - 1][mp.y].can_move_to = false;
mpath.push(mPoint(mp.x - 1, mp.y));
mp = mpArray[mp.x - 1][mp.y];
continue;
}
if (mpArray[mp.x][mp.y + 1].can_move_to)//向右
{
mpArray[mp.x][mp.y + 1].can_move_to = false;
mpath.push(mPoint(mp.x, mp.y + 1));
mp = mpArray[mp.x][mp.y + 1];
continue;
}
if (mpArray[mp.x][mp.y - 1].can_move_to)//向左
{
mpArray[mp.x][mp.y - 1].can_move_to = false;
mpath.push(mPoint(mp.x, mp.y - 1));
mp = mpArray[mp.x][mp.y - 1];
continue;
}
if (0 == mpath.getLength())//栈空
{
cout << "没有路" << endl;
return -1;
}
mpath.pop();
mp = mpath.getTop();
}
cout << "路径:" << endl;
mpath.printStack();//输出路径
return 0;
}
mStack.h
#include
using namespace std;
struct mPoint
{
int x;
int y;
bool can_move_to;
mPoint(int rx = 0, int ry = 0, bool rcan_move_to = false)
{
x = rx;
y = ry;
can_move_to = rcan_move_to;
next = NULL;
}
mPoint *next;
};
class mStack
{
public:
mStack();//构造函数
int push(mPoint point);//入栈
mPoint pop();//出栈
int getLength();//长度
mPoint getTop();//栈顶
void printStack();//遍历
private:
mPoint *base;//基指针
mPoint *top; //顶指针
int length; //栈长度
}; mStack.cpp
#include "mStack.h"
#include
using namespace std;
mStack::mStack()
{
length = 0;
base = NULL;
top = NULL;
}
int mStack::push(mPoint point)
{
mPoint *mpNode = new mPoint();
*mpNode = point;
if (length == 0)
top = base = mpNode;
else
{
top->next = mpNode;
top = mpNode;
}
return ++length;
}
mPoint mStack::getTop()
{
return *top;
}
mPoint mStack::pop()
{
if (length <= 0)
return NULL;
mPoint retPoint = *top;
top = base;
while (top->next != NULL)
{
if (top->next->next == NULL)
{
delete(top->next);
top->next = NULL;
break;
}
top = top->next;
}
if (length == 1)
{
delete(base);
base = top = NULL;
}
length--;
return retPoint;
}
int mStack::getLength()
{
return length;
}
void mStack::printStack()
{
mPoint *p = base;
while (p != NULL)
{
cout << "(" << p->x << "," << p->y << ")" << endl;
p = p->next;
}
}