2020大厂面试必备——HashMap1.7和1.8源码解析
2020大厂面试必备——HashMap1.7和1.8源码解析
1.HashMap
(1)数据结构
在JDK1.7中,HashMap中的数据结构是数组+单链表的组合;在JDK1.8中的HashMap存储结构是由数组、链表、红黑树这三种数据结构形成。
(2)JDK1.7中HashMap源码分析
(2.1)首先看一张图片:
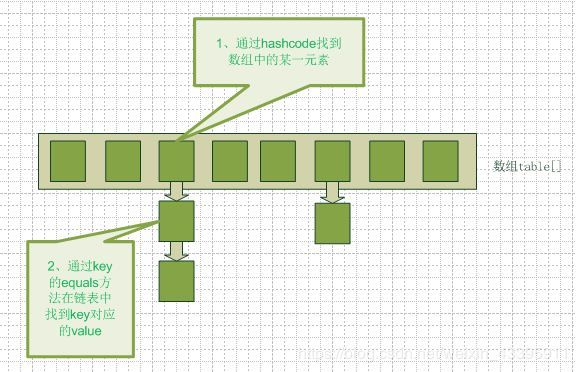
这张图片非常清晰直观地表示了HashMap底层的数据结构,即数组+链表。
(2.2)实现原理
成员变量:
/** 初始容量,默认16 */
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/** 最大初始容量,2^30 */
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/** 负载因子,默认0.75,负载因子越小,hash冲突机率越低 */
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/** 初始化一个Entry的空数组 */
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
/** 将初始化好的空数组赋值给table,table数组是HashMap实际存储数据的地方,并不在EMPTY_TABLE数组中 */
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
/** HashMap实际存储的元素个数 */
transient int size;
/** 临界值(HashMap 实际能存储的大小),公式为(threshold = capacity * loadFactor) */
int threshold;
/** 负载因子 */
final float loadFactor;
/** HashMap的结构被修改的次数,用于迭代器 */
transient int modCount;
构造方法:
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 判断设置的容量和负载因子合不合理
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// 设置负载因子,临界值此时为容量大小,后面第一次put时由inflateTable(int toSize)方法计算设置
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
inflateTable(threshold);
putAllForCreate(m);
}
put方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 如果table引用指向成员变量EMPTY_TABLE,那么初始化HashMap(设置容量、临界值,新的Entry数组引用)
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {//如果当前数组为空
inflateTable(threshold);//延迟加载
}
// 若“key为null”,则将该键值对添加到table[0]处,遍历该链表,如果有key为null,则将value替换。没有就创建新Entry对象放在链表表头
// 所以table[0]的位置上,永远最多存储1个Entry对象,形成不了链表。key为null的Entry存在这里
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 若“key不为null”,则计算该key的哈希值
int hash = hash(key);
// 搜索指定hash值在对应table中的索引
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 循环遍历table数组上位置为i的链表,链表有Entry对象组成,用于判断该位置上key是否已存在
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
// 哈希值相同并且对象相同
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
// 如果这个key对应的键值对已经存在,就用新的value代替老的value,然后退出!
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
//调用value的回调函数,其实这个函数也为空实现
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
// table数组中没有key对应的键值对,就将key-value添加到table[i]处
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
/**
* Inflates the table.
*/
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
//一个很重要的方法,返回一个比toSize大或相等的2的n次幂的整数
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
/**
* 将一个数换算成2的n次幂
* @param number
* @return
*/
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) {
// assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative";
return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
: (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1;
// 理解 Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1)
// 比如 number = 23,23 - 1 = 22,二进制是:10110
// 22 左移一位(右边补1个0),结果是:101100
// Integer.highestOneBit() 函数的作用是取左边最高一位,其余位取0,
// 即:101100 -> 100000,换成十进制就是 32
}
要研究roundUpToPowerOf2方法,必须看看下面的方法,该方法返回一个比i小的或相等的2的整数次幂:
public static int highestOneBit(int i) {
// HD, Figure 3-1
i |= (i >> 1);
i |= (i >> 2);
i |= (i >> 4);
i |= (i >> 8);
i |= (i >> 16);
return i - (i >>> 1);
}
将i的二进制表示右移,并与i自身做异或运算,例如10的二进制表示为0000 1010,10>>1的二进制表示为0000 0101,再异或运算得到:0000 1111,此时i=0000 1111。再进行后面的运算即可。最后的结果为8,方法验证成功。然后结合Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) ,就可以得到一个比number大或相等的2的n次幂的整数。
总之,初始化数组的时候,HashMap的容量总是一个2的整数次幂。
计算Hash值的方法
//用了很多的异或,移位等运算,对key的hashcode进一步进行计算以及二进制位的调整等来保证最终获取的存储位置尽量分布均匀
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {//这里针对String优化了Hash函数,是否使用新的Hash函数和Hash因子有关
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
返回数组下标的方法:
//返回数组下标
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
h&(length-1)保证获取的index一定在数组范围内,举个例子,默认容量16,length-1=15,h=18,转换成二进制计算,最终计算出的index=2。有些版本的对于此处的计算会使用取模运算,也能保证index一定在数组范围内,不过位运算对计算机来说,性能更高一些(HashMap中有大量位运算)。使用 h & (length-1)是为了使得数组的下标肯定在[0,length-1]内。相当于求余,效率高。
HashCode是通过Key算出来的,Key的HashCode直接决定了这个K-V对放在数组的哪个位置上。这个缺点还是有的,如果多个K-V对放在同一个位置,会导致数组对应的链表很长很长,会影响到get的效率。
将K-V对象放入到链表中:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);//当size超过临界阈值threshold,并且即将发生哈希冲突时进行扩容,新容量为旧容量的2倍
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);//扩容后重新计算插入的位置下标
}
//把元素放入HashMap的桶的对应位置
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
//创建元素
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; //获取待插入位置元素
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);//这里执行链接操作,使得新插入的元素指向原有元素。
//这保证了新插入的元素总是在链表的头
size++;//元素个数+1
}
这里采用的是头插法
扩容操作
//按新的容量扩容Hash表
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;//老的数据
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;//获取老的容量值
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {//老的容量值已经到了最大容量值
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//修改扩容阀值
return;
}
//新的结构
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));//将老的表中的数据拷贝到新的结构中
table = newTable;//修改HashMap的底层数组
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);//修改阀值
}
//将老的表中的数据拷贝到新的结构中
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;//容量
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { //遍历所有桶
while(null != e) { //遍历桶中所有元素(是一个链表)
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {//如果是重新Hash,则需要重新计算hash值
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);//定位Hash桶
e.next = newTable[i];//元素连接到桶中,这里相当于单链表的插入,总是插入在最前面
newTable[i] = e;//newTable[i]的值总是最新插入的值
e = next;//继续下一个元素
}
}
}
JDK1.7的HashMap在多线程的扩容情况下(“transfer”方法)会出现问题,容易出现循环链表。
(3)JDK1.8中HashMap源码分析及改进
节点类:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
成员变量
//默认初始容量,即数组长度为16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
//最大容量,2的30次方
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//负载因子为0.75,可以确保一个拉姆达为0.5的泊松分布,使得时间和空间复杂度最优
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//链表转为红黑树的阈值为8,节点类从Node改为TreeNode
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
//红黑树转为链表的阈值为6,节点类从TreeNode改为Node
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
//Node[] table 数组长度转换为红黑树的阈值
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
即使 hash 算法 和负载因子设计的再完美,也避免不了拉链过长的情况,一旦出现拉链过长,严重影响 HashMap 的性能,于是在 JDK1.8 中对数据结构做了进一步的优化,引入了红黑树。当链表长度太长(超过 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8)时,当Node[] table 数组长度超过 64(MIN_TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 64) 时,链表就转化为了红黑树,利用红黑树快速增删改查的特点提高 HashMap 的性能。
构造方法:
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
有几个说法,与JDK1.7中的有所区别:
- 一般将数组中的每一个元素称作桶(segment),桶中连的链表或者红黑树中的每一个元素成为bin
- capacity: 源码中没有将它作为属性,但是为了方便,引进了这个概念,是指HashMap中桶的数量。默认值为16。扩容是按照原容量的2倍进行扩。如果在构造函数中指定了Map的大小,那么进行put操作时,初始化后的容量为离传入值最近的2的整数幂,是通过tableSizeFor() 函数达到该目的。总之,容量都是2的幂。 设计成16的好处是可以使用按位与替代取模来提升hash的效率。
- loadFactor: 译为装载因子。装载因子用来衡量HashMap满的程度。loadFactor的默认值为0.75f。计算HashMap的实时装载因子的方法为:size/capacity,而不是占用桶的数量去除以capacity。
- threshold: threshold表示当HashMap的size大于threshold时会执行resize操作。threshold = capacity*loadFactor
- DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY : 默认初始化容量 16。容量必须为2的次方。默认的hashmap大小为16.
- MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :最大的容量大小2^30
- DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR: 默认resize的因子。0.75,即实际数量超过总数DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR的数量即会发生resize动作。在时间和空间比较特殊的情况下,如果内存空间很多而又对时间效率要求很高,可以降低负载因子Load factor的值;相反,如果内存空间紧张而对时间效率要求不高,可以增加负载因子loadFactor的值,这个值可以大于1。
- TREEIFY_THRESHOLD: 树化阈值 8。当单个segment的容量超过阈值时,将链表转化为红黑树。
- UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD :链表化阈值 6。当resize后或者删除操作后单个segment的容量低于阈值时,将红黑树转化为链表。
- MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY :最小树化容量 64。当桶中的bin被树化时最小的hash表容量,低于该容量时不会树化。
HashMap扩容及其树化的具体过程
- 如果在创建 HashMap 实例时没有给定capacity、loadFactor则默认值分别是16和0.75。
- 随着put进HashMap的元素增加,不可避免会发生哈希冲突,当较多bin被映射到同一个桶时,会形成一个较长的链表;如果这个桶(链表)中bin的数量小于等于TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(8),显然不会转化成树形结构存储;
- 如果这个桶中bin的数量大于了 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(8) ,但是capacity小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY (64)则依然使用链表结构进行存储,此时会对HashMap进行扩容,扩容的目的是为了缩短链表的长度;
- 如果capacity大于了MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY ,才有资格进行树化(当bin的个数大于8时)。
综上所述,HashMap的树化,要受到两个因素的制约,一个是capacity(数组的长度,桶的数量),另一个是bin的个数(链表的长度,桶的容量)。
当capacity<64,bin<8时,桶维持链表的数据结构;
当capacity<64,bin>=8时,数组会扩容;
当capacity>=64,bin>=8时,链表会转为红黑树,当bin<=6时,红黑树会转为链表。
hash 值的计算
- 根据存入的key-value对中的key计算出对应的hash值,然后放入对应的桶中,所以好的hash值计算方法十分重要,可以大大避免哈希冲突。
- HashMap是以hash操作作为散列依据。但是又与传统的hash存在着少许的优化。其hash值是key的hashcode与其hashcode右移16位的异或结果。在put方法中,将取出的hash值与当前的hashmap容量-1进行与运算。得到的就是位桶的下标。那么为何需要使用key.hashCode() ^ h>>>16的方式来计算hash值呢。其实从微观的角度来看,这种方法与直接去key的哈希值返回在功能实现上没有差别。但是由于最终获取下表是对二进制数组最后几位的与操作。所以直接取hash值会丢失高位的数据,从而增大冲突引起的可能。由于hash值是32位的二进制数。将高位的16位于低位的16位进行异或操作,即可将高位的信息存储到低位。因此该函数也叫做扰乱函数。目的就是减少冲突出现的可能性。而官方给出的测试报告也验证了这一点。直接使用key的hash算法与扰乱函数的hash算法冲突概率相差10%左右。
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
n = table.length;
index = (n-1) & hash;
根据以上可知,hashcode是一个32位的值,用高16位与低16位进行异或,原因在于求index是是用 (n-1) & hash ,如果hashmap的capcity很小的话,那么对于两个高位不同,低位相同的hashcode,可能最终会装入同一个桶中。那么会造成hash冲突,好的散列函数,应该尽量在计算hash时,把所有的位的信息都用上,这样才能尽可能避免冲突。这就是为什么用高16位与低16位进行异或的原因。
为什么capcity是2的幂?
因为 算index时用的是(n-1) & hash,这样就能保证n -1是全为1的二进制数,如果不全为1的话,存在某一位为0,那么0,1与0与的结果都是0,这样便有可能将两个hash不同的值最终装入同一个桶中,造成冲突。所以必须是2的幂。
在算index时,用位运算(n-1) & hash而不是模运算 hash % n的好处(在HashTable中依旧是取模运算)?
位运算消耗资源更少,更有效率
避免了hashcode为负数的情况
put 操作
put 操作的主要流程如下:
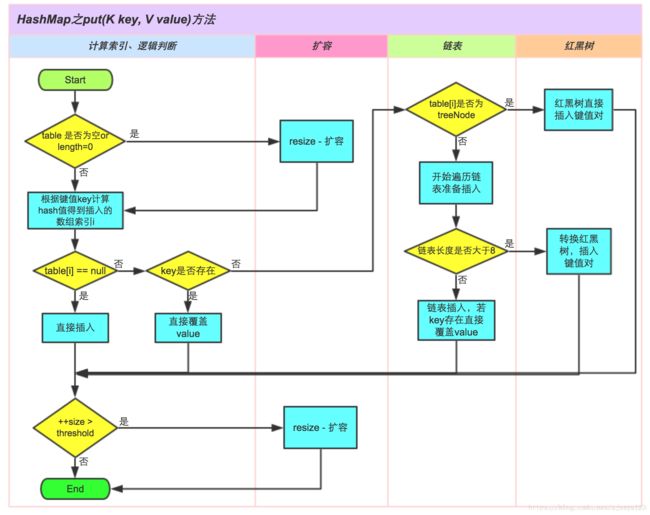
①.判断键值对数组table[i]是否为空或为null,否则执行resize()进行扩容;
②.根据键值key计算hash值得到插入的数组索引i,如果table[i]==null,直接新建节点添加,转向⑥,如果table[i]不为空,转向③;
③.判断table[i]的首个元素是否和key一样,如果相同直接覆盖value,否则转向④,这里的相同指的是hashCode以及equals;
④.判断table[i] 是否为treeNode,即table[i] 是否是红黑树,如果是红黑树,则直接在树中插入键值对,否则转向⑤;
⑤.遍历table[i],判断链表长度是否大于8,大于8的话把链表转换为红黑树,在红黑树中执行插入操作,否则进行链表的插入操作;遍历过程中若发现key已经存在直接覆盖value即可;
⑥.插入成功后,判断实际存在的键值对数量size是否超多了最大容量threshold,如果超过,进行扩容。
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key.
* (A null return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated null with key.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//初始化时,map中还没有key-value
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//利用resize生成对应的tab[]数组
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
//当前桶无元素
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {//桶内有元素
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//桶内第一个元素的key等于待放入的key,用
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//如果此时桶内已经树化
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {//桶内还是一个链表,则插入链尾(尾插)
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
//变成红黑树
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
//检查是否应该扩容
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
resize 扩容操作
resize扩容操作主要用在两处:
向一个空的HashMap中执行put操作时,会调用resize()进行初始化,要么默认初始化,capacity为16,要么根据传入的值进行初始化
put操作后,检查到size已经超过threshold,那么便会执行resize,进行扩容,如果此时capcity已经大于了最大值,那么便把threshold置为int最大值,否则,对capcity,threshold进行扩容操作。
发生了扩容操作,那么必须Map中的所有的数进行再散列,重新装入。
resize扩容操作主要用在两处:
向一个空的HashMap中执行put操作时,会调用resize()进行初始化,要么默认初始化,capacity为16,要么根据传入的值进行初始化
put操作后,检查到size已经超过threshold,那么便会执行resize,进行扩容,如果此时capcity已经大于了最大值,那么便把threshold置为int最大值,否则,对capcity,threshold进行扩容操作。
发生了扩容操作,那么必须Map中的所有的数进行再散列,重新装入。
具体扩容图如下:将一个原先capcity为16的扩容成32的:
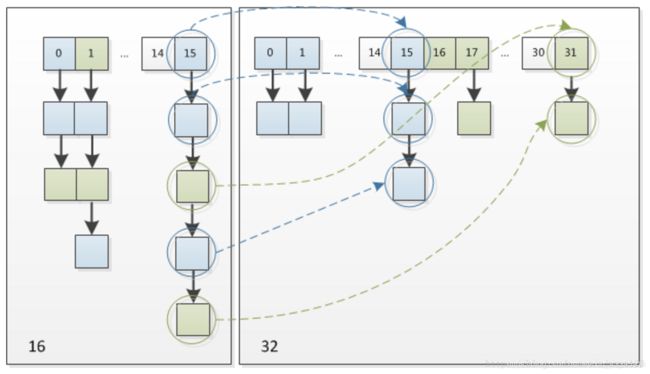
在扩充HashMap的时候,不需要像JDK1.7的实现那样重新计算hash,只需要看看原来的hash值新增的那个bit是1还是0就好了,是0的话索引没变(因为任何数与0与都依旧是0),是1的话index变成“原索引+oldCap”。
例如:n为table的长度,图(a)表示扩容前的key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,图(b)表示扩容后key1和key2两种key确定索引位置的示例,其中hash1是key1对应的哈希与高位运算结果。

元素在重新计算hash之后,因为n变为2倍,那么n-1的mask范围在高位多1bit(红色),因此新的index就会发生这样的变化:
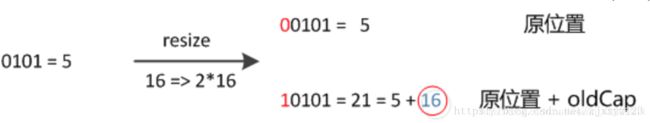
2.总结
jdk 7 与 jdk 8 中关于HashMap的对比
- 8时红黑树+链表+数组的形式,当桶内元素大于8时,便会树化
hash值的计算方式不同 - 1.7 table在创建hashmap时分配空间,而1.8在put的时候分配,如果table为空,则为table分配空间。
- 在发生冲突,插入链中时,7是头插法,8是尾插法。
- 在resize操作中,7需要重新进行index的计算,而8不需要,通过判断相应的位是0还是1,要么依旧是原index,要么是oldCap + 原index