基于Android10的Service的启动流程
一直与Service打交道,确从来没有真正了解过Service的启动流程是怎样的,onCreate,onStartCommand等是在哪里被调用的,所以今天打算通过Android Q的代码来重新认识它。
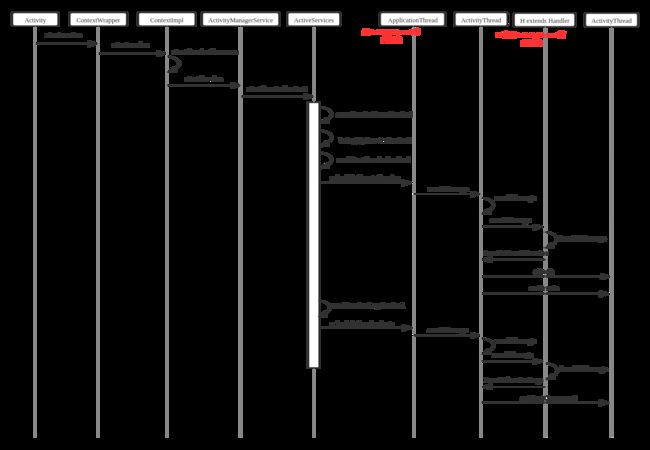
首先添加一张不怎么标准的时序图,仅供参考
Android的Activity,Service,Broadcast,Provider都有一个共同的父类Context,比如我们在activity中启动一个Service,我们就需要调用Context的startService方法,Context是一个抽象类,它的方法实现都在ContextImpl中
@Nullable
public abstract ComponentName startService(Intent service);Context中startService的实现在ContextImpl中
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);
}ContextImpl的startServiceCommon实现
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground,
UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
//注释1,这里是通过AIDL的方式获取到ActivityManagerService,然后调用AMS的startService
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), requireForeground,
getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
//...........
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}ActivityManagerService中startService的实现
@Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...............
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,
"*** startService: " + service + " type=" + resolvedType + " fg=" + requireForeground);
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res;
try {
//注释2,调用ActivityService的startServiceLocked
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid,
requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return res;
}
}
ActiveService中startServiceLocked的实现
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage,
final int userId, boolean allowBackgroundActivityStarts)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//.................................
//注释3
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, null, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false, false);
//.................................
//注释4
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
return cmp;
}注释3,retrieveServiceLocked获取目标service对应的ServiceRecord,查找是先从本地的ServiceMap中查找,如果没有找到,就会通过PackageManagerServie获取目标service对应的信息,并封装到ServiceRecord中,最会将ServiceRecord封装到ServiceLookupResuslt中返回。
注释4调用了ActiveServices的startServiceInnerLocked方法
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//调用ActiveServices的bringUpServiceLocked方法
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
//............
return r.name;
}ActiveService的bringUpServiceLocked方法
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...........................
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
final String procName = r.processName;
HostingRecord hostingRecord = new HostingRecord("service", r.instanceName);
ProcessRecord app;
//如果目标service所在的进程已经启动
if (!isolated) {
//首先获取到processRecord
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
//然后把目标service的信息添加到processRecord
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
//最后启动service
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortInstanceName, e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
} else {
// If this service runs in an isolated process, then each time
// we call startProcessLocked() we will get a new isolated
// process, starting another process if we are currently waiting
// for a previous process to come up. To deal with this, we store
// in the service any current isolated process it is running in or
// waiting to have come up.
app = r.isolatedProc;
if (WebViewZygote.isMultiprocessEnabled()
&& r.serviceInfo.packageName.equals(WebViewZygote.getPackageName())) {
hostingRecord = HostingRecord.byWebviewZygote(r.instanceName);
}
if ((r.serviceInfo.flags & ServiceInfo.FLAG_USE_APP_ZYGOTE) != 0) {
hostingRecord = HostingRecord.byAppZygote(r.instanceName, r.definingPackageName,
r.definingUid);
}
}
// Not running -- get it started, and enqueue this service record
// to be executed when the app comes up.
//如果目标service所在的进程没有启动,需要启动进程,然后添加目标service,启动service
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
hostingRecord, false, isolated, false, r.latestCallerName)) == null) {
String msg = "Unable to launch app "
+ r.appInfo.packageName + "/"
+ r.appInfo.uid + " for service "
+ r.intent.getIntent() + ": process is bad";
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
//.........................
return null;
}本次只分析进程已经启动的情况
调用ActiveServices的realStartServiceLocked
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
//.........
//调用ApplicationThread的scheduleCreateService方法
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackage(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.getReportedProcState());
//........
//注释5
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
//...........
}ApplicationThread是ActivityThread内部类,所以scheduleCreateService是在ActivithThread.java中实现的
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
//send 创建service的msg
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}在scheduleCreateService中发送CREATE_SERVICE msg,然后会经过Android Handler 机制来对消息进行处理,对于Handler部分可以参考上传的ppt文档
最终也会在ActivityThread的内部类H中进行消息的处理
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
//....................
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, ("serviceCreate: " + String.valueOf(msg.obj)));
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
}
}handleCreateService方法
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
//通过反射 获取到Service
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
//.........................
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//最终调用service的attach方法和onCreate方法
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
//......................
}最后终于看到了,我们每次写service都要写的onCreate,知道了它最终是被谁调用的,还有一个很重要的方法还没看到,就是onStartCommand方法,在上面我们还留下了一个伏笔, 就是注释5 sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true)
在create Service完成后,会调用sendServiceArgsLocked方法,和上面的CreateService流程类似,通过Handler机制最终调用
handleServiceArgs来调用onStartCommand方法
private void handleServiceArgs(ServiceArgsData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
//...............
if (!data.taskRemoved) {
res = s.onStartCommand(data.args, data.flags, data.startId);
} else {
s.onTaskRemoved(data.args);
res = Service.START_TASK_REMOVED_COMPLETE;
}
}具体的细节没有描述,仅仅描述了函数调用的大体流程,还有很多是借鉴他人,仅供参考,欢迎提供意见!