Android广播之注册广播(包括静态广播和动态广播的注册)源码分析
Android广播按发送方式分类有三种:无序广播、有序广播(OrderedBroadcast)和粘性广播(StickyBroadcast)。
静态广播的注册流程:
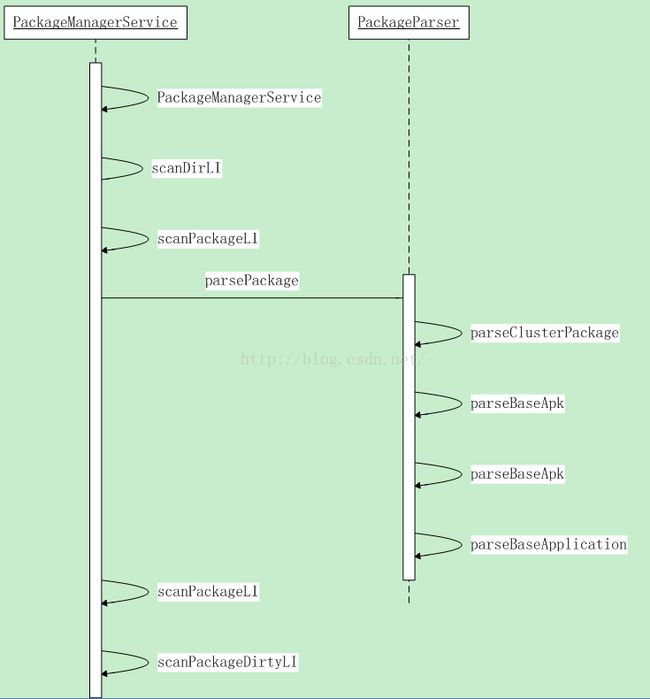
在系统服务启动时会添加PackageManagerService,在该类的构造方法中就会对各个应用安装目录的apk文件进行扫描解析。先看下时序图:
先看PackageManagerService类的构造方法:
// Keys are String (package name), values are Package. This also serves
// as the lock for the global state. Methods that must be called with
// this lock held have the prefix "LP".
@GuardedBy("mPackages")// 域注解:是对类里面成员变量加的注解.受与mPackages引用相关联的锁保护
final ArrayMap mPackages =
new ArrayMap();
public PackageManagerService(Context context, Installer installer,
boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) {
. . .
// Collect ordinary system packages.
final File systemAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(),
"app");
scanDirLI(systemAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanFlags, 0);
// 扫描其他路径
. . .
}
private void scanDirLI(File dir, int parseFlags, int scanFlags, long currentTime) {
final File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(files)) {
Log.d(TAG, "No files in app dir " + dir);
return;
}
if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) {
Log.d(TAG, "Scanning app dir " + dir + " scanFlags=" + scanFlags
+ " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(parseFlags));
}
Log.d(TAG, "start scanDirLI:"+dir);
// use multi thread to speed up scanning
int iMultitaskNum = SystemProperties.getInt("persist.pm.multitask", 6);
Log.d(TAG, "max thread:" + iMultitaskNum);
final MultiTaskDealer dealer = (iMultitaskNum > 1) ? MultiTaskDealer.startDealer(
MultiTaskDealer.PACKAGEMANAGER_SCANER, iMultitaskNum) : null;
for (File file : files) {
final boolean isPackage = (isApkFile(file) || file.isDirectory())
&& !PackageInstallerService.isStageName(file.getName());
if (!isPackage) {
// Ignore entries which are not packages
continue;
}
if (RegionalizationEnvironment.isSupported()) {
if (RegionalizationEnvironment.isExcludedApp(file.getName())) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Regionalization Excluded:" + file.getName());
continue;
}
}
final File ref_file = file;
final int ref_parseFlags = parseFlags;
final int ref_scanFlags = scanFlags;
final long ref_currentTime = currentTime;
Runnable scanTask = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
// 扫描文件
scanPackageLI(ref_file, ref_parseFlags | PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK,
ref_scanFlags, ref_currentTime, null);
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to parse " + ref_file + ": " + e.getMessage());
// Delete invalid userdata apps
if ((ref_parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) == 0 &&
e.error == PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK) {
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Deleting invalid package at " + ref_file);
if (ref_file.isDirectory()) {
mInstaller.rmPackageDir(ref_file.getAbsolutePath());
} else {
ref_file.delete();
}
}
}
}
};
if (dealer != null)
dealer.addTask(scanTask);
else
scanTask.run();
}
if (dealer != null)
dealer.waitAll();
Log.d(TAG, "end scanDirLI:"+dir);
}
/*
* Scan a package and return the newly parsed package.
* Returns null in case of errors and the error code is stored in mLastScanError
*/
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(File scanFile, int parseFlags, int scanFlags,
long currentTime, UserHandle user) throws PackageManagerException {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Parsing: " + scanFile);
parseFlags |= mDefParseFlags;
PackageParser pp = new PackageParser();
pp.setSeparateProcesses(mSeparateProcesses);
pp.setOnlyCoreApps(mOnlyCore);
pp.setDisplayMetrics(mMetrics);
if ((scanFlags & SCAN_TRUSTED_OVERLAY) != 0) {
parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_TRUSTED_OVERLAY;
}
final PackageParser.Package pkg;
try {
// 根据文件路径解析文件
pkg = pp.parsePackage(scanFile, parseFlags);
} catch (PackageParserException e) {
throw PackageManagerException.from(e);
}
. . .
// Note that we invoke the following method only if we are about to unpack an application
PackageParser.Package scannedPkg = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags
| SCAN_UPDATE_SIGNATURE, currentTime, user);
. . .
return scannedPkg;
}
上面scanPackageLI方法中主要执行两个方法:PackageParser类中的parsePackage方法和PackageManagerService类中的scanPackageLI重载方法,这里按顺序看,先看parsePackage方法:
/** File name in an APK for the Android manifest. */
private static final String ANDROID_MANIFEST_FILENAME = "AndroidManifest.xml";
/** Path prefix for apps on expanded storage */
private static final String MNT_EXPAND = "/mnt/expand/";
/**
* Parse the package at the given location. Automatically detects if the
* package is a monolithic style (single APK file) or cluster style
* (directory of APKs).
*/
public Package parsePackage(File packageFile, int flags) throws PackageParserException {
if (packageFile.isDirectory()) {
// 解析文件夹下所有apk文件
return parseClusterPackage(packageFile, flags);
} else {
// 解析apk文件
return parseMonolithicPackage(packageFile, flags);
}
}
/**
* Parse all APKs contained in the given directory, treating them as a
* single package. This also performs sanity checking, such as requiring
* identical package name and version codes, a single base APK, and unique
* split names.
*/
private Package parseClusterPackage(File packageDir, int flags) throws PackageParserException {
// 解析文件夹下所有apk文件的基本信息
final PackageLite lite = parseClusterPackageLite(packageDir, 0);
if (mOnlyCoreApps && !lite.coreApp) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED,
"Not a coreApp: " + packageDir);
}
final AssetManager assets = new AssetManager();
try {
// Load the base and all splits into the AssetManager
// so that resources can be overriden when parsing the manifests.
loadApkIntoAssetManager(assets, lite.baseCodePath, flags);
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(lite.splitCodePaths)) {
for (String path : lite.splitCodePaths) {
// 把文件夹下所有apk文件都添加到assets中
loadApkIntoAssetManager(assets, path, flags);
}
}
final File baseApk = new File(lite.baseCodePath);
// 解析apk文件返回一个Package对象
final Package pkg = parseBaseApk(baseApk, assets, flags);
if (pkg == null) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NOT_APK,
"Failed to parse base APK: " + baseApk);
}
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(lite.splitNames)) {
final int num = lite.splitNames.length;
pkg.splitNames = lite.splitNames;
pkg.splitCodePaths = lite.splitCodePaths;
pkg.splitRevisionCodes = lite.splitRevisionCodes;
pkg.splitFlags = new int[num];
pkg.splitPrivateFlags = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
// 解析分包apk,后续流程跟parseBaseApk类似,这里不再详解
parseSplitApk(pkg, i, assets, flags);
}
}
pkg.codePath = packageDir.getAbsolutePath();
return pkg;
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(assets);
}
}
private Package parseBaseApk(File apkFile, AssetManager assets, int flags)
throws PackageParserException {
final String apkPath = apkFile.getAbsolutePath();
String volumeUuid = null;
if (apkPath.startsWith(MNT_EXPAND)) {
final int end = apkPath.indexOf('/', MNT_EXPAND.length());
volumeUuid = apkPath.substring(MNT_EXPAND.length(), end);
}
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
mArchiveSourcePath = apkFile.getAbsolutePath();
if (DEBUG_JAR) Slog.d(TAG, "Scanning base APK: " + apkPath);
final int cookie = loadApkIntoAssetManager(assets, apkPath, flags);
Resources res = null;
XmlResourceParser parser = null;
try {
res = new Resources(assets, mMetrics, null);
assets.setConfiguration(0, 0, null, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
Build.VERSION.RESOURCES_SDK_INT);
parser = assets.openXmlResourceParser(cookie, ANDROID_MANIFEST_FILENAME);
final String[] outError = new String[1];
// 解析apk文件的AndroidManifest.xml
final Package pkg = parseBaseApk(res, parser, flags, outError);
if (pkg == null) {
throw new PackageParserException(mParseError,
apkPath + " (at " + parser.getPositionDescription() + "): " + outError[0]);
}
pkg.volumeUuid = volumeUuid;
pkg.applicationInfo.volumeUuid = volumeUuid;
pkg.baseCodePath = apkPath;
pkg.mSignatures = null;
return pkg;
} catch (PackageParserException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_UNEXPECTED_EXCEPTION,
"Failed to read manifest from " + apkPath, e);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(parser);
}
}
/**
* Parse the manifest of a base APK.
*/
private Package parseBaseApk(Resources res, XmlResourceParser parser, int flags,
String[] outError) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
final boolean trustedOverlay = (flags & PARSE_TRUSTED_OVERLAY) != 0;
AttributeSet attrs = parser;
final String pkgName;
final String splitName;
try {
// parsePackageSplitNames方法校验包名的有效性
Pair packageSplit = parsePackageSplitNames(parser, attrs, flags);
pkgName = packageSplit.first;
splitName = packageSplit.second;
} catch (PackageParserException e) {
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_PACKAGE_NAME;
return null;
}
. . .
int type;
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(splitName)) {
outError[0] = "Expected base APK, but found split " + splitName;
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_PACKAGE_NAME;
return null;
}
final Package pkg = new Package(pkgName);
boolean foundApp = false;
int outerDepth = parser.getDepth();
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT
&& (type != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > outerDepth)) {
if (type == XmlPullParser.END_TAG || type == XmlPullParser.TEXT) {
continue;
}
String tagName = parser.getName();
// 解析application节点
if (tagName.equals("application")) {
if (foundApp) {
if (RIGID_PARSER) {
outError[0] = " has more than one ";
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
return null;
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, " has more than one ");
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
}
}
foundApp = true;
if (!parseBaseApplication(pkg, res, parser, attrs, flags, outError)) {
return null;
}
// 中间还有好多节点的解析,这里省略了
. . .
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unknown element under : " + parser.getName()
+ " at " + mArchiveSourcePath + " "
+ parser.getPositionDescription());
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
}
}
if (!foundApp && pkg.instrumentation.size() == 0) {
outError[0] = " does not contain an or ";
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_EMPTY;
}
. . .
return pkg;
}
/**
* Parse the {@code application} XML tree at the current parse location in a
* base APK manifest.
*/
private boolean parseBaseApplication(Package owner, Resources res,
XmlPullParser parser, AttributeSet attrs, int flags, String[] outError)
throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
. . .
final int innerDepth = parser.getDepth();
int type;
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT
&& (type != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > innerDepth)) {
if (type == XmlPullParser.END_TAG || type == XmlPullParser.TEXT) {
continue;
}
String tagName = parser.getName();
if (tagName.equals("activity")) {
. . .
} else if (tagName.equals("receiver")) {
Activity a = parseActivity(owner, res, parser, attrs, flags, outError, true, false);
if (a == null) {
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
return false;
}
// 静态注册的广播都添加在receivers列表中
owner.receivers.add(a);
// 后面还有解析其他节点,这里不再讲解
. . .
} else {
if (!RIGID_PARSER) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unknown element under : " + tagName
+ " at " + mArchiveSourcePath + " "
+ parser.getPositionDescription());
XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser);
continue;
} else {
outError[0] = "Bad element under : " + tagName;
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
return false;
}
}
}
. . .
return true;
}
经过上面方法解析后,所有静态注册的广播都被添加到了receivers列表中了,再来看PackageManagerService类中的scanPackageLI方法:
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg, int parseFlags,
int scanFlags, long currentTime, UserHandle user) throws PackageManagerException {
boolean success = false;
try {
final PackageParser.Package res = scanPackageDirtyLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags,
currentTime, user);
success = true;
return res;
} finally {
if (!success && (scanFlags & SCAN_DELETE_DATA_ON_FAILURES) != 0) {
removeDataDirsLI(pkg.volumeUuid, pkg.packageName);
}
}
}private PackageParser.Package scanPackageDirtyLI(PackageParser.Package pkg, int parseFlags,
int scanFlags, long currentTime, UserHandle user) throws PackageManagerException {
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
. . .
N = pkg.receivers.size();
r = null;
for (i=0; i
上面方法会把PackageParser类中解析好的广播又添加到mReceivers中,以便后续发送广播。
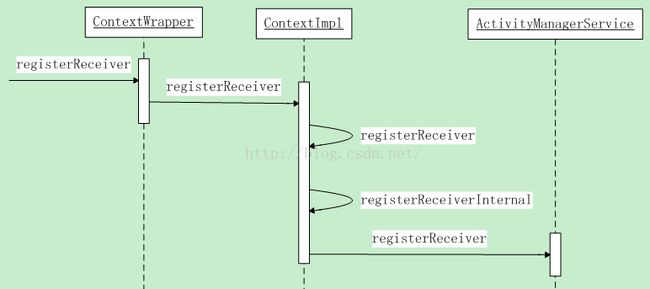
动态注册广播的流程
惯例先看时序图:
根据时序图显示,先看ContextWrapper类的registerReceiver方法:
@Override
public Intent registerReceiver(
BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter) {
return mBase.registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
}
调用ContextImpl类中的registerReceiver方法:
@Override
public Intent registerReceiver(BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter) {
return registerReceiver(receiver, filter, null, null);
}
@Override
public Intent registerReceiver(BroadcastReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter,
String broadcastPermission, Handler scheduler) {
return registerReceiverInternal(receiver, getUserId(),
filter, broadcastPermission, scheduler, getOuterContext());
}
private Intent registerReceiverInternal(BroadcastReceiver receiver, int userId,
IntentFilter filter, String broadcastPermission,
Handler scheduler, Context context) {
IIntentReceiver rd = null;
if (receiver != null) {
// mPackageInfo 是LoadedApk类的实例,在构造方法中赋值
if (mPackageInfo != null && context != null) {
if (scheduler == null) {
scheduler = mMainThread.getHandler();
}
// 返回一个IIntentReceiver接口对象,它是一个Binder对象
rd = mPackageInfo.getReceiverDispatcher(
receiver, context, scheduler,
mMainThread.getInstrumentation(), true);
} else {
if (scheduler == null) {
scheduler = mMainThread.getHandler();
}
rd = new LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher(
receiver, context, scheduler, null, true).getIIntentReceiver();
}
}
try {
return ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().registerReceiver(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mBasePackageName,
rd, filter, broadcastPermission, userId);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return null;
}
}
上面方法中rd是一个IIntentReceiver对象,这是一个Binder对象,接下来会把它传递给ActivityManagerService,AMS在收到相应的广播时,就是通过这个Binder对象来通知各接收者的。
下面先看下LoadedApk类中的getReceiverDispatcher方法:
public IIntentReceiver getReceiverDispatcher(BroadcastReceiver r,
Context context, Handler handler,
Instrumentation instrumentation, boolean registered) {
synchronized (mReceivers) {
LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher rd = null;
ArrayMap map = null;
if (registered) {
map = mReceivers.get(context);
if (map != null) {
// 要获取的ReceiverDispatcher对象已经存在,直接获取并返回
rd = map.get(r);
}
}
if (rd == null) {
// 要获取的ReceiverDispatcher不存在,则新建并保存
rd = new ReceiverDispatcher(r, context, handler,
instrumentation, registered);
if (registered) {
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap();
mReceivers.put(context, map);
}
map.put(r, rd);
}
} else {
// 校验context和handler的有效性
rd.validate(context, handler);
}
rd.mForgotten = false;
return rd.getIIntentReceiver();
}
}
static final class ReceiverDispatcher {
final static class InnerReceiver extends IIntentReceiver.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
final LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher mStrongRef;
InnerReceiver(LoadedApk.ReceiverDispatcher rd, boolean strong) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(rd);
mStrongRef = strong ? rd : null;
}
. . .
}
final IIntentReceiver.Stub mIIntentReceiver;
final BroadcastReceiver mReceiver;
final Context mContext;
final Handler mActivityThread;
final Instrumentation mInstrumentation;
final boolean mRegistered;
final IntentReceiverLeaked mLocation;
RuntimeException mUnregisterLocation;
boolean mForgotten;
ReceiverDispatcher(BroadcastReceiver receiver, Context context,
Handler activityThread, Instrumentation instrumentation,
boolean registered) {
if (activityThread == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Handler must not be null");
}
mIIntentReceiver = new InnerReceiver(this, !registered);
mReceiver = receiver;
mContext = context;
// 保存activityThread以便后面在发布广播时使用
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mInstrumentation = instrumentation;
mRegistered = registered;
mLocation = new IntentReceiverLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
}
void validate(Context context, Handler activityThread) {
if (mContext != context) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Receiver " + mReceiver +
" registered with differing Context (was " +
mContext + " now " + context + ")");
}
if (mActivityThread != activityThread) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Receiver " + mReceiver +
" registered with differing handler (was " +
mActivityThread + " now " + activityThread + ")");
}
}
IIntentReceiver getIIntentReceiver() {
return mIIntentReceiver;
}
. . .
}
上面getReceiverDispatcher方法中的map是以BroadcastReceiver对象r为key,以ReceiverDispatcher对象rd为value保存在一个ArrayMap中,而这个ArrayMap又以Context为key,自己为value保存在LoadedApk类中的成员变量mReceivers中。这样,只要给定Context和BroadcastReceiver就可以查看LoadedApk中是否已经存在相应的广播接收分发器ReceiverDispatcher了。
在新建广播接收分发器ReceiverDispatcher时,会在构造方法中创建一个InnerReceiver类的实例,这是一个Binder对象,实现了IIntentReceiver接口,可以通过ReceiverDispatcher.getIIntentReceiver方法来获得,获得后会把它传给AMS,以便接收广播。
下面看AMS类中的registerReceiver方法:
public Intent registerReceiver(IApplicationThread caller, String callerPackage,
IIntentReceiver receiver, IntentFilter filter, String permission, int userId) {
// 执行根据调用者uid判断调用者不是独立进程的操作
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("registerReceiver");
ArrayList stickyIntents = null;
ProcessRecord callerApp = null;
int callingUid;
int callingPid;
synchronized(this) {
if (caller != null) {
// 获取调用者的ProcessRecord对象callerApp
callerApp = getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp == null) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid()
+ ") when registering receiver " + receiver);
}
// 非系统应用判断调用者是否在正确的进程中执行
if (callerApp.info.uid != Process.SYSTEM_UID &&
!callerApp.pkgList.containsKey(callerPackage) &&
!"android".equals(callerPackage)) {
throw new SecurityException("Given caller package " + callerPackage
+ " is not running in process " + callerApp);
}
callingUid = callerApp.info.uid;
callingPid = callerApp.pid;
} else {
callerPackage = null;
callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
}
// 处理调用者的uid
userId = handleIncomingUser(callingPid, callingUid, userId,
true, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "registerReceiver", callerPackage);
// 迭代filter中所有的action
Iterator actions = filter.actionsIterator();
if (actions == null) {
ArrayList noAction = new ArrayList(1);
noAction.add(null);
actions = noAction.iterator();
}
// Collect stickies of users
// 根据uid获取调用者所有的粘性广播Intents并添加到stickyIntents列表中
int[] userIds = { UserHandle.USER_ALL, UserHandle.getUserId(callingUid) };
while (actions.hasNext()) {
String action = actions.next();
for (int id : userIds) {
ArrayMap> stickies = mStickyBroadcasts.get(id);
if (stickies != null) {
ArrayList intents = stickies.get(action);
if (intents != null) {
if (stickyIntents == null) {
stickyIntents = new ArrayList();
}
stickyIntents.addAll(intents);
}
}
}
}
}
ArrayList allSticky = null;
if (stickyIntents != null) {
final ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver();
// Look for any matching sticky broadcasts...
for (int i = 0, N = stickyIntents.size(); i < N; i++) {
Intent intent = stickyIntents.get(i);
// If intent has scheme "content", it will need to acccess
// provider that needs to lock mProviderMap in ActivityThread
// and also it may need to wait application response, so we
// cannot lock ActivityManagerService here.
// 判断filter和intent是否匹配
if (filter.match(resolver, intent, true, TAG) >= 0) {
if (allSticky == null) {
allSticky = new ArrayList();
}
allSticky.add(intent);
}
}
}
// The first sticky in the list is returned directly back to the client.
Intent sticky = allSticky != null ? allSticky.get(0) : null;
if (DEBUG_BROADCAST) Slog.v(TAG_BROADCAST, "Register receiver " + filter + ": " + sticky);
if (receiver == null) {
return sticky;
}
synchronized (this) {
if (callerApp != null && (callerApp.thread == null
|| callerApp.thread.asBinder() != caller.asBinder())) {
// Original caller already died
return null;
}
// 根据Binder对象获取已注册的ReceiverList
ReceiverList rl = mRegisteredReceivers.get(receiver.asBinder());
if (rl == null) {
// 这里其实是把广播接收器receiver保存在一个ReceiverList列表中
rl = new ReceiverList(this, callerApp, callingPid, callingUid,
userId, receiver);
// rl.app是ReceiverList列表的宿主进程
if (rl.app != null) {
// rl.app.receivers是宿主进程中的一个列表,专门用来保存这个进程注册的广播
rl.app.receivers.add(rl);
} else {
try {
receiver.asBinder().linkToDeath(rl, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return sticky;
}
rl.linkedToDeath = true;
}
mRegisteredReceivers.put(receiver.asBinder(), rl);
} else if (rl.uid != callingUid) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Receiver requested to register for uid " + callingUid
+ " was previously registered for uid " + rl.uid);
} else if (rl.pid != callingPid) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Receiver requested to register for pid " + callingPid
+ " was previously registered for pid " + rl.pid);
} else if (rl.userId != userId) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Receiver requested to register for user " + userId
+ " was previously registered for user " + rl.userId);
}
// 创建BroadcastFilter把广播接收器列表rl和filter关联起来
BroadcastFilter bf = new BroadcastFilter(filter, rl, callerPackage,
permission, callingUid, userId);
rl.add(bf);
if (!bf.debugCheck()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "==> For Dynamic broadcast");
}
// 所有动态注册的广播都放在mReceiverResolver中,以便以后能够接收到广播并进行处理
mReceiverResolver.addFilter(bf);
// Enqueue broadcasts for all existing stickies that match
// this filter.
if (allSticky != null) {
ArrayList receivers = new ArrayList();
receivers.add(bf);
final int stickyCount = allSticky.size();
for (int i = 0; i < stickyCount; i++) {
Intent intent = allSticky.get(i);
// 处理粘性广播
BroadcastQueue queue = broadcastQueueForIntent(intent);
BroadcastRecord r = new BroadcastRecord(queue, intent, null,
null, -1, -1, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, receivers,
null, 0, null, null, false, true, true, -1);
queue.enqueueParallelBroadcastLocked(r);
queue.scheduleBroadcastsLocked();
}
}
return sticky;
}
}
执行完上面方法后,所有动态注册的广播都添加到mReceiverResolver中了。
这里介绍下StickyIntent:在最后一次调用sendStickyBroadcast方法来发送某个Action类型的广播时,系统会把代表这个广播的Intent保存下来,这样后来调用registerReceiver来注册相同Action类型的广播接收器时,就会得到这个最后发出的广播。这个最后发出的广播虽然被处理完了,但是仍然被粘住在AMS中,以便下一个注册相应Action类型的广播接收器还能继续处理。
下面看下IntentFilter类中的actionsIterator方法和match方法:
// mActions在构造方法中进行创建初始化
private final ArrayList mActions;
/**
* Add a new Intent action to match against. If any actions are included
* in the filter, then an Intent's action must be one of those values for
* it to match. If no actions are included, the Intent action is ignored.
*
* @param action Name of the action to match, i.e. Intent.ACTION_VIEW.
*/
public final void addAction(String action) {
if (!mActions.contains(action)) {
mActions.add(action.intern());
}
}
/**
* Return an iterator over the filter's actions. If there are no actions,
* returns null.
*/
public final Iterator actionsIterator() {
return mActions != null ? mActions.iterator() : null;
}
. . .
/**
* Test whether this filter matches the given intent.
*
* @param intent The Intent to compare against.
* @param resolve If true, the intent's type will be resolved by calling
* Intent.resolveType(); otherwise a simple match against
* Intent.type will be performed.
* @param logTag Tag to use in debugging messages.
*
* @return Returns either a valid match constant (a combination of
* {@link #MATCH_CATEGORY_MASK} and {@link #MATCH_ADJUSTMENT_MASK}),
* or one of the error codes {@link #NO_MATCH_TYPE} if the type didn't match,
* {@link #NO_MATCH_DATA} if the scheme/path didn't match,
* {@link #NO_MATCH_ACTION} if the action didn't match, or
* {@link #NO_MATCH_CATEGORY} if one or more categories didn't match.
*
* @see #match(String, String, String, android.net.Uri , Set, String)
*/
public final int match(ContentResolver resolver, Intent intent,
boolean resolve, String logTag) {
String type = resolve ? intent.resolveType(resolver) : intent.getType();
return match(intent.getAction(), type, intent.getScheme(),
intent.getData(), intent.getCategories(), logTag);
}
/**
* Test whether this filter matches the given intent data. A match is
* only successful if the actions and categories in the Intent match
* against the filter, as described in {@link IntentFilter}; in that case,
* the match result returned will be as per {@link #matchData}.
*/
public final int match(String action, String type, String scheme,
Uri data, Set categories, String logTag) {
if (action != null && !matchAction(action)) {
if (false) Log.v(
logTag, "No matching action " + action + " for " + this);
return NO_MATCH_ACTION;
}
int dataMatch = matchData(type, scheme, data);
if (dataMatch < 0) {
if (false) {
if (dataMatch == NO_MATCH_TYPE) {
Log.v(logTag, "No matching type " + type
+ " for " + this);
}
if (dataMatch == NO_MATCH_DATA) {
Log.v(logTag, "No matching scheme/path " + data
+ " for " + this);
}
}
return dataMatch;
}
String categoryMismatch = matchCategories(categories);
if (categoryMismatch != null) {
if (false) {
Log.v(logTag, "No matching category " + categoryMismatch + " for " + this);
}
return NO_MATCH_CATEGORY;
}
// It would be nice to treat container activities as more
// important than ones that can be embedded, but this is not the way...
if (false) {
if (categories != null) {
dataMatch -= mCategories.size() - categories.size();
}
}
return dataMatch;
}
到这里动态注册广播的流程就执行完了。