Android_自定义可定制步长的双向SeekBar
还记得几年前写过一个双向seekbar吗,不足的是不支持步长扩展,老的双向seekbar链接
这几天正好做需求,要扩展一个支持步长,一次只能滑动50个,松开,即刻回弹到距离它最近的单位坐标上,WFK.那么我们要开车了.
需求理一下
- 双向拖动
- 定义步长
- 回弹确定最终值
- 文字描述不能因为太近而遮盖
- …..还有一堆扩展属性不说了
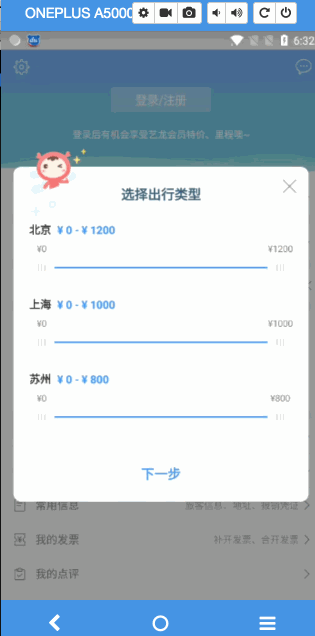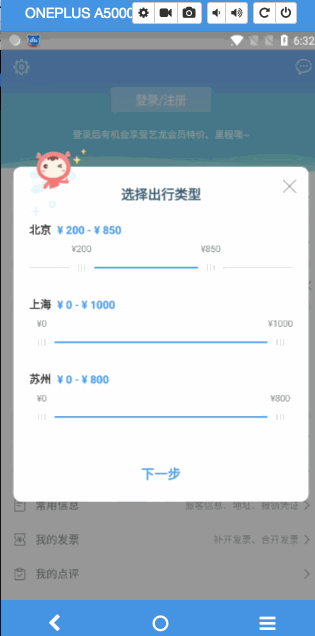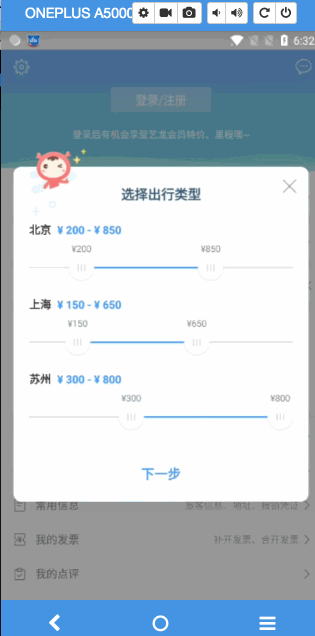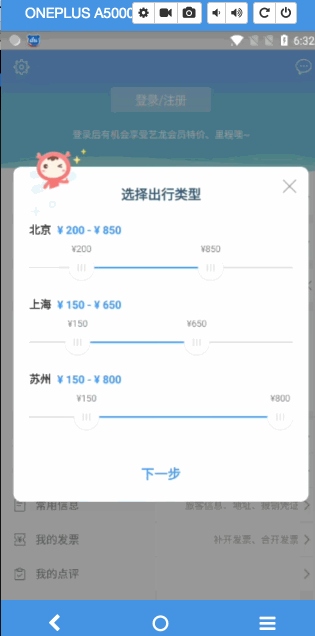
直接看做出来的成品
接下里就手把手,我们来实现一下这个支持定制步长的拖拽seekbar
GIF岂不是更爽
实现步骤
- 分析自定义属性扩展
- 定义并且获取属性
- 计算要绘制的区域的坐标以及范围
- 暴露接口返回数据
1.自定义属性
<declare-styleable name="MyElongScaleSeekBar">
<attr name="scale_progress_normal_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_progress_section_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_left_ball_bg_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_left_ball_stroke_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_left_ball_stroke_with" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_right_ball_bg_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_right_ball_stroke_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_right_ball_stroke_with" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_ball_radio" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_ball_shadow_radio" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_ball_shadow_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_seek_height" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_left_text_color" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_left_text_size" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_right_text_color" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_right_text_size" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_text_margin_ball" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_ball_stick_height" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_ball_stick_width" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_ball_stick_margin" format="dimension" />
<attr name="scale_ball_stick_color" format="color" />
<attr name="scale_progress_unit" format="integer" />
<attr name="scale_symbol_front" format="string" />
declare-styleable>这里就不多解释了,思路就是和你用Android原生textview一样,尽可能的考虑到每个属性的扩展,比如这次我们seekbar的步数,小球的颜色,阴影的颜色,等等.
2.获取自定义属性
TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyElongScaleSeekBar, 0, R.style.default_scale_seekbar_style);
int indexCount = typedArray.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < indexCount; i++) {
int attr = typedArray.getIndex(i);
switch (attr) {
case R.styleable.MyElongScaleSeekBar_scale_progress_normal_color:
scaleProgressNormalColor = typedArray.getColor(attr, Color.BLACK);
break;
....省略.....自定义属性的获取,其实就是view在购置的时候,我们用context拿到TypedArray,去循环遍历我们声明的扩展属性,循环到一个属性,根据你定义的类型,去getvalue即可获取到
3.确定要绘制的图案分几部分组成
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
// 背景进度条
drawScaleSeekNormal(canvas);
// 当前选中的进度
drawScaleSeekSection(canvas);
// 左边的球
drawLeftBall(canvas);
// 右边的球
drawRightBall(canvas);
// 左边球的文字
drawLeftText(canvas);
// 右边球的文字
drawRightText(canvas);
// 说了这么多,其实就是画圆圈和画方块的小把戏
}4.我们定义了要画哪些东西,接下里就是调用canvas的api
// 画方块
canvas.drawRect(...)
// 画圆圈
canvas.drawCircle(...)
// 本效果就用到了这两个api5.绘制之前,我们要重写view的测量.这个要根据你的效果图自己设置,我们view的宽度肯定是充满父布局的,所以直接外面给match就行主要的是高度,因为效果图分两部分,上半部分是文字区域,下半部分是拖拽区域所以view的高度要在测量模式中改成EXACTLY模式,因为高度你自己从定义的属性里面能获取到.
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int measureHeight;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST || heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
//确定view的高度(文字高度+距离+拖拽高度)
measureHeight = Math.max(scaleLeftTextSize, scaleRightTextSize) + 2 + scaleTextMarginBall + scaleBallRadio * 2;
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(measureHeight, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
}
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}6.确定绘制的图形的原始位置,展现静态图
思路很简单,把UI给你的效果图,在一张纸上画一下,
你用铅笔画的过程,就是你转换代码确定位置的过程,
你的纸就是Android的坐标系,画圆圈要确定圆心位置,画方块要确定方块的四个顶点.那么接下来你只要确定了圆心位置,和方块位置定点,那么静态图就出来了.
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
//球的半径包含描边
radioWithStroke = scaleBallRadio + scaleLeftBallStrokeWith * 0.5F;
xCoordinateUnit = radioWithStroke * 2;
valueEntities = calculateAllXCoordinate(scaleProgressUnit, w - radioWithStroke * 2, maxValue);
if (valueEntities != null && valueEntities.size() > 0) {
currentLeft = valueEntities.get(0);
currentRight = valueEntities.get(valueEntities.size() - 1);
leftDesc = creatCurrentDataDesc(currentLeft);
rightDesc = creatCurrentDataDesc(currentRight);
if (this.seekBarDragListener != null) {
this.seekBarDragListener.seekMoveValue(currentLeft.value, currentRight.value);
}
}
if (currentLeft != null && currentRight != null) {
// 背景进度条的区域
scaleSeekNormalRectF = new RectF();
scaleSeekNormalRectF.left = 0;
float top = h - (scaleBallRadio + scaleLeftBallStrokeWith * 0.5F) - scaleSeekHeight * 0.5F - scaleBallShadowRadio;
scaleSeekNormalRectF.top = top;
scaleSeekNormalRectF.bottom = top + scaleSeekHeight;
scaleSeekNormalRectF.right = w;
// 左边球的圆心坐标
leftBallPoint = new SeekPoint();
leftBallPoint.x = currentLeft.xCoordinat + radioWithStroke;
leftBallPoint.y = h - radioWithStroke - scaleBallShadowRadio;
// 左边球中间的猴三棍
calculateLeftSticks();
// 右边球的坐标
rightBallPoint = new SeekPoint();
rightBallPoint.x = currentRight.xCoordinat + radioWithStroke;
rightBallPoint.y = h - radioWithStroke - scaleBallShadowRadio;
// 右边球中间的猴三棍
calculateRightSticks();
// 选中背景条的间距部分
scaleSeekSectionRectF = new RectF();
scaleSeekSectionRectF.left = leftBallPoint.x - radioWithStroke;
scaleSeekSectionRectF.right = rightBallPoint.x - radioWithStroke;
scaleSeekSectionRectF.top = scaleSeekNormalRectF.top;
scaleSeekSectionRectF.bottom = scaleSeekNormalRectF.bottom;
// 圆球的路径和区域
scaleLeftBallPath = new Path();
scaleLeftBallPath.addCircle(leftBallPoint.x, leftBallPoint.y, radioWithStroke, Path.Direction.CW);
scaleRightBallPath = new Path();
scaleRightBallPath.addCircle(rightBallPoint.x, rightBallPoint.y, radioWithStroke, Path.Direction.CW);
scaleLeftBallRegion = updateRegionByPath(scaleLeftBallPath);
scaleRightBallRegion = updateRegionByPath(scaleRightBallPath);
}
}7.最后一步就是拖拽,将静态图改变成动态刷新的静态图
因为你每次的拖拽都执行的move,那么成千上万的move组成的静态图在一zhen一zhen的过的时候,是不是所谓的连续动画,类似于小时候的动画书…
- 动起来,根据ontouch的位置x坐标实时计算圆心的坐标和矩形的四个顶点
- 确定拖拽的是哪个圆圈?
//这里大概都猜到用什么实现的了,没错就是传说中path+Region...直接看代码
// 圆球的路径和区域
scaleLeftBallPath = new Path();
scaleLeftBallPath.addCircle(leftBallPoint.x, leftBallPoint.y, radioWithStroke, Path.Direction.CW);
Region region = new Region();
if (path != null) {
RectF tempRectF = new RectF();
path.computeBounds(tempRectF, true);
region.setPath(path, new Region((int) tempRectF.left, (int) tempRectF.top, (int) tempRectF.right, (int) tempRectF.bottom));
}
return region;我们把圆圈的坐标放到path里面,根据path生成一个他的region,那么我们在触摸的时候,能拿到当前触摸的坐标x,y,那么我们在ACTION_DOWN里面就可以判断你触摸的点是左边的球还是右边的球,那么拖动那个就对那个进行坐标帧刷新即可.
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
boolean touchLeftBall = scaleLeftBallRegion.contains((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY()) && !scaleRightBallRegion.contains((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY());
boolean touchRightBall = scaleRightBallRegion.contains((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY()) && !scaleLeftBallRegion.contains((int) event.getX(), (int) event.getY());8.最后一步,弹性回到当前坐标对应的步长.
这个就是一个经常面试的时候一个小问题,给你一个任意数字,在一个数组里面找到与他最接近的数字并返回.
对应到我们onTouch里面就是,你触摸的任意一点,要从你生成的步长数据集合中找到与之对应的最接近的值即可
public UnitValueEntity binarySearchKey(List data, int targetNum) {
if (data != null && data.size() > 0) {
int left = 0, right = 0;
for (right = data.size() - 1; left != right; ) {
int midIndex = (right + left) / 2;
int mid = (right - left);
int midValue = (int) data.get(midIndex).xCoordinat;
if (targetNum == midValue) {
return data.get(midIndex);
}
if (targetNum > midValue) {
left = midIndex;
} else {
right = midIndex;
}
if (mid <= 1) {
break;
}
}
UnitValueEntity rightnum = data.get(right);
UnitValueEntity leftnum = data.get(left);
return Math.abs((rightnum.xCoordinat - leftnum.xCoordinat) / 2) > Math.abs(rightnum.xCoordinat - targetNum) ? rightnum : leftnum;
}
return null;
}
// 我们这边就用二分查找,来找到这个值,并且返回.