基于多分类非线性SVM(+交叉验证法)的MNIST手写数据集训练(无框架)算法
基于多分类非线性SVM(+交叉验证法)的MNIST手写数据集训练(无框架)算法
- 程序流程
- 数据结构
- 数据处理
- 样本数据由28 x 28 -> 1 x 784
- 将每类数据各自分好
- 任意选取其中两类,合并后将特征和样本按同一乱序打乱。取前X个X<=10000
- 核函数
- K折交叉验证法
- SMO
- 测试
- 效果
- 不足
程序流程
1.将数据进行预处理。
2.通过一对一方法将45类训练样本((0,1),(0,2),…(1,2)…(2,3))送入交叉验证法,训练算法为smo
3.得出45个模型,测试时在利用投票法判定
数据结构
'''***************************************************************
* @Fun_Name : judgeStruct:
* @Function : 存放训练后的分类器参数
* @Parameter :
* @Return :
* @Creed : Talk is cheap , show me the code
***********************xieqinyu creates in 1:28 2020/5/8***'''
class judgeStruct:
def __init__(self):
self.Alpha = []
self.label = []
self.B = 0
self.feature = []
'''***************************************************************
* @Fun_Name : class svmStruct
* @Function : 数据结构
* @Parameter :
* @Return :
* @Creed : Talk is cheap , show me the code
***********************xieqinyu creates in 1:29 2020/5/8***'''
class svmStruct:
def __init__(self, dataMatIn, classLabels, C, toler, kTup):
self.X = dataMatIn #数据矩阵
self.labelMat = classLabels #数据标签
self.C = C #松弛变量
self.tol = toler #容错率
self.m = np.shape(dataMatIn)[0] #数据矩阵行数
self.alphas = np.mat(np.zeros((self.m,1))) #根据矩阵行数初始化alpha参数为0
self.b = 0 #初始化b参数为0
self.eCache = np.mat(np.zeros((self.m,2))) #根据矩阵行数初始化虎误差缓存,第一列为是否有效的标志位,第二列为实际的误差E的值。
self.K = np.mat(np.zeros((self.m,self.m))) #初始化核K
for i in range(self.m): #计算所有数据的核K
self.K[:,i] = kernelTrans(self.X, self.X[i,:], kTup)
数据处理
样本数据由28 x 28 -> 1 x 784
'''***************************************************************
* @Fun_Name : def dealData(images,n):
* @Function : 将60000*28*28 => 60000 * 784
* @Parameter : images 传入特征 n维数
* @Return : 6000 * 784 维度
* @Creed : Talk is cheap , show me the code
***********************xieqinyu creates in 16:30 2020/5/4***'''
def dealData(images,n):
feature = np.empty(shape=[n,784])
for i in range(n):
feature[i] = images[i].reshape(1,-1)
return feature
将每类数据各自分好
'''***************************************************************
* @Fun_Name : def classify_feature(feature,label,n):
* @Function : 分类
* @Parameter : 将每一类的样本各自分好
* @Return :
* @Creed : Talk is cheap , show me the code
***********************xieqinyu creates in 16:33 2020/5/4***'''
zero_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[5923,784])
zero_train_label = np.empty(5923)
one_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[6742,784])
one_train_label = np.empty(6742)
two_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[5958,784])
two_train_label = np.empty(5958)
three_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[6131,784])
three_train_label = np.empty(6131)
four_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[5842,784])
four_train_label = np.empty(5842)
five_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[5421,784])
five_train_label = np.empty(5421)
six_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[5918,784])
six_train_label = np.empty(5918)
seven_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[6265,784])
seven_train_label = np.empty(6265)
eight_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[5851,784])
eight_train_label = np.empty(5851)
nine_train_feature = np.empty(shape=[5949,784])
nine_train_label = np.empty(5949)
list_train_feature = [zero_train_feature,one_train_feature,two_train_feature,three_train_feature,four_train_feature,\
five_train_feature,six_train_feature,seven_train_feature,eight_train_feature,nine_train_feature]
list_train_label = [zero_train_label,one_train_label,two_train_label,three_train_label,four_train_label,\
five_train_label,six_train_label,seven_train_label,eight_train_label,nine_train_label]
def classify_feature(feature,label,n):
num = np.zeros(10,int)
for i in range(n):
k = int(label[i])
list_train_feature[k][num[k]] = feature[i]
list_train_label[k][num[k]] = k
num[k] += 1
任意选取其中两类,合并后将特征和样本按同一乱序打乱。取前X个X<=10000
这边 m是训练样本数,n的话可以用来训练好后自己测试下结果对不对,最后用不到的,调试时候用。
'''***************************************************************
* @Fun_Name : def disruptData(a,b,rand,m,n)
* @Function : 打乱两类数据
* @Parameter : 比如 a=1 b=0 打乱 1,0,训练样本 因为每两种样本数量不太一致 不太方便
交叉检验,所以只取打乱后前10000个样本
* @Return : 第一个是特征 第二个是标签
* @Creed : Talk is cheap , show me the code
***********************xieqinyu creates in 21:40 2020/5/4***'''
def disruptData(a,b,rand,m,n):
np.random.seed(rand)
new_train_feature = np.vstack((list_train_feature[a], list_train_feature[b]))
np.random.shuffle(new_train_feature)
np.random.seed(rand)
new_train_label = np.hstack((list_train_label[a], list_train_label[b]))
np.random.shuffle(new_train_label)
new_test_feature = new_train_feature[-n:,:]
new_test_label = new_train_label[-n:]
new_train_feature = new_train_feature[0:m,:]
new_train_label = new_train_label[0:m]
for i in range(m):
if (new_train_label[i] == a):
new_train_label[i] = -1
else:
new_train_label[i] = 1
for c in range(n):
if (new_test_label[c] == a):
new_test_label[c] = -1
else:
new_test_label[c] = 1
return new_train_feature , new_train_label, new_test_feature,new_test_label
核函数
本例使用高斯核(也可使用线性核)
'''***************************************************************
* @Fun_Name : def kernelTrans(X, A, kTup):
* @Function : 和函数选择 这边选gass
* @Parameter : X 整个训练样本 A一个训练样本 kTup核参数
* @Return :
* @Creed : Talk is cheap , show me the code
***********************xieqinyu creates in 1:27 2020/5/8***'''
def kernelTrans(X, A, kTup):
m,n = np.shape(X)
K = np.mat(np.zeros((m,1)))
if kTup[0] == 'lin': K = X * A.T #线性核函数,只进行内积。
elif kTup[0] == 'rbf': #高斯核函数,根据高斯核函数公式进行计算
for j in range(m):
deltaRow = X[j,:] - A
K[j] = deltaRow*deltaRow.T
K = np.exp(K/(-1*kTup[1]**2)) #计算高斯核K
return K
#返回计算的核K
K折交叉验证法
每次训练样本分十份,九份训练,一份验证。交叉验证10次
选取正确率最高的一次作为本次最优模型
'''***************************************************************
* @Fun_Name : def crossValidation(train_feature,train_label,k1 =100):
* @Function : 交叉验证加训练
* @Parameter : k1为高斯参数
* @Return :
* @Creed : Talk is cheap , show me the code
***********************xieqinyu creates in 1:20 2020/5/8***'''
def crossValidation(train_feature,train_label,k1 =100):
m,n = np.shape(train_feature)
accuracy = np.zeros(10)
B = np.zeros(10)
label = []
Alphas = []
feature =[]
x = int(m/10)
for i in range(10): #交叉验证法 分成10份 0-999,1000-1999 ..
#验证集
featureMatrix_verify = train_feature[i*x:(i+1)*x,:]
labelMatrix_verify = train_label[i*x:(i+1)*x]
#训练集
featureMatrix_train = np.vstack((train_feature[0:i*x,:],train_feature[(i+1)*x:int(m),:]))
labelMatrix_train = np.hstack((train_label[0:i*x],train_label[(i+1)*x:int(m)]))
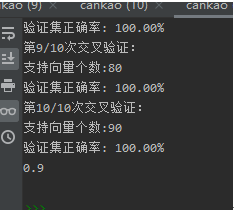
print("第%d/10次交叉验证:" %(i+1))
b, alphas = smoP(featureMatrix_train, labelMatrix_train, 0.1, 0.0001, 10, ('rbf', k1)) # 根据训练集计算b和alphas
datMat = np.mat(train_feature);
labelMat = np.mat(train_label).transpose()
svInd = np.nonzero(alphas.A > 0)[0] # 获得支持向量
sVs = datMat[svInd] # 支持向量的特征样本
labelSV = labelMat[svInd]; # 支持向量的标签样本
print("支持向量个数:%d" % np.shape(sVs)[0])
rightCount = 0
datMat = np.mat(featureMatrix_verify);
labelMat = np.mat(labelMatrix_verify).transpose()
m, n = np.shape(datMat)
for j in range(m):
kernelEval = kernelTrans(sVs, datMat[j, :], ('rbf', k1)) # 计算各个点的核
predict = kernelEval.T * np.multiply(labelSV, alphas[svInd]) + b # 根据支持向量的点,计算超平面,返回预测结果
if np.sign(predict) == labelMatrix_verify[j]: rightCount += 1 # 返回数组中各元素的正负符号,用1和-1表示,并统计错误个数
accuracy[i] = (float(rightCount) / m)*100
# print(alphas[svInd])
print("验证集正确率: %.2f%%" % (accuracy[i]))
feature.append(sVs)
label.append(labelSV)
B[i] = b
Alphas.append(alphas[svInd])
best = np.argmax(accuracy)
return feature[best], label[best],B[best],Alphas[best]
SMO
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/c406495762/article/details/78158354
测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载数据库
train_images = decode.load_train_images()
train_labels = decode.load_train_labels()
test_images = decode.load_test_images()
test_labels = decode.load_test_labels()
# #
f = dealData(train_images,60000)
classify_feature(f,train_labels,60000)
judge = [[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()],
[judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(),
judgeStruct(), judgeStruct(), judgeStruct()], ]
# 开始训练
for i in range(10):
for j in range(i+1,10):
print("第%d,%d次训练"%(i,j))
new_train_feature, new_train_label ,new_test_feature,new_test_label= disruptData(i, j, 16,1000,100) #i 是-1
judge[i][j].feature,judge[i][j].label,judge[i][j].B ,judge[i][j].Alpha = crossValidation(new_train_feature,new_train_label)
# 开始验证
f = dealData(test_images, 10000)
f =f[0:20,]
accuracy = 0
m,n = np.shape(f)
vote = np.zeros(10)
for k in range(m):
# print(test_labels[k])
for i in range(10):
for j in range(i+1,10):
kernelEval = kernelTrans(judge[i][j].feature, f[k, :], ('rbf', 100)) # 计算各个点的核
predict = kernelEval.T * np.multiply(judge[i][j].label, judge[i][j].Alpha) + judge[i][j].B # 根据支持向
if(predict<0):
vote[i] += 1
if(predict>0):
vote[j] += 1
if(vote.argmax() == test_labels[k]):
accuracy += 1
vote = np.zeros(10)
print(accuracy/m)
效果
这边训练了一千个,测试100个(程序忘记改了),100个有点少了,如果测试1000+准确率还得上升。但是训练时长有点长,程序就没改了。

不足
刚刚看资料发现K折交叉验证是为了更好的选取参数,使得模型最优。
而这边的模型的参数有松弛参数C,核函数参数sigma,alpha,和当时的训练样本及标签。本程序中将C 和 sigma提前选取好了,交叉验证法只对其他几个参数进行了筛选,有点不足,后续应该在交叉验证法外面再补上两层循环–C和sigma的循环选取。计算量进一步增大。