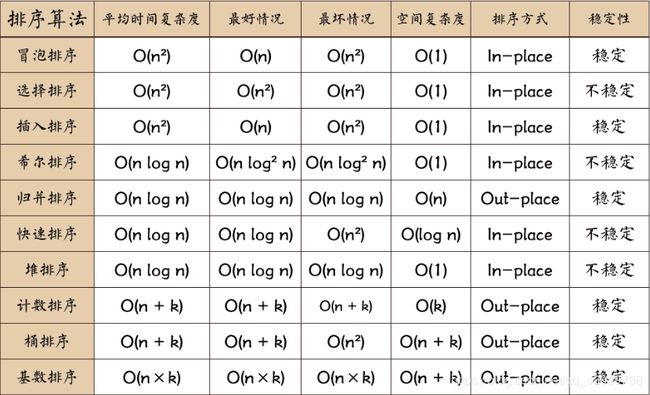
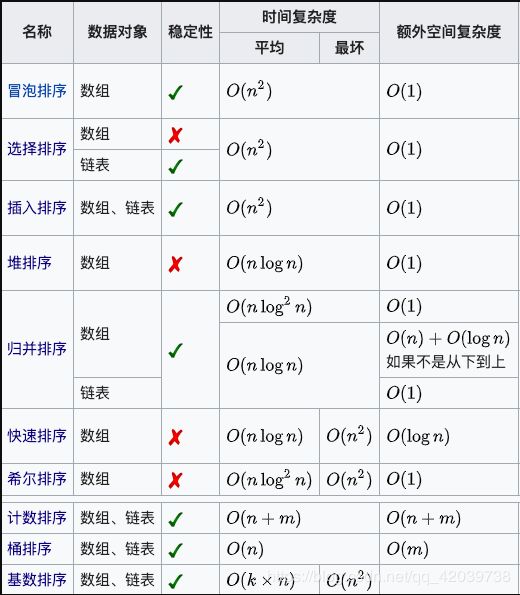
十大基础排序
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 20);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
int[] sort = bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range);
}
return array;
}
public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] array) {
//拷贝数组
int[] copyArray = Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length);
int length = copyArray.length, temp, count;
//每趟排序,将最大的数排在后面
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
//重置count
count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < length - 1 - i; j++) {
//如果前面的数比后面的数大,则交换
if (copyArray[j] > copyArray[j + 1]) {
temp = copyArray[j];
copyArray[j] = copyArray[j + 1];
copyArray[j + 1] = temp;
count++;
}
}
//如果该循环交换次数只有等于0的情况下则不用再排了
if (count == 0) {
break;
}
}
return copyArray;
}
}
采用8万个数据测试冒泡排序的性能
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int[] sort = bubbleSort(array);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
public class SelectSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 20);
int[] sort = selectSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range);
}
return array;
}
public static int[] selectSort(int[] array){
int[] copyArray = Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length);
int length = copyArray.length, min, minIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length-1; i++) {
//每次假定第一个数是最小的
min = copyArray[i];
minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
//比较,重置最小值
if(copyArray[j]<min){ //如果按从大到小排序只需修改成大于号
min = copyArray[j];
minIndex = j;
}
}
//判断最小值是否仍是第一个数,避免不必要的交换
if(minIndex!=i){
//交换最小值和第一个数
copyArray[minIndex] = copyArray[i];
copyArray[i] = min;
}
}
return copyArray;
}
}
采用8万个数据测试选择排序的性能
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int[] sort = selectSort(array);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
3、插入排序 (时间复杂度——O(n^2))
写代码时,前一个元素进行后移的体现是,将前一个元素覆盖后一个元素(插入值已经被存起来)


public class InsertSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 20);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
int[] sort = insertSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range);
}
return array;
}
public static int[] insertSort(int[] array) {
int[] copyArray = Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length);
int length = copyArray.length, insertVal, insertIndex;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
insertIndex = i; //保存插入值的前一个进行比较的元素的下标
insertVal = copyArray[i + 1]; //保存插入数据的值
/*
如果插入值小于前一个元素,则让前一个元素覆盖掉插入元素的位置;往前比较的同时也要注意数组下标的越界问题insertIndex >= 0。以此类推。
如果插入值大于前一个元素,则不用进行操作。
*/
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertVal < copyArray[insertIndex]) {
copyArray[insertIndex + 1] = copyArray[insertIndex];
insertIndex--;
}
/*
判断是否要替换元素。
两种情况:
第一种:插入值大于前一个元素,即插入原来的位置
第二种:插入值小于前一个元素,while循环中最后insertIndex每次都自减一次,所以这里必须加一才可以正确表示插入位置
*/
if (i + 1 != insertIndex + 1) {
copyArray[insertIndex + 1] = insertVal;
}
}
return copyArray;
}
}
采用8万个数据测试插入排序的性能
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int[] sort = insertSort(array);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
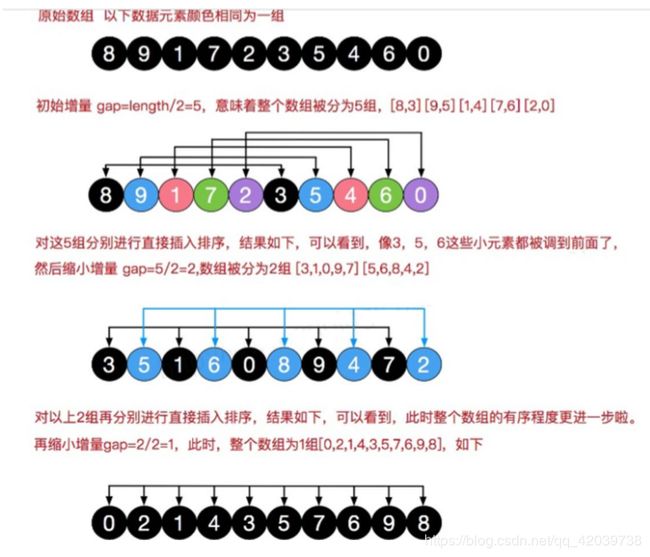
4、希尔排序(插入排序的增强版)(时间复杂度——O(nlogn)
通过步长gap分多个组,每个组进行插入排序。随着gap不断缩小,插入排序最后面向整个数组
注意:
但代码中体现的是同时对所有分组进行插入排序,而不是一个个分组按顺序来操作。它是交叉操作的
public class HillSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 20);
int[] sort = hillSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range);
}
return array;
}
public static int[] hillSort(int[] array) {
//拷贝数组
int[] copyArray = Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length);
int length = copyArray.length, temp, insertIndex, insertVal;
for (int gap = length/2; gap > 0; gap/=2) {
for (int i = gap; i < length; i++) {
insertIndex = i;
insertVal = copyArray[i];
while (insertIndex-gap>=0&&insertVal<copyArray[insertIndex-gap]){
copyArray[insertIndex] = copyArray[insertIndex-gap];
insertIndex-=gap;
}
if(insertIndex!=i){
copyArray[insertIndex] = insertVal;
}
}
}
return copyArray;
}
}
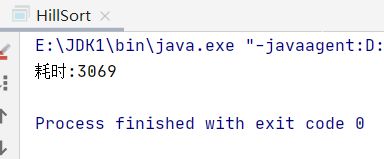
采用8万个数据测试希尔排序的性能
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int[] sort = insertSort(array);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
采用8百万个数据测试希尔排序的性能
5、快速排序 (时间复杂度——O(nlogn)

其实最后我觉得快排的最重要思想就是根据第一个基准元素,轮流按j->i的顺序去比较,挖坑填坑,
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 20);
// int[] array = {18, 12, 17, 2, 11, 8, 3, 7, 14, 2};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
int[] sort = quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range);
}
return array;
}
public static int[] quickSort(int array[], int l, int r) {
/*
1、判断这个序列是否只有一个元素,一个元素就不用再排序了
2、防止递归传递l,r参数时造成数组越界,比如 quickSort(array, i + 1, r); 当i就是数组最后一个元素时,i+1会越界
*/
if (l < r) {
int flagVal = array[l], i = l, j = r;
//i与j相遇之时就是该分组排序结束之时
while (i < j) {
/*
进行交换
*/
while (i < j && array[j] > flagVal) {
j--;
}
if (i < j) {
array[i++] = array[j];
}
while (i < j && array[i] <= flagVal) {
i++;
}
if (i < j) {
array[j--] = array[i];
}
}
//最后把坑补上
array[i] = flagVal;
quickSort(array, l, i - 1);
quickSort(array, i + 1, r);
}
return array;
}
}
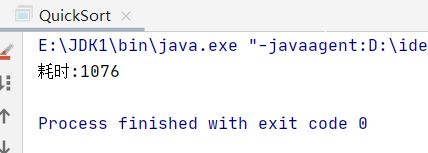
采用80000个数据测试快速排序的性能
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int[] sort = insertSort(array);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
采用8百万个数据测试快速排序的性能
6、归并排序(时间复杂度——O(nlogn)
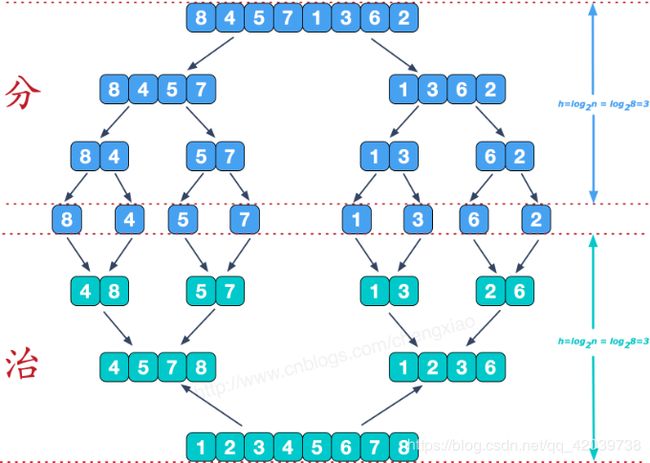
最后一次合并两个有序数组过程

public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String []args){
int []arr = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
public static void sort(int []arr){
int []temp = new int[arr.length];//在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1,temp);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right,int []temp){
if(left<right){
int mid = (left+right)/2;
sort(arr,left,mid,temp);//左边归并排序,使得左子序列有序
sort(arr,mid+1,right,temp);//右边归并排序,使得右子序列有序
merge(arr,left,mid,right,temp);//将两个有序子数组合并操作
}
}
private static void merge(int[] arr,int left,int mid,int right,int[] temp){
int i = left;//左序列指针
int j = mid+1;//右序列指针
int t = 0;//临时数组指针
while (i<=mid && j<=right){
if(arr[i]<=arr[j]){
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}else {
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){//将左边剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[i++];
}
while(j<=right){//将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中
temp[t++] = arr[j++];
}
t = 0;
//将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中
while(left <= right){
arr[left++] = temp[t++];
}
}
}
采用80000个数据测试归并排序的性能
public static void main(String []args){
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
sort(array);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
多次测试平均0.018秒左右
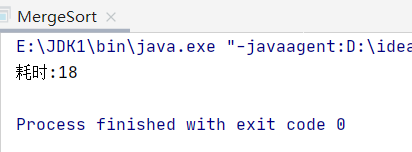
性能上是ok的(牺牲了空间换取了性能)
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 20);
heap_sort(array, array.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range);
}
return array;
}
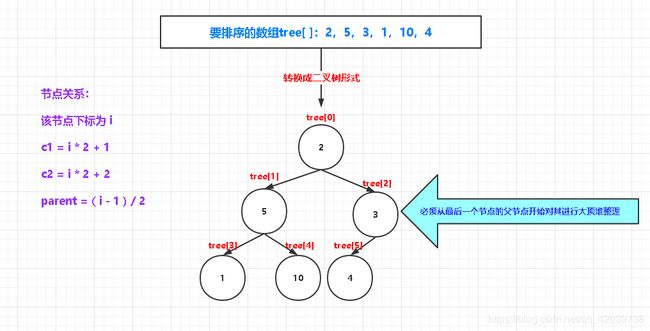
//交换堆顶(最大值)和最后一个节点的值,再进行大顶堆整理
public static void heap_sort(int tree[], int n) {
build_heap(tree, n);
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
swap(tree, i, 0);
heapify(tree, i, 0);
}
}
//构建所有父节点的大顶堆
public static void build_heap(int[] tree, int n) {
int lastIndex = n - 1;
int parent = (lastIndex - 1) / 2;
for (int i = parent; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(tree, n, i);
}
}
/**
*构建其中一个大顶堆
* @param tree
* @param n 数组长度
* @param i 将要操作的节点下标
*/
public static void heapify(int[] tree, int n, int i) {
int c1 = i * 2 + 1;
int c2 = i * 2 + 2;
int max = i;
if (c1 < n && tree[c1] > tree[max]) {
max = c1;
}
if (c2 < n && tree[c2] > tree[max]) {
max = c2;
}
if (max != i) {
swap(tree, i, max);
heapify(tree, n, max);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] tree, int i, int max) {
int temp = tree[i];
tree[i] = tree[max];
tree[max] = temp;
}
}
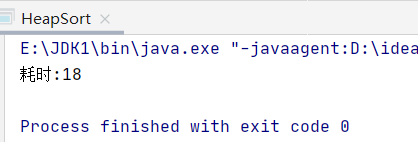
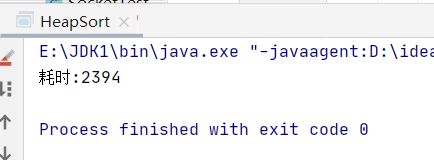
采用8万个数据测试堆排序的性能
public static void main(String []args){
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
heap_sort(array, array.length);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
采用8百万个数据测试堆排序的性能
8、计数排序(时间复杂度——O(N + k)
注意:
该排序只适合数据范围小,量大的数组(排序成绩、年龄是最好的)
计数排序思想简单,但要注意两个点:
1、计数数组的空间优化
2、排序后元素的稳定性
稳定意思是说原本键值一样的元素排序后相对位置不变
稳定性对于简单数据看不出差别,但对于复杂类型就有差别了,比如年龄一样的学生,但不是同一个人
public class CountSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 10, 20);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
//获取数组值的范围(最大值-最小值)
Map map = getMaxAndMin(array);
int[] sort = countSort(array, (Integer) map.get("min"), (Integer) map.get("max"));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range1, int range2) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range2 - range1 + 1) + range1; //注意,这里的元素大小是[range1, range2]
}
return array;
}
public static int[] countSort(int[] array, int range1, int range2) {
int size = range2 - range1 + 1;
int[] countArray = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
countArray[array[i] - range1]++;
}
return copy(countArray, array, range1);
}
public static int[] copy(int[] countArray, int[] array, int range1) {
//新建一个和原始数组一样的数组
int[] copy = new int[array.length];
//记录每个元素出现在copy数组出现的最后位置
for (int i = 1; i < countArray.length; i++) {
countArray[i] = countArray[i] + countArray[i - 1];
}
//根据原始数组从后往前遍历,再根据countArray记录的最后出现的下标,可以保证排序的稳定性
for (int i = array.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
copy[--countArray[array[i] - range1]] = array[i];
}
return copy;
}
public static Map getMaxAndMin(int[] array) {
int max = array[0], min = array[0];
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] > max) {
max = array[i];
}
if (array[i] < min) {
min = array[i];
}
}
map.put("max", max);
map.put("min", min);
return map;
}
}
采用8万个数据测试堆排序的性能
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 10, 20);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Map map = getMaxAndMin(array);
int[] sort = countSort(array, (Integer) map.get("min"), (Integer) map.get("max"));
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
9、基数排序(时间复杂度——O(N + k)
基数排序基本思路:
1、先计算出数组最大值的位数,作为排序的总次数
2、创建二维数组储存排序过程(二维数组使用ArrayList,可动态扩容)
3、第一次循环先排序个位,将按个位排序的结果放到二维数组中,在从二维数组中按顺序取出来,以此
类推
4、最后得到从小到大的数组
public class BasicSort {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] array = randomArray(10, 20);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
//获取数组中值最大值的位数
int position = countHighestPosition(array);
basicSort(array, position);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static int[] randomArray(int size, int range) {
int[] array = new int[size];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = random.nextInt(range);
}
return array;
}
private static void basicSort(int[] array, int position) {
ArrayList<ArrayList> queue = new ArrayList<>(10);
int x;
//创建一个二维数组(二维数组适使用ArrayList,可变)
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
queue.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
//排的总次数取决于数组最大值的位数
for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) {
//先按个位->十位->百位......
for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
x = (int) (array[j]%Math.pow(10, i+1)/Math.pow(10, i));
queue.get(x).add(array[j]);
}
//将二维数组中的元素按顺序取出来放到初始数组中
int flag = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
ArrayList<Integer> q = queue.get(j);
while (q.size()>0){
array[flag++] = q.get(0);
q.remove(0);
}
}
}
}
public static int countHighestPosition(int[] array){
int max = array[0], position = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if(array[i]>max){
max = array[i];
}
}
while (max>0){
max /= 10;
position++;
}
return position;
}
}
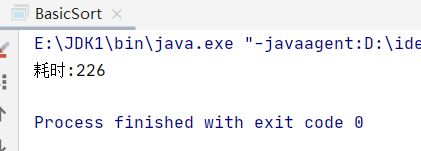
采用8万个数据测试堆排序的性能
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
long start, end;
int[] array = randomArray(80000, 80000);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//获取数组中值最大值的位数
int position = countHighestPosition(array);
basicSort(array, position);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (end - start));
}
采用8百万个数据测试堆排序的性能
很久,太久了。。。。
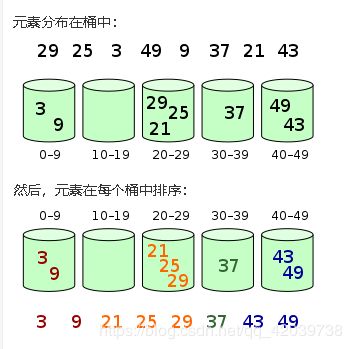
10、桶排序(时间复杂度——O(N * k)
桶排序的基本思路:
1、找到数组的最小值和最大值,最为该数组的区间范围
2、根据区间范围平均划分,每个区间相当于一个桶。(几个区间随意)
3、将数组元素放进区间桶内
4、对桶中的元素进行排序(采用哪种排序随你)
5、按照桶顺序输出就是从小到大的有序数组