百度Apollo5.0规划模块代码学习(一)RTK规划器
一 前言
关于百度Apollo中的规划模块,我也是第一次看。希望通过这个平台做好笔记。其中部分内容如果有误,希望看到的人可以给我留言。
规划模块的架构及介绍可以参考以下文章,写的非常好:
https://www.cnblogs.com/liuzubing/p/11058612.html
https://blog.csdn.net/shixiaolu63/article/details/86504786
从文章中可以知道,规划模块的核心就是规划器,百度Apollo5.0中采用了以下规划器:
1, RTK 根据录制的轨迹规划行车路线;
2,PUBLIC ROAD 实现了EM算法的规划器;
3,LATTICE 基于网格算法的轨迹规划器;
4,NAVI 基于实时相对地图的规划器;
5,OPEN SPACE ;
由于RTK规划器基于已有的轨迹,因此比较简单,在本文中主要是对RTK规划器的算法代码进行解析。
二 RTK规划器
RTK规划器共200行代码,具体解析如下:
构造函数,需要读取轨迹文件,轨迹文件可以参考modules/planning/testdata/garage.csv。
轨迹中包含以下信息:
x,y,z坐标;
车速;
加速度;
曲率;
角速度;
时间戳;
航向角;
档位;
路程;
油门;
刹车;
方向盘转角;
RTKReplayPlanner::RTKReplayPlanner() {
ReadTrajectoryFile(FLAGS_rtk_trajectory_filename);
}
规划器状态初始化。
Status RTKReplayPlanner::Init(const PlanningConfig&) { return Status::OK(); }
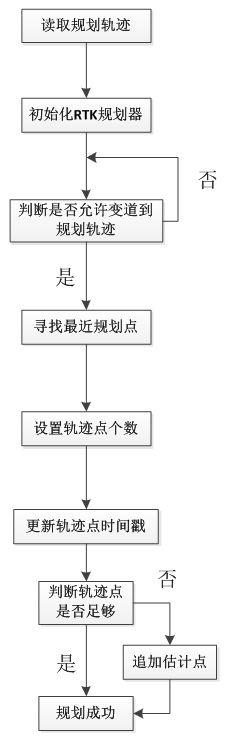
重载父类规划器中的规划算法。输入包括轨迹开始的规划点,目前的规划帧。返回规划器的状态,是否规划成功。
轨迹开始的规划点:x,y坐标值;
frame:保存一个规划周期内的所有数据。
Frame和ADCTrajectory是两个类,framehe ptr_computed_trajectory是定义了两个类指针。
Status RTKReplayPlanner::Plan(const TrajectoryPoint& planning_start_point,
Frame* frame,
ADCTrajectory* ptr_computed_trajectory) {
auto status = Status::OK();
bool has_plan = false;
寻找规划轨迹中的第一个可变道点。
auto it = std::find_if(
frame->mutable_reference_line_info()->begin(),
frame->mutable_reference_line_info()->end(),
[](const ReferenceLineInfo& ref) { return ref.IsChangeLanePath(); });
如果it 不是指向最后一个迭代器(即轨迹末尾),即则在加载的规划轨迹中重新规划轨迹。函数定义在后面。
if (it != frame->mutable_reference_line_info()->end()) {
status = PlanOnReferenceLine(planning_start_point, frame, &(*it));
如果起始点是可行驶的,且是可以变道的,且变道的距离大于最小编导阈值。
则输出变道规划失败。
has_plan =
(it->IsDrivable() && it->IsChangeLanePath() &&
it->trajectory().GetSpatialLength() > FLAGS_change_lane_min_length);
if (!has_plan) {
AERROR << "Fail to plan for lane change.";
}
}
如果变道规划失败,或者变道策略有更高的优先级,则重新规划轨迹。
if (!has_plan || !FLAGS_prioritize_change_lane) {
for (auto& reference_line_info : *frame->mutable_reference_line_info()) {
if (reference_line_info.IsChangeLanePath()) {
continue;
}
status = PlanOnReferenceLine(planning_start_point, frame,
&reference_line_info);
if (status != Status::OK()) {
AERROR << "planner failed to make a driving plan for: "
<< reference_line_info.Lanes().Id();
}
}
}
return status;
}
更新规划轨迹。
如果规划轨迹为空或者规划轨迹大小小于2,则输出故障信息。
Status RTKReplayPlanner::PlanOnReferenceLine(
const TrajectoryPoint& planning_init_point, Frame*,
ReferenceLineInfo* reference_line_info) {
if (complete_rtk_trajectory_.empty() || complete_rtk_trajectory_.size() < 2) {
std::string msg(
"RTKReplayPlanner doesn't have a recorded trajectory or "
"the recorded trajectory doesn't have enough valid trajectory "
"points.");
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
在complete_rtk_trajectory中寻找一个点,这个轨迹点距离车辆的初始状态planning_init_point距离最短。
forward_buffer是matched_point之后RTK轨迹中轨迹点的个数。
end_index 是最后一个规划点。
std::uint32_t matched_index =
QueryPositionMatchedPoint(planning_init_point, complete_rtk_trajectory_);
std::uint32_t forward_buffer =
static_cast(FLAGS_rtk_trajectory_forward);
// end_index is excluded.
std::uint32_t end_index = std::min(
static_cast(complete_rtk_trajectory_.size()),
matched_index + forward_buffer);
加载规划矩阵。
// auto* trajectory_points = trajectory_pb->mutable_trajectory_point();
std::vector trajectory_points(
complete_rtk_trajectory_.begin() + matched_index,
complete_rtk_trajectory_.begin() + end_index);
更新起始点和所有规划点的时间戳。
// reset relative time
double zero_time = complete_rtk_trajectory_[matched_index].relative_time();
for (auto& trajectory_point : trajectory_points) {
trajectory_point.set_relative_time(trajectory_point.relative_time() -
zero_time);
}
检查保存的轨迹点个数是否足够,如果不够,在最后一个点之后追加多次并调整相应的时间戳。
// check if the trajectory has enough points;
// if not, append the last points multiple times and
// adjust their corresponding time stamps.
while (trajectory_points.size() <
static_cast(FLAGS_rtk_trajectory_forward)) {
const auto& last_point = trajectory_points.rbegin();
auto new_point = last_point;
new_point->set_relative_time(new_point->relative_time() +
FLAGS_rtk_trajectory_resolution);
trajectory_points.push_back(*new_point);
}
reference_line_info->SetTrajectory(DiscretizedTrajectory(trajectory_points));
return Status::OK();
}
void RTKReplayPlanner::ReadTrajectoryFile(const std::string& filename) {
if (!complete_rtk_trajectory_.empty()) {
complete_rtk_trajectory_.clear();
}
std::ifstream file_in(filename.c_str());
if (!file_in.is_open()) {
AERROR << "RTKReplayPlanner cannot open trajectory file: " << filename;
return;
}
std::string line;
// skip the header line.
getline(file_in, line);
while (true) {
getline(file_in, line);
if (line == "") {
break;
}
auto tokens = apollo::common::util::StringTokenizer::Split(line, "\t ");
if (tokens.size() < 11) {
AERROR << "RTKReplayPlanner parse line failed; the data dimension does "
"not match.";
AERROR << line;
continue;
}
TrajectoryPoint point;
point.mutable_path_point()->set_x(std::stod(tokens[0]));
point.mutable_path_point()->set_y(std::stod(tokens[1]));
point.mutable_path_point()->set_z(std::stod(tokens[2]));
point.set_v(std::stod(tokens[3]));
point.set_a(std::stod(tokens[4]));
point.mutable_path_point()->set_kappa(std::stod(tokens[5]));
point.mutable_path_point()->set_dkappa(std::stod(tokens[6]));
point.set_relative_time(std::stod(tokens[7]));
point.mutable_path_point()->set_theta(std::stod(tokens[8]));
point.mutable_path_point()->set_s(std::stod(tokens[10]));
complete_rtk_trajectory_.push_back(std::move(point));
}
file_in.close();
}
std::uint32_t RTKReplayPlanner::QueryPositionMatchedPoint(
const TrajectoryPoint& start_point,
const std::vector& trajectory) const {
auto func_distance_square = [](const TrajectoryPoint& point, const double x,
const double y) {
double dx = point.path_point().x() - x;
double dy = point.path_point().y() - y;
return dx * dx + dy * dy;
};
double d_min =
func_distance_square(trajectory.front(), start_point.path_point().x(),
start_point.path_point().y());
std::uint32_t index_min = 0;
for (std::uint32_t i = 1; i < trajectory.size(); ++i) {
double d_temp =
func_distance_square(trajectory[i], start_point.path_point().x(),
start_point.path_point().y());
if (d_temp < d_min) {
d_min = d_temp;
index_min = i;
}
}
return index_min;
}