OpenCL环境配置及测试程序
OpenCL环境配置及测试程序
==============================================================
目录结构
1、OpenCL环境配置
2、测试程序
3、参考
==============================================================
关键词:OpenCL 环境配置 测试程序
OpenCL(Open Computing Language)是面向异构系统的并行编程语言,最初由苹果开放,得到了许多厂商的支持并不断完善,如Intel,AMD,NVIDIA等,许多博客中似乎都使用AMD的SDK,本文使用Intel的开放SDK。
1、OpenCL环境配置
下载Intel OpenCL的SDK文件并安装,记住安装目录:
https://software.intel.com/ru-ru/intel-opencl
安装Visual Studio,我安装的是Visual Studio Professional 2017。
以下是测试案例,打开VS,新建项目,新建一个空的Win控制台应用程序工程项目,命名为test。
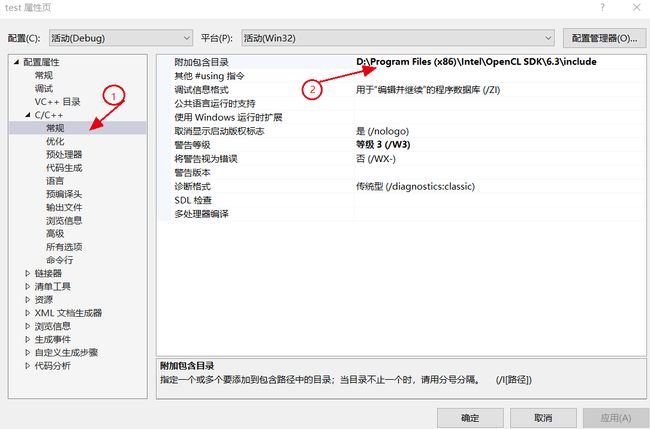
以下配置OpenCL的库文件和头文件路径
项目→ test属性→C/C++→常规→附加包含路径
D:\Program Files (x86)\Intel\OpenCL SDK\6.3\include
项目→test属性→链接器→常规→附加库目录
D:\Program Files (x86)\Intel\OpenCL SDK\6.3\lib\x86
项目→test属性→链接器→输入→附加依赖项
OpenCL.lib;
配置完成后,将test.cpp中的文件内容替换为附件test.cpp的内容,在资源管理器中加入核文件Helloworld_kernel.cl
按F5编译运行后,出现控制台显示如下信息表示已经成功配置环境。
2、测试程序
test.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
cl_int ConvertToString(const char *pFileName, std::string &str);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
cl_int iStatus = 0; // 函数返回状态
cl_uint uiNumPlatforms = 0; // 平台个数
cl_platform_id Platform = NULL; // 选择的平台
size_t uiSize = 0; // 平台版本名字字节数
cl_int iErr = 0; // 返回参数
char *pName = NULL; // 平台版本名
cl_uint uiNumDevices = 0; // 设备数量
cl_device_id *pDevices = NULL; // 设备
cl_context Context = NULL; // 设备环境
cl_command_queue CommandQueue = NULL; // 命令队列
const char *pFileName = "HelloWorld_Kernel.cl"; // cl文件名
string strSource = ""; // 用于存储cl文件中的代码
const char *pSource; // 代码字符串指针
size_t uiArrSourceSize[] = { 0 }; // 代码字符串长度
cl_program Program = NULL; // 程序对象
const char *pInput = "gdkknvnqkc"; // 输入字符串
size_t uiStrlength = strlen(pInput); // 输入字符串长度
char *pOutput = NULL; // 输出字符串
cl_mem memInutBuffer = NULL; // 输入内存对象
cl_mem memOutputBuffer = NULL; // 输出内存对象
cl_kernel Kernel = NULL; // 内核对象
size_t uiGlobal_Work_Size[1] = { 0 }; // 用于设定内核分布
//-------------------1. 获得并选择可用平台-----------------------------
// 查询可用的平台个数,并返回状态
iStatus = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &uiNumPlatforms);
if (CL_SUCCESS != iStatus)
{
cout << "Error: Getting platforms error" << endl;
return 0;
}
// 获得平台地址
if (uiNumPlatforms > 0) // 如果有可用平台
{
// 根据平台数为平台分配内存空间
cl_platform_id *pPlatforms = (cl_platform_id *)malloc(uiNumPlatforms * sizeof(cl_platform_id));
// 获得可用的平台
iStatus = clGetPlatformIDs(uiNumPlatforms, pPlatforms, NULL);
Platform = pPlatforms[0]; // 获得第一个平台的地址
free(pPlatforms); // 释放平台占用的内存空间
}
// 获得平台版本名
// 获得平台版本名的字节数
iErr = clGetPlatformInfo(Platform, CL_PLATFORM_VERSION, 0, NULL, &uiSize);
// 根据字节数为平台版本名分配内存空间
pName = (char *)alloca(uiSize * sizeof(char));
// 获得平台版本名字
iErr = clGetPlatformInfo(Platform, CL_PLATFORM_VERSION, uiSize, pName, NULL);
cout << pName << endl;
//--------------2. 查询GPU设备,并选择可用设备------------------------
// 获得GPU设备数量
iStatus = clGetDeviceIDs(Platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 0, NULL, &uiNumDevices);
if (0 == uiNumDevices) // 如果没有GPU设备
{
cout << "No GPU device available." << endl;
cout << "Choose CPU as default device." << endl;
// 选择CPU作为设备,获得设备数
iStatus = clGetDeviceIDs(Platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU, 0, NULL, &uiNumDevices);
// 为设备分配空间
pDevices = (cl_device_id *)malloc(uiNumDevices * sizeof(cl_device_id));
// 获得平台
iStatus = clGetDeviceIDs(Platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU, uiNumDevices, pDevices, NULL);
}
else
{
pDevices = (cl_device_id *)malloc(uiNumDevices * sizeof(cl_device_id));
iStatus = clGetDeviceIDs(Platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, uiNumDevices, pDevices, NULL);
}
// -------------------3.创建设备环境---------------------------------
// 创建设备环境
Context = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, pDevices, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (NULL == Context)
{
cout << "Error: Can not create context" << endl;
return 0;
}
// -------------------4.创建命令队列--------------------------------------
// 创建第1个设备的命令队列
CommandQueue = clCreateCommandQueue(Context, pDevices[0], 0, NULL);
if (NULL == CommandQueue)
{
cout << "Error: Can not create CommandQueue" << endl;
return 0;
}
// ----------------------5. 创建程序对象------------------------------
// 将cl文件中的代码转为字符串
iStatus = ConvertToString(pFileName, strSource);
pSource = strSource.c_str(); // 获得strSource指针
uiArrSourceSize[0] = strlen(pSource); // 字符串大小
// 创建程序对象
Program = clCreateProgramWithSource(Context, 1, &pSource, uiArrSourceSize, NULL);
if (NULL == Program)
{
cout << "Error: Can not create program" << endl;
return 0;
}
// -----------------------------6. 编译程序--------------------------------
// 编译程序
iStatus = clBuildProgram(Program, 1, pDevices, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (CL_SUCCESS != iStatus) // 编译错误
{
cout << "Error: Can not build program" << endl;
char szBuildLog[16384];
clGetProgramBuildInfo(Program, *pDevices, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG, sizeof(szBuildLog), szBuildLog, NULL);
cout << "Error in Kernel: " << endl << szBuildLog;
clReleaseProgram(Program);
return 0;
}
//-------------------------7. 并创建输入输出内核内存对象--------------------------------
// 创建输入内存对象
memInutBuffer = clCreateBuffer(
Context,
CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, // 输入内存为只读,并可以从宿主机内存复制到设备内存
(uiStrlength + 1) * sizeof(char), // 输入内存空间大小
(void *)pInput,
NULL);
// 创建输出内存对象
memOutputBuffer = clCreateBuffer(
Context,
CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY, // 输出内存只能写
(uiStrlength + 1) * sizeof(char), // 输出内存空间大小
NULL,
NULL);
if ((NULL == memInutBuffer) || (NULL == memOutputBuffer))
{
cout << "Error creating memory objects" << endl;
return 0;
}
//--------------------------8. 创建内核对象-------------------------------------
Kernel = clCreateKernel(Program,
"helloworld", // cl文件中的入口函数
NULL);
if (NULL == Kernel)
{
cout << "Error: Can not create kernel" << endl;
return 0;
}
//----------------------------9. 设置内核参数----------------------------------
iStatus = clSetKernelArg(Kernel,
0, // 参数索引
sizeof(cl_mem),
(void *)&memInutBuffer);
iStatus |= clSetKernelArg(Kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&memOutputBuffer);
if (CL_SUCCESS != iStatus)
{
cout << "Error setting kernel arguments" << endl;
}
// --------------------------10.运行内核---------------------------------
uiGlobal_Work_Size[0] = uiStrlength; // 输入字符串大小
// 利用命令队列使将再设备上执行的内核排队
iStatus = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(
CommandQueue,
Kernel,
1,
NULL,
uiGlobal_Work_Size, // 确定内核在设备上的多个处理单元间的分布
NULL, // 确定内核在设备上的多个处理单元间的分布
0,
NULL,
NULL);
if (CL_SUCCESS != iStatus)
{
cout << "Error: Can not run kernel" << endl;
return 0;
}
// ----------------------------11. 将输出读取到主机内存
pOutput = (char *)malloc(uiStrlength + 1); // uiStrlength 为 输入字符串长度
iStatus = clEnqueueReadBuffer(
CommandQueue, // 命令队列
memOutputBuffer, // 输出内存对象
CL_TRUE, // 内核读取结束之前该函数不会返回
0,
uiStrlength * sizeof(char),
pOutput,
0,
NULL,
NULL);
if (CL_SUCCESS != iStatus)
{
cout << "Error: Can not reading result buffer" << endl;
return 0;
}
// ---------------------12--输出计算结果---------------
pOutput[uiStrlength] = '\0';
cout << "Input String:" << endl;
cout << pInput << endl;
cout << "Output String:" << endl;
cout << pOutput << endl;
// -------------------------------13. 释放资源--------------------------------
iStatus = clReleaseKernel(Kernel);
iStatus = clReleaseProgram(Program);
iStatus = clReleaseMemObject(memInutBuffer);
iStatus = clReleaseMemObject(memOutputBuffer);
iStatus = clReleaseCommandQueue(CommandQueue);
iStatus = clReleaseContext(Context);
if (NULL != pOutput)
{
free(pOutput);
pOutput = NULL;
}
if (NULL != pDevices)
{
free(pDevices);
pDevices = NULL;
}
system("pause");//避免执行完闪退
return 0;
}
// 将cl文件代码转为字符串
cl_int ConvertToString(const char *pFileName, std::string &Str)
{
size_t uiSize = 0;
size_t uiFileSize = 0;
char *pStr = NULL;
std::fstream fFile(pFileName, (std::fstream::in | std::fstream::binary));
if (fFile.is_open())
{
fFile.seekg(0, std::fstream::end);
uiSize = uiFileSize = (size_t)fFile.tellg(); // 获得文件大小
fFile.seekg(0, std::fstream::beg);
pStr = new char[uiSize + 1];
if (NULL == pStr)
{
fFile.close();
return 0;
}
fFile.read(pStr, uiFileSize); // 读取uiFileSize字节
fFile.close();
pStr[uiSize] = '\0';
Str = pStr;
delete[] pStr;
return 0;
}
cout << "Error: Failed to open cl file\n:" << pFileName << endl;
return -1;
}
HelloWorld_Kernel.cl
__kernel void helloworld(__global char*pIn, __global char *pOut)
{
int iNum = get_global_id(0);
pOut[iNum] = pIn[iNum] + 1;
} 3、参考
OpenCL “速成”冲刺【第一天】:
https://blog.csdn.net/zhoubo616819598/article/details/10977915