二叉树的各种操作(递归和非递归遍历,树深度,结点个数等等)
目录
- 建立二叉树
- 递归前序和非递归前序
- 递归中序和非递归中序
- 递归后续和非递归后续(包括双栈法和设置pre结点)
- 层次遍历
- 寻找树中有没有值为x的结点
- 统计树中结点的个数
- 计算树的高度
- 判断两颗树是不是相等
- 前序中序,中序后续建立二叉树
- 树的子结构
- 二叉树镜像
- 完整测试代码
二叉树建立
先给出结点结构:
private static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
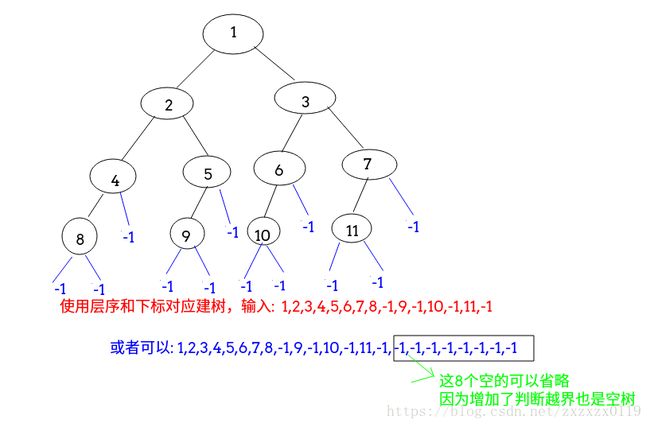
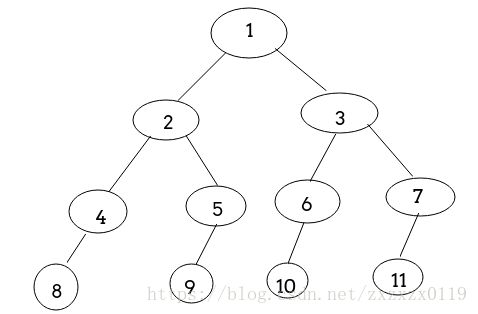
- 可以根据二叉树根节点和左右子结点的下标关系递归建立二叉树,层次输入二叉树结点;
- 也可以使用输入流前序建立二叉树(注意空树要输入-1);
// given a arr to build
public static Node createTree(int arr[],int i) {
if(i >= arr.length || arr[i] == -1)
return null;
Node T = new Node(arr[i]);
T.left = createTree(arr,2*i + 1);
T.right = createTree(arr,2*i + 2);
return T;
}
// cin method
public static Node buildTree(Scanner cin) {
Node root = null;
int data = cin.nextInt();
if (data != -1) {
root = new Node(data);
root.left = buildTree(cin);
root.right = buildTree(cin);
}
return root;
}
前序遍历
递归前序:
public static void preOrder(Node T) {
if(null != T) {
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
preOrder(T.left);
preOrder(T.right);
}
}
非递归前序遍历:
前序遍历可以归纳为: 根结点->左子树->右子树,所以对于正在访问的根结点,可以直接访问,访问完之后,按照相同的方式访问左子树,再访问右子树,过程如下 :
- 访问结点p,并将结点p入栈。
- 判断结点p的左孩子是否为空,若不为空,则继续访问左孩子,否则将栈顶元素出栈,并访问栈顶的元素的右孩子。
- 直到栈为空且p为空,循环结束。
public static void iterativePre(Node T) {
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = T;
while(!s.empty() || p != null) {
if(p != null) {
s.push(p);
System.out.print(p.val + " ");
p = p.left;
}
else {
p = s.pop();
p = p.right;
}
}
}
或者:(这里使用一个List存储遍历结果)
原题链接
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer>res = new ArrayList<>();
if(res == null)
return res;
Stack<TreeNode>stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null){
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
res.add(cur.val); //先根
cur = cur.left;
}
cur = stack.pop();
cur = cur.right;
}
return res;
}
还有另外一种更加容易理解的写法是:
- 先把根节点入栈,然后每次出栈一个元素,先访问这个元素,然后如果它的右子树存在,就入栈,如果它的左子树存在也入栈;
- 为什么要先入右子树呢,因为,前序遍历是中->左->右,而栈可以逆序,所以先右再左;
- 这个方法在后续遍历的双栈法中有体现,那个只是这个稍微的修改;
/** 理解 : push右子树,再push左子树,这样的话弹栈的时候就是先访问左子树,再右子树*/
public static void iterativePre_2(Node T){
if(T == null)
return;
Stack<Node>stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(T);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
T = stack.pop();
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
if(T.right != null)
stack.push(T.right);
if(T.left != null)
stack.push(T.left);
}
System.out.println();
}
中序遍历
递归中序:
public static void inOrder(Node T) {
if(null != T) {
inOrder(T.left);
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
inOrder(T.right);
}
}
非递归中序:
中序遍历 : 左子树->根->右子树,过程如下:
- 当前节点为空,从栈中拿出一个并且打印 ,当前节点向右;
- 当前节点不空,压入栈中,当前节点向左;
直到栈为空且p为空,循环结束。
/**
* 非递归中序
* 理解: 就是两步
* 1): 当前节点为空 ,从栈中拿出一个并且打印 ,当前节点向右
* 2): 当前节点不空, 压入栈中, 当前节点向左
*/
public static void iterativeIn(Node T) {
if(T == null)
return;
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = T;
while(!s.empty() || p != null) {
if(p != null) {
s.push(p);
p = p.left;
}else {
p = s.pop();
System.out.print(p.val + " ");
p = p.right;
}
}
}
后序遍历
递归后序:
public static void postOrder(Node T) {
if(null != T) {
postOrder(T.left);
postOrder(T.right);
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
}
}
非递归后序:
①.双栈法:
- 这个其实就是非递归前序的稍微一点改进,首先 前序遍历入栈的顺序是先 右 再左,这时,我们可以做到反过来先 左 再右,这样遍历的顺序可以做到 “中右左”,而后续遍历是 “左右中”,正好是前面那个的相反,所以我们再使用一个栈保存即可。
2.设置pre结点:
- 对于任一结点p,先将其入栈;
- 若p不存在左孩子和右孩子,则可以直接访问它;
- 或者p存在左孩子或者右孩子,但是左孩子和右孩子都已经被访问过了,则可以直接访问该结点;
- 若非上述两种情况,则将右孩子和左孩子依次入栈。这样可以保证每次取栈顶元素时,左孩子在右孩子前面被访问,根结点在左孩子和右孩子访问之后被访问;
/**
* 非递归后续1(双栈法解决非递归后续)
* 后续遍历是要实现 左->右->中
* 这个方法和前序遍历的第二种方法 只是多了一个栈而已
* 因为 前序遍历是 中->左->右 压栈顺序是 右->左
* 这样,我们就很容易实现 中->右->左遍历 压栈顺序是 左->右
* 而后续遍历是要实现 左->右->中,
* 我们把上面的 中右左 压入到另一个栈中 就实现了 左右中
*/
public static void iterativePos(Node T){
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>(),s2 = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = T;
s.push(T);
while(!s.empty()) {
p = s.pop();
s2.push(p);
if(p.left != null)s.push(p.left);
if(p.right != null)s.push(p.right);
}
while(!s2.empty())System.out.print(s2.pop().val + " ");
}
/** 非递归后续2(设置pre结点) */
public static void iterativePos_2(Node T){
Node cur,pre = null;
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>();
s.push(T);
while(!s.empty()) {
cur = s.peek();
if((cur.left == null && cur.right == null) || ((pre != null) && (pre == cur.left || pre == cur.right))) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
s.pop();
pre = cur;
}else {
if(cur.right != null)s.push(cur.right);
if(cur.left != null)s.push(cur.left);
}
}
}
层次遍历
利用队列BFS即可,每次访问完p,若左右孩子存在,则入队,直至队空;
public static void levelOrder(Node T) {
Queue<Node>q = new LinkedList<Node>();
if(T != null) {
q.add(T);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node now = q.poll();
System.out.print(now.val + " ");
if(now.left != null)q.add(now.left);
if(now.right != null)q.add(now.right);
}
}
}
寻找树中有没有值为x的结点
递归条件有两个,一个是为空代表没找到,找到了的话直接返回,否则递归查找左右子树。
//查找某个值为x的结点
public static Node search(Node T,int x) {
if(T == null)
return null;
if(T.val == x)
return T;
else {
if(search(T.left,x) == null) return search(T.right,x);
else return search(T.left,x);
}
}
统计树中结点的个数
树中结点的个数等于根节点(1) + 左子树结点个数 + 右子树的个数,递归求解即可。
//统计结点个数
public static int count(Node T) {
if(T != null) {
return count(T.left) + count(T.right) + 1;
}else
return 0;
}
计算树的高度
也是递归求解,左右子树的高度中的比较高的加上根节点就是树的高度
//计算二叉树的深度
public static int depth(Node T) {
if(T == null)
return 0;
int l = depth(T.left);
int r = depth(T.right);
return l > r ? l + 1 : r + 1;
}
判断两棵树是不是相等
也是递归求解,两棵树相等,既要根节点的值相等,而且左右子树也要相等。
//判断两棵树是不是相等
public static boolean is_SameTree(Node T1,Node T2) {
if(T1 == null && T2 == null)
return true;
else {
return T1 != null && T2 != null && T1.val == T2.val
&& is_SameTree(T1.left,T2.left) && is_SameTree(T1.right,T2.right);
}
}
前序中序,中序后续建立二叉树
这个知识请看剑指offer刷题小结一的第四题。
树的子结构
这个知识请看剑指offer刷题小结三的第五题。
二叉树镜像
这个知识请看剑指offer刷题小结四的第六题。
完整测试代码
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class BinaryTree {
private static class Node{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
// given a arr to build
public static Node createTree(int arr[],int i) {
if(i >= arr.length || arr[i] == -1)
return null;
Node T = new Node(arr[i]);
T.left = createTree(arr,2*i + 1);
T.right = createTree(arr,2*i + 2);
return T;
}
// cin method
public static Node buildTree(Scanner cin) {
Node root = null;
int data = cin.nextInt();
if (data != -1) {
root = new Node(data);
root.left = buildTree(cin);
root.right = buildTree(cin);
}
return root;
}
public static void preOrder(Node T) {
if(null != T) {
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
preOrder(T.left);
preOrder(T.right);
}
}
public static void iterativePre(Node T) {
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = T;
while(!s.empty() || p != null) {
if(p != null) {
s.push(p);
System.out.print(p.val + " ");
p = p.left;
}
else {
p = s.pop();
p = p.right;
}
}
}
/** 理解 : push右子树,再push左子树,这样的话弹栈的时候就是先访问左子树,再右子树*/
public static void iterativePre_2(Node T){
if(T == null)
return;
Stack<Node>stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(T);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
T = stack.pop();
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
if(T.right != null)stack.push(T.right);
if(T.left != null)stack.push(T.left);
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void inOrder(Node T) {
if(null != T) {
inOrder(T.left);
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
inOrder(T.right);
}
}
/**
* 非递归中序
* 理解: 就是两步
* 1): 当前节点为空 ,从栈中拿出一个并且打印 ,当前节点向右
* 2): 当前节点不空, 压入栈中, 当前节点向左
*/
public static void iterativeIn(Node T) {
if(T == null)
return;
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = T;
while(!s.empty() || p != null) {
if(p != null) {
s.push(p);
p = p.left;
}else {
p = s.pop();
System.out.print(p.val + " ");
p = p.right;
}
}
}
public static void postOrder(Node T) {
if(null != T) {
postOrder(T.left);
postOrder(T.right);
System.out.print(T.val + " ");
}
}
/**
* 非递归后续1(双栈法解决非递归后续)
* 后续遍历是要实现 左->右->中
* 这个方法和前序遍历的第二种方法 只是多了一个栈而已
* 因为 前序遍历是 中->左->右 压栈顺序是 右->左
* 这样,我们就很容易实现 中->右->左遍历 压栈顺序是 左->右
* 而后续遍历是要实现 左->右->中,
* 我们把上面的 中右左 压入到另一个栈中 就实现了 左右中
*/
public static void iterativePos(Node T){
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>(),s2 = new Stack<Node>();
Node p = T;
s.push(T);
while(!s.empty()) {
p = s.pop();
s2.push(p);
if(p.left != null)s.push(p.left);
if(p.right != null)s.push(p.right);
}
while(!s2.empty())System.out.print(s2.pop().val + " ");
}
/** 非递归后续2(设置pre结点) */
public static void iterativePos_2(Node T){
Node cur,pre = null;
Stack<Node>s = new Stack<Node>();
s.push(T);
while(!s.empty()) {
cur = s.peek();
if((cur.left == null && cur.right == null) || ((pre != null) && (pre == cur.left || pre == cur.right))) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
s.pop();
pre = cur;
}else {
if(cur.right != null)s.push(cur.right);
if(cur.left != null)s.push(cur.left);
}
}
}
public static void levelOrder(Node T) {
Queue<Node>q = new LinkedList<Node>();
if(T != null) {
q.add(T);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node now = q.poll();
System.out.print(now.val + " ");
if(now.left != null)q.add(now.left);
if(now.right != null)q.add(now.right);
}
}
}
//查找某个值为x的结点
public static Node search(Node T,int x) {
if(T == null)
return null;
if(T.val == x)
return T;
else {
if(search(T.left,x) == null) return search(T.right,x);
else return search(T.left,x);
}
}
//统计结点个数
public static int count(Node T) {
if(T != null) {
return count(T.left) + count(T.right) + 1;
}else
return 0;
}
//计算二叉树的深度
public static int depth(Node T) {
if(T == null)
return 0;
int l = depth(T.left);
int r = depth(T.right);
return l > r ? l + 1 : r + 1;
}
//判断两棵树是不是相等
public static boolean is_SameTree(Node T1,Node T2) {
if(T1 == null && T2 == null)
return true;
else {
return T1 != null && T2 != null && T1.val == T2.val
&& is_SameTree(T1.left,T2.left) && is_SameTree(T1.right,T2.right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
// int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,-1,9,-1,10,-1,11,-1, -1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1};
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,-1,9,-1,10,-1,11,-1};
Node root = createTree(arr,0);
// 树结构和上面相同,输入: 1 2 4 8 -1 -1 -1 5 9 -1 -1 -1 3 6 10 -1 -1 -1 7 11 -1 -1 -1
Node root2 = buildTree(cin);
System.out.println("-------前序遍历-------");
preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
iterativePre(root);
System.out.println();
iterativePre_2(root);
System.out.println("\n" + "-------中序遍历-------");
inOrder(root);
System.out.println();
iterativeIn(root);
System.out.println("\n" + "-------后序遍历-------");
postOrder(root);
System.out.println();
iterativePos(root);
System.out.println();
iterativePos_2(root);
System.out.println("\n" + "-------层次遍历-------");
levelOrder(root);
System.out.println("\n" + "------结点个数-------");
System.out.println(count(root));
System.out.println("\n" + "------二叉树深度-------");
System.out.println(depth(root));
System.out.println("\n" + "-----判断两棵树是不是相同-----");
System.out.println(is_SameTree(root,root2));
System.out.println("\n" + "-----寻找树中有没有值为3的结点-----");
Node Find = search(root,3);
if(null == Find)
System.out.println("没有找到结点");
else
System.out.println("这个结点的左右子结点的值是" + Find.left.val + " " + Find.right.val);
}
}