左神进阶班笔记Part5:树形DP、LRU、LFU、
【TIP】二叉树的题目,不是遍历就是改递归
树形DP:在树上做动态规划,套在递归里。
计算顺序一定是从小树到大树,难在分析可能性。
【步骤】
1.分析完可能性,列出信息全集,推出返回值类型结构(用类封装)。
2.默认每棵子树返回这些信息,用子树信息加工出父节点信息,返回。
3.单独考虑 basecase.
题目一:最大搜索二叉子树
求整颗二叉树的最大搜索二叉子树
逻辑:将整个题目转成以每个节点作为头的最大搜索二叉子树,最大的搜索二叉子树一定在其中。基本二叉树的题目都可以利用这样的思想进行求解。
【思路】当前节点的最大搜索子树可能来自于
左子树的某个子树,
右子树的某个子树,
左子树是搜索二叉树,右子树也是搜索二叉树,并且左子树的最大值小于我,右子树的最小值大于我,则以我为头为整个搜索二叉子树
主逻辑:对每个节点进行上述的分析
详细点:子树如何进行判断上述的过程,需要搜集哪些信息。
- 左树最大搜索二叉树大小,头部
- 右部最大搜索二叉树大小,头部
- 左树上的最大值
- 右树上的最小值
有了以上的信息,则可以计算出上述的三种情况。
因为整个信息会在递归中展示,所以需要将上述消息体进行整合
- 搜大小
- 搜头部
- 当前树最大
- 当前树最小
上述三点为精简后的消息体,对于左边还是右边,最后上传的内容体都相同,不区分左右。这样会更加具有普遍性,此时可以进行递归,从而实现算法。
整体套路
递归的整个过程:
- 明确可能性情况
- 明确需要的参数内容
- 将参数当做黑盒对待,假设下面的节点可以直接返回该形式,改递归。
- 将可能性分别列出
- 将黑盒展开,明确当前节点需要返回的内容,编写代码实现。
【TIP】递归想要返回多个信息时,新建一个包含多个成员的类,返回该类。
//首先明确好返回值的类型,都需要返回的内容
public static class ReturnType{
public int size;
public Node head;
public int min;
public int max;
public ReturnType(int a,Node b,int c,int d){
this.size = a;
this.head = b;
this.min = c;
this.max = d;
}
}
//递归的整个过程,按照上述所分的三种可能进行分析
public static ReturnType process(Node head){
//如果现在的节点为空了,则证明无节点,所以将对应的信息放进去,最小的设置成系统最大值,最大的设置成系统最小值,不影响其他非空节点。
if(head == null){
return new ReturnType(0,null,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
//明确好需要返回的值,此时相信左子树和右子树会给我我想要的内容。递归形式在这里确立
Node left = head.left;
ReturnType leftSubTreessInfo = process(left);
Node right = head.right;
ReturnType rightSubTreessInfo = process(right);
int includeItself = 0;
//如果满足下面的if判断,则意味着包含当前节点可以形成搜索二叉树
if(leftSubTreessInfo.head == left
&&rightSubTreessInfo.head ==right
&&head.value > leftSubTreessInfo.max
&&head.value < rightSubTreessInfo.min
){
includeItself = leftSubTreessInfo.size +1+ rightSubTreessInfo.size;
}
//无论上面判断是否成立,下面的代码都将执行,确立递归中元素的值,下面分别确定maxsize,和maxHead。
int p1 = leftSubTreessInfo.size;
int p2 = rightSubTreessInfo.size;
int maxSize = Math.max(Math.max(p1,p2),includeItself);
Node maxHead = p1 >p2 ? leftSubTreessInfo.head :rightSubTreessInfo.head;
if(maxSize == includeItself){
maxHead =head;
}
return new ReturnType(maxSize,
maxHead,
Math.min(Math.min(leftSubTreessInfo.min,rightSubTreessInfo.min),head.value),
Math,max(Math.max(leftSubTreessInfo.max,rightSubTreessInfo.max),head.value));
}
题目二:二叉树最大距离
class Solution {
public:
int maxpath=0;
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
helper(root);
return maxpath;
}
int helper(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)
return -1;
int leftdepth=helper(root->left);
int rightdepth=helper(root->right);
maxpath=max(maxpath,leftdepth+rightdepth+2);
return max(leftdepth,rightdepth)+1;
}
};
题目三 最大活跃度
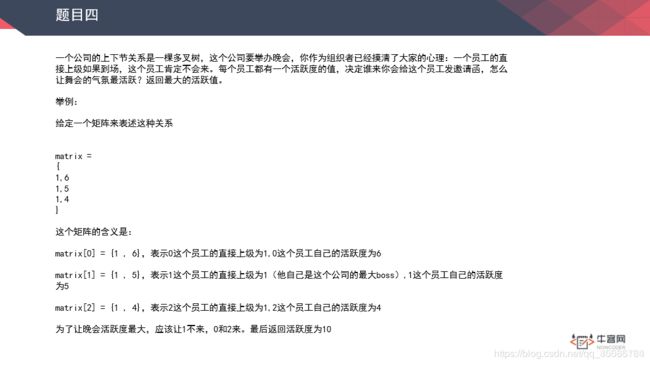
【思路】同样的情况,如果我可以求出每一个节点子树中最活跃的情况,则最后最活跃的情况一定包含在其中。
可能性分析:
- 最活跃包含当前节点,子节点一定不来,子节点不来的最大活跃度
- 不包含当前节点,最大值为所有子节点来或不来中的最大值之和。
需要的信息:
- 来的最大活跃度
- 不来的最大活跃度
【TIP】可以不创建结果类,而是用 pair 或 数组huo来表示,huo[0]、huo[1]分别表示来的活跃度和不来的活跃度。
【TIP2】如果不创建结果类,也不用数组表示,而是递归形参加一个bool变量表示来\不来的活跃度,将会多出很多重复子问题,时间复杂度大大增加,不可取!
public static class ReturnData{
public int lai_huo;
public int bulai_huo;
public ReturnData(int lai_huo,int bulai_huo){
this.lai_huo = laihuo;
this.bulai_huo = bulai_huo;
}
}
public static ReturnData process(Node head){
int lai_huo = head.huo;
int bulai_huo = 0;
//遍历每一个后代,拿到每一个后代之后,返回信息。
for(int i = 0;i < head.nexts.size();i++){
Node next = head.nexts.get(i);
ReturnData nextData = process(next);
lai_huo += nexData.bulai_huo;
bulai_huo += Math.max(nextData.lai_huo,nextData.bulai_huo);
}
return new ReturnData(lai_huo,bulai_huo);
LRU
详细
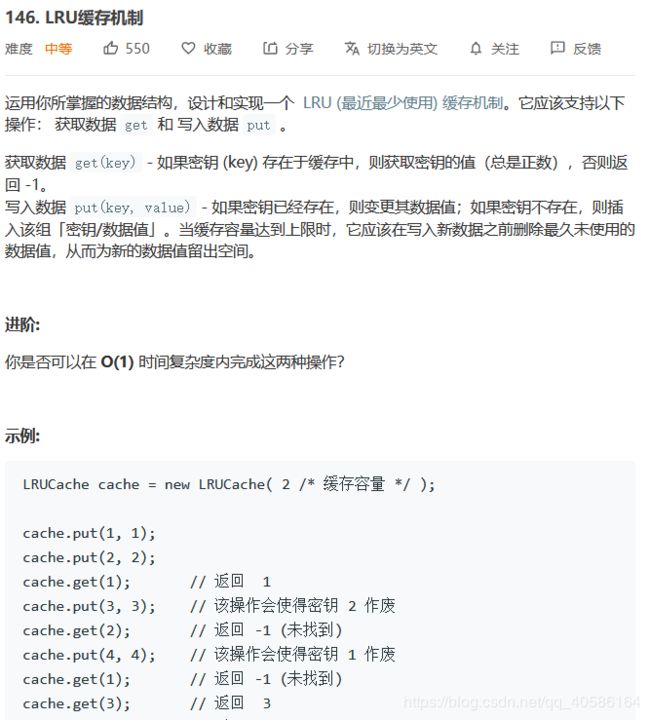
【思路】哈希表+双向链表list
使用节点为pair
注意:因为从哈希表中删除尾结点时,需要知道尾结点对应的key,所以链表节点必须储存key。
class LRUCache {
private:
int capacity;
list<pair<int,int>> mylist;
unordered_map<int,list<pair<int,int>>::iterator> ump;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
this->capacity=capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
if(ump.count(key)==0)
return -1;
auto it=ump[key];
//splice函数:将mylist中的it迭代器切除,加入到mylist.begin()前面
mylist.splice(mylist.begin(),mylist,it);//迭代器it没有改变,但是迭代器的位置变了
return it->second;//等价于(*it).second;注意.优先级比*高
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(ump.count(key)!=0){//若已存在key
auto it=ump[key];
it->second=value;
mylist.splice(mylist.begin(),mylist,it);
return;
}
if(mylist.size()==capacity){
ump.erase(mylist.back().first);
mylist.pop_back();
}
mylist.push_front({key,value});
ump[key]=mylist.begin();
}
};
LFU
详细