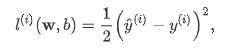线性回归模型代码实现
线性回归
注:本文主要是对伯禹教育平台线性回归课程总结学习用
一、线性回归基本要素
1.模型
2.数据集
- 我们通常收集一系列的真实数据,例如多栋房屋的真实售出价格和它们对应的面积和房龄。对模型训练以及测试,一栋房屋被称为一个样本(sample),其真实售出价格叫作标签(label),用来预测标签的两个因素叫作特征(feature)。本例中通过自己生成数据集用来训练和测试。
3.损失函数
4.模型优化-随机梯度下降
- 当模型和损失函数形式较为简单时,上面的误差最小化问题的解可以直接利用正规方程代入公式求解。这类解叫作解析解(analytical solution)。本节使用的线性回归和平方误差刚好属于这个范畴。然而,大多数深度学习模型并没有解析解,只能通过优化算法有限次迭代模型参数来尽可能降低损失函数的值。这类解叫作数值解(numerical solution)。
- 在求数值解的优化算法中,小批量随机梯度下降(mini-batch stochastic gradient descent)在深度学习中被广泛使用。它的算法很简单:先选取一组模型参数的初始值,如随机选取;接下来对参数进行多次迭代,使每次迭代都可能降低损失函数的值。在每次迭代中,先随机均匀采样一个由固定数目训练数据样本所组成的小批量(mini-batch)β,然后求小批量中数据样本的平均损失有关模型参数的导数(梯度),最后用此结果与预先设定的一个正数的乘积作为模型参数在本次迭代的减小量。
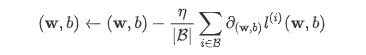
- 模型优化主要是利用减小损失函数的值,从而使模型预测值不断靠近真实值,损失函数是参数w,b的函数,当w和b沿着损失函数导数负方向移动时,损失函数随之减小。
注:
矢量直接计算比起简单for循环速度快更简洁,python中的广播学习很重要。
二、线性回归模型从头开始建立(jupyter中)
1.导入基本库
# import packages and modules
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from IPython import display
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
print(torch.__version__)
2.生成数据集
num_inputs = 2 #特征个数
num_examples = 1000 #样本个数
true_w = [2, -3.4] #已知模型参数的真实值
true_b = 4.2
#模型输入:样本和其特征的矩阵
features = torch.randn(num_examples, num_inputs,dtype=torch.float32)
#利用已知参数和输入矩阵计算真实值
labels = true_w[0] * features[:, 0] + true_w[1] * features[:, 1] +true_b
#真实值不可能完全符合线性模型,加上通过正态分布随机生成的偏置值
labels += torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=labels.size()),
dtype=torch.float32)
可通过图像展示生成的数据
plt.scatter(features[:, 1].numpy(), labels.numpy(), 1);
3.读取数据集
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
num_examples = len(features)
indices = list(range(num_examples))
random.shuffle(indices) # random read 10 samples
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
j = torch.LongTensor(indices[i: min(i + batch_size, num_examples)]) # the last time may be not enough for a whole batch
#index_select方法中0是维度:行,j是索引
yield features.index_select(0, j), labels.index_select(0, j)
4.初始化模型参数
w = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, (num_inputs, 1)), dtype=torch.float32)
b = torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.float32)
w.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)
b.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)
5.定义模型
def linreg(X, w, b):
return torch.mm(X, w) + b
6.定义损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat, y):
return (y_hat - y.view(y_hat.size())) ** 2 / 2
7.定义优化函数
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size):
for param in params:
param.data -= lr * param.grad / batch_size # ues .data to operate param without gradient track
8.训练
# super parameters init
lr = 0.03 #学习率
num_epochs = 5 #迭代次数
batch_size = 10 #批量大小
net = linreg #网络即线性回归模型
loss = squared_loss #损失函数
# training
for epoch in range(num_epochs): # training repeats num_epochs times
# in each epoch, all the samples in dataset will be used once
# X is the feature and y is the label of a batch sample
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y).sum()
# calculate the gradient of batch sample loss
l.backward()
# using small batch random gradient descent to iter model parameters
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
# reset parameter gradient
w.grad.data.zero_() #参数清零
b.grad.data.zero_()
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print('epoch %d, loss %f' % (epoch + 1, train_l.mean().item()))
注:将训练好的参数与真实参数比较
w, true_w, b, true_b
三、使用Pytorch的简洁实现
1.导入所需库
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
torch.manual_seed(1)
print(torch.__version__)
torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.FloatTensor')
2.生成数据集
num_inputs = 2
num_examples = 1000
true_w = [2, -3.4]
true_b = 4.2
features = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, num_inputs)), dtype=torch.float)
labels = true_w[0] * features[:, 0] + true_w[1] * features[:, 1] + true_b
labels += torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=labels.size()), dtype=torch.float)
3.读取数据集
import torch.utils.data as Data
batch_size = 10
# combine featues and labels of dataset
dataset = Data.TensorDataset(features, labels)
# put dataset into DataLoader
data_iter = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=dataset, # torch TensorDataset format
batch_size=batch_size, # mini batch size
shuffle=True, # whether shuffle the data or not
num_workers=2, # read data in multithreading
)
4.定义模型
class LinearNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature):
super(LinearNet, self).__init__() # call father function to init
self.linear = nn.Linear(n_feature, 1) # function prototype: `torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True)`
def forward(self, x):
y = self.linear(x)
return y
net = LinearNet(num_inputs)
print(net)
注:初始化多层网络三种方法
# ways to init a multilayer network
# method one
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1)
# other layers can be added here
)
# method two
net = nn.Sequential()
net.add_module('linear', nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
# net.add_module ......
# method three
from collections import OrderedDict
net = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('linear', nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
# ......
]))
print(net)
print(net[0])
5.初始化模型参数
from torch.nn import init
init.normal_(net[0].weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
init.constant_(net[0].bias, val=0.0) # or you can use `net[0].bias.data.fill_(0)` to modify it directly
6.定义损失函数
loss = nn.MSELoss() # nn built-in squared loss function
# function prototype: `torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')`
7.定义优化函数
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.03) # built-in random gradient descent function
print(optimizer) # function prototype: `torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False)`
8.训练
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs + 1):
for X, y in data_iter:
output = net(X)
l = loss(output, y.view(-1, 1))
optimizer.zero_grad() # reset gradient, equal to net.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('epoch %d, loss: %f' % (epoch, l.item()))
注:与真实参数比较
# result comparision
dense = net[0]
print(true_w, dense.weight.data)
print(true_b, dense.bias.data)
四、总结
- 从零开始的实现(推荐用来学习)
能够更好的理解模型和神经网络底层的原理 - 使用pytorch的简洁实现
能够更加快速地完成模型的设计与实现