将keras或tensorflow模型迁移到android端(AndroidStudio)
经历了多次采坑,终于是现实了将keras模型迁移到android端上。
网上的一些教程实在太少,而且我也是走了很多弯路,有很多是使用Bazel工具把TensoFlow编译成.so库文件和jar包,再进行Android配置,实现模型移植。但是。。。我可能太笨了没成功。。放弃了。
后来发现了机器之心翻译后的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/Uwr44UOuQcNsUQb60zk2/article/details/81108374
非常激动,终于实现了迁移。但是原文中也是存在着一些小陷阱,所以我在此基础上完善了一下教程。
本人的环境如下:
- Windows 10
- Python3.6
- TensoFlow 1.6.0(2018年3月)
- Android Studio 3.2(2018年10月)
- AndroidSDK android9.0 API28
总之把模型部署到安卓设备上总体的步骤如下:
-
将训练好的模型转换成 TensorFlow 格式;
-
向安卓应用添加 TensorFlow Mobile 依赖项;
-
编写相关的 Java 代码,在你的应用中使用 TensorFlow 模型执行推断。
一、将训练好的模型转换成 TensorFlow 格式
如果本来就是tensorflow训练出的模型的话,可以跳过这一步直接进行AndroidStudio的配置就好啦。
假设有了keras保存的h5模型文件,则需要以下转换:
新建python脚本文件:(本代码实现了keras的h5模型转换到tensorflow的pd模型格式,对应着keras_to_tensorflow的函数)
转化自己已经训练好的模型,直接把第100行的load_weights("squeezenet.h5")改成load_model("squeezenet.h5")就行了。
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import *
import os
import tensorflow as tf
def keras_to_tensorflow(keras_model, output_dir, model_name,out_prefix="output_", log_tensorboard=True):
if os.path.exists(output_dir) == False:
os.mkdir(output_dir)
out_nodes = []
for i in range(len(keras_model.outputs)):
out_nodes.append(out_prefix + str(i + 1))
tf.identity(keras_model.output[i], out_prefix + str(i + 1))
sess = K.get_session()
from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util, graph_io
init_graph = sess.graph.as_graph_def()
main_graph = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, init_graph, out_nodes)
graph_io.write_graph(main_graph, output_dir, name=model_name, as_text=False)
if log_tensorboard:
from tensorflow.python.tools import import_pb_to_tensorboard
import_pb_to_tensorboard.import_to_tensorboard(
os.path.join(output_dir, model_name),
output_dir)
"""
We explicitly redefine the Squeezent architecture since Keras has no predefined Squeezenet
"""
def squeezenet_fire_module(input, input_channel_small=16, input_channel_large=64):
channel_axis = 3
input = Conv2D(input_channel_small, (1,1), padding="valid" )(input)
input = Activation("relu")(input)
input_branch_1 = Conv2D(input_channel_large, (1,1), padding="valid" )(input)
input_branch_1 = Activation("relu")(input_branch_1)
input_branch_2 = Conv2D(input_channel_large, (3, 3), padding="same")(input)
input_branch_2 = Activation("relu")(input_branch_2)
input = concatenate([input_branch_1, input_branch_2], axis=channel_axis)
return input
def SqueezeNet(input_shape=(224,224,3)):
image_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
network = Conv2D(64, (3,3), strides=(2,2), padding="valid")(image_input)
network = Activation("relu")(network)
network = MaxPool2D( pool_size=(3,3) , strides=(2,2))(network)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=16, input_channel_large=64)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=16, input_channel_large=64)
network = MaxPool2D(pool_size=(3,3), strides=(2,2))(network)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=32, input_channel_large=128)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=32, input_channel_large=128)
network = MaxPool2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(network)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=48, input_channel_large=192)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=48, input_channel_large=192)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=64, input_channel_large=256)
network = squeezenet_fire_module(input=network, input_channel_small=64, input_channel_large=256)
#Remove layers like Dropout and BatchNormalization, they are only needed in training
#network = Dropout(0.5)(network)
network = Conv2D(1000, kernel_size=(1,1), padding="valid", name="last_conv")(network)
network = Activation("relu")(network)
network = GlobalAvgPool2D()(network)
network = Activation("softmax",name="output")(network)
input_image = image_input
model = Model(inputs=input_image, outputs=network)
return model
keras_model = SqueezeNet()
keras_model.load_weights("squeezenet.h5")
output_dir = os.path.join(os.getcwd(),"checkpoint")
keras_to_tensorflow(keras_model,output_dir=output_dir,model_name="squeezenet.pb")
print("MODEL SAVED")
二、配置AndroidStudio依赖:
请在 Android Studio 中创建一个新的工程。在你的 app:build.gradle 文件中添加 TensorFlow Mobile 依赖
implementation 'org.tensorflow:tensorflow-android:+'笔者在此遇到过一些坑,不能下载tensorflow-android-1.11.0-rc1.aar文件导致sync时失败。但是不知为何过了几天就突然好了。。(笔者尝试过从网上直接下载tensorflow-android-1.11.0-rc1.aar这个文件,然后放入lib文件中,再进行添加依赖。但是AS突然不报错了,所以我并没有尝试。遇到这个问题的小伙伴们可以尝试一下这个解决方案)
三、android端代码编写:
此时走到这步的话,你的环境就已经完全设置好了。剩下的就是java代码的书写了,我是借用了上文提到的博客里的代码,但是原博客代码中有Snackbar等控件导致编译老是出错,在安卓领域我还是刚入门能力还是不够看不太懂。所以我就修改了下代码,只使用了最简单的Button、TextView、ImageVIew控件。
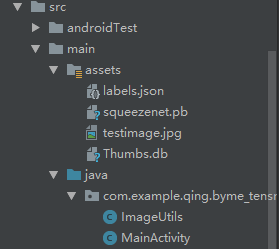
1、在编写代码进行实际推断之前,你需要将转换后的模型(squeezenet.pb)添加到应用程序的资源文件夹中。在 Android Studio 中,右键点击你的项目,跳转至「Add Folder」(添加文件夹)部分,并选择「Assets Folder」(资源文件夹)。这将在你的应用程序目录中创建一个资源文件夹。接下来,你需要将模型复制到资源文件夹中。如下:
其中squeezenet.pb为tensorflow的模型文件,testimage.jpg为要预测的图片,labels.json为模型输出数值后对应的label具体含义。
2、将一个新的 Java 类添加到项目的主程序包中,并将其命名为 ImageUtils,把下面的代码复制到其中。
package com.example.qing.byme_tensroflow;
import android.content.res.AssetManager;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.os.Environment;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.json.*;
/**
* Utility class for manipulating images.
**/
public class ImageUtils {
/**
* Returns a transformation matrix from one reference frame into another.
* Handles cropping (if maintaining aspect ratio is desired) and rotation.
*
* @param srcWidth Width of source frame.
* @param srcHeight Height of source frame.
* @param dstWidth Width of destination frame.
* @param dstHeight Height of destination frame.
* @param applyRotation Amount of rotation to apply from one frame to another.
* Must be a multiple of 90.
* @param maintainAspectRatio If true, will ensure that scaling in x and y remains constant,
* cropping the image if necessary.
* @return The transformation fulfilling the desired requirements.
*/
public static Matrix getTransformationMatrix(
final int srcWidth,
final int srcHeight,
final int dstWidth,
final int dstHeight,
final int applyRotation,
final boolean maintainAspectRatio) {
final Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
if (applyRotation != 0) {
// Translate so center of image is at origin.
matrix.postTranslate(-srcWidth / 2.0f, -srcHeight / 2.0f);
// Rotate around origin.
matrix.postRotate(applyRotation);
}
// Account for the already applied rotation, if any, and then determine how
// much scaling is needed for each axis.
final boolean transpose = (Math.abs(applyRotation) + 90) % 180 == 0;
final int inWidth = transpose ? srcHeight : srcWidth;
final int inHeight = transpose ? srcWidth : srcHeight;
// Apply scaling if necessary.
if (inWidth != dstWidth || inHeight != dstHeight) {
final float scaleFactorX = dstWidth / (float) inWidth;
final float scaleFactorY = dstHeight / (float) inHeight;
if (maintainAspectRatio) {
// Scale by minimum factor so that dst is filled completely while
// maintaining the aspect ratio. Some image may fall off the edge.
final float scaleFactor = Math.max(scaleFactorX, scaleFactorY);
matrix.postScale(scaleFactor, scaleFactor);
} else {
// Scale exactly to fill dst from src.
matrix.postScale(scaleFactorX, scaleFactorY);
}
}
if (applyRotation != 0) {
// Translate back from origin centered reference to destination frame.
matrix.postTranslate(dstWidth / 2.0f, dstHeight / 2.0f);
}
return matrix;
}
public static Bitmap processBitmap(Bitmap source,int size){
int image_height = source.getHeight();
int image_width = source.getWidth();
Bitmap croppedBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(size, size, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Matrix frameToCropTransformations = getTransformationMatrix(image_width,image_height,size,size,0,false);
Matrix cropToFrameTransformations = new Matrix();
frameToCropTransformations.invert(cropToFrameTransformations);
final Canvas canvas = new Canvas(croppedBitmap);
canvas.drawBitmap(source, frameToCropTransformations, null);
return croppedBitmap;
}
public static float[] normalizeBitmap(Bitmap source,int size,float mean,float std){
float[] output = new float[size * size * 3];
int[] intValues = new int[source.getHeight() * source.getWidth()];
source.getPixels(intValues, 0, source.getWidth(), 0, 0, source.getWidth(), source.getHeight());
for (int i = 0; i < intValues.length; ++i) {
final int val = intValues[i];
output[i * 3] = (((val >> 16) & 0xFF) - mean)/std;
output[i * 3 + 1] = (((val >> 8) & 0xFF) - mean)/std;
output[i * 3 + 2] = ((val & 0xFF) - mean)/std;
}
return output;
}
public static Object[] argmax(float[] array){
int best = -1;
float best_confidence = 0.0f;
for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){
float value = array[i];
if (value > best_confidence){
best_confidence = value;
best = i;
}
}
return new Object[]{best,best_confidence};
}
public static String getLabel( InputStream jsonStream,int index){
String label = "";
try {
byte[] jsonData = new byte[jsonStream.available()];
jsonStream.read(jsonData);
jsonStream.close();
String jsonString = new String(jsonData,"utf-8");
JSONObject object = new JSONObject(jsonString);
label = object.getString(String.valueOf(index));
}
catch (Exception e){
}
return label;
}
}
假如只是用来开发的话对于ImageUtils这个类不需要理解代码实现,会用就好啦。
2、在你的主活动(main activity)添加代码。它们将被用于显示图像和预测结果。
package com.example.qing.byme_tensroflow;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.renderscript.ScriptGroup;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar;
import android.util.JsonReader;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import org.json.*;
import org.tensorflow.contrib.android.TensorFlowInferenceInterface;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.tensorflow.contrib.android.TensorFlowInferenceInterface;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
/*
* 在需要调用TensoFlow的地方,加载so库“System.loadLibrary("tensorflow_inference");
* 并”import org.tensorflow.contrib.android.TensorFlowInferenceInterface;就可以使用了
* */
//Load the tensorflow inference library
//static{}(即static块),会在类被加载的时候执行且仅会被执行一次,一般用来初始化静态变量和调用静态方法。
static {
System.loadLibrary("tensorflow_inference");
}
//PATH TO OUR MODEL FILE AND NAMES OF THE INPUT AND OUTPUT NODES
//各节点名称
private String MODEL_PATH = "file:///android_asset/squeezenet.pb";
private String INPUT_NAME = "input_1";
private String OUTPUT_NAME = "output_1";
private TensorFlowInferenceInterface tf;
//ARRAY TO HOLD THE PREDICTIONS AND FLOAT VALUES TO HOLD THE IMAGE DATA
//保存图片和图片尺寸的
float[] PREDICTIONS = new float[1000];
private float[] floatValues;
private int[] INPUT_SIZE = {224,224,3};
ImageView imageView;
TextView resultView;
Button buttonSub;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tf = new TensorFlowInferenceInterface(getAssets(),MODEL_PATH);
imageView=(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.imageView1);
resultView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.text_show);
buttonSub=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
buttonSub.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
try{
InputStream imageStream = getAssets().open("testimage.jpg");
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(imageStream);
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
predict1(bitmap);
}catch(Exception e){
}
}
});
}
//FUNCTION TO COMPUTE THE MAXIMUM PREDICTION AND ITS CONFIDENCE
public Object[] argmax(float[] array){
int best = -1;
float best_confidence = 0.0f;
for(int i = 0;i < array.length;i++){
float value = array[i];
if (value > best_confidence){
best_confidence = value;
best = i;
}
}
return new Object[]{best,best_confidence};
}
public void predict(final Bitmap bitmap){
//Runs inference in background thread
new AsyncTask(){
@Override
protected Integer doInBackground(Integer ...params){
//Resize the image into 224 x 224
Bitmap resized_image = ImageUtils.processBitmap(bitmap,224);
//Normalize the pixels
floatValues = ImageUtils.normalizeBitmap(resized_image,224,127.5f,1.0f);
//Pass input into the tensorflow
tf.feed(INPUT_NAME,floatValues,1,224,224,3);
//compute predictions
tf.run(new String[]{OUTPUT_NAME});
//copy the output into the PREDICTIONS array
tf.fetch(OUTPUT_NAME,PREDICTIONS);
//Obtained highest prediction
Object[] results = argmax(PREDICTIONS);
int class_index = (Integer) results[0];
float confidence = (Float) results[1];
try{
final String conf = String.valueOf(confidence * 100).substring(0,5);
//Convert predicted class index into actual label name
final String label = ImageUtils.getLabel(getAssets().open("labels.json"),class_index);
//Display result on UI
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
resultView.setText(label + " : " + conf + "%");
}
});
} catch (Exception e){
}
return 0;
}
}.execute(0);
}
}
其中模型的推理部分放入到了predic函数中,并且将其耗时操作加入到了子线程中。
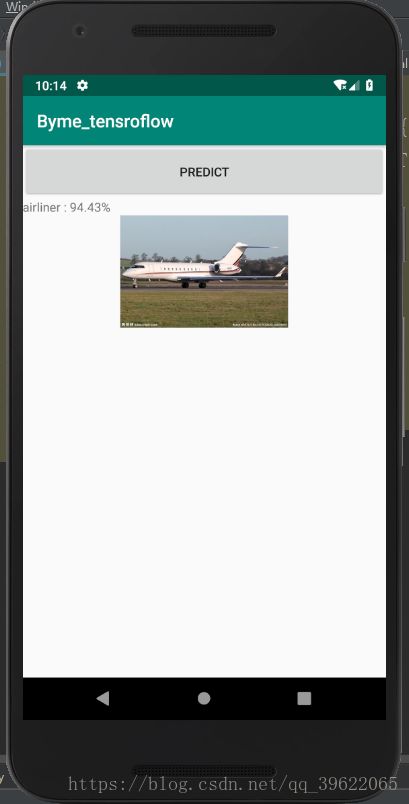
4、如果以上都进展顺利,点击Run,基本就大功告成啦!
package com.example.jinquan.pan.mnist_ensorflow_androiddemo;
import android.content.res.AssetManager;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.util.Log;
import org.tensorflow.contrib.android.TensorFlowInferenceInterface;
public class PredictionTF {
private static final String TAG = "PredictionTF";
//设置模型输入/输出节点的数据维度
private static final int IN_COL = 1;
private static final int IN_ROW = 28*28;
private static final int OUT_COL = 1;
private static final int OUT_ROW = 1;
//模型中输入变量的名称
private static final String inputName = "input/x_input";
//模型中输出变量的名称
private static final String outputName = "output";
TensorFlowInferenceInterface inferenceInterface;
static {
//加载libtensorflow_inference.so库文件
System.loadLibrary("tensorflow_inference");
Log.e(TAG,"libtensorflow_inference.so库加载成功");
}
PredictionTF(AssetManager assetManager, String modePath) {
//初始化TensorFlowInferenceInterface对象
inferenceInterface = new TensorFlowInferenceInterface(assetManager,modePath);
Log.e(TAG,"TensoFlow模型文件加载成功");
}
/**
* 利用训练好的TensoFlow模型预测结果
* @param bitmap 输入被测试的bitmap图
* @return 返回预测结果,int数组
*/
public int[] getPredict(Bitmap bitmap) {
float[] inputdata = bitmapToFloatArray(bitmap,28,28);//需要将图片缩放带28*28
//将数据feed给tensorflow的输入节点
inferenceInterface.feed(inputName, inputdata, IN_COL, IN_ROW);
//运行tensorflow
String[] outputNames = new String[] {outputName};
inferenceInterface.run(outputNames);
///获取输出节点的输出信息
int[] outputs = new int[OUT_COL*OUT_ROW]; //用于存储模型的输出数据
inferenceInterface.fetch(outputName, outputs);
return outputs;
}
/**
* 将bitmap转为(按行优先)一个float数组,并且每个像素点都归一化到0~1之间。
* @param bitmap 输入被测试的bitmap图片
* @param rx 将图片缩放到指定的大小(列)->28
* @param ry 将图片缩放到指定的大小(行)->28
* @return 返回归一化后的一维float数组 ->28*28
*/
public static float[] bitmapToFloatArray(Bitmap bitmap, int rx, int ry){
int height = bitmap.getHeight();
int width = bitmap.getWidth();
// 计算缩放比例
float scaleWidth = ((float) rx) / width;
float scaleHeight = ((float) ry) / height;
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0, width, height, matrix, true);
Log.i(TAG,"bitmap width:"+bitmap.getWidth()+",height:"+bitmap.getHeight());
Log.i(TAG,"bitmap.getConfig():"+bitmap.getConfig());
height = bitmap.getHeight();
width = bitmap.getWidth();
float[] result = new float[height*width];
int k = 0;
//行优先
for(int j = 0;j < height;j++){
for (int i = 0;i < width;i++){
int argb = bitmap.getPixel(i,j);
int r = Color.red(argb);
int g = Color.green(argb);
int b = Color.blue(argb);
int a = Color.alpha(argb);
//由于是灰度图,所以r,g,b分量是相等的。
assert(r==g && g==b);
// Log.i(TAG,i+","+j+" : argb = "+argb+", a="+a+", r="+r+", g="+g+", b="+b);
result[k++] = r / 255.0f;
}
}
return result;
}
}
package com.example.jinquan.pan.mnist_ensorflow_androiddemo;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
// Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup.
static {
System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
}
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
private static final String MODEL_FILE = "file:///android_asset/mnist.pb"; //模型存放路径
TextView txt;
TextView tv;
ImageView imageView;
Bitmap bitmap;
PredictionTF preTF;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// Example of a call to a native method
tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text);
txt=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_id);
imageView =(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.imageView1);
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.test_image);
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
preTF =new PredictionTF(getAssets(),MODEL_FILE);//输入模型存放路径,并加载TensoFlow模型
}
public void click01(View v){
String res="预测结果为:";
int[] result= preTF.getPredict(bitmap);
for (int i=0;i